Overview
This documentation provides a detailed walkthrough on how to set up Google Cloud Run to send the traces directly to SigNoz. By the end of this guide, you will have a setup that automatically sends your Cloud Run traces to SigNoz.
Here's a quick summary of what we will be doing in this guide
- Create and configure Cloud Run service
- Invoke the deployed Cloud Run service to generate traces
- Send and Visualize the traces in SigNoz Cloud
Prerequisites
- Google Cloud account with administrative privilege or Cloud Run Admin and Artifact Registry Admin privileges.
- SigNoz Cloud Account (we are using SigNoz Cloud for this demonstration, we will also need ingestion details. To get your Ingestion Key and Ingestion URL, sign-in to your SigNoz Cloud Account and go to Settings >> Ingestion Settings)
- Access to a project in GCP
Setup
Get started with Cloud Run service setup
Follow the steps mentioned in the Cloud Run Service Setup page to create Cloud Run Service.
We will now make slight changes to the application to include tracing.
In the project's root directory, create a new file tracing.js.
vi tracing.js
This file will contain the instrumentation code to send out traces to SigNoz.
You need to configure the endpoint for SigNoz Cloud in this file. You can find your ingestion key from SigNoz Cloud account details sent on your email.
// tracing.js
'use strict'
const process = require('process')
const opentelemetry = require('@opentelemetry/sdk-node')
const { getNodeAutoInstrumentations } = require('@opentelemetry/auto-instrumentations-node')
const { OTLPTraceExporter } = require('@opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-http')
const { Resource } = require('@opentelemetry/resources')
const { SemanticResourceAttributes } = require('@opentelemetry/semantic-conventions')
// do not set headers in exporterOptions, the OTel spec recommends setting headers through ENV variables
// https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-specification/blob/main/specification/protocol/exporter.md#specifying-headers-via-environment-variables
// highlight-start
const exporterOptions = {
url: 'https://ingest.{region}.signoz.cloud:443/v1/traces',
}
// highlight-end
const traceExporter = new OTLPTraceExporter(exporterOptions)
const sdk = new opentelemetry.NodeSDK({
traceExporter,
instrumentations: [getNodeAutoInstrumentations()],
resource: new Resource({
// highlight-next-line
[SemanticResourceAttributes.SERVICE_NAME]: 'cloudrun_nodejs_app',
}),
})
// initialize the SDK and register with the OpenTelemetry API
// this enables the API to record telemetry
sdk.start()
// gracefully shut down the SDK on process exit
process.on('SIGTERM', () => {
sdk
.shutdown()
.then(() => console.log('Tracing terminated'))
.catch((error) => console.log('Error terminating tracing', error))
.finally(() => process.exit(0))
})
In this example, we have used cloudrun_nodejs_app as the service name. You can feel free to change it appropriately as per your use-case.
Depending on the choice of your region for SigNoz cloud, the ingest endpoint will vary according to this table.
| Region | Endpoint |
|---|---|
| US | ingest.us.signoz.cloud:443 |
| IN | ingest.in.signoz.cloud:443 |
| EU | ingest.eu.signoz.cloud:443 |
Save and close the file when you’ve finished making changes.
Next, modify the package.json file with the following contents in the dependencies section.
{
"name": "cars_project",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "NodeJS project on Cars",
"author": "John Doe <john.doe@example.com>",
"license": "MIT",
"main": "app.js",
"keywords": [
"nodejs",
"bootstrap",
"express"
],
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.16.4",
"@opentelemetry/api": "1.7.0",
"@opentelemetry/sdk-node": "0.45.1",
"@opentelemetry/auto-instrumentations-node": "0.39.4",
"@opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-http": "0.45.1"
}
}
Next, we will change the Dockerfile to start NodeJS application taking tracing file into account. The last line that invokes the NodeJS command contains the change.
FROM node:10-alpine
RUN mkdir -p /home/node/app/node_modules && chown -R node:node /home/node/app
WORKDIR /home/node/app
COPY package*.json ./
USER node
RUN npm install
COPY --chown=node:node . .
EXPOSE 8080
CMD [ "node", "-r", "./tracing.js", "app.js" ]
You can now perform the following steps by referring the Cloud Run Service Setup page:
- Building the image of the application, and uploading it to Artifact Registry
- Deploying the new image from Artifact Registry to Cloud Run
Note that you may choose to delete the existing Cloud Run service deployment, and perform the deployment with the same service name as you choose before. Or, you can let the existing deployment(s) be as is, and put a new service name for this deployment of Cloud Run service.
