Honeycomb vs Datadog - Choosing the Right Observability Tool
As software stacks grows with microservices, distributed databases, and multi-cloud setups, keeping track of what's happening gets harder. That’s where observability tools come in. Honeycomb and Datadog are two popular choices, each with its own strengths. This article compares Honeycomb and Datadog, exploring their features, philosophies, and best use cases to help you make an informed decision.
What Are Honeycomb and Datadog?
Honeycomb
Honeycomb is a modern observability platform designed to help engineers understand and debug production systems effectively. It stands out by focusing on high-cardinality data (data with many unique values) and providing deep insights into complex systems.
Honeycomb excels at event-driven instrumentation. Instead of just monitoring static metrics like CPU usage or request count, Honeycomb lets you analyze individual events (e.g., a user login, API call, or database query). This approach allows engineers to uncover patterns and anomalies, even in highly dynamic environments.
Key Features
- High-Dimensionality Analysis
- Honeycomb can analyze data with numerous unique attributes (e.g., user IDs, transaction IDs, and API endpoints). This makes it particularly useful for debugging problems that involve multiple variables.
- Real-Time Querying
-
Honeycomb allows sub-second query responses, enabling interactive debugging. Engineers can explore data in real-time, trying different filters and aggregations without delays.
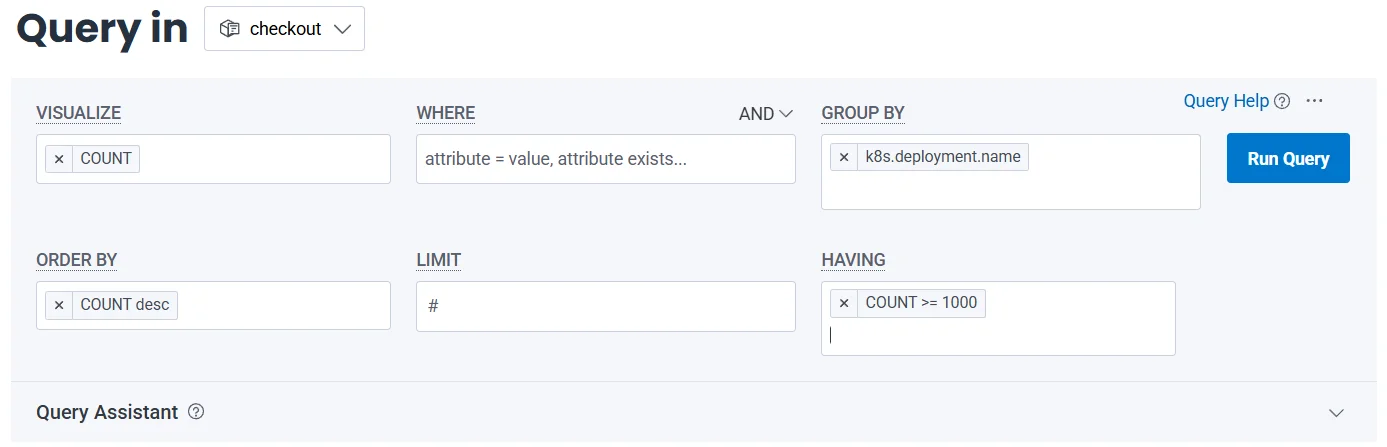
Real-Time Querying in Honeycomb
-
- Event-Based Data Model
- Unlike traditional monitoring tools that focus on pre-aggregated metrics (e.g., average CPU usage), Honeycomb uses wide, structured events. Each event captures all relevant details in a single record, enabling richer analysis.
Datadog
Datadog is a comprehensive monitoring and analytics platform built to support cloud-scale applications. It provides a unified interface for tracking metrics, logs, traces, and more, helping teams monitor the health and performance of their systems.
Datadog emphasizes integration and unification, offering a wide range of tools in a single platform. It covers everything from basic infrastructure monitoring to advanced security and real user monitoring (RUM).
Key Features
- Unified Platform
-
Datadog brings together metrics, logs, traces, and user activity in one interface. This makes it easier for teams to correlate issues across different parts of their stack.
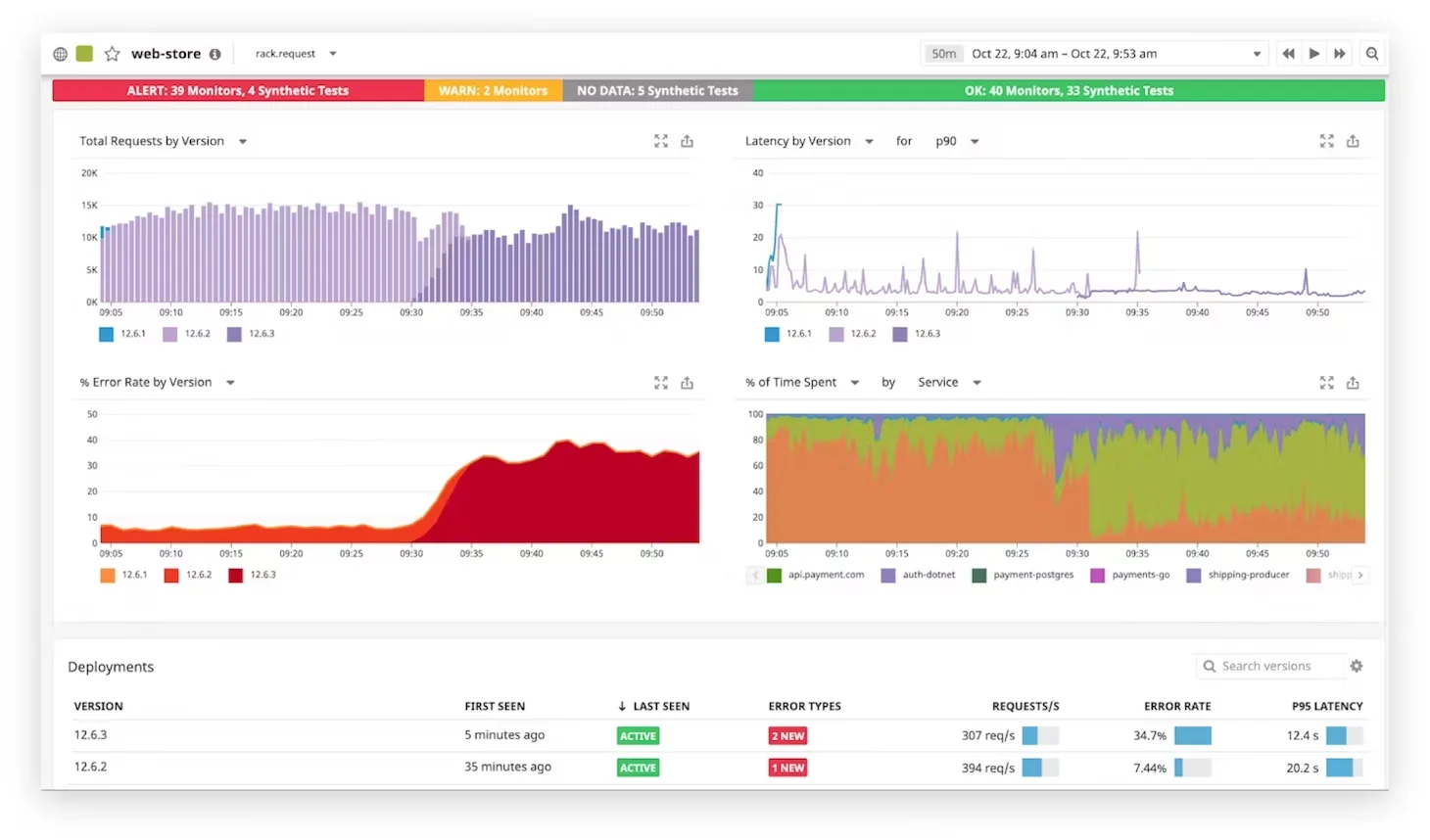
Unified Platform : Datadog
-
- Extensive Integrations
- Datadog supports hundreds of integrations with cloud providers (e.g., AWS, Azure, GCP), container platforms (e.g., Kubernetes, Docker), and third-party applications (e.g., Redis, MySQL, Elasticsearch).
