8 Best Open Source Log Management Tools in 2026
Choosing the right open source log management tool is critical for modern engineering teams. It can save you hundreds of hours in debugging and prevent critical outages. While there are many commercial options, many orgs prefer open source log analysis tools that can provide the flexibility and control that growing engineering teams need without the hefty price tag and data privacy concerns.
In this guide, we list down the 8 best open source log management tools for 2026. We’ve filtered out the noise to focus on tools that are actively maintained, widely adopted, and capable of handling modern scale. Whether you need a simple open source logs collector for your home lab setup or a full-blown observability platform, this list has you covered.
Top 8 Open Source Log Management Tools
Log management tools can be broadly categorized into two types:
- Log Collectors: These tools are used to collect logs from various sources and forward them to a central location before sending them to a log storage and analytics tool.
- Log Management Platforms: These tools are used to collect, store, analyze, and visualize logs. They either use popular log collectors or have their own mechanism to collect logs.
We have included the popular log collectors in this list along with the log management platforms. Based on your requirements or the current setup, you might need a combination of these tools to build a complete logging stack.
1. SigNoz
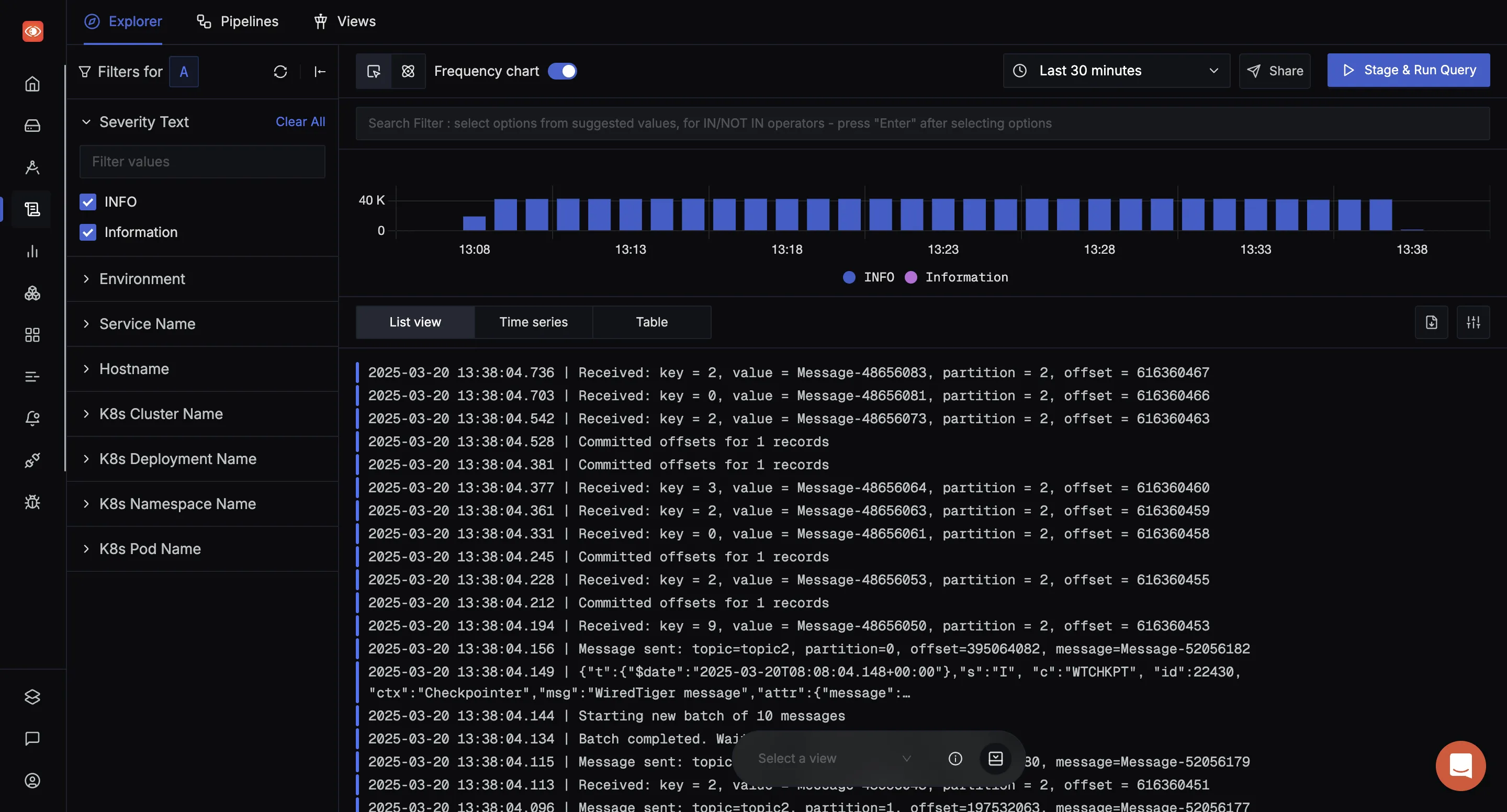
SigNoz uses a columnar datastore, making log queries fast and cost-efficient. It includes built-in pipelines to parse unstructured logs into structured fields, allowing you to easily filter by attributes and run powerful aggregations to find patterns instead of just searching raw text.
Beyond just logging, SigNoz stands out as a unified observability platform that also handles metrics and traces. Consolidating all your telemetry signals in a single pane of glass significantly reduces operational overhead and speeds up troubleshooting, eliminating the need to context-switch between fragmented tools. Even if your current focus is solely on logs, opting for a comprehensive solution like SigNoz is a wiser long-term choice.
Additionally, if you are using OpenTelemetry for instrumentation, you unlock powerful correlation capabilities—allowing you to seamlessly link logs with traces and metrics to pinpoint root causes faster.
You can find instructions to self-host SigNoz here.
If you want a quick experience, then you can sign up for SigNoz cloud. The cost of sending and storing logs in SigNoz is significantly lower compared to other tools. It's also simple and predictable at just $0.3 per GB of logs ingested and comes with volume discounts. You can check out the pricing here.
2. Grafana Loki
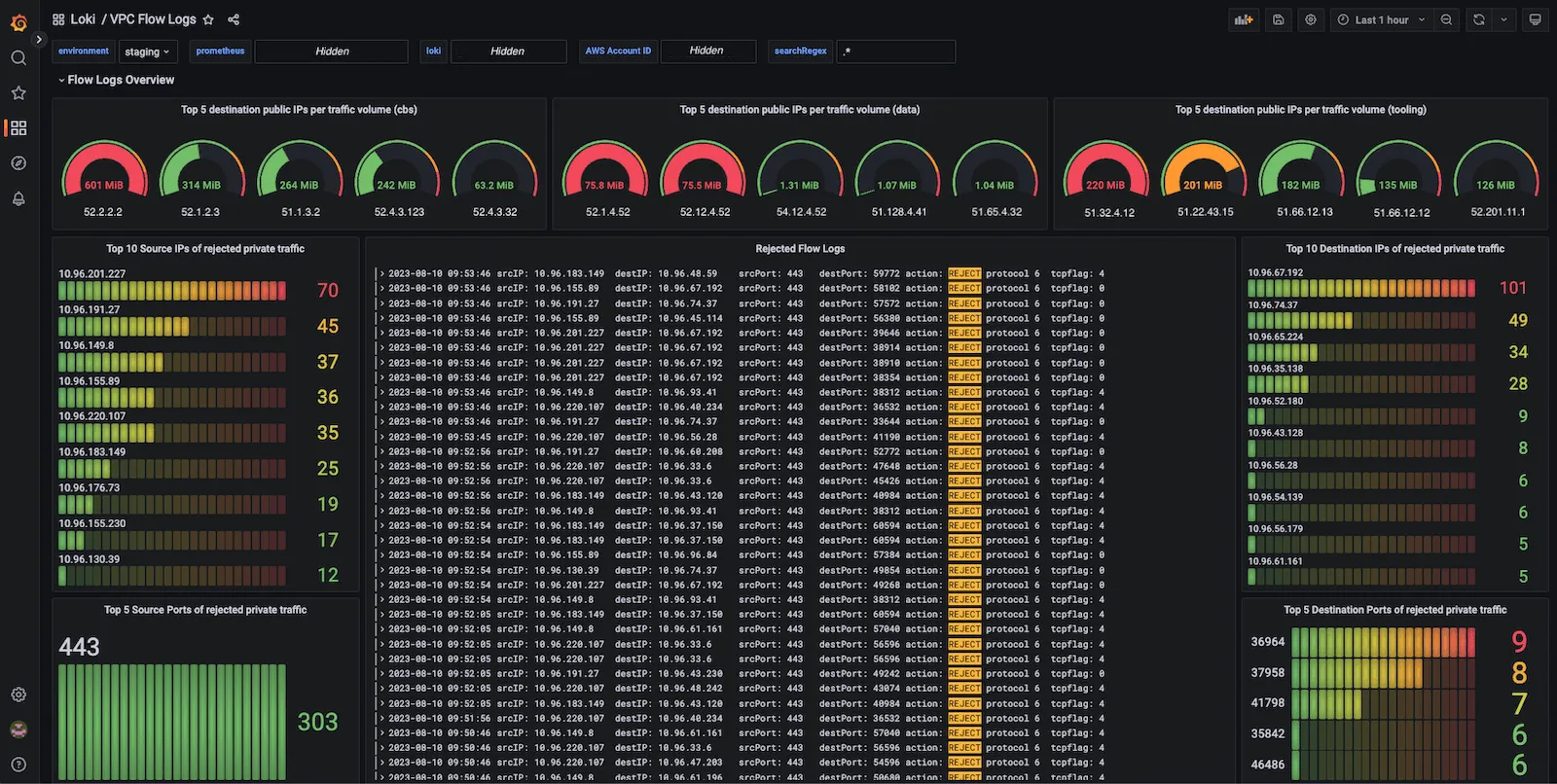
Grafana Loki is a set of components that can be composed into a fully featured logging stack. Unlike other logging systems, Loki is built around the idea of only indexing metadata about your logs: labels (just like Prometheus labels). Log data itself is compressed and stored in object stores like S3 or GCS.
