As applications grow in complexity, the ability to gather, process, and analyze logs becomes crucial for maintaining system health and troubleshooting issues. Two popular open-source log collectors have emerged as frontrunners in this space: FluentD and FluentBit.
But how do you choose between them? This article dives deep into the FluentD vs FluentBit debate, exploring their features, performance, and use cases to help you make an informed decision.

What are FluentD and FluentBit?
Log collectors are essential tools in modern infrastructure that gather, process, and forward log data from various sources to centralized storage or analysis platforms. They play a critical role in maintaining observability and troubleshooting across complex, distributed systems.
FluentD and FluentBit are both open-source log collectors developed under the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF).
FluentD, created in 2011, is a more mature project written in Ruby. It aims to unify log collection and processing across multiple data sources and destinations.
FluentBit, introduced in 2015, is a lightweight C implementation designed for resource-constrained environments and edge computing scenarios.
The core purpose of both tools is to simplify log management by providing a unified logging layer. This layer abstracts the complexities of dealing with diverse log formats and destinations. While FluentD excels in complex data processing and routing scenarios, FluentBit shines in lightweight deployments where resource efficiency is paramount.
Both tools have active communities and support a variety of integrations, organizations can choose the one that fits their specific requirements. Let’s compare the two in depth.
Key Differences Between FluentD and FluentBit
The choice between FluentD and FluentBit often comes down to specific use cases and infrastructure requirements. Let's explore the key differences that set these tools apart:
Language and Architecture:
- FluentD: Written in Ruby with some C extensions
- FluentBit: Implemented entirely in C
This fundamental difference impacts performance, resource usage, and extensibility.
Resource Consumption:
- FluentD: Higher memory footprint (typically 30-40MB)
- FluentBit: Significantly lower memory usage (usually < 1MB)
FluentBit's lower resource consumption makes it ideal for constrained environments.
Scalability:
- FluentD: Designed for high-throughput, complex log processing at scale
- FluentBit: Optimized for lightweight deployments but can scale with proper configuration
Plugin Ecosystem:
- FluentD: Extensive plugin ecosystem with over 1000 community-contributed plugins
- FluentBit: Smaller but growing plugin set, focused on core functionalities
Performance Benchmarks
Performance is one of the key factors that organizations consider when choosing between Fluentd and Fluentbit. Both tools have different performance characteristics when it comes to latency and throughput.
1. Throughput
- Fluentd: Fluentd can handle a high throughput of data, as it can be scaled horizontally and vertically to handle large amounts of data. Its plugin system allows for handling large amounts of data.
- Fluent Bit: Fluent Bit also can handle a high throughput of data. It's designed to be lightweight and with low resource usage, which means it can be deployed in large numbers of small instances, which can help to handle a high throughput of data.
2. Latency
- Fluentd: Latency in Fluentd is generally higher compared to Fluentbit. This is due to the fact that Fluentd processes and transforms log data before forwarding it, which can add to the latency.
- Fluent Bit: Fluent Bit is designed to be highly performant, with low latency. It is lightweight and has minimal overhead, which makes it well-suited for edge computing and IoT use cases where low latency is important.
Resources such as memory and CPU usage
Fluentd and Fluentbit have different resource usage characteristics when it comes to memory and CPU.
- FluentD: CPU usage can reach 5-10% under heavy load
- FluentBit: Generally stays below 1-2% CPU usage
Fluentd uses more memory and CPU resources than Fluentbit. Fluentd has a larger codebase and additional features, which can increase its memory and CPU usage. Fluentbit, on the other hand, is designed to be lightweight and with low resource usage, which helps keep its memory and CPU usage low. This makes Fluentbit a more suitable option for use cases where resource usage is a concern, such as edge computing and IoT.
Scalability
Scalability is another important factor to consider when comparing Fluentd and Fluent Bit. Both tools can be scaled horizontally and vertically to handle large amounts of data, but they have different scalability characteristics.
1. Horizontal Scaling
- Fluentd: Fluentd can be horizontally scaled by adding more instances of Fluentd running on different machines. This can be done by using a load balancer to distribute incoming data to multiple Fluentd instances.
- Fluent Bit: Fluent Bit can also be horizontally scaled by adding more instances running on different machines. Fluent Bit uses a smaller footprint, which means that it can be deployed in a large number of small instances which can handle a high throughput of data.
