Overview
This documentation provides detailed instructions on configuring the OpenTelemetry Collector to read logs from systemd's journal (journald) and push them to SigNoz. Logs from systemd are structured and contain rich metadata that can help you monitor system services, troubleshoot issues, and track service performance.
Prerequisites
- Linux-based operating system
- The
journalctlbinary is available in your$PATH - Systemd logs are available. Verify this by running:
sudo journalctl -n 10
The systemd journal contains structured logs for all services managed by it. Typical journal entries look like this:
Jun 25 10:30:45 hostname systemd[1]: Started myapp.service.
Jun 25 10:30:46 hostname myapp[1234]: Application started successfully
Setup
Step 1: Install OpenTelemetry Collector Contrib
Follow the installation guide to install the OpenTelemetry Collector. The journald receiver is available in the OpenTelemetry Collector Contrib distribution.
Step 2: Configure the journald receiver
Add the journald receiver to your config.yaml file and enable it in the logs pipeline:
receivers:
journald:
directory: /var/log/journal
start_at: end
If /var/log/journal doesn't exist on your host, try directory: /run/journal or directory: /run/log/journal (common default).
Then enable the receiver in your logs pipeline:
service:
pipelines:
logs:
receivers: [otlp, journald]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlp]
If you don't already have an OTLP exporter configured for SigNoz Cloud, add the following snippet (or update your existing otlp exporter):
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443
tls:
insecure: false
headers:
signoz-ingestion-key: <your-ingestion-key>
Replace the placeholders:
<region>: Your SigNoz Cloud region (e.g.,us,eu, orin)<your-ingestion-key>: Your SigNoz ingestion key
Additional Configuration Options:
start_at: end- Only collect new logs after the collector starts (default)start_at: beginning- Read all messages from the current bootunits- Filter logs from specific systemd servicespriority- Filter by log level (debug, info, notice, warning, err, crit, alert, emerg)matches- Advanced filtering using journalctl match syntaxstorage- Track cursor position across restarts to avoid reading the entries again (see Cursor tracking)
See the journald receiver documentation for all available options.
Step 3: Start the OTel Collector
Start the OpenTelemetry Collector:
./otelcol-contrib --config ./config.yaml
Running the collector as root may be required to access journal files. In production, consider creating a dedicated user with journal access permissions by adding the user to the systemd-journal group.
Validate
After starting the collector, verify that systemd logs are being ingested:
- Navigate to Logs Explorer in SigNoz from Sidebar
- You should see logs with systemd-specific fields like
_SYSTEMD_UNIT,PRIORITY, and_PID
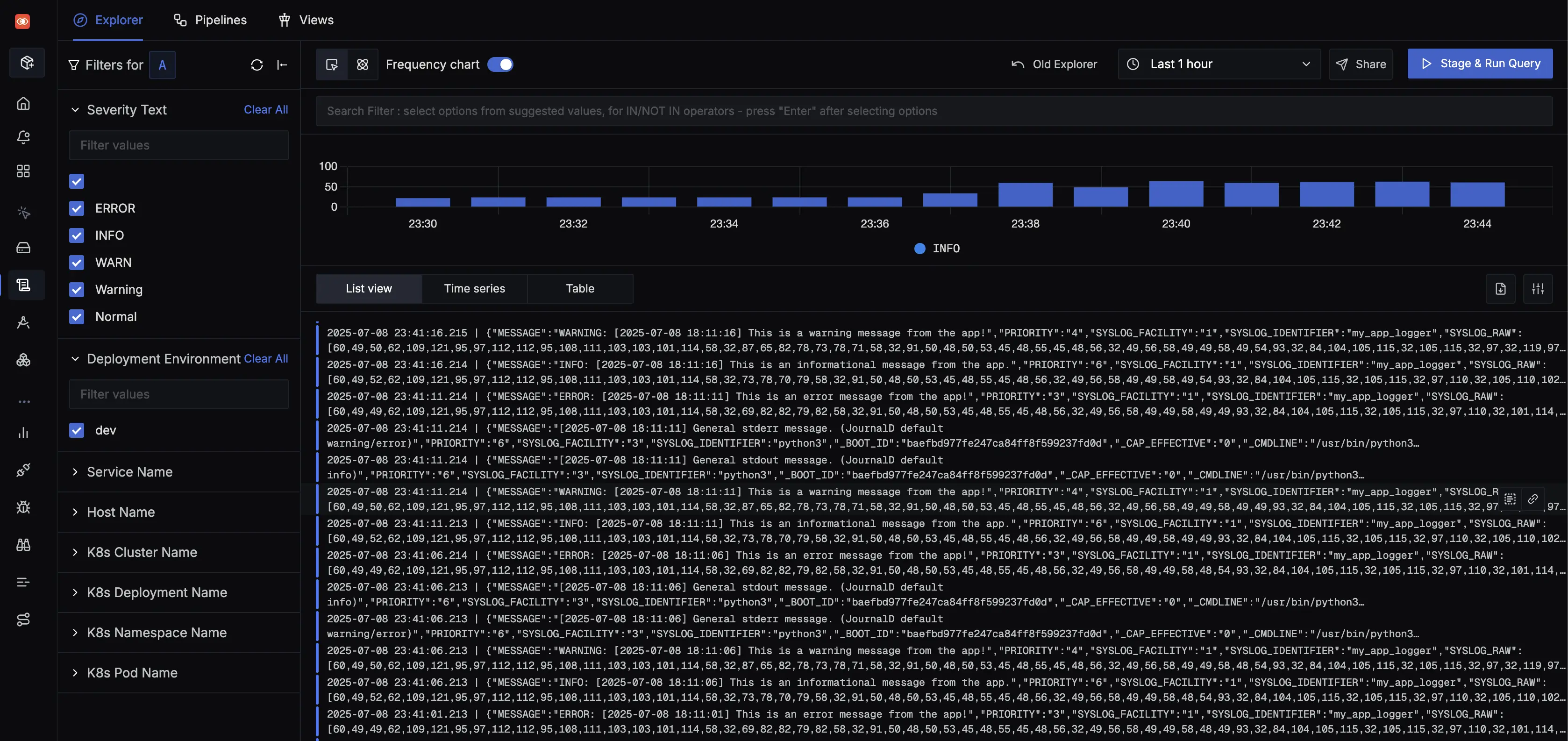
If you don't see logs within a few minutes, check the Troubleshooting section.