This design makes it cost-effective and easy to operate, as it doesn't index the content of the logs. It integrates natively with Grafana, allowing users already in that ecosystem to switch between metrics and logs using shared labels. However, this label-based approach has a significant drawback: it does not support high cardinality well. If you try to label logs with unique identifiers like user_id or ip_address, the index size explodes, causing performance to degrade. Additionally, because it doesn't index the full log content, performing complex aggregations on the raw log data can be slower compared to columnar stores.
Strength: Best for teams deeply invested in the Grafana/Prometheus ecosystem who need a simple, cost-effective solution without full-text search requirements.
Instructions to self-host Loki can be found here.
3. ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana)
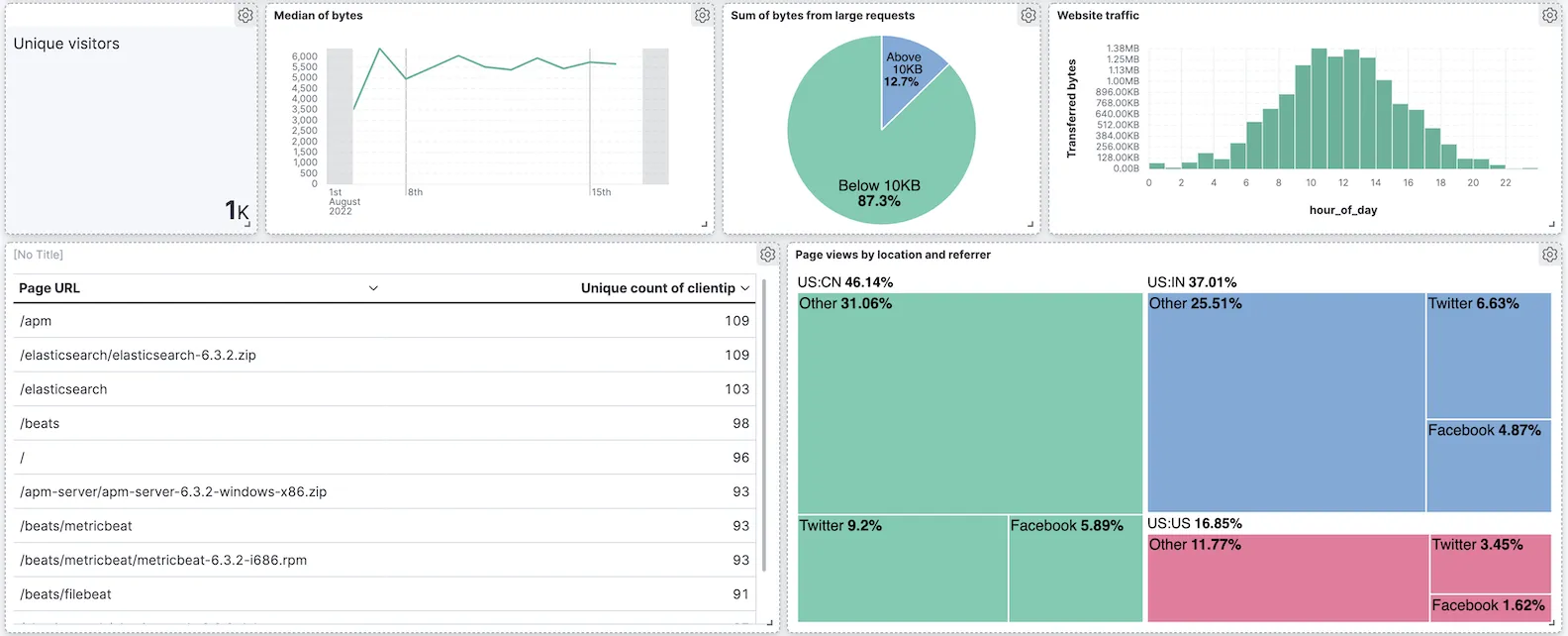
The ELK Stack is one of the most widely used solutions for log analytics, offering powerful full-text search and visualization capabilities. Elasticsearch acts as the search and analytics engine, Logstash handles server-side data processing, and Kibana provides the dashboarding interface.
It is well-suited for complex analysis where you need to search through large volumes of unstructured text data using specific queries. Its ecosystem is extensive, with Beats for lightweight data shipping and a wide range of plugins.
Strength: Strong full-text search capabilities and a long-standing ecosystem for log analysis and visualization.
Instructions to download Elastic Stack can be found here.
4. OpenSearch
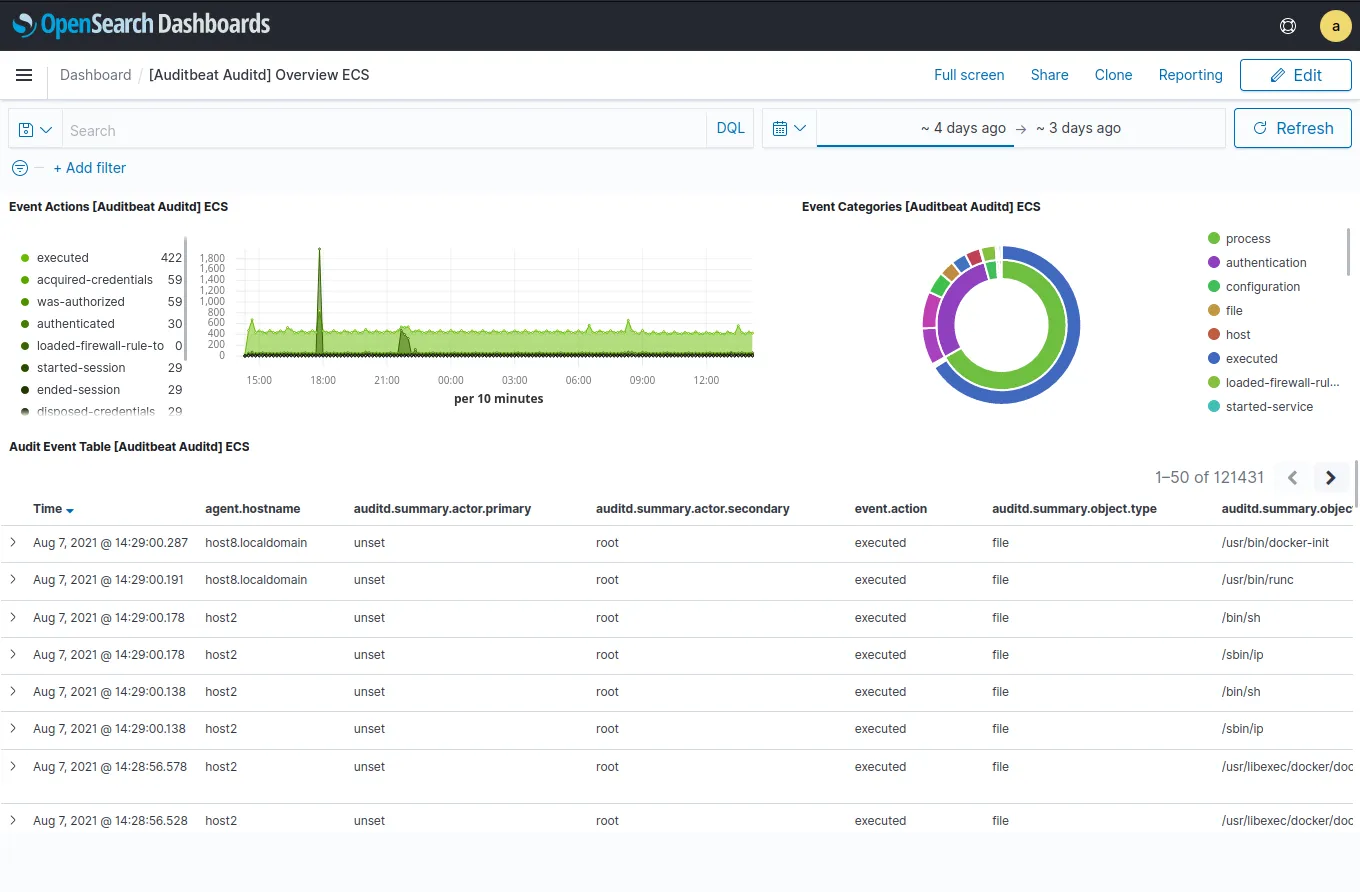
