Top 10 Incident Management Tools for IT Teams in 2026
In today’s fast-paced digital world, incident management tools are essential for IT teams to ensure smooth and uninterrupted operations. As technology and IT ecosystems become increasingly complex, quickly identifying, responding, and resolving incidents has never been more crucial.
With a wide range of tools available in 2024, how do you determine which best suits your team’s needs? This article provides a detailed overview of the top incident management solutions and offers practical advice to help you choose the right tool for your organization.
What is Incident Management and Why is it Crucial for IT Teams?
Incident management is a structured process that IT teams use to identify, analyze, and resolve disruptions to IT services. As a critical component of IT Service Management (ITSM), it prioritizes restoring normal operations swiftly and effectively to minimize the impact on business operations.
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, where even brief downtimes can lead to significant revenue loss or reputational damage, incident management is no longer optional.
Why Incident Management Matters
- Ensures Business Continuity: Rapid incident detection and resolution are crucial for maintaining seamless business operations, safeguarding revenue, and upholding organizational reputation.
- Ensures Customer Satisfaction: Consistently high service quality and availability directly translate to satisfying customers, fostering trust and loyalty.
- Boosts Team Efficiency: A streamlined incident management process allows IT teams to handle disruptions methodically, freeing them to focus on strategic, high-value initiatives.
- Reduces Operational Costs: Proactive incident management minimizes downtime and prevents minor issues from escalating into costly crises.
Core Components of Effective Incident Management
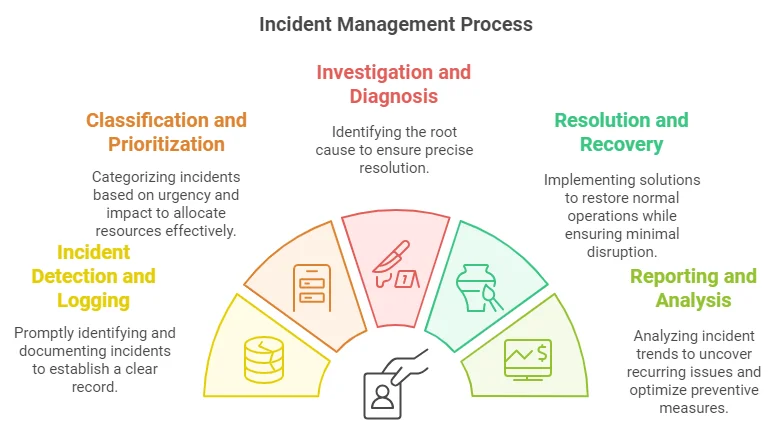
- Incident Detection and Logging: Promptly identifying and documenting incidents to establish a clear record.
- Classification and Prioritization: Categorizing incidents based on urgency and impact to allocate resources effectively.
- Investigation and Diagnosis: Identifying the root cause to ensure precise resolution.
- Resolution and Recovery: Implementing solutions to restore normal operations while ensuring minimal disruption.
- Incident Closure: Verify that the issue is resolved and document the resolution process for future reference.
- Reporting and Analysis: Analysing incident trends to uncover recurring issues and optimize preventive measures.
By adopting a systematic approach to incident management, IT teams can transform unexpected disruptions into opportunities for growth and improvements. This process safeguards operations and strengthens an organization's resilience in an increasingly dynamic digital ecosystem.
Essential Features to Look for in Incident Management Tools
Selecting the right incident management tool can significantly impact your IT team’s efficiency and effectiveness. When evaluating options, look for these essential features to ensure the tool aligns with your organizational needs:
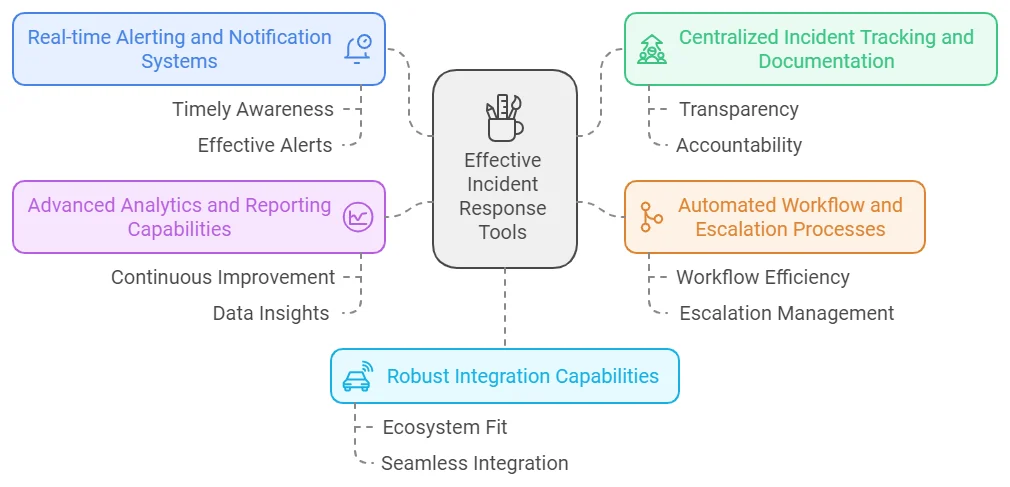
- Real-time Alerting and Notification Systems: Effective incident response starts with timely awareness. Look for tools offering:
- Multi-Channel Alerts: Instant notifications via email, SMS, push notifications, and integrated chat platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams.
