This guide explains how to configure the OpenTelemetry Collectors deployed by the SigNoz K8s-Infra Helm chart. You'll learn how to set up telemetry data collection and enable the collection of metrics, logs, and traces from your Kubernetes cluster.
To install K8s-Infra in your Kubernetes cluster, please check out the k8s-infra Installation guide
Send Data from Instrumented Applications
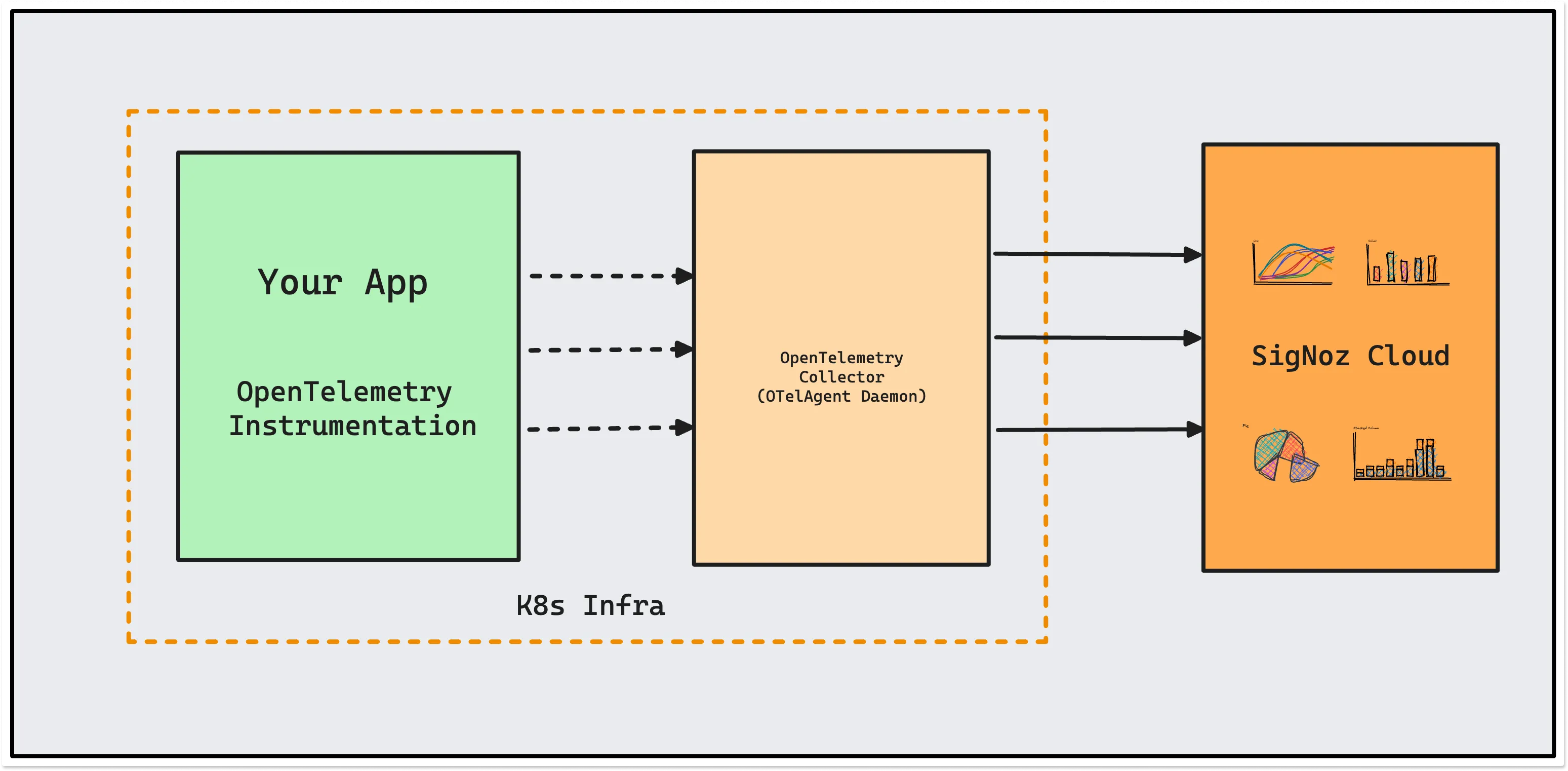
OpenTelemetry instrumented application sends data to OTelAgent Daemon deployed in your k8s infra. The OTelAgent daemon sends the collected data to SigNoz.
