AWS vs GCP vs Azure - Choosing the Right Cloud Platform
Cloud computing has transformed business operations, providing unprecedented flexibility, scalability, and innovation. Among the leading cloud platforms, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure stand out for their extensive service offerings. Choosing the right platform can be challenging, given their unique strengths and capabilities.
This comprehensive guide will help you understand the key differences between AWS, GCP, and Azure, enabling you to make an informed decision that aligns with your organization’s needs and goals.
Understanding Cloud Computing Platforms
Cloud computing revolutionizes the way businesses access technology. Instead of managing physical hardware, companies can now tap into a pool of on-demand computing resources like servers, storage, databases, and artificial intelligence tools. Using the cloud, businesses can scale quickly, cut costs, and innovate without the overhead of maintaining their IT infrastructure.
One of the key offerings of cloud -platforms is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). This service model lets you rent virtualized computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking, on a pay-as-you-go basis. With IaaS, companies gain the flexibility to adjust their infrastructure based on current needs, avoiding the long-term commitments and costs associated with physical servers. This capability supports dynamic scaling, enabling businesses to respond efficiently to changing demands.
History and Market Share
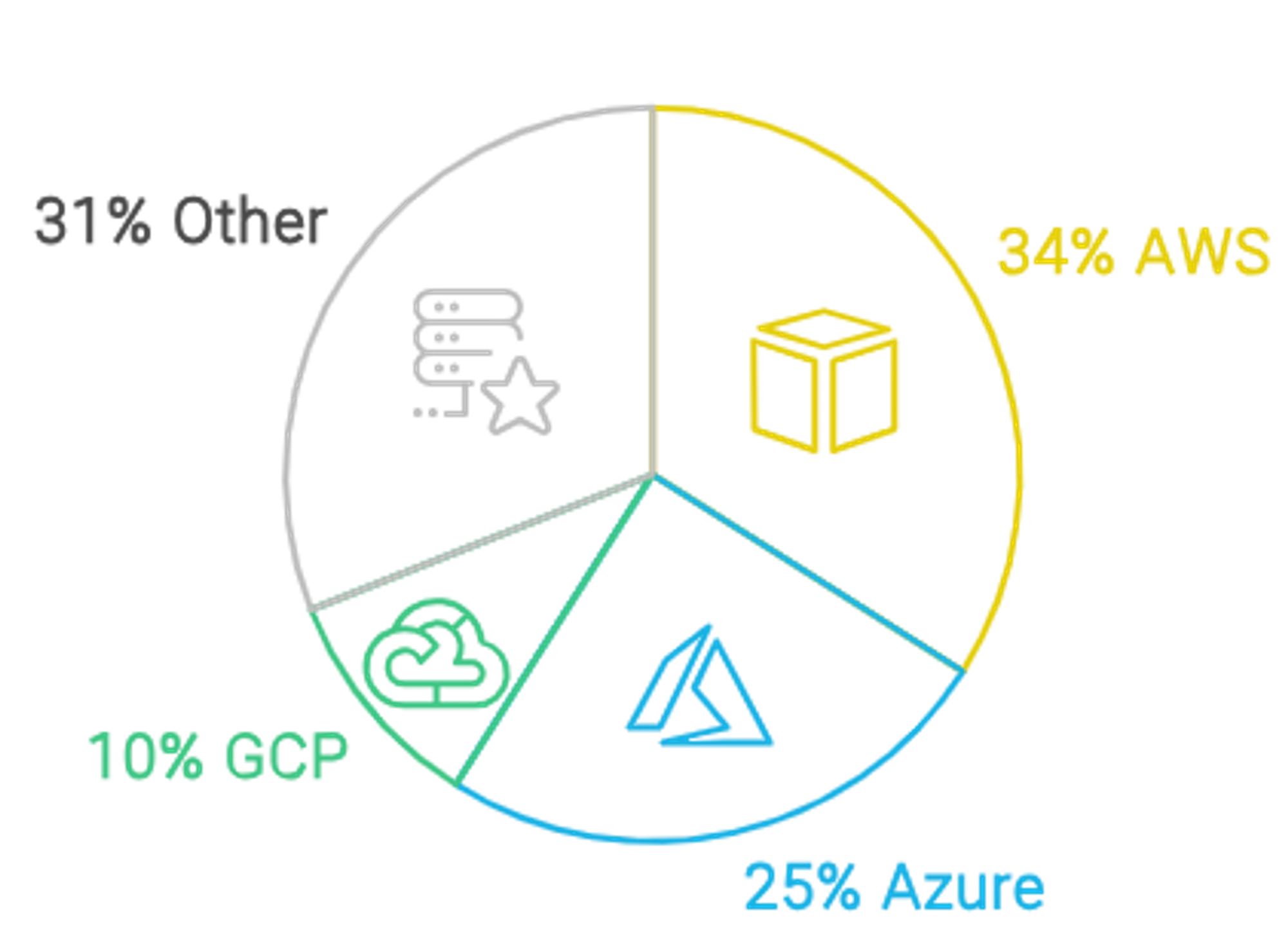
- AWS (Amazon Web Services): Launched in 2006, AWS was the first to bring cloud computing to the mainstream. Today, it dominates the market with a 34% share.