- Customizable Alert Rules: Tailor alerts based on thresholds, service levels, or specific metrics.
- Intelligent Alert Grouping: Consolidate related alerts to minimize noise and avoid alert fatigue.
- Centralized Incident Tracking and Documentation: A unified platform for incident management is critical for transparency and accountability:
- Unified Dashboard: Centralize incident data for a complete, real-time view.
- Detailed Incident Timelines and Audit Trails: Maintain comprehensive records of incident history for accountability and compliance.
- Knowledge-Based Integration: Provide teams quick access to solutions and troubleshooting guides for recurring issues.
- Automated Workflow and Escalation Processes: Streamlining workflows and ensuring accountability is vital for efficient incident resolution:
- Configurable Routing: Automatically assign incidents based on severity, type, or team expertise.
- Automatic Escalation: Trigger escalations for unresolved incidents within specified timeframes.
- Collaboration Integration: Integrate with tools like Jira or ServiceNow to enable seamless communication and task management.
- Advanced Analytics and Reporting Capabilities: Data-driven insights are essential for continuous improvement.
- Performance Metrics: Track key indicators like mean time to detect (MTTD) and mean time to resolve (MTTR).
- Customizable Reporting: Generate detailed reports tailored to specific stakeholders or objectives.
- Proactive Insights: Identify trends and potential bottlenecks to optimize processes and prevent future incidents.
- Robust Integration Capabilities: A tool that fits seamlessly into your existing ecosystem is a must:
- Monitoring Tool Integration: Connect with solutions like Prometheus, Grafana, or SigNoz for enhanced visibility.
- ITSM and ChatOps Support: Streamline workflows with platforms like ServiceNow or PagerDuty and enable real-time collaboration.
- API Access: Facilitate custom integrations to tailor the tool to your specific operational needs.
Top 10 Incident Management Tools for 2024
Incident management tools are pivotal in ensuring IT service reliability and responsiveness. Here's a curated list of the top 10 tools that stand out in 2024 for their features, usability, and value:
1. SigNoz
SigNoz takes a modern, open-source approach to observability and incident management, making it a compelling choice for organizations looking for transparency, flexibility, and cost savings.
Key Features:
- Comprehensive Observability: Provides end-to-end tracing, metrics collection, and logs in a unified platform, enabling faster incident resolution.
- Custom Dashboards and Alerts: Build tailored dashboards to monitor key metrics and set up intelligent alerts to stay ahead of potential issues.
- Root Cause Analysis: Leverages distributed tracing to identify and precisely resolve performance bottlenecks.
Open-source Advantage:
- Community-Driven Development: Backed by an active community, offering constant improvements and shared expertise.
- Flexibility Customization: Adapt and extend SigNoz to fit your organization’s specific needs without vendor lock-in.
Cost-effectiveness:
- Self-Hosted Option: Completely free for unlimited users, providing budget-friendly observability for startups and growing teams.
- Cloud Offering: Competitive pricing for managed services, delivering convenience without compromising affordability.
Idea Use Cases: Teams seeking transparency, flexibility, and a strong observability foundation for managing complex incidents. Organizations want a cost-effective, community-backed alternative to proprietary tools.
To explore SigNoz, visit their website at https://signoz.io and dive into their comprehensive documentation for seamless setup and integration.
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
2. PagerDuty
PagerDuty is a market leader in digital operations management, trusted by organizations worldwide for its powerful incident response capabilities.
Key Features:
- Event Intelligence: Leverages AI to reduce noise and highlight critical incidents.
- On-Call Management: Flexible scheduling, rotations, and automated escalation workflows.
- Seamless Integration: Connects with over 700 tools, including monitoring, ticketing, and communication platforms.
Ideal Use Cases: Enterprises with large, distributed teams requiring sophisticated automation and real-time insights.
Pricing: Starts at $19/user/month for small teams, with enterprise pricing available for larger organizations.
3. Opsgenie
As part of the Atlassian suite, Opsgenie offers a comprehensive approach to alert management and on-call scheduling, making it a strong contender for IT teams needing structured incident response processes.
Standout Functionalities:
- Advanced Routing and Scheduling: Configurable routing rules to direct alerts based on severity, time of day, or team role.
- Incident Timeline and Context: Detailed incident timeline and notes to maintain context across team shifts.
