OpenTelemetry vs. CloudWatch - Choosing the Right Monitoring Tool
In today's complex software landscape, choosing the right monitoring tool is crucial for maintaining healthy, performant applications. OpenTelemetry and CloudWatch are two popular options, each with its strengths and use cases. This leads you to ask the following questions
- How do you decide which one is right for your project?
- What are the key differences between these tools?
This comprehensive guide will help you navigate the OpenTelemetry vs CloudWatch debate, providing insights into their features, use cases, and potential trade-offs.
What Is OpenTelemetry?
OpenTelemetry is an open-source observability framework designed to standardize the collection of telemetry data, traces, metrics and logs across distributed systems. It’s vendor-agnostic and supports various programming languages, offering flexibility in collecting and processing observability data.
Key features include:
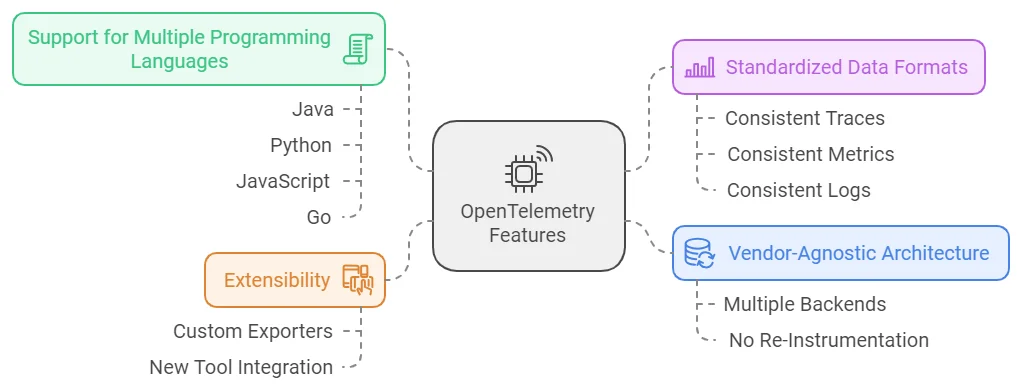
- Vendor-Agnostic Architecture: You can send your telemetry data to multiple backends like Prometheus, Jaeger, Zipkin, and CloudWatch. This flexibility allows you to switch between tools without re-instrumenting your code.
- Support for Multiple Programming Languages: OpenTelemetry provides SDKs for popular programming languages like Java, Python, JavaScript, Go, and more, ensuring that teams can use it across various services and applications.
- Extensibility: Its modular design means you can extend OpenTelemetry to fit the specific needs of your infrastructure or applications, whether it’s adding custom exporters or integrating with new tools.
- Standardized Data Formats: OpenTelemetry enforces standardized formats for telemetry data, ensuring that traces, metrics, and logs are collected consistently. This makes it easier to integrate with various backends and visualization tools.
This standardization and flexibility make OpenTelemetry ideal for organizations managing multi-cloud or hybrid-cloud environments, where observability needs to extend beyond a single provider.
OpenTelemetry is part of the larger Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) ecosystem, aligning it with other cloud-native tools like Kubernetes and Prometheus.
What is CloudWatch?
CloudWatch is a fully managed observability solution built specifically for AWS users. It is deeply integrated with AWS services, providing a real-time view of the performance and health of AWS resources such as EC2 instances, Lambda functions, and S3 buckets.
CloudWatch’s primary focus is on offering a turnkey solution for monitoring AWS infrastructure and applications, so you don’t have to worry about setting up and maintaining a monitoring stack.
Key features of CloudWatch include:
.webp)
- Real-Time Metrics Collections and Visualization: CloudWatch automatically collects and monitors performance data from AWS services, making it easy to track key performance indicators like CPU usage, memory utilization, and network activity.
- Log Aggregation and Analysis: CloudWatch logs allow you to collect, monitor, and analyze log data from AWS services and applications. The service offers log filtering, searching, and automated log analysis, helping you troubleshoot issues quickly.
- Alerts, Alarms, and Notifications: CloudWatch provides built-in alerting and alarms, enabling you to set thresholds for metrics and receive notifications when they exceed defined limits. Integrated with services like SNS (Simple Notification Service) ensures that you’re notified via email, SMS, or other methods when something goes wrong.
- Pre-Built Dashboards: CloudWatch has customizable dashboards that allow you to visualize performance metrics and logs in real-time. AWS services automatically populate CloudWatch with metrics, reducing the manual setup typically required.
CloudWatch is tightly coupled with AWS, making it the natural choice for users who are heavily invested in the AWS ecosystem. It is highly optimized for AWS services to automatically populate CloudWatch with metrics, reducing the manual setup typically required.
Why Compare OpenTelemetry and CloudWatch?
The growing complexity of modern applications has made observability a critical concern for developers and operations teams. Choosing between open-source and proprietary solutions like OpenTelemetry and CloudWatch can significantly impact your monitoring strategy. Here's why this comparison matters:
-
Cloud Adoption: As more organizations embrace cloud-native architectures and microservices, observability becomes more complex. Applications often run across multiple cloud providers and environments, requiring tools to handle distributed tracing, log aggregation, and real-time metric collection.
- OpenTelemetry provides a cloud-agnostic solution, making it easier to manage observability across multi-cloud setups.
- CloudWatch offers a seamless experience for those fully committed to the AWS ecosystem, making the decision highly dependent on your cloud strategy.
-
Standardization: With the rise of cloud-native practices, there’s a growing push for standardized observability tools that work across environments. OpenTelemetry’s role in standardizing telemetry data formats for traces, logs, and metrics is especially valuable for organizations that need consistency across systems.
- OpenTelemetry enables faster onboarding of new tools, easier integration into existing observability stacks, and reduces complexity in managing diverse telemetry data sources.
- CloudWatch is optimized for AWS but lacks vendor-agnostic standardization, which can become a bottleneck if your infrastructure spans multiple cloud providers.
-
Vendor lock-in: When you rely on a proprietary observability service like CloudWatch, you’re locking yourself into the AWS ecosystem. This can limit your flexibility in the future, especially if your organization plans to adopt a multi-cloud strategy or switch providers.
- OpenTelemetry’s vendor-agnostic approach helps you maintain freedom and flexibility by allowing you to switch between backend systems or integrate with multiple tools without having to re-instrument your codebase.
- OpenTelemetry can be a strategic advantage for companies prioritizing portability and flexibility in their tech stack.
-
Cost considerations: Proprietary cloud-based observability solutions like CloudWatch often come with usage-based costs for metrics, logs, and alerting. These costs can add up quickly for large-scale applications, especially when monitoring multiple services in production environments.
- OpenTelemetry allows you to self-host and customize your observability stack, offering more control over costs.
- However, self-hosting OpenTelemetry can involve infrastructure overhead, requiring careful consideration of hardware, storage, and scaling.
The trade-off here is between cost predictability and control with OpenTelemetry versus managed convenience with CloudWatch.
-
Customization vs Ease of Use: OpenTelemetery offers extensive customization options, allowing teams to tailor their observability stack to their specific needs, choosing the best-in-class tools for their use cases.
- OpenTelemetry’s flexiblity makes it an attractive choice for organizations with complex requirements or multi-cloud deployments.
- CloudWatch provides a fully managed service that integrates deeply with AWS, offering ease of use and quick setup.
For organizations focused primarily on AWS, CloudWatch might deliver faster time to insight with minimal setup and maintenance effort.
Key Differences: OpenTelemetry vs. CloudWatch
| Feature | OpenTelemetry | CloudWatch |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | - Lets you add code to collect detailed telemetry data from your app - Lots of control over what data is collected - Requires more setup and coding | - Uses a built-in agent to collect data from AWS services - Easy setup for AWS monitoring - Less control, especially for non-AWS services |
| Data Processing and Storage | - Sends data to different systems using an extra component (OpenTelemetry Collector) - You can choose where to send your data (multiple platforms supported) - You must manage extra infrastructure | - Automatically processes and stores data in AWS - No setup is needed for scaling or storage in AWS - Only works well within AWS, with less flexibility |
| Visualization and Analysis | - You must use other tools (like Grafana or Prometheus) to see and analyze your data - You can pick the tools you prefer - Requires more learning and setup | - Comes with built-in dashboards and tools to view and analyze data in AWS - Ready to use dashboards for AWS services - Limited options for customization, AWS-specific |
When to Choose OpenTelemetry
OpenTelemetry shines in scenarios such as:
- Multi-Cloud or Hybrid Environments: If you’re using multiple cloud providers (like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud) and need a single, consistent way to monitor everything, OpenTelemetry helps unify your data.
- Avoiding Vendor Lock-In: If you want the freedom to switch between cloud providers without being tied to one, OpenTelemetry offers the flexibility to move your monitoring data wherever you want.
- Custom Monitoring: If your application requires specific types of data collection or you want to integrate with multiple tools for deeper analysis, OpenTelemetry provides the customization you need.
- Open-Source Tools: If you prefer open-source solutions or want to contribute to or build on community-driven tools, OpenTelemetry is the right choice.
When to Choose CloudWatch
CloudWatch is ideal in scenarios such as:
- AWS-Focused Setup: If your system is mainly built on AWS, CloudWatch integrates seamlessly, making monitoring AWS services easier without additional setup.
- Managed Solution: If you prefer a monitoring tool that doesn’t require you to manage any extra infrastructure, CloudWatch offers a fully managed service where everything is taken care of for you.
- Cost Effective for AWS: For smaller setups on AWS, CloudWatch can be more cost-effective and easier to manage than setting up and maintaining OpenTelemetry.
- Compliance and Security: If you have strict security or compliance requirements, CloudWatch integrates well with AWS’s security and compliance services, making it easier to meet those standards.
Combining OpenTelemetry and CloudWatch
Interestingly, you don't always have to choose between OpenTelemetry and CloudWatch. AWS’s monitoring service provides insights into application performance and operational health. For example, integrating OpenTelemetry with CloudWatch allows you to collect and visualize telemetry data from non-AWS services alongside native AWS metrics, all in a single dashboard.
This unified view makes it easier to monitor complex, multi-cloud environments, detect performance bottlenecks across your entire infrastructure, and troubleshot issues quickly by correlating data from different sources in one place.
Steps to Use OpenTelemetry with CloudWatch
-
Set Up AWS Distro for OpenTelemetry (ADOT):
Begin by installing the AWS Distro for OpenTelemetry (ADOT) Collector, which simplifies collecting metrics and traces from your applications.
Installing Command:
curl -sSL https://get.opentelemetry.io/collector | shAfter installation, edit the configuration file (
/etc/otelcol/config.yaml) to define how the telemetry data will be gathered and exported. Below is an example configuration snippet:receivers: otlp: protocols: grpc: endpoint: localhost:4317 http: endpoint: localhost:4318 processors: batch: timeout: 60s exporters: awsemf: namespace: "YourNamespace" log_group_name: "YourLogGroup" log_stream_name: "YourLogStream" service: pipelines: metrics: receivers: [otlp] processors: [batch] exporters: [awsemf] -
Collect Metrics Using CloudWatch EMF:
The ADOT (AWS Distro for OpenTelemetry ) Collector can send application performance data (metrics) to CloudWatch using a specific format called Embedded Metric Format (EMF). This format is designed to handle complex datasets, such as those with many unique labels or values (high-cardinality metrics), which can happen in large-scale applications.
- To make sure your metrics are sent correctly, you’ll need to configure the
awsemfexporter, a tool that sends this formatted data to CloudWatch for monitoring and analysis.
- To make sure your metrics are sent correctly, you’ll need to configure the
-
Integrate Tracing with AWS X-Ray:
To collect traces, configure the ADOT Collector to send trace data to AWS X-Ray by adding the following exporter to your configuration:
exporters: xray: region: "us-west-2" # Specify your AWS regionUse OpenTelemetry SDKs within your application code to instrument your services, enabling trace data collection and sending it to X-Ray.
-
Leverage CloudWatch Container Insights:
For containerized applications, CloudWatch Container Insights can provide aggregated and summarized metrics. Configure the ADOT Collector to capture both infrastructure-level such as CPU and memory usage, and application-level metrics like request latency or error rates, using the following configuration:
receivers: awscontainerinsightreceiver: cluster_name: "YourClusterName" -
Monitor and Analyze Your Data:
After configuring the ADOT Collector, you can visualize your collected metrics and traces using the AWS Management Console. Create CloudWatch dashboards to display real-time performance data from your applications. Use AWS X-Ray insights to troubleshoot performance bottlenecks or identify issues across your services.
SigNoz: A Modern Alternative for OpenTelemetry-based Monitoring
If you're considering OpenTelemetry, you should also explore SigNoz. It's a full observability platform built on top of OpenTelemetry, offering:
- Easy-to-Use Interface: It provides a simple way to see your traces, metrics, and logs.
- Flexible Hosting: You can either run it on your servers (self-hosted) or use their cloud-based service.
- Integrated Experience: SigNoz offers an all-in-one platform like CloudWatch but with the added flexibility of OpenTelemetry.
SigNoz is a great modern alternative to traditional monitoring tools. It combines the advantages of open-source technology with a smooth, easy-to-use interface, giving you both power and simplicity in monitoring your applications.
SigNoz leverages OpenTelemetry for vendor-agnostic data collection, allowing you to trace requests across distributed systems while visualizing metrics and logs in real-time dashboards all without being locked into any specific vendor. This flexibility makes it easier to troubleshoot issues and optimize performance in complex, multi-cloud environments.
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Performance Considerations
When comparing OpenTelemetry and CloudWatch, consider their impact on your application's performance:
- Resource usage:
- OpenTelemetry: The performance impact of OpenTelemetry largely depends on how it’s set up. By carefully configuring your data collection, you can minimize the overhead on your application. For example, you can adjust the frequency of data collection or selectively choose which data to capture, helping optimize resource usage.
- CloudWatch: The performance of CloudWatch is influenced by the configuration of the CloudWatch Agent. Depending on how you set it up, you might see different levels of impact on system resources.
- Scalability:
- Both are designed to scale with your application, but OpenTelemetry offers greater control over data sampling and filtering. This means you can define how much data to collect based on your specific needs, allowing for more efficient scaling in high-traffic environments.
- In contrast, while CloudWatch can also scale, it may not provide as much flexibility regarding what data gets collected.
- Network usage: CloudWatch may lead to higher network costs, particularly if you monitor resources across different regions or at high frequencies. This is due to the need for data to be sent over the internet to AWS servers, which can add up depending on your usage patterns.
- OpenTelemetry, however, allows you to manage and optimize your data flow, potentially reducing network costs.
Cost Analysis: OpenTelemetry vs. CloudWatch
The cost structures for OpenTelemetry and CloudWatch differ significantly, affecting your budgeting decisions:
CloudWatch Costs:
- It operates on a pay-per-use model. You’ll incur costs charges for various services, including data ingestion, data storage, and queries. For a detailed breakdown of every billing bucket, see our CloudWatch pricing guide.
- This model can be cost-effective for small to medium workloads but may become more expensive as usage increases. See our CloudWatch cost optimization playbook for practical tips on reducing spend.
OpenTelemetry Costs:
- It is open-source, which means there are no licensing fees. However, you have to invest in the infrastructure to support data collection, processing, and storage.
- This can include costs related to servers, databases, and any additional tools you choose to integrate for analysis and visualization.
Hidden Costs:
Be aware of potential hidden costs, such as:
- Data Transfer Fees: CloudWatch may incur additional charges for transferring data across regions, especially if you have a multi-region setup.
- Operational Overhead: If you choose to self-host OpenTelemetry, you must consider the ongoing costs of managing your infrastructure, including maintenance, updates, and potential scaling needs.
- Savings from Optimized Data Sampling: OpenTelemetry allows you to implement optimized data sampling techniques, which can reduce the volume of data sent for processing and lead to cost savings.
Migration Considerations
If you’re contemplating a switch between CloudWatch and OpenTelemetry, consider the following factors to ensure a smooth transition:
- Data Compatibility:
- Check if your existing data can be successfully transferred or maintained during the migration.
- Understanding the format and structure of your data in both systems is crucial to avoid data loss.
- Code Changes:
- Transitioning to OpenTelemetry typically requires updates to the instrumentation in your codebase.
- This means developers must adjust the code to use OpenTelemetry libraries and APIs to capture telemetry data effectively.
- Team Training:
- Both tools have unique learning curves, so it’s essential to plan to upskill your team.
- Training sessions or resources may be necessary to help your team understand how to use the new system effectively and leverage its features.
- Parallel Development:
- To minimize data loss and ensure a smoother transition, consider a phased migration. Running both systems in parallel for a period allows you to validate the new setup while still relying on the existing system.
- This approach can help you identify and resolve any issues before fully committing to the switch.
Future Trends and Developments
The observability landscape is evolving rapidly:
- OpenTelemetry’s Growing Popularity:
- Increased Adoption: OpenTelemetry is gaining widespread use across industries. With backing from major tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and others, it’s becoming the go-to standard for collecting and analyzing observability data.
- Why It Matters: As more companies adopt OpenTelemetry, it’s creating a more unified and vendor-neutral standard for telemetry data, making it easier for businesses to integrate various tools without being tied to a specific vendor.
- Enhanced AWS Support for OpenTelemetry:
- AWS Integration: Amazon Web Services (AWS) is increasingly improving its support for OpenTelemetry, recognizing the need to offer more flexibility to its users.
- By allowing OpenTelemetry to work seamlessly within the AWS ecosystem, AWS gives users more choice in how they monitor and analyze their infrastructure.
- What This Means: In the future, we’re likely to see more cross-compatibility between proprietary services like CloudWatch and open-source solutions like OpenTelemetry.
- This trend indicates that AWS may continue embracing open-source standards alongside its own managed services, giving users the best of both worlds.
- AWS Integration: Amazon Web Services (AWS) is increasingly improving its support for OpenTelemetry, recognizing the need to offer more flexibility to its users.
- New Standards Shaping the Market:
- Open-Source Influence: The growing adoption of open-source observability frameworks like OpenTelemetry pushes the industry towards more standardized solutions.
- This could impact the development of CloudWatch and other proprietary tools, which may need to evolve to remain competitive and meet user demands for flexibility and interoperability.
- Looking Forward: As more organizations prioritize open standards, we could see new features in CloudWatch and other services that focus on seamless integration with open-source tools.
- This shift would allow businesses to avoid vendor lock-in and choose the most effective tools for their observability needs.
- Open-Source Influence: The growing adoption of open-source observability frameworks like OpenTelemetry pushes the industry towards more standardized solutions.
Key Takeaways
- OpenTelemetry offers a vendor-agnostic, standardized approach to observability, ideal for diverse environments.
- CloudWatch provides tight integration with AWS services, suiting AWS-centric architectures.
- Combining OpenTelemetry and CloudWatch can offer standardization and AWS integration benefits.
- Consider factors like data types, scalability, cost, and future-proofing when choosing a solution.
- SigNoz presents a modern alternative, combining OpenTelemetry's flexibility with user-friendly interfaces.
FAQs
Can I use OpenTelemetry with AWS services?
AWS offers the AWS Distro for OpenTelemetry (ADOT), which allows you to collect and send telemetry data from AWS services to various backends, including CloudWatch and other third-party observability platforms.
This makes it easy to integrate OpenTelemetry with AWS infrastructure while maintaining the flexibility to choose your preferred data destination.,
How does CloudWatch pricing compare to self-hosted OpenTelemetry?
CloudWatch uses a pay-per-use pricing model, meaning you’re charged based on the volume of data ingested, stored, and queried. In contrast, self-hosted OpenTelemetry has no licensing fees but incurs infrastructure costs for running and maintaining your telemetry collection and storage systems.
- For small to medium AWS deployments, CloudWatch is often more cost-effective because it eliminates the need to manage infrastructure.
- However, self-hosted OpenTelemetry may provide greater control and potential cost savings for larger environments or multi-cloud setups.
Is it possible to migrate from CloudWatch to OpenTelemetry without data loss?
- Migrating from CloudWatch to OpenTelemetry requires careful planning. Historical data migration can be complex, but it is to export CloudWatch logs and metrics and then import them into an OpenTelemetry-compatible backend, depending on your tools.
- To ensure a smooth transition and avoid data loss, you can run both CloudWatch and OpenTelemetry in parallel during the migration period. This allows you to validate the new system without interrupting monitoring.
What are the main advantages of using SigNoz over traditional monitoring tools?
SigNoz is a modern, full-stack observability platform built on OpenTelemetry. Its key advantages include:
- A user-friendly interface that makes it easy to visualize and analyze traces, metrics, and logs in one place.
- The ability to be self-hosted or used as a cloud service, providing flexibility for different operational needs.
- Seamless integration with OpenTelemetry gives you the benefits of an open-source ecosystem with the ease of use of a traditional platform. SigNoz combines the flexibility of open-source monitoring with a polished, cohesive user experience, making it a powerful alternative to traditional, proprietary tools.