Invoke Cloud Run service
You can click on the URL present on the top of the Cloud Run service page to invoke the Cloud Run service application.
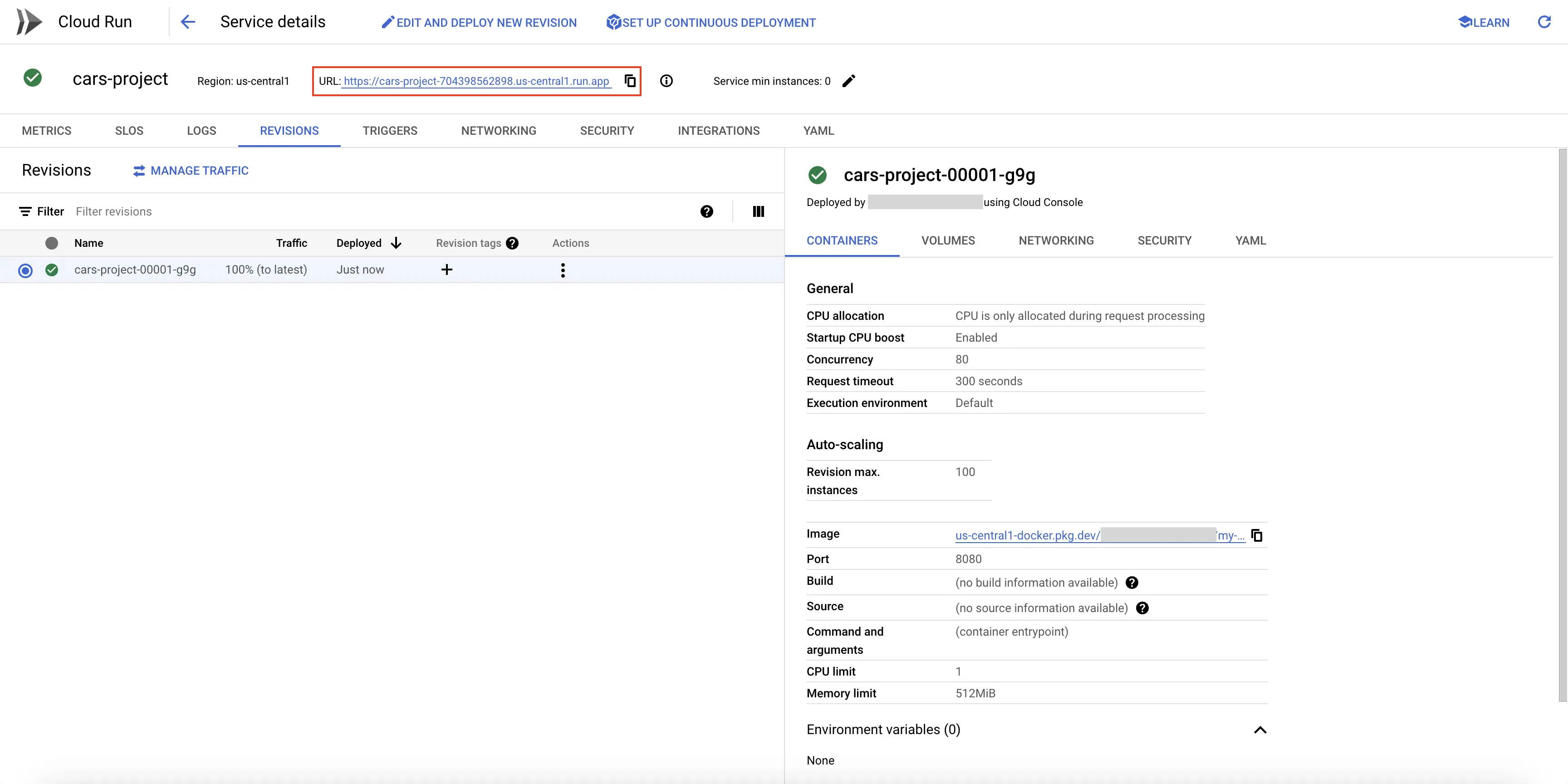
Cloud Run Service URL
Send and Visualize the traces in SigNoz Cloud
The opening of the URL in the browser has triggered the Cloud Run service, and it will result in the traces which would now also start appearing in the SigNoz Cloud as we have instrumented the tracing.