2. Vertical Scaling
- Fluentd: Fluentd can be vertically scaled by increasing the resources of a single instance, such as adding more CPU and memory.
- Fluent Bit: Fluent Bit can also be vertically scaled by increasing the resources of a single instance, such as adding more CPU and memory, but due to its minimal overhead, it might require fewer resources to handle the same amount of data compared to Fluentd.
Features
1. Input and output plugins
Both Fluentd and Fluent Bit provide a wide range of input and output plugins that allow you to collect data from various sources, such as log files, databases, message queues, and cloud services, and forward them to different destinations, such as files, databases, message queues, and cloud services. This allows you to collect and process data from different sources and forward it to the desired location for further analysis and storage. Fluentd has around 650 plugins, and Fluent Bit has only 35 plugins available.
2. Filter and transformation capabilities
Both Fluentd and Fluent Bit have filter and transformation capabilities, which allow you to process and modify data before it is forwarded to its final destination. This can include things like filtering out specific log levels, renaming fields, adding new fields, and more. This allows you to pre-process data to make it more useful for your specific use case.
3. Extensibility
In terms of extensibility, Fluentd has a larger community and ecosystem of plugins compared to Fluent Bit. This means that there are more plugins available for Fluentd, which can make it easier to add new functionality to your data collection and logging pipeline. Additionally, Fluentd has more advanced routing and buffering capabilities, which can be useful for managing and processing large amounts of data.
Fluent Bit, on the other hand, is written in C and is more lightweight and less resource-intensive compared to Fluentd. This makes Fluent Bit well-suited for use cases where low resource usage and high performance is needed, such as in embedded systems, edge computing, and IoT applications. Fluent Bit also has a smaller footprint and can be easily integrated into existing systems.
Community and support system
Both Fluentd and Fluent Bit have strong community support and a wide range of resources available for users. Fluentd has a larger and more established community with a more extensive ecosystem of plugins and integrations, while Fluent Bit has a smaller but growing and focused user base with strong support systems from the company.
Use cases of FluentD and FluentBit
- Logging and monitoring: Fluentd and Fluent Bit can be used to collect, process, and forward log data from various sources to a centralized location for analysis and storage. This can be used for monitoring the performance and stability of systems, as well as troubleshooting and debugging issues.
- Data integration: Fluentd and Fluent Bit can be used to collect and process data from different sources and forward it to different destinations. This can be used for integrating data from different systems and applications, such as databases, message queues, and cloud services.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Fluentd and Fluent Bit can be used to collect and process data from IoT devices and forward it to a centralized location for analysis and storage. Fluent Bit is particularly well suited for this use case due to its lightweight and low resource usage.
- Cloud-native: Fluentd and Fluent Bit can be used to collect, process, and forward data in cloud environments. Fluent Bit has been designed to work well in cloud-native environments and can be used in the Kubernetes cluster to collect and forward logs and metrics from the containers.
Fluentd and Fluent Bit are versatile data collection and logging tools that can be used in a wide range of use cases, such as logging and monitoring, data integration, stream processing, IoT, and cloud-native environments. Fluentd is more versatile and can handle more complex use cases, while Fluent Bit is more suitable for resource-constrained environments and cloud-native use cases.
When to Choose FluentD
FluentD is the go-to choice for scenarios that require:
- Complex log processing with extensive data manipulation
- Integration with a wide variety of data sources and destinations
- Advanced buffering and queuing mechanisms for reliability
- Flexibility in handling both structured and unstructured data
FluentD's Strengths
- Rich Plugin Ecosystem: With over 1000 community-contributed plugins, FluentD can integrate with almost any data source or destination.
- Advanced Data Handling: FluentD excels at complex data manipulation, including filtering, parsing, and transforming logs.
- Reliability Features: Built-in support for buffering, retrying, and load balancing ensures data integrity in unstable network conditions.
- Community Support: A large, active community provides extensive documentation and support resources.
When to Choose FluentBit
FluentBit is ideal for:
- Lightweight deployments in IoT or edge computing scenarios
- Kubernetes and containerized environments
- Situations where resource efficiency is critical
- Simple log forwarding with minimal processing requirements
FluentBit's Advantages
- Resource Efficiency: With a tiny memory footprint and low CPU usage, FluentBit is perfect for resource-constrained environments.