Log fields from systemd
Logs from systemd include rich metadata. Common fields include:
MESSAGE- The actual log message_SYSTEMD_UNIT- systemd unit that generated the logPRIORITY- Log priority (0-7, where 0 is emergency, 7 is debug)_PID- Process ID_HOSTNAME- System hostnameSYSLOG_IDENTIFIER- Program name_COMM- Command name
Advanced Configuration
Filtering Logs
You can filter systemd logs in several ways:
By systemd units
receivers:
journald:
directory: /var/log/journal
units:
- "nginx.service"
- "postgresql.service"
- "myapp.service"
By Priority Level
receivers:
journald:
directory: /var/log/journal
priority: warning # Only warning, err, crit, alert, emerg
By Custom Matches
The matches option allows advanced filtering using journalctl match fields. Each entry in the matches list is a map of field-value pairs. Entries in the list are OR'd together, and within each entry, the field-value pairs are AND'd.
receivers:
journald:
directory: /var/log/journal
matches:
- _TRANSPORT: kernel
- _SYSTEMD_UNIT: ssh
_UID: "1000"
This configuration collects logs that match either:
_TRANSPORTiskernel, OR_SYSTEMD_UNITissshAND_UIDis1000
Common journald fields for matching include:
_SYSTEMD_UNIT: systemd unit name (e.g.,nginx.service)_TRANSPORT: Log transport method (kernel,syslog,journal,stdout,audit)_UID: User ID that generated the log_GID: Group ID that generated the log_COMM: Command name (executable name)_PID: Process IDPRIORITY: Log priority level (0-7)
For a complete list, see the systemd.journal-fields documentation.
Combining Multiple Filter Options
When using multiple filter options (units, priority, matches, identifiers, grep, dmesg), the conditions between different options are logically AND'd, while conditions within each option are logically OR'd:
( dmesg )
AND
( priority )
AND
( units[0] OR units[1] OR units[2] ... )
AND
( identifiers[0] OR identifiers[1] OR identifiers[2] ... )
AND
( matches[0] OR matches[1] OR matches[2] ... )
AND
( grep )
Example: Filtering by units, priority, and custom matches:
receivers:
journald:
directory: /var/log/journal
priority: info
units:
- ssh
- nginx
matches:
- _SYSTEMD_UNIT: ssh
- _SYSTEMD_UNIT: nginx
_UID: "0"
This configuration collects logs where:
- Priority is
infoor higher (0-6), AND - Unit is
sshornginx, AND - Entry matches either:
_SYSTEMD_UNITissshOR (_SYSTEMD_UNITisnginxAND_UIDis0)
When combining units with matches, ensure the unit names are consistent. Since conditions are AND'd together, using different unit names in units and matches (e.g., units: [kubelet] with matches: [{_SYSTEMD_UNIT: ssh}]) will result in no logs being collected because no entry can match both kubelet (from units) and ssh (from matches) simultaneously.
Different Log Levels for Different Services
A common requirement is to collect logs at different priority levels for different services. For example, you might want:
- All logs (including debug) for your application service
- Only warning and above for system services
Since the journald receiver applies a single priority filter to all units, you can achieve this by using multiple receiver instances:
receivers:
# Receiver for application logs - collect all logs including info and debug
journald/app:
directory: /var/log/journal
priority: debug
units:
- myapp.service
# Receiver for system services - only warning and above
journald/system:
directory: /var/log/journal
priority: warning
units:
- nginx.service
- postgresql.service
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4317
http:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4318
processors:
batch: {}
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: "ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443"
tls:
insecure: false
headers:
signoz-ingestion-key: <your-ingestion-key>
service:
pipelines:
logs:
receivers: [otlp, journald/app, journald/system]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlp]
In this configuration:
journald/appcollects all logs frommyapp.serviceat prioritydebugand above (all logs)journald/systemcollects onlywarningand above fromnginx.serviceandpostgresql.service
The receiver instance name after the / (e.g., journald/app, journald/system) can be any descriptive string that helps identify the receiver's purpose. Each instance operates independently with its own filter configuration.
Troubleshooting
Permission Issues
If you see permission errors:
# Check journal access
sudo journalctl --verify
Log Generation
Check if systemd is generating logs:
sudo journalctl -n 10
Next Steps
Now that you're collecting systemd logs, explore these related features:
- Set up log pipelines to parse, transform, and enrich your logs
- Create alerts based on specific log patterns or error rates
- Build custom dashboards to visualize system service health
- Explore other log collection methods:
