OpenTelemetry vs AWS X-Ray - Which Tracing Tool to Choose?
Modern distributed systems need effective tracing to ensure both performance and reliability. As applications grow more complex, selecting the right tool, such as OpenTelemetry or AWS X-Ray, becomes quite important. OpenTelemetry and AWS X-Ray offer distributed tracing but serve different needs with unique trade-offs.
This article introduces each tool and provides a comparison to help you choose the one that best meets your specific requirements.
Understanding Distributed Tracing Basics
Distributed tracing tracks requests across multiple services within an application, similar to GPS tracking for data. It allows developers to monitor and diagnose system performance by visualizing how data flows through the infrastructure.
Key Components
Let's now look at the key components of the Distributed Tracing.
- Spans: It represents individual operations within a trace. It gives a detailed insight into execution times and errors for each operation.
- Traces: Trace captures the entire journey of a request through the application. It also links the related spans.
- Context Propagation: It ensures the continuity of trace by linking spans across service boundaries. It also maintains visibility across microservices.
Common Challenges
Distributed tracing brings benefits but also presents challenges in distributed environments. So, let's take a look at some of them.
- Lost Traces Across Services: Spans can fail to link when requests move between services, causing fragmented traces. However, even lost or fragmented spans can offer value by providing partial insights into performance issues or bottlenecks, which is preferable to having no trace data at all.
- Incomplete Visibility in Third-party Services: Full tracing coverage may not extend to third-party integrations.
- High Overhead in Trace Collection: Tracing can introduce latency, especially in high-throughput environments.
- Complex Setup and Maintenance: Configuring tracing across diverse services can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Business Impact of Effective Tracing Solutions
Implementing distributed tracing effectively improves operational efficiency and hence it helps in reducing debugging time and enhancing system reliability. Tracing allows teams to address bottlenecks by tracking request journeys in real-time. It also improves user experience and reduces operational costs.
OpenTelemetry Deep Dive
OpenTelemetry is a vendor-neutral, open-source framework for collecting, processing, and exporting telemetry data—spanning traces, metrics, and logs—across diverse platforms. You can think of OpenTelemetry as a universal adapter for observability: collect once, send anywhere.
Core Architecture and Components of OpenTelemetry
Let's first look at OpenTelemetry's architecture and components.
- Software Development Kits (SDKs): SDKs provide language-specific implementations to collect telemetry data. SDKs offer:
- Automatic Instrumentation: It can autogenerate spans for supported libraries, minimizing manual effort.
- Manual Instrumentation: It allows users to customize trace data with specific spans for unique operations.
- Collector: A collector receives data, processes it, and exports it to the designated backend. The collector handles:
- Data Reception: It collects data from multiple SDKs and agents.
- Processing: It supports filtering, batching, and enhancing data before sending.
- Export Configuration: It defines how and where to export collected data (e.g., SigNoz, Prometheus).
An example for OpenTelemetry Collector configuration:
receivers:
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
http:
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: "your-backend-endpoint:4317"
Supported Languages and Integration Capabilities
OpenTelemetry supports a wide range of languages such as Python, Java, and JavaScript which makes it suitable for various tech stacks. It has a vendor-neutral design which enhances flexibility for integration with numerous platforms and backends.
Key Features
OpenTelemetry’s features provide flexibility and precision.
- Automatic and Manual Instrumentation: It lets you align trace data collection with your application’s architecture.
- SDK Flexibility: It allows adaptation for different language-specific requirements to fit complex setups.
Vendor-agnostic Approach and Ecosystem Benefits
OpenTelemetry’s vendor-neutral design avoids vendor lock-in. It also supports future-proof observability by exporting data to various backends.
The OpenTelemetry ecosystem is robust. Its growing community of contributors ensures that the toolset stays updated, adaptable, and compatible with emerging observability standards.
Customization Capabilities
OpenTelemetry offers flexible options for customizing telemetry data collection, processing, and export, providing developers with a customized observability experience.
For example, developers can add custom attributes to spans, such as user IDs or specific transaction details, to gain more granular insights. They can also configure sampling rates to reduce data volume in high-traffic environments or selectively export data to different backends, ensuring performance without compromising on essential metrics.
OpenTelemetry Implementation Specifics
To sett up OpenTelemetry, you should be careful as it involves a few critical steps (from installing SDKs to configuring exporters).