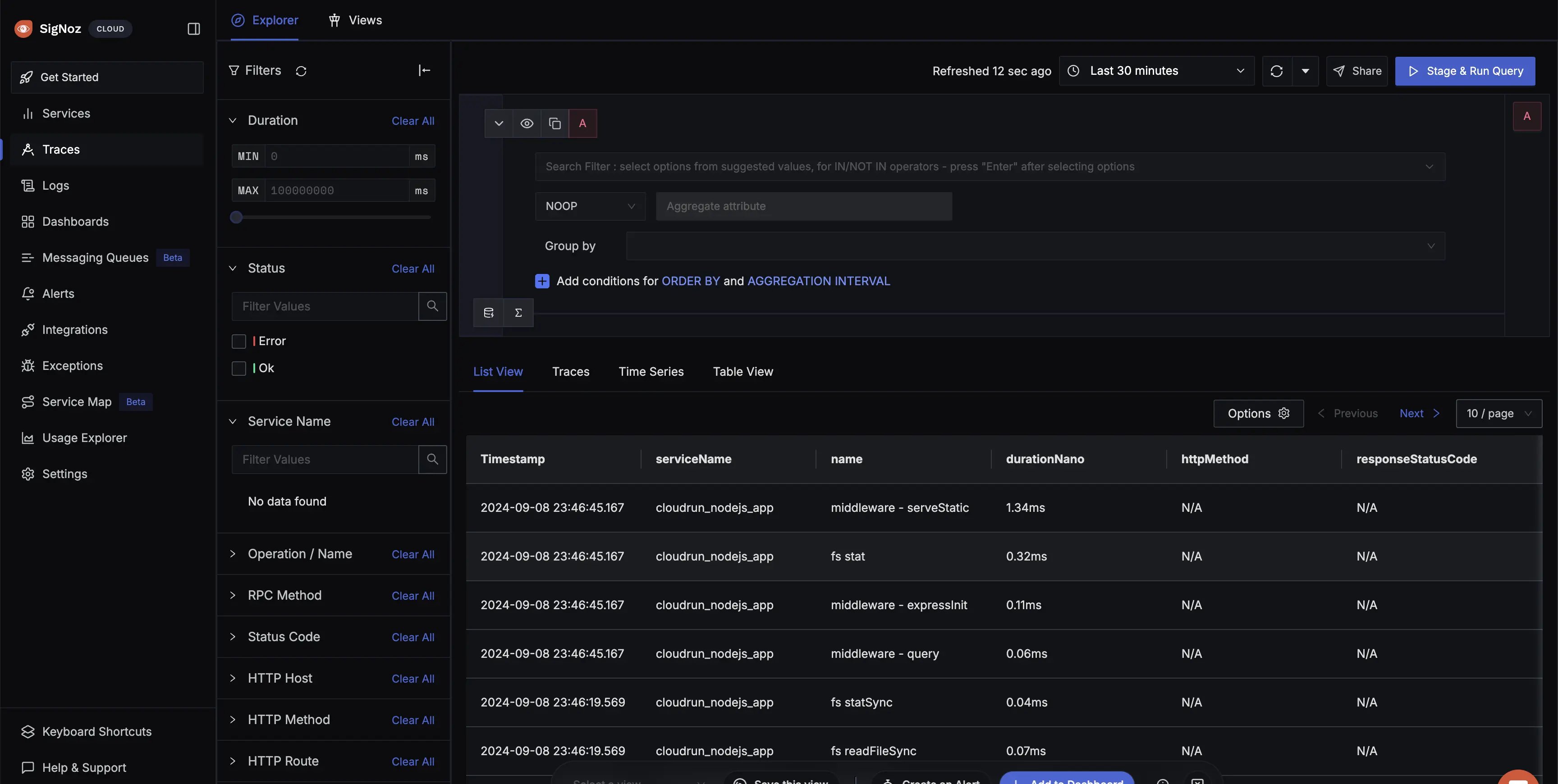
Cloud Run Traces in SigNoz Cloud
Here's a quick summary of what we will be doing in this guide
- Create and configure Cloud Run
- Invoke the deployed Cloud Run service to generate traces
- Send and Visualize the traces in SigNoz
Prerequisites
- Google Cloud account with administrative privilege or Cloud Run Admin and Artifact Registry Admin privileges.
- Access to a project in GCP
- Self-Hosted SigNoz
For more details on how to configure Self-Hosted SigNoz for Logs, check official documentation by Self-Hosted SigNoz and navigate to the "Send Logs to Self-Hosted SigNoz" section.
Setup
Get started with Cloud Run service setup
Follow the steps mentioned in the Cloud Run Service Setup page to create Cloud Run Service.
We will now make slight changes to the application to include tracing.
In the project's root directory, create a new file tracing.js.
vi tracing.js
This file will contain the instrumentation code to send out traces to SigNoz.
You need to configure the endpoint for SigNoz Cloud in this file. You can find your ingestion key from SigNoz Cloud account details sent on your email.
// tracing.js
'use strict'
const process = require('process')
const opentelemetry = require('@opentelemetry/sdk-node')
const { getNodeAutoInstrumentations } = require('@opentelemetry/auto-instrumentations-node')
const { OTLPTraceExporter } = require('@opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-http')
const { Resource } = require('@opentelemetry/resources')
const { SemanticResourceAttributes } = require('@opentelemetry/semantic-conventions')
// do not set headers in exporterOptions, the OTel spec recommends setting headers through ENV variables
// https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-specification/blob/main/specification/protocol/exporter.md#specifying-headers-via-environment-variables
// highlight-start
const exporterOptions = {
url: 'https://ingest.{region}.signoz.cloud:443/v1/traces',
}
// highlight-end
const traceExporter = new OTLPTraceExporter(exporterOptions)
const sdk = new opentelemetry.NodeSDK({
traceExporter,
instrumentations: [getNodeAutoInstrumentations()],
resource: new Resource({
// highlight-next-line
[SemanticResourceAttributes.SERVICE_NAME]: 'cloudrun_nodejs_app',
}),
})
// initialize the SDK and register with the OpenTelemetry API
// this enables the API to record telemetry
sdk.start()
// gracefully shut down the SDK on process exit
process.on('SIGTERM', () => {
sdk
.shutdown()
.then(() => console.log('Tracing terminated'))
.catch((error) => console.log('Error terminating tracing', error))
.finally(() => process.exit(0))
})
In this example, we have used cloudrun_nodejs_app as the service name. You can feel free to change it appropriately as per your use-case.
Depending on the choice of your region for SigNoz cloud, the ingest endpoint will vary according to this table.
| Region | Endpoint |
|---|---|
| US | ingest.us.signoz.cloud:443 |
| IN | ingest.in.signoz.cloud:443 |
| EU | ingest.eu.signoz.cloud:443 |
Save and close the file when you’ve finished making changes.
Next, modify the package.json file with the following contents in the dependencies section.
{
"name": "cars_project",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "NodeJS project on Cars",
"author": "John Doe <john.doe@example.com>",
"license": "MIT",
"main": "app.js",
"keywords": [
"nodejs",
"bootstrap",
"express"
],
"dependencies": {
"express": "^4.16.4",
"@opentelemetry/api": "1.7.0",
"@opentelemetry/sdk-node": "0.45.1",
"@opentelemetry/auto-instrumentations-node": "0.39.4",
"@opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-http": "0.45.1"
}
}
Next, we will change the Dockerfile to start NodeJS application taking tracing file into account. The last line that invokes the NodeJS command contains the change.
FROM node:10-alpine
RUN mkdir -p /home/node/app/node_modules && chown -R node:node /home/node/app
WORKDIR /home/node/app
COPY package*.json ./
USER node
RUN npm install
COPY --chown=node:node . .
EXPOSE 8080
CMD [ "node", "-r", "./tracing.js", "app.js" ]
You can now perform the following steps by referring the Cloud Run Service Setup page:
- Building the image of the application, and uploading it to Artifact Registry
- Deploying the new image from Artifact Registry to Cloud Run
Note that you may choose to delete the existing Cloud Run service deployment, and perform the deployment with the same service name as you choose before. Or, you can let the existing deployment(s) be as is, and put a new service name for this deployment of Cloud Run service.
Invoke Cloud Run service
You can click on the URL present on the top of the Cloud Run service page to invoke the Cloud Run service application.

Cloud Run Service URL
Send and Visualize the traces in SigNoz
The opening of the URL in the browser has triggered the Cloud Run service, and it will result in the traces which would now also start appearing in the SigNoz as we have instrumented the tracing.