OpenSearch began as a community-driven, open source fork of Elasticsearch and Kibana, largely led by AWS to ensure a fully open (Apache 2.0) future for the technology. What started as a direct clone has now diverged significantly.
While the core search engine remains familiar, the UI (OpenSearch Dashboards) is evolving separately from Kibana. It is introducing new features like a "workspace" concept to organize views and heavily investing in Piped Processing Language (PPL) for a more intuitive, query-based analysis experience compared to Kibana's traditional filter capabilities.
Strength: The true open-source alternative to ELK, offering a rapidly evolving ecosystem with strong backing from major cloud providers.
5. Graylog
Graylog is a centralized log management solution that combines the power of OpenSearch (or Elasticsearch) with a user-friendly interface. While it serves as a general-purpose log manager, it has increasingly pivoted towards security and compliance use cases (SIEM).
It aims to simplify the operational experience by providing a packaged solution with built-in features for user access control, log parsing, and alerting. This makes it a popular choice for teams that need strict governance over their log data without managing complex, piecemeal architectures.
Strength: A cohesive, security-oriented platform excellent for teams needing strong compliance features and granular user management.
Download links for Graylog can be found here.
6. FluentBit & FluentD
Fluentd and Fluent Bit are open source data collectors used to unify data collection and consumption. They serve similar roles as vendor-neutral "pipes" for your logs but differ in their resource footprint. Fluent Bit is extremely lightweight and is now the preferred choice for collecting logs at the edge (like Kubernetes nodes) due to its high performance. Fluentd is historically used as a heavier aggregator for complex transformations.
In modern architectures, a growing pattern is to use Fluent Bit as a DaemonSet to collect container logs, which can then be forwarded to a central OpenTelemetry Collector for processing before being sent to a log management platform like SigNoz.
Strength: The standard for vendor-neutral log collection, offering flexibility to route data to multiple backends simultaneously.
7. Logstash
Logstash is an open source, server-side data processing pipeline that ingests data from a multitude of sources simultaneously, transforms it, and then sends it to your favorite "stash." It is the original "L" in the ELK stack but works as a standalone powerhouse for log parsing.
It is famous for its vast library of filters and distinct capabilities to normalize varying data schemas. Whether you need to grok complex patterns, scrub sensitive data, or geo-locate IP addresses, Logstash allows you to create sophisticated pipelines.
Strength: Powerful, extensible data processing and transformation capabilities for complex log pipelines.
8. Syslog-ng
Syslog-ng is a powerful open source syslog server capable of collecting logs from any source, processing them in near real-time, and delivering them to a wide variety of destinations. It builds upon the basic syslog protocol, adding content-based filtering, rich parsing, and authentication capabilities.