Instrumentation Setup Process
Let's look at a Python example for better understanding:
Install the SDK for Your Language:
pip install opentelemetry-api opentelemetry-sdkConfigure the Tracer:
from opentelemetry import trace from opentelemetry.sdk.trace import TracerProvider provider = TracerProvider() trace.set_tracer_provider(provider)Set Up Exporters:
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.grpc.trace_exporter import OTLPSpanExporter otlp_exporter = OTLPSpanExporter(endpoint="<http://your-collector:4317>")
Data Collection and Export Options
OpenTelemetry enables flexibility in data collection and export configurations. It supports integrations with multiple backend systems. So, you can define export formats and endpoints suited to your observability needs.
Configuration Best Practices
When implementing OpenTelemetry in your application, consider some configuration best practices, such as efficient batching, processing adjustments, and minimal network overhead. These can enhance OpenTelemetry's performance.
Performance Considerations
Setting up OpenTelemetry allows you to monitor your systems effectively while using minimal resources. It also ensures that the performance remains smooth without slowing down your applications
AWS X-Ray Explained
AWS X-Ray is a tracing tool made for AWS. It helps users in tracking and analyzing requests across different AWS services. It’s like a built-in radar that traces everything from Lambda functions to EC2 instances. It gives you a clear view of how each part of your AWS setup performs.
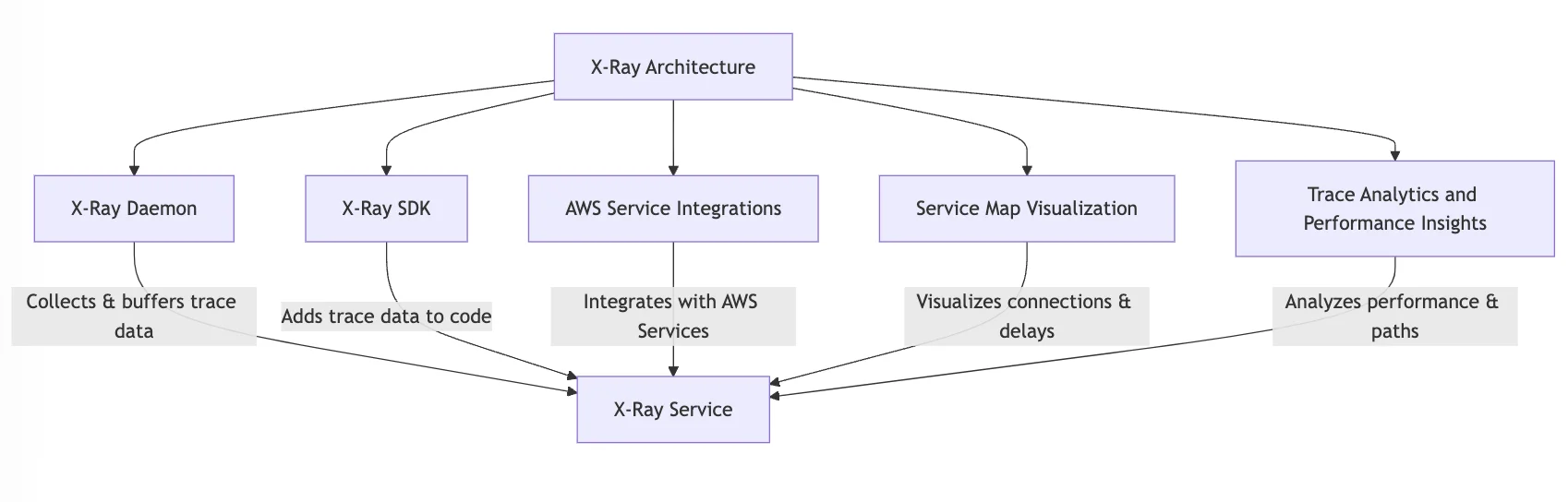
X-Ray Architecture and Core Components
Let us now look at the architecture and components of X-Ray.
- X-Ray Daemon: It is a background process that collects trace data from your services and sends it to X-Ray. It helps in reduce delays by locally buffering data.
- X-Ray SDK: These are language-specific tools (for Java, Python, Node.js, etc.) that let automatically let you add trace data to your code or with custom segments.
- AWS Service Integrations: X-Ray works smoothly with AWS services like Lambda, API Gateway, EC2, etc., and lets you trace requests with an extra setup.
- Service Map Visualization: X-Ray automatically creates a map showing how services connect and where delays might occur.
- Trace Analytics and Performance Insights: It breaks down request paths and performance data and helps you troubleshoot and improve AWS applications.
Native AWS Service Integrations
AWS X-Ray has pre-built support for many AWS services, making setup easy. It connects with various AWS services like Lambda, API Gateway, and DynamoDB to automatically collect trace data, giving you get a full view of requests flowing through your AWS infrastructure.