- Azure: Microsoft introduced Azure in 2010, building on its vast enterprise software ecosystem. It’s now the second-largest cloud platform, holding a 25% share of the market.
- GCP (Google Cloud Platform): Google entered the cloud arena in 2011, focusing on innovation and data analytics. GCP has grown steadily, capturing around 10% of the market.
Comparing AWS, GCP, and Azure: Key Features

When choosing a cloud platform, it’s essential to understand the strengths and unique offerings of each provider. Here’s a breakdown of key features across compute services, storage solutions, database offerings, and networking capabilities for AWS, GCP, and Azure.
Compute Services
- AWS EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud): AWS has a broad array of instances, each tailored to specify workloads, whether you need general-purpose instances, compute-optimized instances, or memory-intensive configurations. This flexibility allows businesses to find the perfect match for their computing needs.
- GCP Compute Engine: Google takes a different approach with custom machine types, giving you granular control over CPU and memory configurations. This means you can fine-tune your resources to precisely fit your workloads, avoiding over-provisioning and saving costs.
- Azure Virtual Machines: Azure seamlessly integrates with Microsoft’s extensive product suite, making it an ideal choice for enterprises that rely on Windows Server, SQL Server, and other Microsoft technologies. It’s built for a smooth experience for users already within the Microsoft ecosystem.
| Feature | AWS EC2 | GCP Compute Engine | Azure Virtual Machines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Instance Variety | Extensive array of instances for various workloads | Custom machine types for granular control | Wide range of VMs with seamless Microsoft integration |
| Customization | Predefined instance types | Customizable CPU and memory configurations | Predefined VMs with Microsoft software integration |
| Best For | General-purpose, compute-optimized and memory-intensive tasks. | Precise workload tailoring and cost-efficiency | Microsoft ecosystem users |
Storage Solutions
- AWS S3 (Simple Storage Service): Renowned for its unmatched durability and scalability, AWS S3 is a go-to for businesses needing reliable object storage. Its virtually unlimited storage capacity and robust protection features make it a cornerstone of cloud storage.
- GCP Cloud Storage: Google Cloud Storage stands out with its strong consistency and geo-redundancy, ensuring that your data is available and secure across multiple regions. It’s particularly well-suited for global applications that demand high availability.
- Azure Blob Storage: Azure Blob Storage excels when it comes to integrating with other Azure services. It’s optimized for large-scale object storage and is a natural fit for businesses that are already leveraging Azure’s wide array of tools and services.
| Feature | AWS S3 | GCP Cloud Storage | Azure Blob Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Durability & Scalability | Unmatched durability and virtually unlimited storage | Strong consistency and geo-redundancy | Optimized for integration with Azure services |
| Global Availability | Highly available, robust protection features | Secure data availability across regions | Ideal for large-scale object storage |
| Best For | Reliable object storage | Global applications requiring high availability | Businesses leveraging Azure’s tools and services |
Relational Database Offerings
- AWS RDS (Relational Database Service): AWS RDS supports multiple database engines, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server, giving you flexibility in choosing the right database for your application. Its managed service takes care of backups, patching, and scaling, so you can focus on your data.
- GCP Cloud SQL: Google’s Cloud SQL offers high performance and automatic replication, making it a strong choice for applications that need reliable and fast access to relational databases. It’s designed for scalability and ease of management, with built-in redundancy to ensure data availability.
- Azure SQL Database: Azure’s SQL Database stands out with intelligent performance recommendations, using AI to optimize your database queries and improve overall efficiency. It’s a fully managed service that integrates smoothly with other Azure tools, making it a powerful option for data-driven applications.
| Feature | AWS RDS | GCP Cloud SQL | Azure SQL Database |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supported Engines | MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server | High performance with automatic replication | AI-powered performance recommendations |
| Management | Fully managed, includes backups and scaling | Scalable with built-in redundance | Fully managed, integrates with Azure tools |
| Best For | Flexibility in database choice | Reliable and fast access to relational databases | Data-driven applications within Azure ecosystem |
Non-Relational Database Offerings
- AWS DynamoDB: AWS DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service known for its low latency and high availability. It’s ideal for applications that require consistent, single-digit millisecond response times and the ability to scale seamlessly as your application’s demand grows.