- Container-Friendly: Native support for container logging makes FluentBit a natural fit for Kubernetes environments.
- Simplified Configuration: For basic use cases, FluentBit offers a more straightforward configuration process.
- Cloud Integration: Built-in support for major cloud platforms simplifies log shipping to cloud-based analytics services.
Configuring FluentD vs FluentBit
While both tools serve similar purposes, their configuration approaches differ:
Configuration Format:
- FluentD uses a Ruby-like DSL
- FluentBit employs an INI-style format
Input Configuration:
# FluentD <source> @type tail path /var/log/nginx/access.log tag nginx.access </source> # FluentBit [INPUT] Name tail Path /var/log/nginx/access.log Tag nginx.accessOutput Configuration:
# FluentD <match nginx.**> @type elasticsearch host elasticsearch.example.com port 9200 </match> # FluentBit [OUTPUT] Name es Match nginx.* Host elasticsearch.example.com Port 9200Filtering and Parsing: Both tools support filtering and parsing, but FluentD's Ruby-based filters offer more flexibility for complex transformations.
Final Thoughts: Choosing between FluentD and FluentBit
In conclusion, Fluentd and Fluent Bit are both open-source data collection and logging tools that provide powerful and flexible ways to collect, process, and forward data from various sources to different destinations. They have similar features, such as input/output plugins, extensibility, and filter and transformation capabilities. However, Fluentd is more advanced in terms of