It is widely trusted in the Unix/Linux world for its reliability and performance. It allows for flexible log management, including the ability to classify, tag, and correlate log messages, making it a staple for infrastructure and network device logging.
Strength: High-performance, reliable log collection and processing with deep roots in Unix/Linux infrastructure.
Instructions to self-host Syslog-ng can be found here.
Open Source Logging Tools at a glance: Comparison Table
Here is our curated list of the top open source logging tools, categorized by their primary strengths:
| Tool | Best For | Collection | Analysis | Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. SigNoz | One-Stop Observability Tool (logs, metrics, traces) | ✅ (OTel) | ✅ | ✅ (Columnar DB) |
| 2. Grafana Loki | Kubernetes & Cost Efficiency | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ (Object Store) |
| 3. ELK Stack | Elastic Scalability | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ (Elasticsearch) |
| 4. OpenSearch | Apache 2.0 ELK Alternative | ⚠️ | ✅ | ✅ |
| 5. Graylog | Enterprise Log Management | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ (OpenSearch) |
| 6. FluentBit / Fluentd | Infrastructure Pipes | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| 7. Logstash | Complex ETL | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| 8. Syslog-ng | Reliable Unix Logging | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
Now that you have a better understanding of the top open source logging tools, let's look at how they work together to build a modern logging stack.
Architecture of Modern Open Source Log Management Stack
To help you visualize how these tools work together, let's look at a practical, real-world logging pipeline. While many modern teams run Kubernetes (EKS, GKE), most organizations actually maintain a "hybrid" reality: standard Virtual Machines (EC2, Linux/Windows on-prem), Serverless functions, and direct logs from application frameworks.
A robust modern stack needs to handle all of these. Here is what a typical OpenTelemetry-native logging architecture looks like:
The Workflow: From Source to Dashboard
1. Log Collection Layer (Fluent Bit / OTel Collector)
This runs everywhere your apps do—as a DaemonSet on Kubernetes, a binary on VMs, or a sidecar for serverless apps. It acts as a universal agent that captures raw logs, parses them into JSON, and adds context like host names or environment tags.
2. Log Aggregation & Processing Layer (OpenTelemetry Collector)
Typically deployed as a central gateway, this acts as a unified funnel for all log sources. Here you can filter out noisy logs, redact sensitive PII, and standardize log formats across different languages.
3. Log Storage & Analysis Layer (SigNoz)
SigNoz ingests your processed logs into a high-performance columnar database for blazing fast queries. It provides a single pane of glass to view logs in real-time and correlate them with traces and metrics, helping you debug issues across hybrid infrastructure.
You can get started quickly with SigNoz Cloud or deploy the Self-Hosted version on your own infrastructure.
This is how a typical logging setup in modern cloud-native applications can look like.
Choosing the right open source logging tool
One of the most challenging parts of analyzing log data is the sheer volume of data generated. An effective log analytics tool should efficiently collect and store logs at scale. But storage is just the beginning—the real value lies in analysis. Enabling users to search through logs quickly and run complex aggregates to identify the root cause of issues is a critical capability.
While choosing a log analytics tool, a few key factors should be kept in mind:
- Storage Efficiency: How efficiently can the tool store massive volumes of log data?
- Query Performance: How fast can you run complex queries and aggregates on high-cardinality data?
- User Experience: Is the UI intuitive enough to analyze log data from multiple sources seamlessly?
- Correlation: Does the tool natively correlate logs, metrics, and traces for deeper insights?
SigNoz excels in all these areas. It supports efficient log storage, provides an intuitive UI, and lets you correlate your logs with traces and metrics for quicker troubleshooting. Because it is powered by a high-performance columnar datastore, running aggregates is significantly faster than traditional search engines. It is also open source and can be self-hosted within your infrastructure.
Getting Started with SigNoz
You can choose between various deployment options in SigNoz. The easiest way to get started with SigNoz is SigNoz cloud. We offer a 30-day free trial account with access to all features.
Those who have data privacy concerns and can't send their data outside their infrastructure can sign up for either enterprise self-hosted or BYOC offering.
Those who have the expertise to manage SigNoz themselves or just want to start with a free self-hosted option can use our community edition.