- Metrics-First Approach
- Datadog collects and processes time-series metrics at scale, making it ideal for monitoring system performance and setting up robust dashboards and alerts.
How Do Honeycomb and Datadog Differ in Their Approach?
Honeycomb and Datadog tackle observability from distinct angles. Honeycomb is designed for engineers who need deep, flexible debugging capabilities in complex systems, while Datadog provides a broad, all-in-one monitoring suite for tracking infrastructure, applications, and security. Let’s see how they differ and when you might prefer one over the other.
Honeycomb’s High-Cardinality, Event-Driven Analysis
Honeycomb excels in monitoring large-scale systems by focusing on individual events rather than aggregated metrics, offering deep insights into system behavior. It is built to handle high-cardinality data—such as unique user IDs, session identifiers, request IDs, or build SHAs—that traditional metrics systems struggle with.
Honeycomb’s ability to store and query this detailed data in real-time helps teams quickly identify and resolve performance bottlenecks, errors, or anomalies in complex environments, ensuring a more precise understanding of application behavior at scale.
Why does it matter?
In microservices-heavy architectures, interactions are often ephemeral—short-lived, dynamic, and hard to track with traditional metrics. Honeycomb doesn’t care about aggregate counters (like averages or max values). Instead, it lets you focus on the context of each event, so you can dig into the “who, what, when, and why” of every interaction.
Datadog’s Metrics-First, APM-Centric Strategy
Datadog is built for managing large-scale cloud environments, focusing on metrics-first monitoring. It collects critical system metrics like CPU usage, memory, and network traffic across your stack, while also providing integrated logs, traces, and security monitoring. This combination lets you easily spot issues and troubleshoot in real-time. For example, if a web app slows down, Datadog’s dashboards might show database query spikes, and with a few clicks, you can drill into logs or traces to identify the cause.
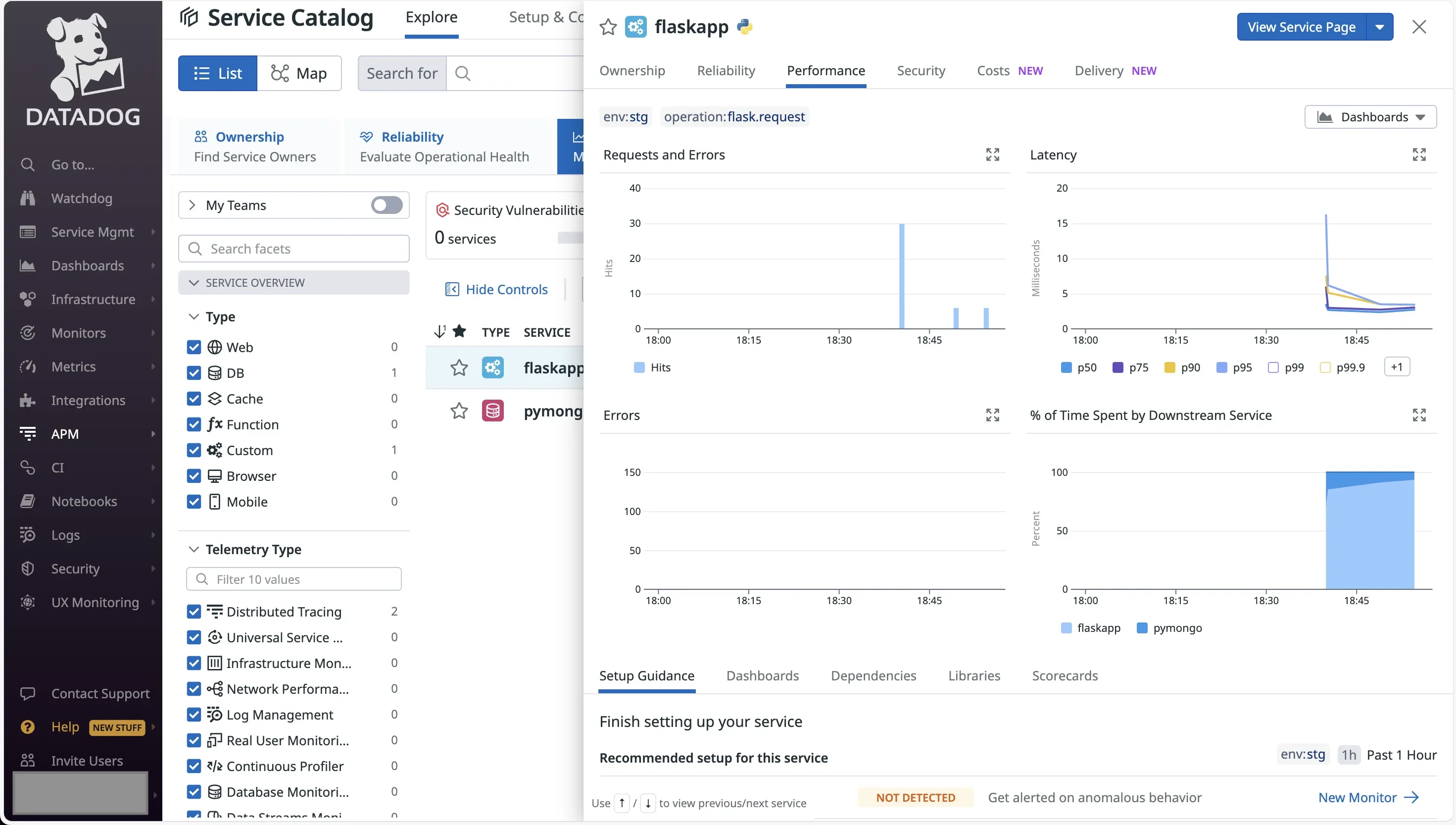
Why does it matter?
Datadog’s strength lies in its broad coverage, acting as a single pane of glass for infrastructure monitoring, application performance, logs, security, and user behavior. Its hundreds of integrations, from AWS to Kubernetes, make it easy to connect your entire system. This approach is ideal for correlating issues across multiple layers, like linking a CPU spike to increased API requests, providing a clear view of your system’s health.
Data Ingestion & Storage
Here’s where Honeycomb gets technical. Instead of pre-aggregating metrics, Honeycomb ingests wide, structured events. Each event is like a detailed snapshot, capturing all the attributes you might need later (e.g., user_id, endpoint, status_code). This data is stored in a columnar-like format, making it fast to filter and query. You get the freedom to ask ad-hoc questions without worrying about predefining metrics.
Datadog’s design starts with time-series metrics. It’s great for tracking trends over time, like CPU usage or request latency. While it also supports logs and traces, its primary design pattern leans on aggregated metrics. To handle large-scale data, Datadog often uses sampling strategies—like keeping only a subset of traces to save storage and improve performance.
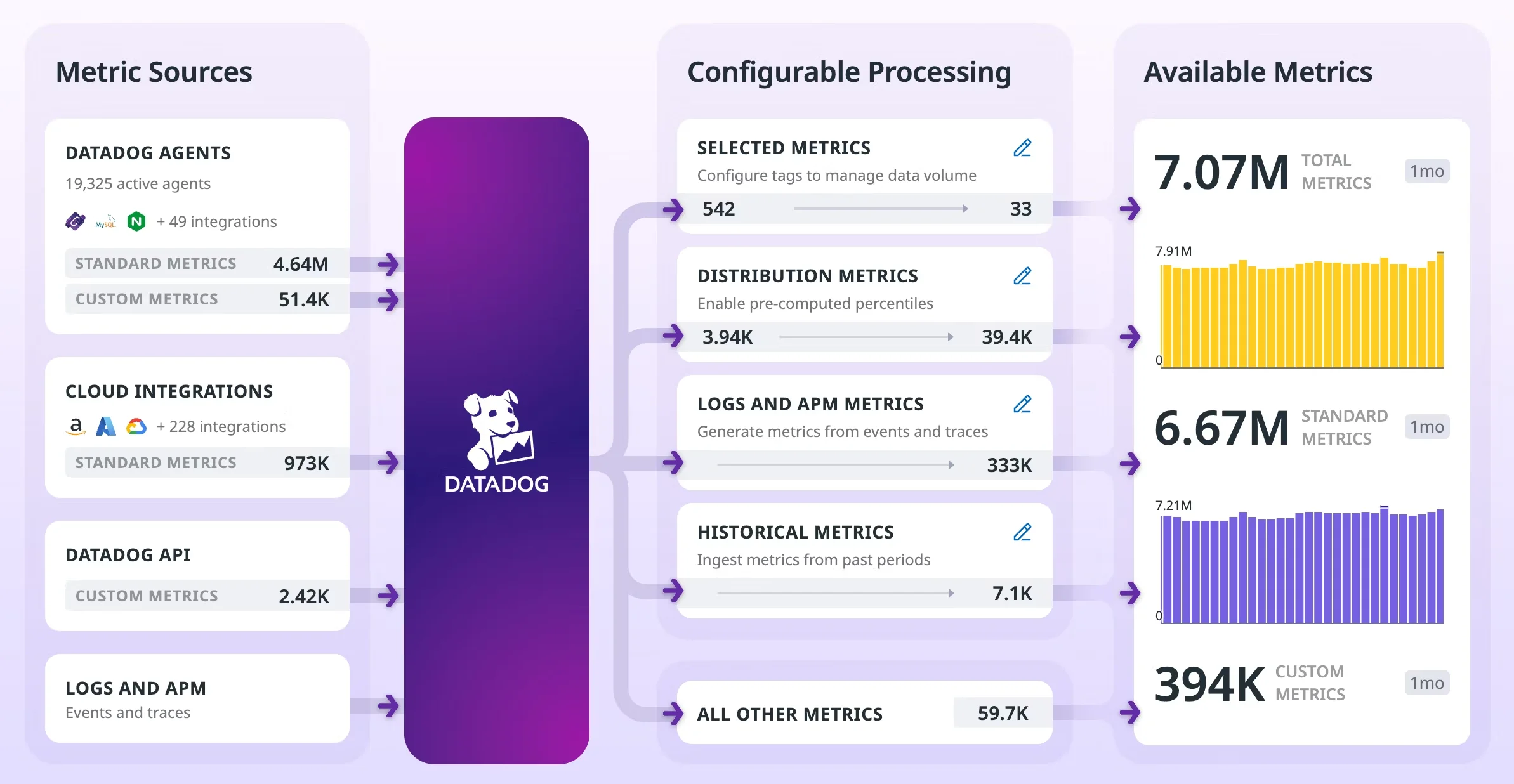
Query Languages & Exploration
For Honeycomb, the UI is built for on-the-fly exploration. You don’t need to define your questions upfront; you can just dive in and start querying. This is especially helpful when you don’t know exactly what you’re looking for but need to explore high-cardinality fields.
On the other hand, While Datadog supports querying logs, metrics, and traces, its strength lies in dashboards and alerts. You can create custom dashboards for key metrics and use them to spot trends at a glance. The query editors are powerful, but Datadog’s interface is optimized for teams who prefer a more structured, dashboard-driven approach.
Understanding Their Core Philosophies
Honeycomb’s “Debugging Production” Mindset
Honeycomb is built for developers who love to interact with their data. If you’re the kind of person who asks, “Why is this happening for just this specific subset of users?” Honeycomb will feel like a natural fit.
Datadog’s “Unified Monitoring” Approach
Datadog is all about providing a big-picture view. If you’re running a cloud-scale environment and want to monitor everything in one place—metrics, logs, traces, security, you name it—Datadog is your go-to.
Key Features: Honeycomb vs Datadog
Let's compare some essential features of both platforms:
| Feature | Honeycomb | Datadog |
|---|---|---|
| Core Focus | Event-driven debugging and high-cardinality data analysis | Broad observability with metrics-first, APM-centric approach |
| Trace Analysis | Detailed, event-centric traces with filtering on unique tags like user_id or X-Request-Id | Distributed tracing integrated with metrics dashboards; search and analytics for traces |
| Dashboards | Interactive, ad-hoc queries for live debugging | Rich, customizable dashboards with real-time visualizations and anomaly detection overlays |
| Alerting | SLO-based alerts focused on user experience | Robust alerting engine with static thresholds, anomaly detection, and multi-channel support |
| Anomaly Detection | Relies on user-driven analysis for transparency | AI/ML-powered anomaly detection, forecasting, and outlier alerts |
| Data Ingestion | Wide, structured events stored for fast, high-dimensional querying | Primarily time-series data with sampling for metrics, logs, and traces |
| Ideal Use Case | Debugging complex microservices with high-cardinality dimensions | Monitoring large, diverse infrastructures with comprehensive metrics and logs integration |
| Strength | Iterative exploration for root cause analysis | Unified monitoring with dashboards, integrations, and AI-driven insights |
1. Trace Analysis
Honeycomb
Honeycomb offers event-centric tracing, allowing you to focus on individual traces filtered by high-cardinality dimensions like X-Request-Id, user_id, or custom tags like build_version. Honeycomb’s traces aren’t just about spans; they’re detailed, context-rich events. You can see everything about a request, from start to finish, and drill into whatever dimension you want without predefined groupings.
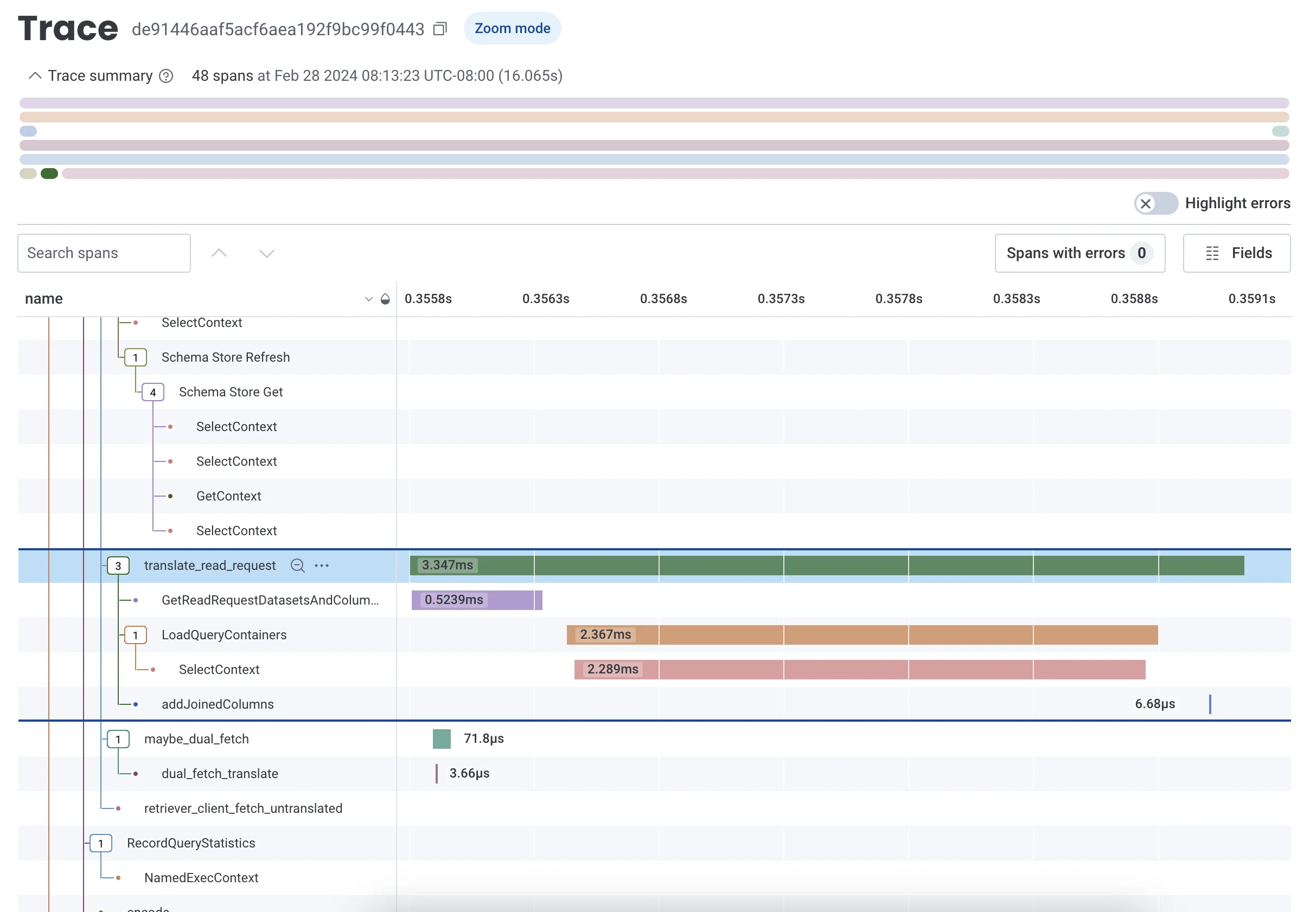
Datadog
Datadog integrates distributed tracing directly with its metrics dashboards. This means you can correlate traces with host-level metrics, like CPU usage or memory consumption. It’s a great way to get a high-level overview, but deep debugging often requires custom instrumentation.
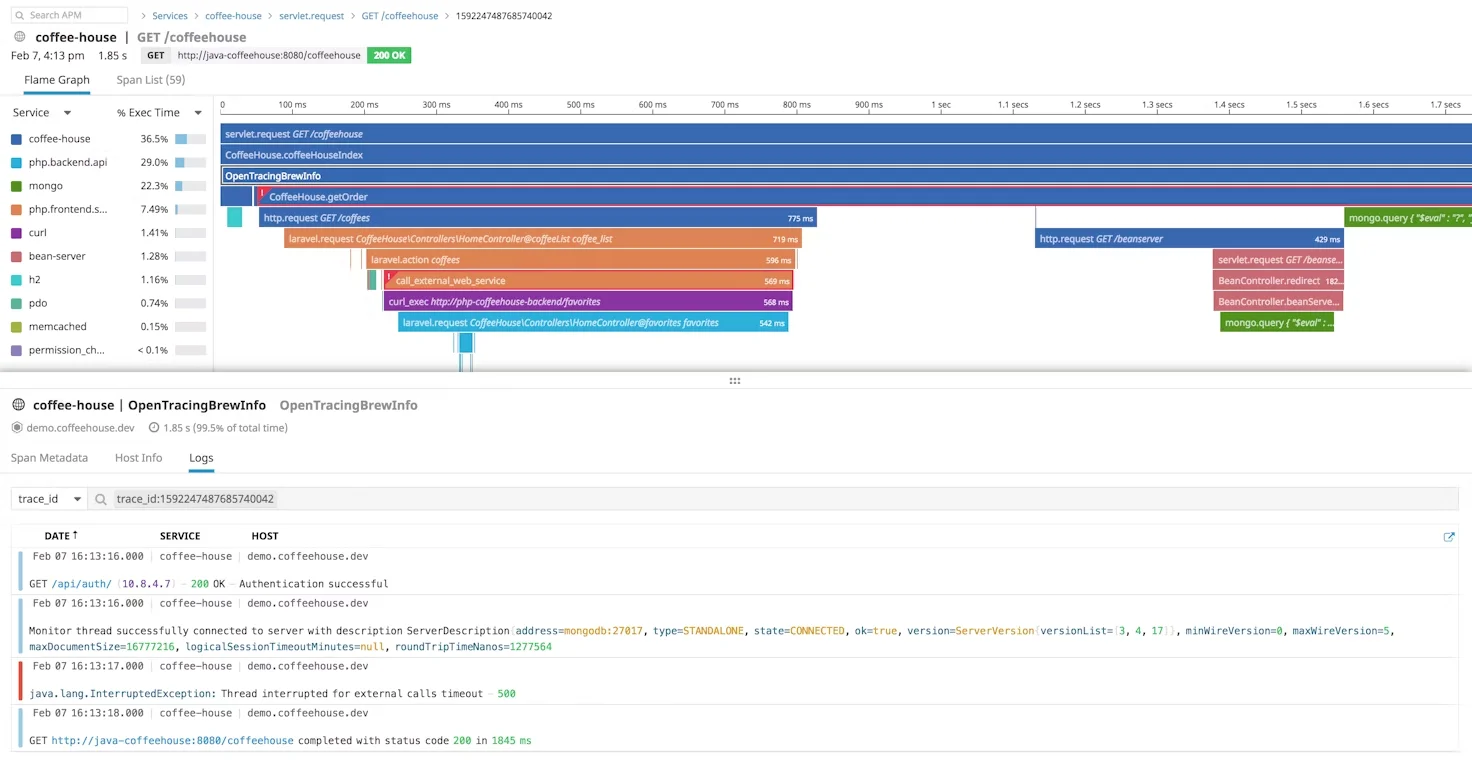
2. Dashboards & Visualizations
Honeycomb
Honeycomb focuses on interactive debugging through ad-hoc queries, allowing you to explore your data in real-time rather than relying on static dashboards. This is ideal for fast-paced production environments where quick investigation is essential.
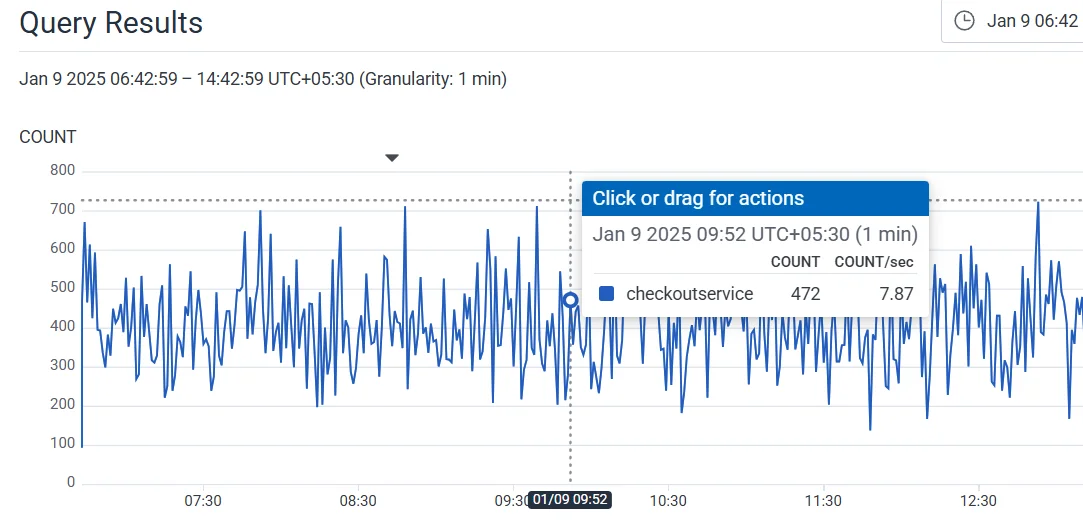
Datadog
Datadog enables users to create highly customizable dashboards, including real-time graphs, anomaly detection overlays, and heatmaps. It simplifies the process of building and sharing rich visualizations, and seamlessly integrates logs, metrics, and traces in a single view. This unified approach provides a comprehensive and holistic perspective of your system’s performance.
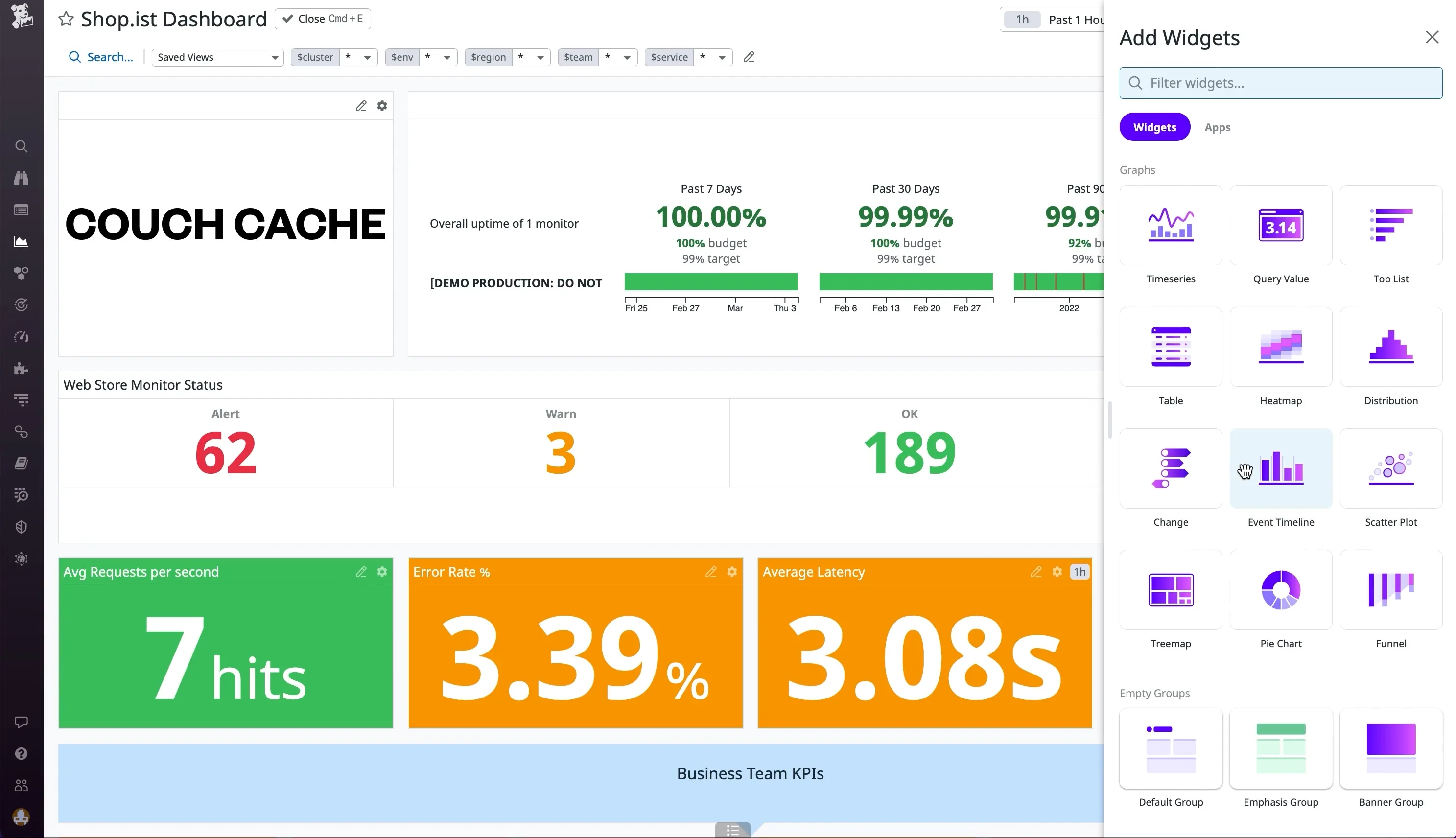
3. Alerting & Notifications
Honeycomb
Honeycomb uses SLO-based alerts, which are tied to specific service-level objectives. This reduces alert fatigue by focusing on alerts that directly affect user experience.
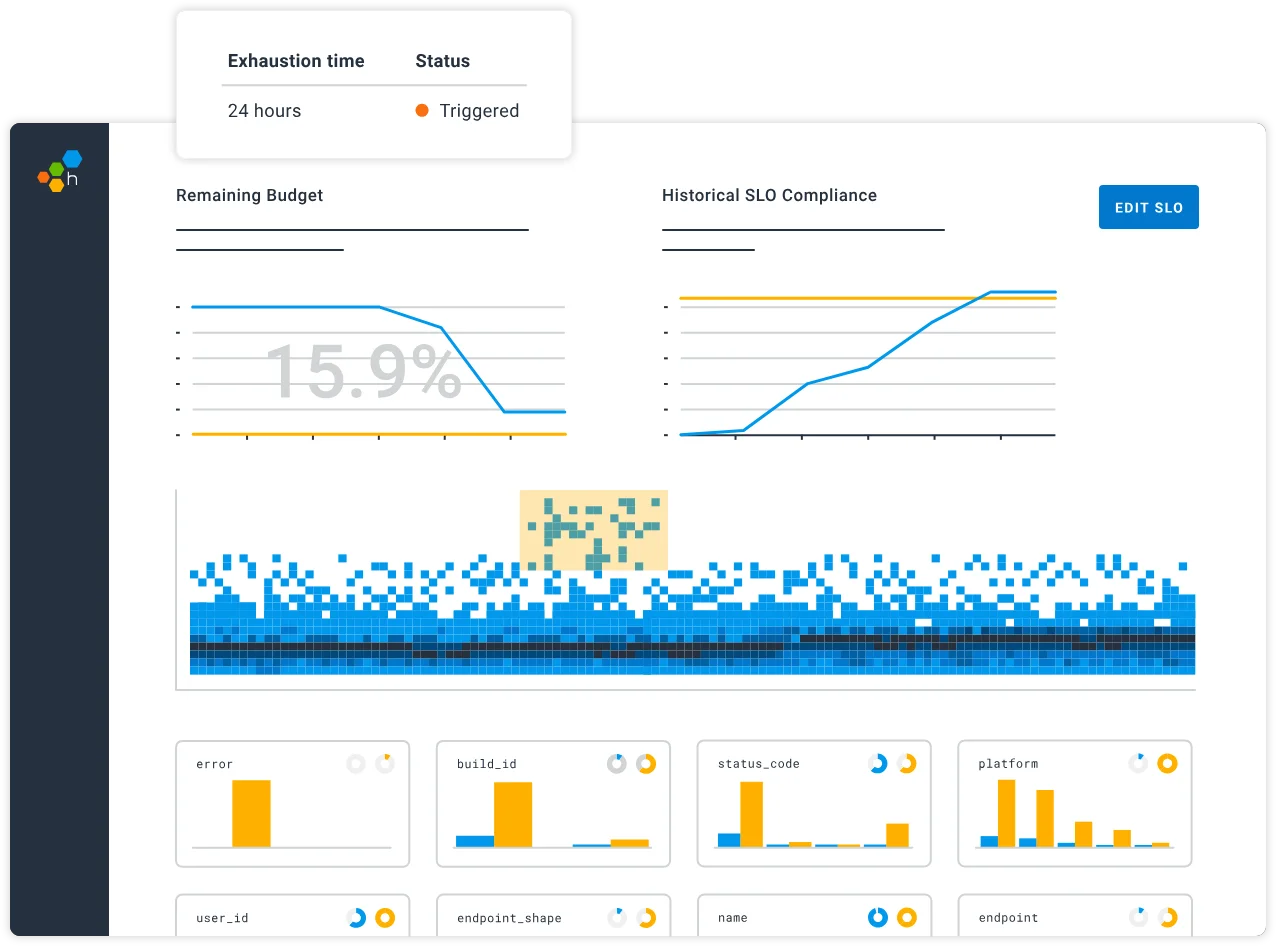
Datadog
Datadog’s alerting engine is robust and highly customizable. You can set static thresholds, enable anomaly detection, or use multi-channel notifications to alert your team via Slack, PagerDuty, email, and more. This flexibility is useful for large teams with complex alerting requirements.