routing and buffering capabilities and has a larger community and ecosystem of plugins, while Fluent Bit is more lightweight and well suited for resource-constrained environments, such as embedded systems, edge computing and IoT applications, and has a smaller but growing and focused user base.
All in all, Fluent Bit to Fluentd is more like beats to logstash - a lightweight shipper that can be installed as agents on edge hosts or devices in a distributed architecture. For e.g. in a Kubernetes environment, Fluent Bit can be deployed as a DaemonSet on each node to collect and forward data to a centralized Fluentd instance, acting as an aggregator, processing the data, and routing it to different sources based on tags, providing efficient and centralized management of the data collected from all nodes in the cluster. This setup allows for efficient resource utilization and flexibility in routing and processing data. Fluent Bit can be used on its own, of course but has far less to offer in terms of aggregation capabilities and a much smaller amount of plugins for integrating with other solutions.
Once the log data is collected and aggregated, you will need a centralized log management tool to store and analyze the logs. That’s where SigNoz comes in.
Log Analytics with SigNoz
SigNoz is a full-stack open-source APM that can be used as a log management tool. SigNoz uses a columnar database ClickHouse to store logs, which is very efficient at ingesting and storing logs data. Columnar databases like ClickHouse are very effective in storing log data and making it available for analysis.
The logs tab in SigNoz has advanced features like a log query builder, search across multiple fields, structured table view, JSON view, etc.
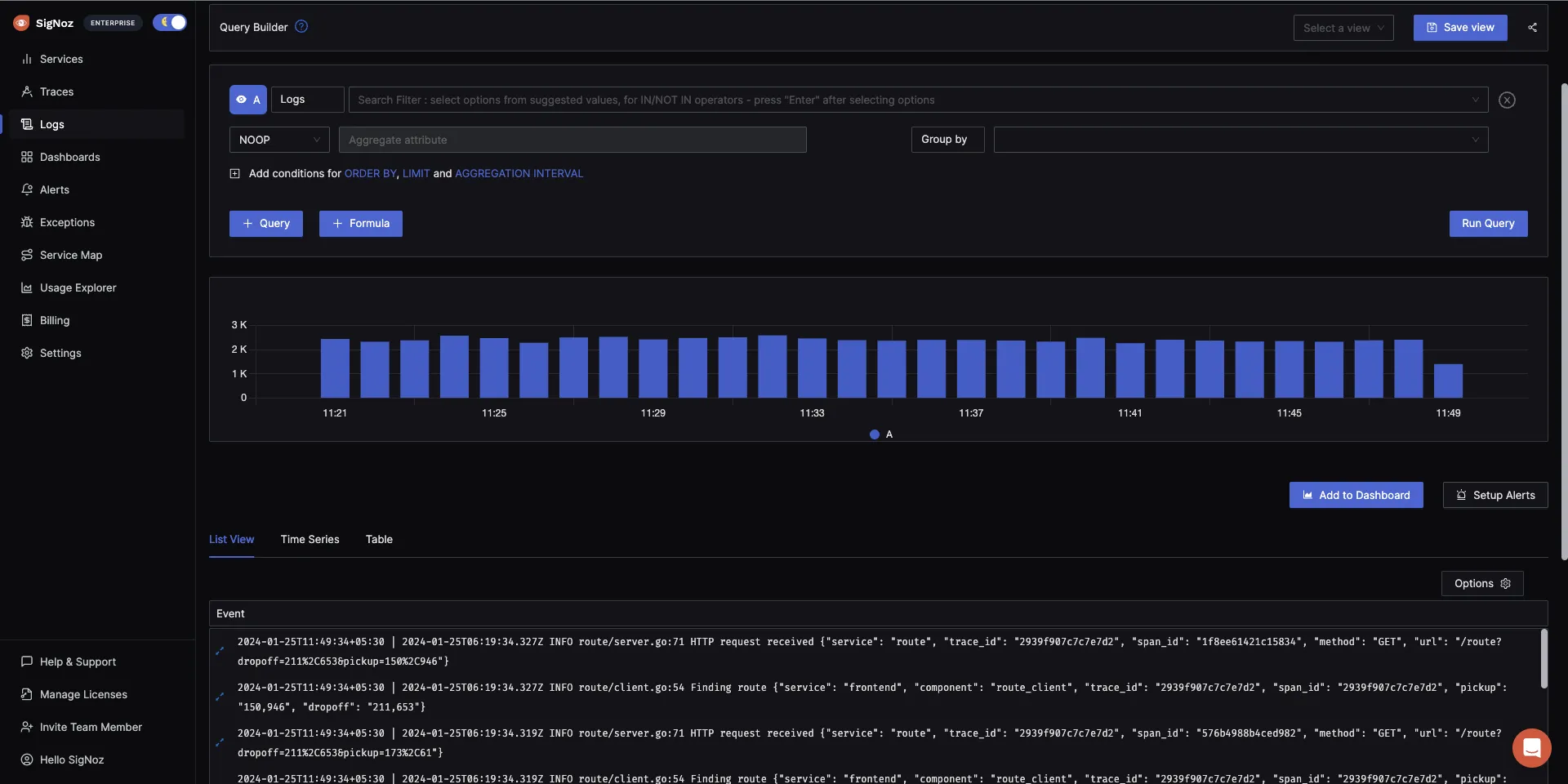
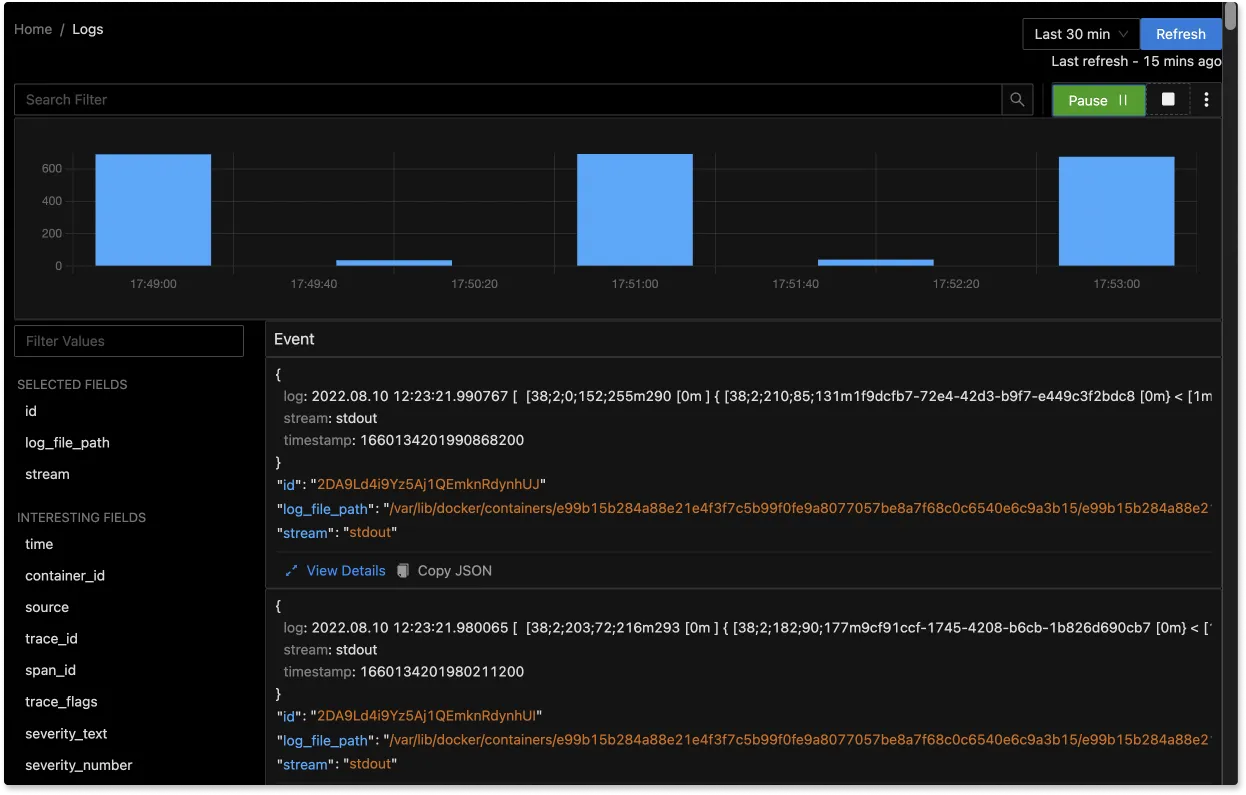
You can also view logs in real time with live tail logging.
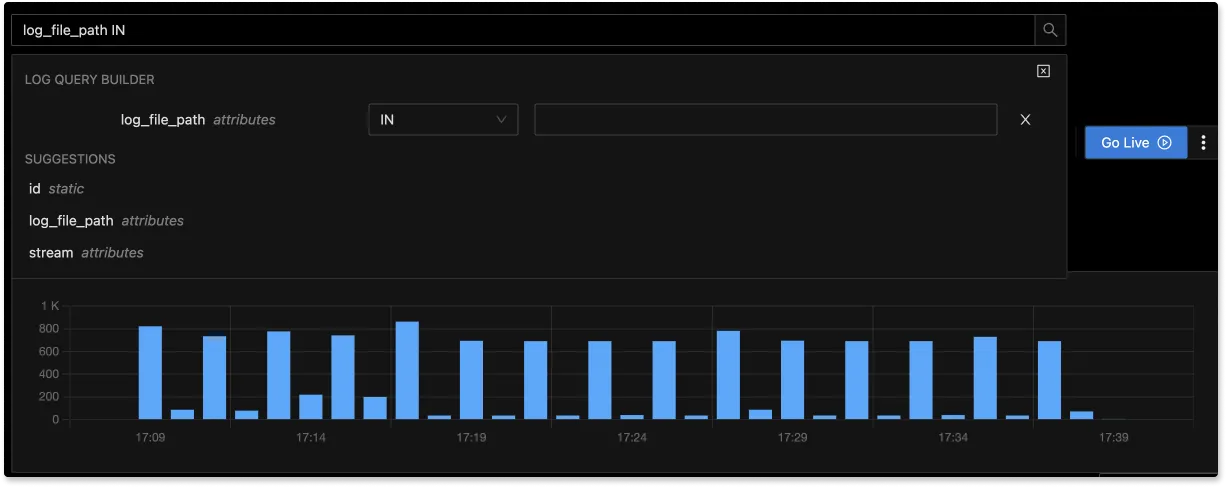
With advanced Log Query Builder, you can filter out logs quickly with a mix and match of fields.
Getting Started with SigNoz
SigNoz cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 20,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
FAQs
Can FluentD and FluentBit be used together?
Yes, many organizations use FluentBit for edge collection and forward logs to FluentD for more complex processing.
How do FluentD and FluentBit handle data loss prevention?
Both tools offer buffering mechanisms and can be configured for persistent storage to prevent data loss during network issues or restarts.
Which tool is better suited for Kubernetes environments?
While both can work well, FluentBit's lower resource footprint and native container support make it a popular choice for Kubernetes logging.
Are there any licensing differences between FluentD and FluentBit?
Both FluentD and FluentBit are open-source and distributed under the Apache License 2.0, allowing for free use in both commercial and non-commercial projects.
Related Posts
SigNoz - A Lightweight Open Source ELK alternative
OpenTelemetry Logs - A complete introduction