Sampling Rules and Trace Collection
To manage costs and data volume, X-Ray offers sampling rules that let you control when and how often traces are recorded. This means you can gather useful data without tracking every single request, helping you balance cost and detail.
Pricing Model and Scalability Aspects
AWS X-Ray’s pricing is based on the number of traces processed and the duration they are stored. It scales automatically as your usage grows, so you don’t have to add capacity manually. The pricing model makes it cost-effective to start small and expand as needed.
Developer Experience for Scaling
AWS X-Ray’s integrations and automation features make scaling easier by capturing trace data across services without requiring a lot of manual setup. Its service maps and analytics tools help developers pinpoint issues even as applications grow in complexity.
Data Retention and Storage Options
X-Ray allows you to store trace data for analysis, though it’s optimized for shorter-term retention. For long-term storage, AWS recommends exporting traces to Amazon S3 or another data lake to keep data accessible for as long as needed.
X-Ray Implementation Details
Let us now take an example to see how you can implement AWS X-Ray.
Steps to set up AWS X-Ray
Getting started with AWS X-Ray is simple, especially for AWS services. Here’s an example of setting up the X-Ray daemon, which collects trace data:
wget <https://s3.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/aws-xray-assets.us-east-2/xray-daemon/aws-xray-daemon-linux-3.x.zip>
Service Map Visualization
Once X-Ray is enabled, it automatically creates a service map. This map shows the flow of requests across services and highlights any delays, making it easy to see where improvements are needed.
Trace Analysis Capabilities
AWS X-Ray provides in-depth trace analysis by breaking down request paths and showing performance data. This analysis helps you identify bottlenecks and optimize your AWS applications based on real data.
Performance Impact Considerations
While AWS X-Ray typically has a low-performance impact (around 2-4%), this may vary with traffic and the complexity of your services. For most setups, it’s minimal, but it’s still good to monitor any impact as your application grows.
Performance benchmarks
OpenTelemetry generally incurs a 3-5% overhead depending on the instrumentation and data volume, making it more suitable for cross-cloud and vendor-neutral setups.
On the other hand, AWS X-Ray generally introduces a 2-4% performance impact, which is optimized for AWS environments directly integrated with native AWS services.
Cost Analysis for Different Scales
The cost of OpenTelemetry varies by the choice of backend. Since it’s vendor-neutral, you can control storage and retention costs by selecting a cost-effective backend like SigNoz.
On the other hand, the pricing of AWS X-Ray is tied to AWS, with costs incurred per trace and storage. AWS-native applications might benefit from X-Ray's efficiency and native integration, but costs can rise with heavy usage across services.
Integration Capabilities
OpenTelemetry offers broad integration capabilities across cloud providers, databases, and third-party services, providing flexibility for multi-cloud architectures.
On the other hand, AWS X-Ray is designed with AWS-centric integrations, delivering excellent performance within AWS but limited to non-AWS environments.
Learning Curve and Developer Experience
OpenTelemetry requires you to be familiar with SDKs, exporters, and configuration. Although setup is more involved, the framework’s flexibility makes it ideal for diverse architectures.
On the other hand, AWS X-Ray has a lower learning curve for AWS users due to its native integration and simplified setup which makes it an excellent choice for teams already invested in AWS.
Head-to-Head Comparison
We have discussed OpenTelemetry and AWS X-Ray in detail. In this section, we’ll compare OpenTelemetry and AWS X-Ray based on several critical features.
| Feature | OpenTelemetry | AWS X-Ray |
|---|---|---|
| Vendor Lock-in | No | Yes (AWS-specific) |
| Setup Complexity | Moderate, customizable | Low for AWS environments |
| Cost | Varies by backend; free core | AWS pricing applies |
| Language Support | Extensive, cross-platform | Limited to AWS SDKs |
| Cloud Support | Multi-cloud | AWS-focused |
| Instrumentation | Automatic & Manual options | Primarily Automatic for AWS services |
| Native Integrations | Platform-agnostic | Deep AWS service integration |
| Data Export Options | Flexible (SigNoz, Prometheus) | Restricted to AWS |
You can check out the article OpenTelemetry vs. X-ray for more clarity.
Using SigNoz as an Alternative
SigNoz offers a hybrid solution bridging the capabilities of OpenTelemetry and AWS X-Ray by combining OpenTelemetry’s open standards with a full-stack observability suite. This approach provides more flexibility, especially for multi-cloud or self-hosted environments.
Benefits of SigNoz
Let us now look at some of the benefits of SigNoz.
- OpenTelemetry Compatibility: SigNoz supports OpenTelemetry natively, allowing seamless integration with OpenTelemetry’s SDK and collector.
- Full-Stack Observability: SigNoz includes logging, metrics, and visual dashboards alongside distributed tracing, giving teams a comprehensive view of system health.
- Self-Hosting Options: SigNoz can be hosted on-premises or in private cloud environments, allowing for secure data control and compliance with internal data governance policies.
- Cost-Effective Scaling: SigNoz offers a straightforward pricing model that can become more budget-friendly over time, particularly for high-traffic systems.
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Making the Right Choice
Both OpenTelemetry and AWS X-Ray have unique strengths that are useful to different requirements. Let's take a look at various criteria that will help you make the best choice.
Decision Framework Based on Use Cases
OpenTelemetry is ideal for multi-cloud strategies, diverse tech stacks, and when vendor flexibility is key. It supports various languages and exporters which makes it an ideal fit for organizations that are aiming to avoid vendor lock-in and support complex, distributed systems.
AWS X-Ray is perfect for AWS-centric environments needing quick, native integration. X-Ray provides seamless AWS service support which makes it a strong choice for AWS-only infrastructures focused on efficient, in-platform observability.
Scaling Considerations
OpenTelemetry scales effectively across multi-cloud and hybrid setups, which is ideal for businesses that may expand to other providers or platforms over time.
On the other hand, AWS X-Ray scales within the AWS ecosystem, handling high traffic for AWS services. However, it may be limited if your infrastructure extends significantly beyond AWS.
Team Expertise Requirements
OpenTelemetry is suitable for teams comfortable with more complex setups, especially if multi-cloud or vendor-agnostic flexibility is needed. It may require advanced skills for custom instrumentation and exporter configurations.
AWS X-Ray works well for teams with existing AWS expertise, offering straightforward setup and operation within AWS. If the team is already familiar with AWS, minimal additional training is required.
Budget Implications
OpenTelemetry allows you to control costs with customizable trace sampling but may require more setup time and potentially higher costs if combined with other data backends.
On the other hand, AWS X-Ray offers cost-effective tracing within AWS, but costs may add up as the volume of traced data grows, especially with high-frequency sampling.
Industry-Specific Recommendations
OpenTelemetry's flexibility supports customized data handling and diverse backends, which is helpful for regulatory compliance. On the other hand, for AWS-dependent industries like e-commerce or media streaming, X-Ray’s native support is efficient, particularly for applications leveraging Lambda and API Gateway.
Future Scalability and Flexibility
OpenTelemetry is built for future-proof observability, which is especially useful if you plan to expand across multiple clouds or adopt new tech stacks.
AWS X-Ray is a great fit for organizations committed to AWS long-term, offering a highly scalable and AWS-integrated observability experience.
Key Takeaways
- OpenTelemetry offers multi-cloud flexibility, while AWS X-Ray is best suited for AWS-native applications.
- AWS X-Ray provides seamless integration within AWS, whereas OpenTelemetry’s setup may require more initial configuration.
- OpenTelemetry provides vendor-agnostic options, allowing you to avoid lock-in, while AWS X-Ray is optimized for AWS infrastructure.
- You should consider your long-term needs for observability and scaling, particularly for high-traffic applications and diverse cloud ecosystems.
- OpenTelemetry is versatile but may require more expertise for setup and maintenance, while X-Ray’s simplified interface suits teams already familiar with AWS.
FAQs
Can OpenTelemetry and X-Ray work together?
Yes, AWS Distro for OpenTelemetry (ADOT) allows integration of OpenTelemetry with X-Ray, enabling you to use OpenTelemetry SDKs with AWS-specific X-Ray features.
How does pricing compare between the two?
AWS X-Ray has usage-based pricing, charging per trace and storage. It can be cost-effective for AWS-centric applications. OpenTelemetry's cost depends on your chosen backend, giving you the flexibility to optimize storage and processing costs according to your data retention policies.
Which option is better for AWS-native applications?
AWS X-Ray is generally a better choice for AWS-native applications, thanks to its seamless integration and lower setup time. However, OpenTelemetry might still be valuable if you need multi-cloud support or plan to migrate from AWS in the future.
What are each's main technical limitations?
- AWS X-Ray limits export options to AWS services, making it less flexible for non-AWS use cases.
- OpenTelemetry requires more configuration and maintenance, especially in multi-cloud or multi-language deployments, where SDK setup and collector configurations may vary.