- GCP Firestore & Bigtable: Google offers two key non-relational database services, Firestore for real-time, document-based NoSQL databases and Bigtable for large-scale, low-latency workloads. Firestore excels in mobile and web app development, while Bigtable is designed for massive analytical and operational workloads.
- Azure Cosmos DB: Azure CosmosDB is a globally distributed, multi-model database service that provides trunked global distribution and horizontal scaling. It supports multiple data models, including document, key-value, graph, and column-family, making it highly versatile for a wide range of applications.
| Feature | AWS DynamoDB | GCP Firestore & Bigtable | Azure Cosmos DB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Model | Key-value and document | Firestore: Document-based, Bigtable: Wide-column store | Document, key-value, graph, column-family |
| Scalability | Seamless scaling with automatic capacity management | Firestore: Automatic scaling; Bigtable: Horizontal scaling for large datasets | Global distribution with automatic horizontal scaling |
| Best For | Consistent, low-latency applications | Firestore: Mobile/web apps; Bigtable: Analytical/operational workloads | Global apps, real-time data, and analytical processing |
Networking Capabilities
- AWS VPC: AWS VPC offers extensive customization options, allowing you to configure your network architecture to meet specific security and performance requirements. It provides robust network isolation, essential for sensitive workloads.
- GCP VPC (Virtual Private Cloud): Google’s global VPC is designed for simplicity and efficiency, offering seamless management across multiple regions. It’s a strong choice for businesses with a global presence, as it allows for easy scaling and centralized network management.
- Azure Virtual Network: Azure’s Virtual Network integrates effortlessly with on-premises networks, making it a top choice for hybrid cloud environments. It’s designed to work hand-in-hand with Azure’s other networking and security services, providing a cohesive and secure cloud experience.
| Feature | AWS VPC | GCP VPC | Azure Virtual Network |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customization | Extensive options for network architecture | Simplified management across multiple regions | Seamless integration with on-premises networks |
| Network Isolation | Robust security for sensitive workloads | Easy scaling and centralized management | Ideal for hybrid cloud environments |
| Best For | Highly customizable network configurations | Global presence with centralized management | Hybrid cloud setups leveraging Azure services |
Pricing Models and Cost Optimization
Understanding the pricing models offered by cloud platforms is crucial for managing costs effectively and maximizing value. Each provider offers a range of options tailored to different usage patterns, along with tools designed to help you monitor and optimize your spending.
Cloud platforms provide flexible pricing to match different needs:
- On-Demand Instances: Pay by the hour with no long-term commitment, ideal for variable workloads.
- Reserved Instances: Save significantly by committing to 1-3 years, perfect for predictable usage.
- Spot instances (AWS) preemptible VMs (GCP) / Spot VMs (Azure): Get steep discounts for interruptible tasks, great for cost-conscious projects.
Free Tiers:
- AWS: 12 months of free tier access
- GCP: $300 credit for new users
- Azure: $200 credit for the first 30 days
Cost Management Tools:
- AWS: AWS Cost Explorer, AWS Budgets
- GCP: Cloud Billing Budget API, Cloud Billing Catalog API
- Azure: Azure Cost Management, Azure Advisor
Performance and Scalability
The performance and scalability of cloud services are heavily influenced by the infrastructure that supports them. This infrastructure, consisting of regions and availability zones, is essential for ensuring high availability, low latency, and redundancy.
- AWS operates across 26 regions with 84 availability zones, providing a solid foundation for reliable performance.
- With 29 regions and 88 availability zones, Google Cloud ensures extensive global coverage.
- Azure leads with over 60 regions and 140 availability zones, offering unparalleled geographical reach.
Each platform also provides advanced auto-scaling and load-balancing services, which dynamically adjust resources based on demand. However, performance can differ depending on specific workloads and use cases. To achieve the best results, it’s advisable to conduct benchmarks tailored to your application’s needs. This approach will help you choose the right cloud provider and configuration for optimal performance and scalability.
Security and Compliance
Security is a top priority in cloud computing, and each platform offers robust features to protect your data and applications:
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Control who can access your resources and what they can do with them.
- Encryption: Data is encrypted both at rest and in transit, ensuring that sensitive information is secure.
- Key Management Services: Manage encryption keys with dedicated tools to enhance security.
- Compliance Certifications: All major platforms adhere to industry standards and regulations, including HIPPA, PCI DSS, and GDPR, among others.