- User-Friendly Mobile Apps: Receive actionable push notifications, allowing users to acknowledge, escalate, or resolve incidents on the go.
Collaboration Features:
- Stakeholder Notifications: Keeps relevant stakeholders informed with tailored notifications, reducing the need for manual updates.
- Integrated Chat and Conference Bridge: Direct access to communication channels enables real-time coordination during incident resolution.
Ideal Use Cases: Teams looking for tight integration with Atlassian products, such as Jira, or needing strong mobile support for on-call teams.
Pricing: Starts at $9/user/month, with advanced features available on premium plans.
4. ServiceNow
ServiceNow is a leading IT Service Management (ITSM) platform that excels in incident management, offering a robust suite of tools for enterprise-grade IT operations.
Enterprise-Grade Features:
- AI-Powered Automation: Automatically categorizes and prioritizes incidents based on impact and urgency, reducing manual workload.
- Visual Workflow Designer: Create and customize workflows with an intuitive drag-and-drop interface.
- Advanced Analytics: Detailed reporting and dashboards provide insights into incident trends and team performance.
- Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) Alignment: Security adheres to ITIL best practices, ensuring compliance with established IT governance frameworks. This makes it an excellent choice for enterprises operating under strict regulatory or operational standards.
- This alignment makes it particularly suitable for enterprises operating under stringent regulatory, operational, or compliance standards.
- It empowers organizations to balance service quality, operational efficiency, and risk management, ensuring robust and reliable IT operations.
- Customization: The platform offers unparalleled flexibility, enabling organizations to design incident management workflows tailored to their specific needs and integrate seamlessly with other enterprise systems.
Ideal Use Cases: Large enterprises with complex IT infrastructures require a highly customizable, ITIL-compliant platform.
Pricing: Custom pricing based on organizational needs, with solutions tailored for mid-sized to large enterprises.
5. Splunk On-Call (formerly VictorOps)
Splunk On-Call specializes in DevOps-focused incident management, combining automation with machine learning to streamline workflows and enhance operational reliability.
DevOps-Centric Features:
- Automated Incident Routing: Directs incidents to the right team or individual based on code ownership or predefined rules.
- Post-Incident Reviews: Comprehensive timelines and reports to facilitate learning and improve future responses.
- Integration with Splunk Observability Suite: Provides rich context for alerts, enabling teams to address issues faster and more effectively.
Machine Learning Capabilities:
- Anomaly Detection: Identifies irregular patterns in system behavior to proactively address potential incidents.
- Intelligent Alert Grouping: Consolidates related alerts to minimize noise and improve focus on critical issues.
Ideal Use Cases: DevOps teams seeking an integrated incident management tool that aligns with observability and CI/CD pipelines.
Pricing: Starts at $10/user/month, with scalable plans available for enterprises.
6. Zenduty
Zenduty provides a modern, collaborative approach to incident management, focusing on automation, streamlined communication, and cost-effectiveness.
Multi-channel Alerting:
- Diverse Notification: Alerts via SMS, phone calls, push notifications, and integrations with Slack or Microsoft Teams.
- Customizable Rules: Fine-tune alert priorities, escalation paths, and delivery methods to match team workflows.
Incident Response Playbooks:
- Predefined Action: Deploy playbooks to handle common incident scenarios efficiently, reducing resolution time.
- Automated Task Assignment: Assign tasks based on predefined criteria and track their status through completion.
- Pricing Advantage: Zenduty stands out with competitive pricing and a free tier for up to 5 users, making it an attractive choice for startups and small to medium-sized teams.
Ideal Use Cases: Teams looking for an affordable, feature-rich solution that prioritizes collaboration and ease of use.
Pricing: Paid plans start at $9/user/month, scaling with additional features for larger teams.