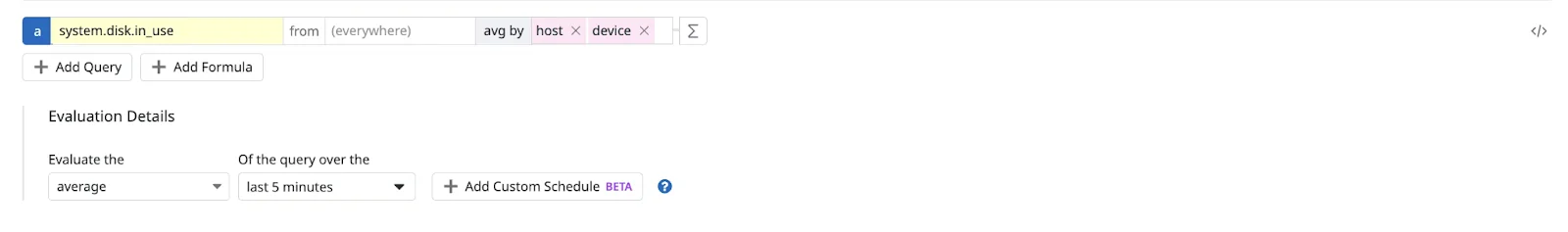
4. Machine Learning & Anomaly Detection
Honeycomb
Honeycomb doesn’t rely on machine learning for anomaly detection. Instead, it empowers you to iteratively analyze your data and find anomalies yourself. This hands-on approach is great if you like to stay in control of the debugging process.
Datadog
Datadog includes built-in AI/ML features for detecting anomalies, forecasting trends, and identifying outliers. These features are especially useful for catching issues before they escalate. This automation can save time and catch potential issues early.
Scalability and Performance: How Do They Compare?
When evaluating observability tools, scalability and performance are critical factors. Here's how Honeycomb and Datadog stack up:
1. Data Ingestion Rates & Query Performance
-
Honeycomb:
Built to handle high volumes of high-cardinality data, Honeycomb excels in ingesting wide, structured events. Its query engine delivers interactive, near-instant results, even for complex data.
-
Datadog:
Datadog efficiently handles vast amounts of metrics via its time-series database. However, log and trace ingestion may be rate-limited depending on your pricing plan. The query performance remains strong for metrics but may slow down with massive log volumes or complex queries.
2. Sampling Strategies & Data Retention
-
Honeycomb:
Honeycomb does not rely on sampling for critical events, meaning it captures every event in full, providing complete visibility for debugging complex issues. However, this approach can lead to higher costs as pricing is based on event volume, especially when dealing with high-cardinality data.
Honeycomb offers a 60-day fixed retention for all datasets, calculated from the date the events are ingested, not based on event timestamps. If your team changes plans, the data retention is maintained up to this 60-day period.
-
Datadog:
Datadog uses partial sampling for distributed traces in large systems, capturing a subset of events to manage data volume and reduce costs. While this approach works well for monitoring trends, it can hinder deep debugging since some events may be missed, especially in high-traffic environments.
Metric retention in Datadog depends on the pricing plan, with shorter retention periods for basic plans (e.g., 15 days) and longer periods for enterprise tiers, which may limit historical data analysis in lower-tier plans.
3. Multi-Region & Multi-Cloud Support
-
Honeycomb:
Honeycomb operates as a SaaS platform with global ingestion endpoints, which makes it suitable for multi-cloud environments. Its lightweight architecture ensures it can scale without adding significant complexity.
-
Datadog:
Datadog shines here with its robust multi-region support and presence in data centers worldwide. It’s well-suited for hybrid cloud environments where infrastructure is spread across on-premises and multiple cloud providers.
4. Cost-Effectiveness at Scale
-
Honeycomb:
Pricing is based on event volume, which can escalate with high-cardinality data. However, the ability to quickly debug complex issues can reduce engineering time and downtime costs, offsetting the higher spend.
-
Datadog:
Datadog’s host-based pricing, combined with charges for logs, custom metrics, and advanced features, can become expensive in large environments. Volume discounts are available, but teams must carefully monitor usage to stay within budget.
Integration Capabilities: Honeycomb vs Datadog
Both platforms offer extensive integration options, but their approaches differ:
1. Supported Languages & Frameworks
- Honeycomb: Offers SDKs for Go, Node.js, Python, Ruby, Java, and others, with strong support for OpenTelemetry, ensuring flexibility and vendor neutrality.
- Datadog: Uses its powerful Datadog Agent to collect metrics, logs, and traces across a variety of languages like Java, Python, Node.js, Ruby, Go, .NET, and PHP, with built-in support for Kubernetes, Docker, and cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP.
2. Third-Party Tool Integrations
-
Honeycomb: Honeycomb’s strength lies in its integration with OpenTelemetry pipelines, which allow ingestion of data from many third-party systems. It also offers integrations for developer workflows like GitHub Actions and collaboration tools like Slack. Its third-party integration ecosystem is smaller compared to Datadog.
-
Datadog: Datadog boasts over 800 built-in integrations, including databases, messaging systems, cloud providers, CI/CD tools, and security tools like Snyk and Jira, providing a comprehensive observability solution.

Datadog Integrations
3. API Flexibility & Extensibility
-
Honeycomb:
Honeycomb offers flexible event ingestion endpoints and GraphQL-like APIs for querying and retrieving data. This flexibility is ideal for teams that want to deeply customize their observability workflows, such as exporting data for custom dashboards or automating certain queries.
-
Datadog:
Datadog provides comprehensive REST APIs for almost every aspect of its platform, including metric ingestion, log and trace submission, dashboard management, and alert configuration. These APIs are commonly used for automating tasks or integrating Datadog with CI/CD workflows.
Collaborative Troubleshooting: How Do They Support Teams?
Effective observability tools should facilitate teamwork. Here's how Honeycomb and Datadog approach collaboration:
1. Team Collaboration Features
-
Honeycomb:
Honeycomb places a strong emphasis on team-based debugging, making it easy for teams to collaborate on complex issues. Key features include:
- Shared Queries: Teams can save and share queries, allowing others to quickly dive into investigations without needing to recreate them.
- Boards for Storing Common Investigations: Teams can create boards to organize ongoing or common investigations, which simplifies team-wide visibility into known issues or exploration paths.
- Guided Query Patterns: Honeycomb’s interface allows teams to follow guided patterns for building queries, making it easier for less experienced team members to contribute to troubleshooting efforts.
-
Datadog:
Datadog fosters collaboration by offering shared dashboards and notebook-style collaboration:
- Dashboards: Custom dashboards with real-time data can be shared across teams, providing visibility into metrics and logs for everyone involved in an issue.
- Notebook Collaboration: Datadog has a notebook feature designed for writing and sharing postmortems or collaborative investigations. These notebooks can include metrics, logs, and traces, alongside commentary to support knowledge sharing.
2. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
-
Honeycomb:
Honeycomb offers granular role-based access control (RBAC), allowing teams to control who can view or modify specific data. Given Honeycomb’s focus on small to medium teams, the complexity of RBAC is relatively simple. The platform allows users to set different access levels, including:
- Read-only: Users can view the data without modifying queries.
- Write: Users can modify or create new queries and boards.
-
Datadog:
Datadog has a much more comprehensive RBAC system, making it suitable for larger enterprises. It supports detailed permissions, including:
- User Access: Administrators can assign roles like read-only, editor, or admin to users.
- Multi-Organization Support: Datadog enables separate environments (e.g., development, production) and different organizations within the same account, which is useful for managing access in larger, complex teams.
Datadog comprehensive RBAC system
3. Knowledge Sharing & Documentation
-
Honeycomb:
Honeycomb emphasizes learning from each other through shared, reusable queries. Its shared queries and boards create a system of knowledge transfer and team collaboration:
- Teams can easily save queries for future use, enabling quick access to previously identified patterns and insights.
- Honeycomb’s boards allow users to document ongoing investigations and solutions, providing a historical record of past issues and resolutions.
-
Datadog:
Datadog supports knowledge sharing with features like tagging and annotating dashboards and monitors:
- Tagging allows teams to mark specific data or dashboards with keywords, making it easier to locate and reference.
- Annotations allow users to add comments or context to monitors and dashboards, improving cross-team understanding of why certain metrics or events are important.
Pricing Models: Honeycomb vs Datadog
Understanding the pricing structure is crucial for long-term planning:
Honeycomb
-
Event-Based Pricing: Billed by the number of events ingested and retention window. Ideal for smaller teams but can get expensive at a large scale.
-
Free Tier: Limited daily event volume and short retention, suitable for testing and proof of concept.
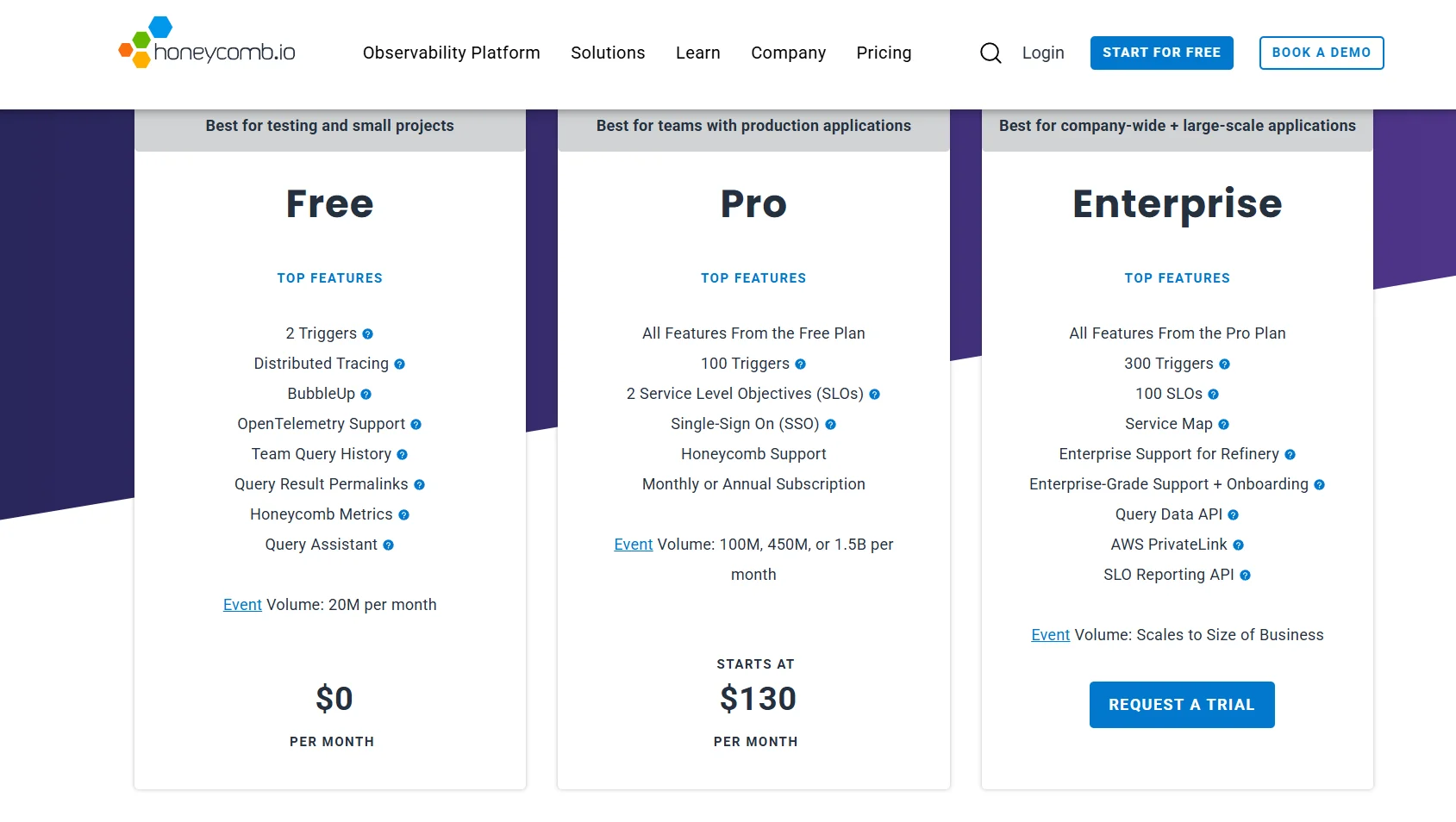
Honeycomb pricing structure
Datadog
-
Host-Based & Add-On Model: Base subscription is per host, with additional charges for custom metrics, logs, and traces. Pricing tiers vary by feature set (e.g., APM, security).
-
Free Tier: 14-day free trial for full feature access; limited free usage for metrics and logs.
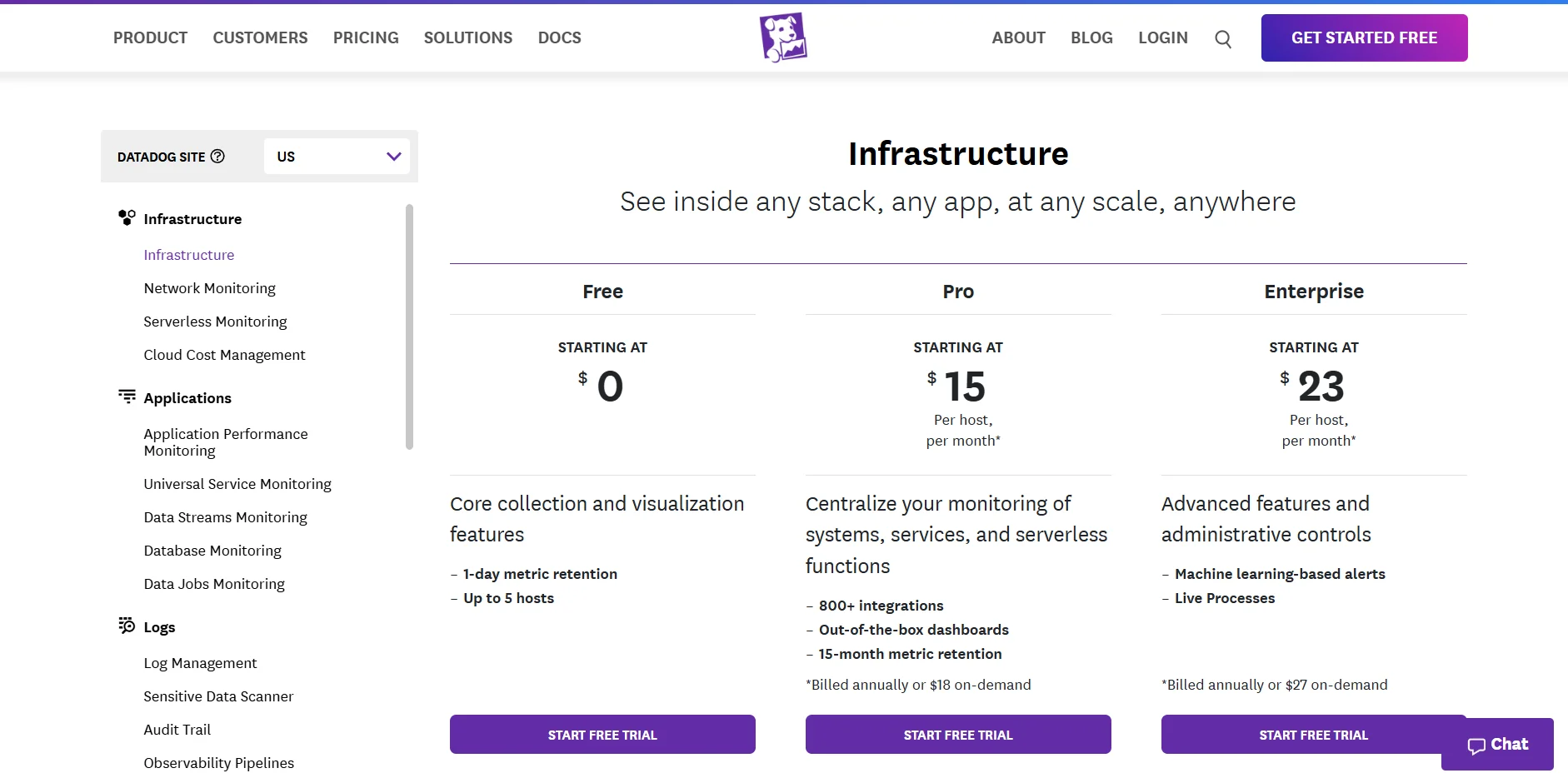
Datadog Pricing structure
How to Choose Between Honeycomb and Datadog
Choosing between Honeycomb and Datadog depends on several factors:
- Team Size & Expertise
- Honeycomb: Ideal for teams with advanced engineers who need deep, event-driven debugging and high-cardinality data analysis.
- Datadog: Best for larger teams or enterprises that need an integrated solution with broad monitoring capabilities for infrastructure and security.
- Use Case Alignment
- Honeycomb: Perfect for microservices with ephemeral or dynamic environments, and for teams focused on interactive debugging workflows.
- Datadog: Suitable for large, multi-product organizations that need comprehensive monitoring across metrics, logs, and APM.
- Learning Curve & Onboarding
- Honeycomb: Requires familiarity with event-driven queries and advanced instrumentation, which may take longer to master.
- Datadog: Easier to set up for basic monitoring with quick onboarding, though advanced features may still require custom instrumentation.
- Long-Term Scalability & Vendor Lock-In
- Consider the impact of volume-based (Honeycomb) or host-based (Datadog) pricing on your future costs as your environment grows.
- Evaluate if adopting open standards like OpenTelemetry is a priority to avoid vendor lock-in and ensure flexibility for future tool-switching.
SigNoz: An Open-Source Alternative Worth Considering
While comparing Honeycomb vs Datadog, it's worth mentioning SigNoz—an open-source observability platform that offers an alternative approach.
SigNoz is an open-source observability platform that provides integrated metrics, logs, and traces in a unified interface. It is based on OpenTelemetry, which is a cloud-native, open-source standard for collecting and exporting telemetry data, making it easy to instrument microservices with minimal vendor lock-in. SigNoz is designed for teams that want full control over their observability infrastructure without relying on commercial SaaS platforms.
Comparison with Honeycomb & Datadog
While Honeycomb and Datadog offer powerful observability solutions, SigNoz provides notable benefits in several key areas:
- Data Control:
- SigNoz offers a self-hosted deployment option, meaning you control where and how your observability data is stored and processed. This is a significant advantage for organizations that need to maintain strict data sovereignty and compliance requirements. Since SigNoz can be deployed on your own infrastructure or in your cloud environment, it ensures you retain full ownership of your data.
- Honeycomb and Datadog, on the other hand, are cloud-based platforms that manage your data for you. While they offer reliability and scalability, you are essentially trusting these third-party services with your telemetry data, which can raise concerns in regulated industries or for organizations that need to keep all data in-house.
- Community-Driven:
- SigNoz is driven by the open-source community, which means that features and updates are often built based on the needs and feedback of its users. This community-driven model allows for rapid innovation and a flexible product that can evolve with changing use cases.
- Honeycomb and Datadog, though both are responsive to customer feedback, are commercial platforms with longer release cycles and a more controlled feature roadmap.
- Cost Savings:
- SigNoz allows you to avoid the per-host or per-event charges typical of cloud-based solutions like Honeycomb and Datadog. Instead, you pay only for the infrastructure you manage (e.g., your cloud or on-prem hardware), which can lead to significant cost savings, particularly at scale. SigNoz's pricing model is more predictable, with no hidden costs based on data volume or event cardinality.
- Honeycomb and Datadog have usage-based pricing that scales with the volume of events, metrics, or hosts being monitored. While this works well for small teams, larger organizations or those with high-cardinality data (many unique tags or identifiers) could see escalating costs as their data grows.
Why Consider SigNoz?
-
Customization & Compliance:
SigNoz, being open-source and self-hosted, offers deep customization, allowing organizations to meet specific compliance needs (e.g., GDPR or data residency). In contrast, Honeycomb and Datadog provide configuration options but are more limited in data storage control, as they rely on their cloud environments.
-
Avoiding Expensive SaaS Models:
SigNoz is cost-effective, with charges only for infrastructure management. This makes it ideal for high-throughput systems. On the other hand, Honeycomb and Datadog can become costly due to usage-based pricing, especially with large volumes of events, hosts, or high-cardinality metrics.
-
Vendor Independence:
Built on OpenTelemetry, SigNoz ensures freedom from vendor lock-in, allowing easy migration to other OpenTelemetry-compatible services. Honeycomb and Datadog are proprietary platforms, making migration harder once integrated into their ecosystems.
Real-World Scenarios Where SigNoz Shines
- Startups & Small Teams: Startups often operate on tight budgets and need a solution that provides full observability without breaking the bank. SigNoz is a great fit for such teams because they can run it on their own infrastructure, paying only for the infrastructure they manage. This can be much more cost-effective than Datadog or Honeycomb, where usage-based pricing can quickly become unaffordable as event volume increases.
- Teams Needing Customization: Imagine a company that operates in a regulated industry, where logs need to be stored in specific geographic regions or encrypted in particular ways. With SigNoz, the team can configure the storage environment according to their specific needs. In contrast, with Honeycomb or Datadog, these kinds of customizations would likely be harder to implement without the support of specific enterprise features or premium plans.
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Key Takeaways
- Honeycomb excels at high-cardinality data and real-time interactive debugging, making it ideal for complex microservices with a "deep dive" mindset.
- Datadog provides a unified, feature-rich platform for metrics, logs, traces, and security monitoring—especially appealing to organizations seeking a "one-stop shop."
- The choice depends on your specific architecture, team skill set, and desired approach to debugging vs. broad monitoring.
- Pricing and scalability can be a deciding factor; carefully assess the cost model and potential vendor lock-in.
- SigNoz offers an open-source alternative, giving you more control over data and avoiding unpredictable SaaS bills.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Tool Is Better for Microservices Architectures?
Honeycomb excels with its high-cardinality tracing and event-centric debugging, ideal for dynamic, microservices environments. Datadog offers strong infrastructure monitoring with integrations for Kubernetes and Docker but may not provide the same granular debugging.
How Do Honeycomb and Datadog Handle Data Privacy and Compliance?
- Honeycomb: Primarily a SaaS offering with compliance certifications (SOC 2), but you must ensure your data meets privacy constraints.
- Datadog: Offers multiple regions for data storage and various compliance frameworks (HIPAA, GDPR, etc.). You may need to configure data residency to match regulatory requirements.
Can I Use Both Honeycomb and Datadog Together in My Stack?
Yes, you can use both tools together to leverage Honeycomb's deep debugging and Datadog's comprehensive monitoring capabilities, though it requires additional configuration.
What are the main differences between Honeycomb and Datadog in terms of learning curves?
Honeycomb has a steeper learning curve, focusing on event-driven queries and advanced instrumentation. Datadog is easier to set up initially, with an out-of-the-box solution but requires more code-level integration for deep trace analysis.