Developer Tools and DevOps Integration
Cloud platforms are tailored to modern development and DevOps practices, offering a range of tools to streamline and automate workflows:
- CI/CD Pipelines: Automate code deployment and integration with services like AWS CodePipeline, GCP Cloud Build, and Azure DevOps, enabling faster and more reliable software releases.
- Containerization: All platforms offer seamless support for Kubernetes, whether it’s EKS (AWS), GKE (GCP), or AKS (Azure), ensuring scalable and efficient container orchestration.
- Serverless Computing: Write and deploy code without managing servers using AWS Lambda, GCP Cloud Functions, or Azure Functions, ideal for microservices and event-driven architectures.
Additionally, AI and machine learning services are becoming integral to application development:
- AWS SageMaker simplifies the building, training, and deployment of machine learning models.
- GCP leverages TensorFlow-based AI services for advanced machine learning capabilities.
- Azure offers cognitive services with pre-built AI models for tasks like vision, speech, and language processing.
Monitoring and Observability with SigNoz
Effective monitoring is critical for managing complex cloud environments. SigNoz provides comprehensive observability solutions compatible with AWS, GCP, and Azure, ensuring you have complete visibility into your systems:
- Distributed Tracing: Track requests across microservices to quickly identify bottlenecks and performance issues.
- Metrics Monitoring: Keep an eye on key performance indicators (KPIs) with real-time metrics for proactive system management.
- Log Management: Centralize and analyze logs for faster troubleshooting and deeper insights.
- Custom Dashboards: Create tailored dashboards to visualize the data that matters most to your operations.
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Migration and Hybrid Cloud Strategies
Migrating workloads to the cloud requires careful planning and the right tools. Each major cloud platform offers solutions to simplify this process:
- AWS Migration Hub: It provides centralized tracking of your migration projects.
- GCP Cloud Migration Center: Streamlines the process of migrating to Google Cloud.
- Azure Migrate: Comprehensive migration tools for seamless transitions to Azure.
For organizations with existing on-premises infrastructure, hybrid cloud solutions offer the flexibility to integrate and extend their current environment:
- AWS Outposts: Bring AWS services on-premises for a consistent hybrid experience.
- GCP Anthos: IT manages hybrid and multi-cloud environments with Kubernetes.
- Azure Stack: extends Azure services to your data centre for hybrid cloud deployment.
Multi-cloud strategies are increasingly popular, allowing you to mitigate vendor lock-in risks and leverage the uniqueness of each platform to meet diverse business needs.
Choosing the Right Cloud Platform
Selecting the most suitable cloud platform requires a comprehensive evaluation of several key factors:
- Organizational Needs: Understand your specific business goals, industry requirements, and compliance mandates.
- Technical Requirements: Consider your current technology stack, your teams' expertise, and any existing integrations.
- Scalability: Evaluate how each platform can support your organization’s growth and evolving workloads over time.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Analyze the long-term costs, including infrastructure, support, and training.
To make an informed decision, utilize the TCO calculators provided by each cloud provider:
By thoroughly assessing these aspects, you can choose the cloud platform that aligns best with your organization’s goals and technical landscape.
Key Takeaways
- AWS dominates the market with the most extensive range of services, making it ideal for diverse and scalable cloud solutions.
- Azure excels at seamless enterprise integration and robust hybrid cloud options, making it a strong choice for organizations with existing Microsoft ecosystems.
- GCP shines in data analytics and machine learning, offering powerful tools for businesses focused on innovation and data-driven decision-making.
- Your decision should be guided by your organization’s specific needs, existing infrastructure, and strategic growth objectives.
FAQs
What are the main differences between AWS, GCP, and Azure?
AWS offers the broadest range of services and global coverage, making it suitable for various applications and industries.
Azure provides seamless integration with Microsoft products and strong hybrid cloud capabilities, making it ideal for businesses heavily invested in Microsoft technologies.
GCP specializes in data analytics and machine learning, with powerful tools for data-driven insights and advanced AI applications.
Which cloud platform is best for startups?
AWS: It is known for its mature ecosystem and extensive resources, which can support rapid scaling and innovation.
GCP: It is attractive for startups due to its generous free credits and strong focus on data and machine learning services.
Azure: It offers excellent support for startups already using Microsoft products, with comprehensive tools and services to accelerate development.
How do the pricing models compare between the three platforms?
All platforms use a pay-as-you-go model with options for reserved capacity discounts. GCP offers unique benefits like per-second billing and sustained use discounts, potentially reducing costs for long-running workloads.
Can I use multiple cloud platforms in a single project?
Yes, multi-cloud strategies are increasingly common to leverage the strengths of different providers. Tools like Kubernetes and Terraform facilitate managing and orchestrating resources across multiple cloud platforms.