7. Jira Service Management
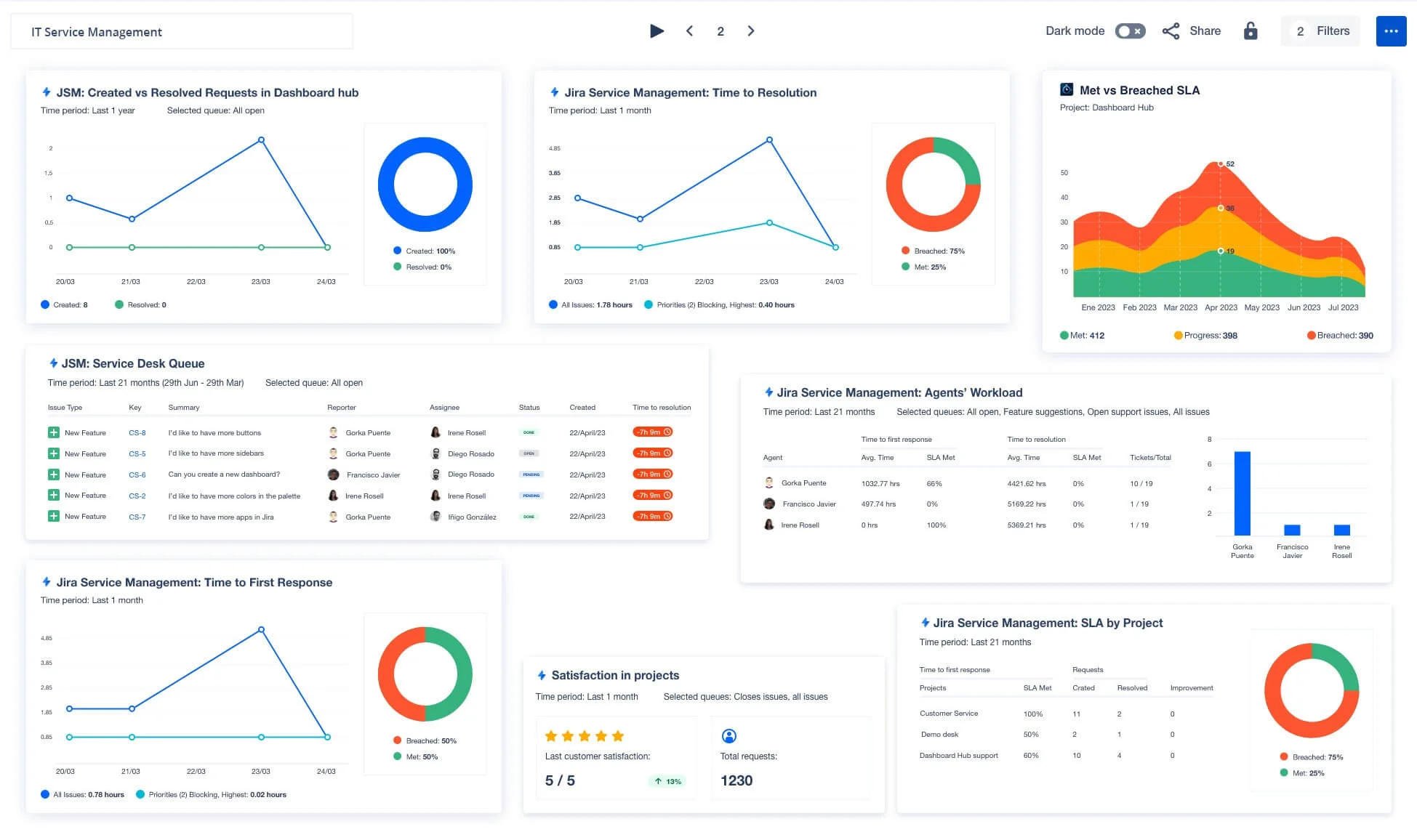
Jira Service Management brings incident management into the powerful Atlassian ecosystem, offering seamless integration and enhanced collaboration for IT teams.
Atlassian Integration:
- Unified Workflow: Integrates effortlessly with Jira Software for bug tracking and confluence for documentation, enabling end-to-end visibility and collaboration.
- Shared Asset Management: Includes a configuration management database (CMDB) for tracking assets and dependencies to aid in root cause analysis.
Knowledge Base:
- Self-Service Portal: Users can access a searchable repository of knowledge articles to resolve common issues independently.
- Smart Suggestions: Recommends relevant articles automatically during incident creation, helping teams and users find solutions faster.
Ideal Use Cases: Organizations already using Atlassian tools seeking a cohesive and scalable incident management solution.
Pricing: Starts at $21/agent/month for standard plans, with additional tiers for premium and enterprise-level features.
8. xMatters
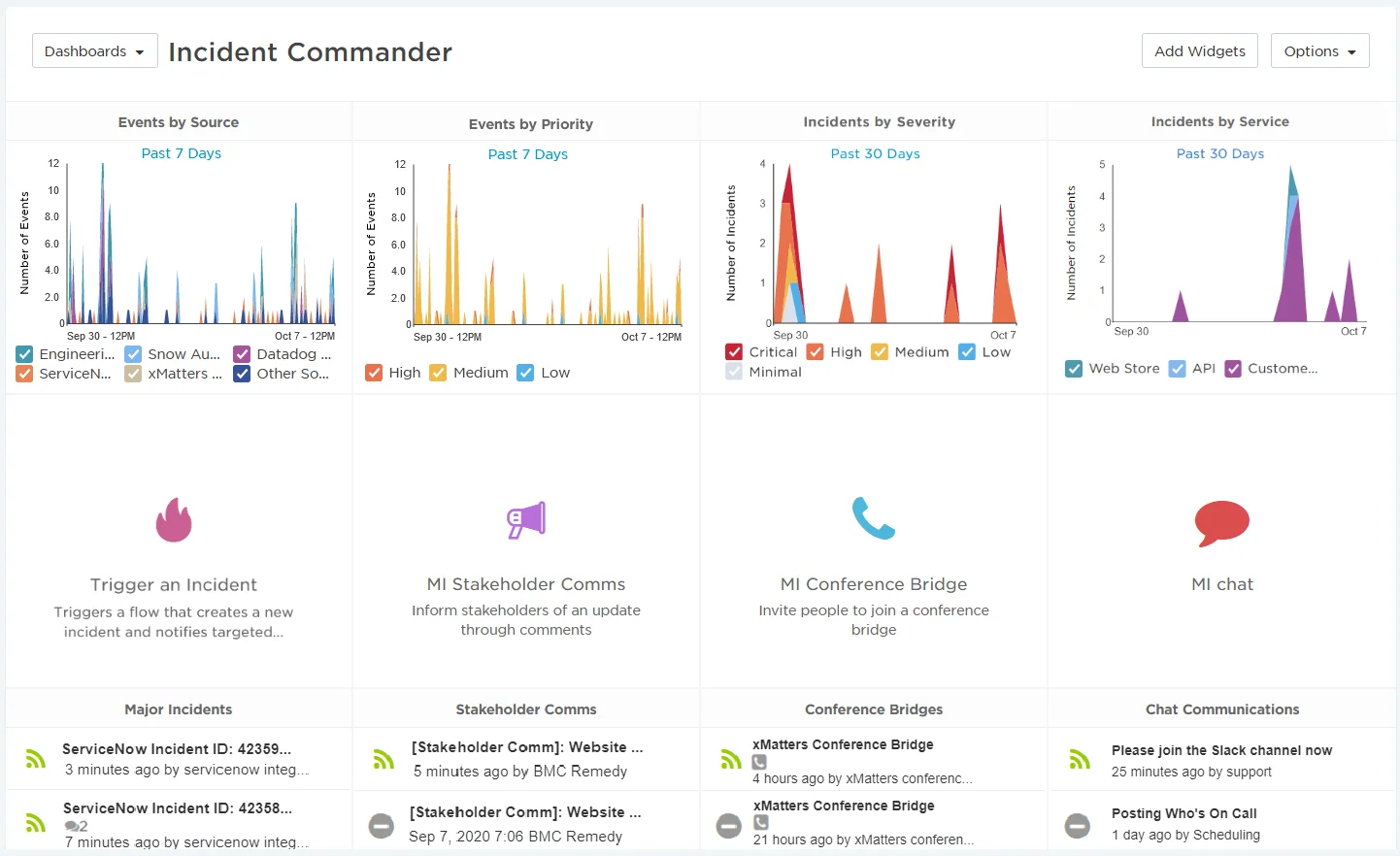
xMatters is a leading incident management tool that excels in intelligent communication and workflow automation for DevOps and IT teams.
Workflow Automation:
- Dynamic Event Routing: Automatically routes incidents to the right teams based on predefined rules and real-time conditions.
- Custom Flow Designer: Build tailored workflows for complex scenarios without needing extensive coding expertise.
Integrations:
- Extensive Ecosystem: Over 200 pre-built integrations with popular tools like Slack, ServiceNow, and Splunk.
- Custom Solutions: Utilize REST APIs to create bespoke integrations for unique organizational needs.
On-call Management:
- Flexible Scheduling: Advanced on-call management with calendar synchronization to ensure coverage.
- Sophisticated Escalation Rules: Configurable escalation layers with multiple conditions to ensure no incident goes unresolved.
Ideal Use Cases: Enterprises seeking a tool that seamlessly integrates communication, automation, and scheduling for efficient incident response. Pricing: Flexible pricing options, starting with a free tier for small teams, with premium plans for more advanced features.
9. Freshservice
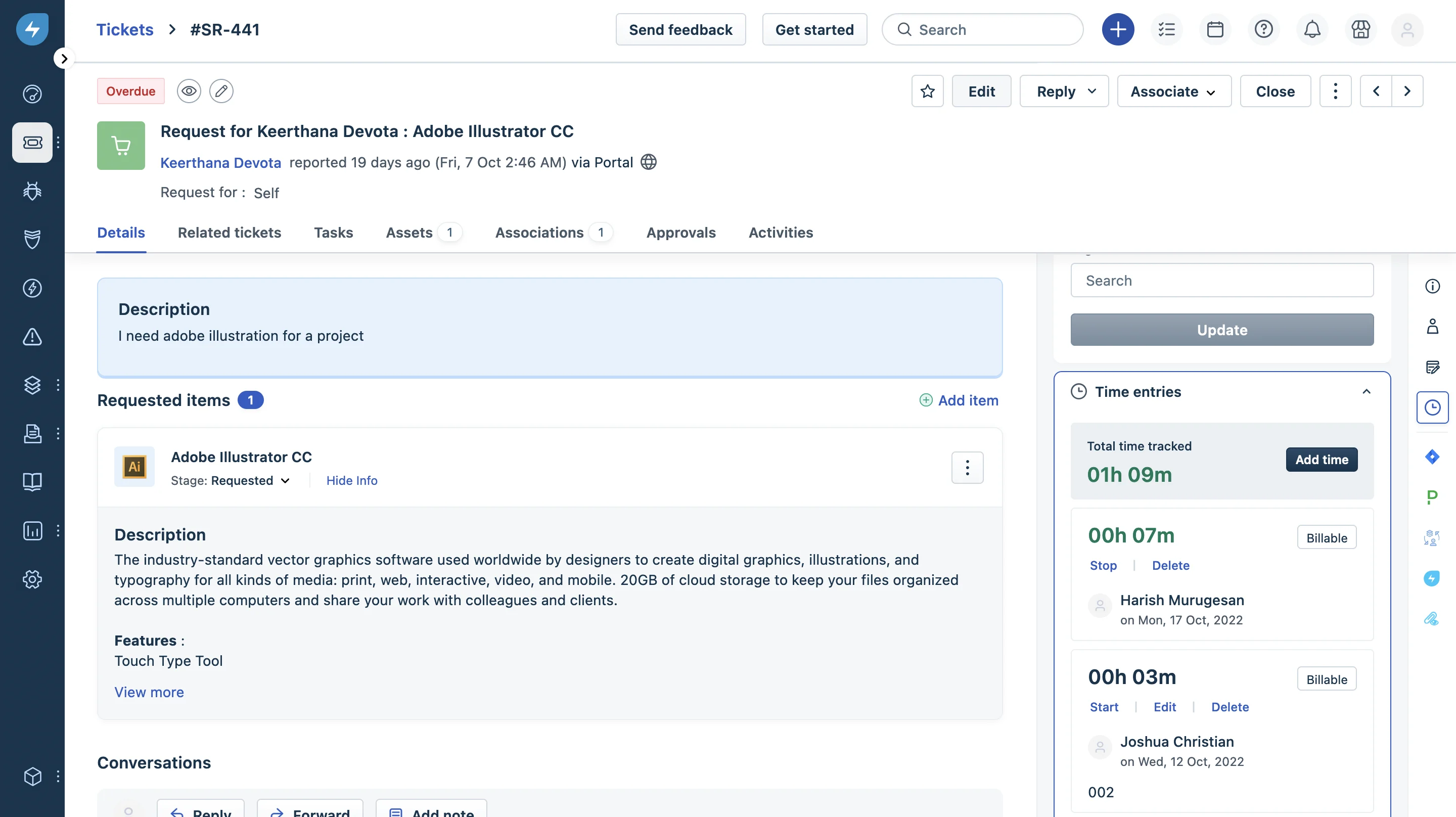
Freshservice delivers a user-friendly IT Service Management (ITSM) platform with robust incident management features, ideal for organizations that prioritize simplicity and efficiency.
User Friendly Interface:
- Intuitive Design: Drag-and-drop capabilities simplify ticket management, enhancing productivity for IT teams.
- Customizable Dashboards: Tailor views and reports to monitor key performance metrics and incident trends.
CMDB and Asset Management:
- Integrated CMDB: Track configurations and relationships between assets for better incident resolution.
- Automated Asset Discovery: Seamlessly identify and manage assets within your network.
AI Chatbot:
- 24/7 Self-Service Support: Handles common queries, reducing the burden on IT teams.
- Automated-Driven: Automatically creates, categorizes, and prioritizes tickets to streamline incident workflows.
Ideal Use Cases: SMBs and enterprises seeking an ITSM tool with easy implementation and a balance of automation and usability. Pricing: Starts at $19/agent/month, with advanced plans offering more customization and automation capabilities.
10. ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus
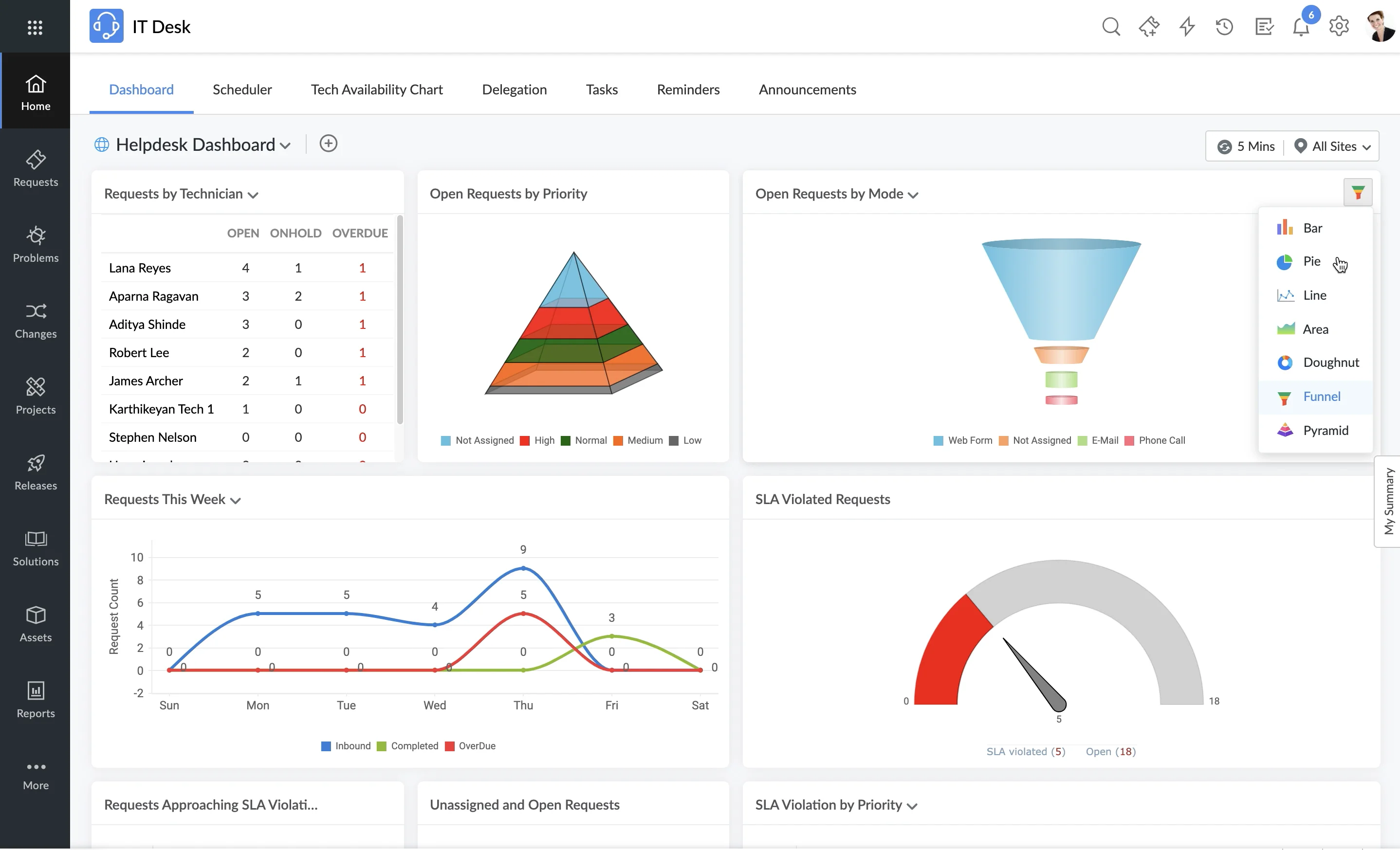
ManageEngine ServiceDesk Plus offers a comprehensive ITSM suite that focuses on deployment flexibility, compliance, and security and caters to a wide range of organizational needs.
Deployment Flexibility:
- Versatile Options: Available as on-premise, cloud-based, and MSP (Managed Service Provider) editions.
- Seamless Migration: Easily switch between deployment models as your organization evolves.
Compliance and Security:
- ITIL and Standards Compliance: Includes built-in reports for ITIL, COBIT, and ISO 20000 to simplify adherence to industry standards.
- Enhanced Security: Features role-based access control, robust audit trails, and encryption to safeguard sensitive data.
Ideal Use Cases: Organizations seeking a customizable ITSM platform with strong compliance features and the ability to scale across different deployment models.
Pricing: Starts at $10/technician/month, with tailored plans for businesses of all sizes.
How to Choose the Right Incident Management Tool for Your Team
Selecting the perfect incident management tool ensures seamless workflows and faster resolution times. Here’s a detailed guide to making the right choice:
- Assess Your Requirements:
- Identify Pain Points: Pinpoint areas where your current incident management process is failing short.
- Prioritize Features: Distinguish between must-have features (like real-time alerting) and nice-to-have functionalities (such as advanced analytics or AI-driven insights).
- Consider Scalability:
- Future-Proofing: Choose tools that can scale with your organization’s growth, whether it’s accommodating more users or handling increased incident volumes.
- Flexible Pricing: Opt for solutions with adaptable pricing models to ensure cost efficiency as your team expands.
- Integration Capabilities:
- Compatibility: Ensure the tool integrates smoothly with your existing ecosystem, including monitoring tools, ITSM platforms, and communication apps.
- API Support: Prefer tools with comprehensive APIs to enable custom integrations and automation for unique workflows.
- Analyze Total Cost of Ownership:
- Budget Beyond Subscription Fees: Evaluate upfront licensing or subscription costs and training, support, and customization expenses.
- Hidden Costs: Consider ongoing maintenance and upgrades that might impact your budget over time.
- User Experience:
- Ease of Use: Test the interface for its intuitiveness, ensuring team members can adopt it without a steep learning curve.
- Mobile-Friendly Features: Check that the mobile app offers full functionality for on-call teams, including alert acknowledgment, escalation, and resolution.
- Trial and Feedback:
- Pilot Runs: Leverage free trials or demos to understand how the tool fits into your team’s workflow.
- Gather Feedback: Involve stakeholders, including on-call engineers and managers, for a holistic view of the tool’s effectiveness.
Best Practices for Implementing Incident Management Tools
Effectively deploying and leveraging an incident management tool goes beyond selection. These best practices can ensure seamless integration and maximum ROI:
- Define Clear Incident Levels:
- Severity Tiers: Establish incident categories (e.g., P1 for critical, p4 for low priority) with well-defined criteria.
- Response Expectations: Assign response and resolution time targets for each severity level.
- Escalation Protocols: Design a clear escalation matrix to ensure unresolved issues move up the chain promptly.
- Foster a Blameless Culture:
- Open Communication: Promote transparency during incident reviews to uncover root causes without fear of retribution.
- Focus on Systemic Solutions: Address underlying issues rather than individual errors, fostering trust and collaboration.
- Encourage Innovation: A blameless culture inspires teams to experiment with improvements without hesitation.
- Conduct Regular Training:
- Incident Drills: Simulate real-world scenarios to test the team’s readiness and the tool’s effectiveness.
- Feature Familiarization: Provide ongoing training on newly added or enhanced features in the tool.
- Cross-Functional Sessions: Involve stakeholders outside the IT team (e.g., customer support) to ensure everyone understands the process.
- Continuously Improve:
- Data-Driven Insights: Regularly analyze incident trends and resolution metrics to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Feedback Loops: Solicit input from end-users and responders to refine workflows and tool configurations.
- Process Optimization: Update incident management practices based on post-mortem learnings and evolving team needs.
By embedding these practices into your implementation strategy, your incident management tool becomes a linchpin for operational excellence, enabling faster resolutions, improved collaboration, and proactive service improvements.
FAQs
What is the difference between incident management and problem management?
- Incident Management: Focuses on resolving issues as quickly as possible to restore normal operations, and minimization impact on users or services. It is reactive and deals with symptoms of issues.
- Problem Management: Aim to identify the underlying root causes of incidents to prevent them from recruiting. It is proactive and centers on eliminating the sources of issues.
How can incident management tools improve MTTR (Mean Time to Resolution)?
Incident management tools help reduce MTTR by:
- Automating Alert Assignments: Automatically routing alerts to the right personnel or team based on predefined rules.
- Contextual Diagnosis: Providing rich context such as logs, metrics, and recent changes to aid in swift troubleshooting.
- Collaboration Features: Enabling real-time communication through chat, video, or integrated communication tools.
- Predefined Playbooks: Offering ready-to-use workflows for common incident types.
- Centralized Knowledge: Providing access to historical incident data and documentation for informed decision-making.
Are open-source incident management tools as effective as commercial solutions?
Open-source tools, such as SigNoz, can be highly effective when:
- Customization: Teams need tailored solutions that align closely with specific workflows.
- Budget Constraints: They offer cost savings compared to proprietary tools.
- Community Support: They benefit from active communities for troubleshooting and improvements.
However, they may require:
- Technical Expertise: Advanced skills for setup, configuration, and maintenance.
- Support Planning: Limited or slower support compared to commercial vendors.
Choosing between open-source and commercial tools depends on your organization’s resources and specific needs.
How do incident management tools integrate with monitoring and observability platforms?
Integration mechanisms typically include:
- APIs: Facilitating real-time data exchange and incident creation from monitoring tools.
- Pre-Built Connectors: Simplified integration with platforms like Prometheus, Nagios, or Datadog.
- Webhooks: Enabling custom alert ingestion and notifications.
- Bi-Directional Sync: Allowing updates between for enriched incident context and resolution tracking.
- Unified Dashboards: Combining observability data with incident timelines for comprehensive insights.
These integrations bridge the gap between detection and resolution, enabling quicker action.
What are the main differences between incident management and incident response tools?
- Scope:
- Incident Management: Covers the entire lifecycle from detection, triage, and resolution to post-mortem analysis.
- Incident Response: Focuses on the immediate actions of an active incident, especially in critical scenarios like security breaches.
- Features:
- Incident Management: Includes knowledge bases, reporting, and trend analysis for IT service improvement.
- Incident Response: Prioritizes real-time collaboration, investigation, and rapid containment.
- Use Cases:
- Incident Management: Broad IT service management and SLA adherence.
- Incident Response: Specialized for handling critical crises, often in security or operations.
- Integration:
- Incident Management: Link with ITSM, observability, and communication platforms.
- Incident Response: Often integrates deeply with security and forensic analysis tools.
Modern tools often merge these functionalities, providing a unified approach to managing and responding to incidents.