In case of GKE Autopilot, you will not be able to send data to OTelAgent Daemon via host port. You will need to use either the SigNoz ingestion endpoint directly or OtelAgent service name.
For OtelAgent service name, the endpoint would be something like my-release-k8s-infra-otel-agent.default.svc:4317. Replace my-release with your helm release name and default with your namespace.
To send data from your applications, you must first instrument it with OpenTelemetry. You can find instrumentation instructions for your specific language [here][10].
Once you're done instrumenting your application, add below to your application manifest files for applications to start sending data to the otel-collectors running as DaemonSet.
For example, you can add the below config to your application manifest file.
env:
- name: HOST_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.hostIP
- name: K8S_POD_IP
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: K8S_POD_UID
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.uid
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_INSECURE
value: "true"
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT
value: $(HOST_IP):4317
- name: OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES
value: service.name=APPLICATION_NAME,k8s.pod.ip=$(K8S_POD_IP),k8s.pod.uid=$(K8S_POD_UID)
- Replace
APPLICATION_NAMEwith your application name that you wish to see in SigNoz. - In cases of some SDKs, you would need to include
http://orhttps://prefix forOTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT
Disable Logs Collection
In case you do not want to collect logs from your Kubernetes cluster, you can disable using presets in k8s-infra chart.
presets:
logsCollection:
enabled: false
Disable Metrics Collection
In case you do not want to collect metrics from your Kubernetes cluster, you can disable using presets in k8s-infra chart.
presets:
hostMetrics:
enabled: false
kubeletMetrics:
enabled: false
clusterMetrics:
enabled: false
otelDeployment:
enabled: false
Essential Presets
SigNoz allows you to use the presets in the k8s-infra Helm chart to easily configure OtelCollector. The following configurations can be set by modifying the values.yml in the k8s-infra Helm chart.
The presets section in the values.yaml file allows you to enable or disable specific configurations. To check the available presets, refer to the k8s-infra Helm chart documentation.
1. OTLP Exporter
presets:
otlpExporter:
enabled: true # Must be enabled for data to reach SigNoz
What it does: Enables sending telemetry data to SigNoz backend. This is required for SigNoz to receive any data.
2. Host Metrics Collection
presets:
hostMetrics:
enabled: true
collectionInterval: 30s # Adjust based on your monitoring needs
scrapers:
cpu: {} # Collects CPU usage, time, and utilization metrics
load: {} # Collects system load averages
memory: {} # Collects memory usage metrics
disk: # Collects disk I/O metrics
exclude:
devices: # Regex patterns to exclude specific devices
- ^ram\d+$
- ^loop\d+$
# Add custom device exclusions here
filesystem: # Collects filesystem metrics
exclude_fs_types:
fs_types:
- tmpfs
- squashfs
# Add filesystem types to exclude
network: # Collects network metrics
exclude:
interfaces:
- ^veth.*$ # Excludes virtual ethernet devices
- ^docker.*$ # Excludes docker interfaces
# Add network interfaces to exclude
Key points:
- Adjust
collectionIntervalbased on your monitoring granularity needs - Customize device exclusions to reduce noise from irrelevant storage devices
- Configure network interface exclusions to focus on relevant network metrics
3. Container Log Collection
presets:
logsCollection:
enabled: true
startAt: beginning # Options: beginning or end
includeFilePath: true # Adds file path as metadata
includeFileName: false # Adds file name as metadata
# Exclusion configuration
blacklist:
enabled: true
signozLogs: true # Excludes SigNoz's own logs
namespaces:
- kube-system # Add namespaces to exclude
pods:
- hotrod # Add pod names to exclude
- locust
containers: [] # Add container names to exclude
# Inclusion configuration (overrides blacklist if enabled)
whitelist:
enabled: false
signozLogs: true
namespaces: [] # Only collect logs from these namespaces
pods: [] # Only collect logs from these pods
containers: [] # Only collect logs from these containers
Best practices:
- Use blacklist for excluding noisy system pods
- Enable whitelist when you need to monitor specific applications only
- Consider disk usage implications when enabling file path/name inclusion
4. Kubernetes Metrics Collection
presets:
kubeletMetrics:
enabled: true
collectionInterval: 30s
authType: serviceAccount # Authentication method
endpoint: ${env:K8S_HOST_IP}:10250
insecureSkipVerify: true # Set to false in production
# Metrics configuration
metrics:
k8s.pod.cpu_limit_utilization:
enabled: true
k8s.pod.memory_limit_utilization:
enabled: true
# Enable other metrics as needed
Important settings:
- Set appropriate
collectionIntervalbased on cluster size - Configure
insecureSkipVerify: falsein production environments - Enable specific metrics based on monitoring requirements
5. Kubernetes Metadata Enrichment
presets:
kubernetesAttributes:
enabled: true
passthrough: false # Set true to disable k8s API calls
# Control which metadata to collect
extractMetadatas:
- k8s.namespace.name
- k8s.deployment.name
- k8s.pod.name
- k8s.node.name
# Add or remove metadata fields
# Pod association configuration
podAssociation:
- sources:
- from: resource_attribute
name: k8s.pod.ip
# This label/annotation extraction rule takes the value of the key from labels/annotations and maps it to the tag_name attribute which will be added to the associated resources
extractLabels:
# Example from pod
- tag_name: service.name
key: app.kubernetes.io/name
from: pod
# Example from node
- tag_name: os.type
key: beta.kubernetes.io/os
from: node
# Annotation extraction configuration
extractAnnotations:
# Example from node
- tag_name: node.ttl
key: node.alpha.kubernetes.io/ttl
from: node
Configuration tips:
- Enable only required metadata fields to optimize performance
- Use
passthrough: truein very large clusters to reduce API load - Configure pod association based on your networking setup
6. Cluster-level Metrics
presets:
clusterMetrics:
enabled: true
collectionInterval: 30s
# Node conditions to monitor
nodeConditionsToReport:
- Ready
- MemoryPressure
- DiskPressure
# Add conditions based on monitoring needs
# Resource types to monitor
allocatableTypesToReport:
- cpu
- memory
# - storage # Uncomment if needed
When to use:
- Enable for cluster health monitoring
- Useful for capacity planning and resource optimization
- Essential for multi-node cluster monitoring
7. Kubernetes Events
presets:
k8sEvents:
enabled: true
authType: serviceAccount
namespaces: [] # Empty for all namespaces, or specify list
Usage scenarios:
- Enable for debugging and audit trails
- Monitor specific namespaces by listing them
- Useful for compliance and security monitoring
8. Prometheus Metrics Scraping
Prometheus preset allows to scrapes metrics from pods that have the appropriate annotations. This enables collecting metrics from applications that expose Prometheus endpoints without manual configuration.
presets:
prometheus:
enabled: true
annotationsPrefix: signoz.io # Prefix for pod annotations
scrapeInterval: 60s # How often to scrape metrics
namespaceScoped: false # Limit to same namespace only
namespaces: [] # Specific namespaces to scrape
includePodLabel: false # Include pod labels (may increase cardinality)
includeContainerName: false # Include container name in metrics
scrapeConfigs: [] # Custom scrape configurations
Custom Scrape Configurations
For more advanced use cases, you can define custom scrape configurations using the scrapeConfigs field. This allows you to specify Prometheus-compatible scrape configs directly:
presets:
prometheus:
enabled: true
scrapeConfigs:
# Scrape metrics from a specific service
- job_name: 'my-custom-service'
static_configs:
- targets: ['my-service.default.svc.cluster.local:9090']
labels:
environment: 'production'
Configurations
The k8s-infra chart exposes the full OpenTelemetry Collector configuration via Helm values, so you can adapt the running agents to your needs. The following are common options you may want to adjust.
Batch Processor
The batch processor batches spans, metrics, and logs before export. That reduces connections and improves compression. It supports both size-based and time-based batching.
Configure the batch processor by overriding otelAgent.config.processors.batch and otelDeployment.config.processors.batch in your Helm values. Example override:
otelAgent:
config:
processors:
# otelAgent.config.processors.batch -- Batch processor config.
batch:
- send_batch_size: 10000
+ send_batch_size: 15000
+ send_batch_max_size: 20000 # settings can be provided as key value pairs
Any setting supported by the OpenTelemetry batch processor can be set under processors.batch in the chart values.
Common Deployment Scenarios
Production Cluster with Full Monitoring
presets:
otlpExporter:
enabled: true
hostMetrics:
enabled: true
collectionInterval: 30s
logsCollection:
enabled: true
blacklist:
enabled: true
namespaces:
- kube-system
kubeletMetrics:
enabled: true
insecureSkipVerify: false
kubernetesAttributes:
enabled: true
clusterMetrics:
enabled: true
k8sEvents:
enabled: true
Resource-Constrained Environment
presets:
otlpExporter:
enabled: true
hostMetrics:
enabled: true
collectionInterval: 60s
logsCollection:
enabled: true
whitelist:
enabled: true
namespaces:
- production
kubeletMetrics:
enabled: true
collectionInterval: 60s
kubernetesAttributes:
enabled: true
passthrough: true
Development Environment
Telemetry data can be tagged with a "deployment environment" attribute (such as development, staging, or production) by setting it globally or explicitly in your application's OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES.
global:
deploymentEnvironment: <DEPLOYMENT_ENVIRONMENT>
You can specify the environment by including deployment.environment in the OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES environment variable of your application manifest. This will take precedence over the global.deploymentEnvironment setting in the k8s-infra chart—or, if not set, the global value will be used.
env:
- name: OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES
value: deployment.environment=<DEPLOYMENT_ENVIRONMENT>
Exposing Ports for Custom Receivers
You may want to use a custom receiver to receive metrics. If the receiver listens on a port, you need to expose that port to the host. The following example shows how to expose port 8125 of statsd receiver:
ports:
statsdReceiverPort:
enabled: true
containerPort: 8125
servicePort: 8125
hostPort: 8125
protocol: UDP
Configuring otelDeployment to collect from additional components
The otelDeployment collector is configured to collect cluster metrics and events by default. There are some use cases where you might want to collect metrics from components other than the ones that are being collected by default.
This section describes how to override the default configuration of the otelDeployment collector to collect metrics from additional components. The override-values.yaml file contains the configurations that you can override.
Example 1: Redis Receiver Configuration
The following configuration shows how to configure the otelDeployment collector to collect metrics from a Redis server running inside a namespace "redis-ns" with the name "redis-server" and port 6379:
otelDeployment:
config:
receivers:
redis:
endpoint: redis-server.redis-ns.svc.cluster.local:6379
service:
pipelines:
metrics/internal:
receivers: [redis]
processors: [batch]
exporters: []
Example 2: Configuring a PostgreSQL receiver
The following configuration shows how to configure the otelDeployment collector to collect metrics from a PostgreSQL server running inside a namespace "postgres-ns" with the name "postgres-server" and port 5432:
otelDeployment:
config:
receivers:
postgres:
endpoint: postgres-server.postgres-ns.svc.cluster.local:5432
service:
pipelines:
metrics/internal:
receivers: [postgres]
processors: [batch]
exporters: []
Example 3: Configuring multiple receivers
The following configuration shows how to configure both Redis and PostgreSQL receivers:
otelDeployment:
config:
receivers:
redis:
endpoint: redis-server.redis-ns.svc.cluster.local:6379
postgres:
endpoint: postgres-server.postgres-ns.svc.cluster.local:5432
service:
pipelines:
metrics/internal:
receivers: [redis, postgres]
processors: [batch]
exporters: []
The above examples are simple and show how to configure the otelDeployment collector to collect metrics from a single component. However, in a real-world scenario, you might need to configure the receiver with a username and password and other configurations.
Resource Requirements
Recommended resource allocations based on preset combinations:
| Configuration | CPU Request | Memory Request | CPU Limit | Memory Limit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimal | 100m | 256Mi | 200m | 512Mi |
| Standard | 200m | 512Mi | 500m | 1Gi |
| Full | 500m | 1Gi | 1000m | 2Gi |
Adjust these values based on your cluster size and monitoring requirements.
