Docker Logs Location: Where are Docker Logs Stored?
When your Docker container crashes at 3 AM, you need to find its logs quickly. No time for guesswork or hunting through documentation—you need the exact path to those log files.
Here's what you need to know immediately:
- Linux:
/var/lib/docker/containers/<container-id>/<container-id>-json.log - Windows:
C:\ProgramData\docker\containers\<container-id>\<container-id>-json.log - macOS: Within Docker Desktop VM, accessible via
docker logscommand - Universal command:
docker logs <container-name>works across all platforms
This guide covers everything from basic log locations to production-grade log management strategies that'll save you hours of troubleshooting.
Quick Access Commands
Before diving into file system paths, here are the essential commands you'll use daily:
# View container logs (works everywhere)
docker logs <container-name>
# Follow logs in real-time
docker logs -f <container-name>
# Get the exact log file path
docker inspect --format='{{.LogPath}}' <container-name>
# Find full container ID for direct file access
docker inspect --format='{{.Id}}' <container-name>
Docker Log Architecture: Container vs Daemon Logs
Docker generates two distinct types of logs:
Container Logs capture your application's stdout/stderr output:
- Application messages and errors
- Debug information
- Runtime events
- Performance metrics
Daemon Logs record Docker engine events:
- Container lifecycle operations
- Image management activities
- Network configuration changes
- System-level Docker errors
Understanding this distinction matters because they're stored differently and accessed through different methods.
Platform-Specific Log Locations
Linux Systems
Docker follows a predictable directory structure on Linux:
/var/lib/docker/containers/<full-container-id>/<full-container-id>-json.log
Each container gets its own subdirectory named with the complete container ID (not the shortened version from docker ps). The log file uses JSON format:
{"log":"Application started successfully\n","stream":"stdout","time":"2025-07-23T10:30:45.123456789Z"}
{"log":"Error: Database connection failed\n","stream":"stderr","time":"2025-07-23T10:30:46.987654321Z"}
Finding Container Logs:
# Get full container IDs
docker ps -q --no-trunc
# Direct file access (requires sudo)
sudo tail -f /var/lib/docker/containers/<full-container-id>/<full-container-id>-json.log
Daemon Logs:
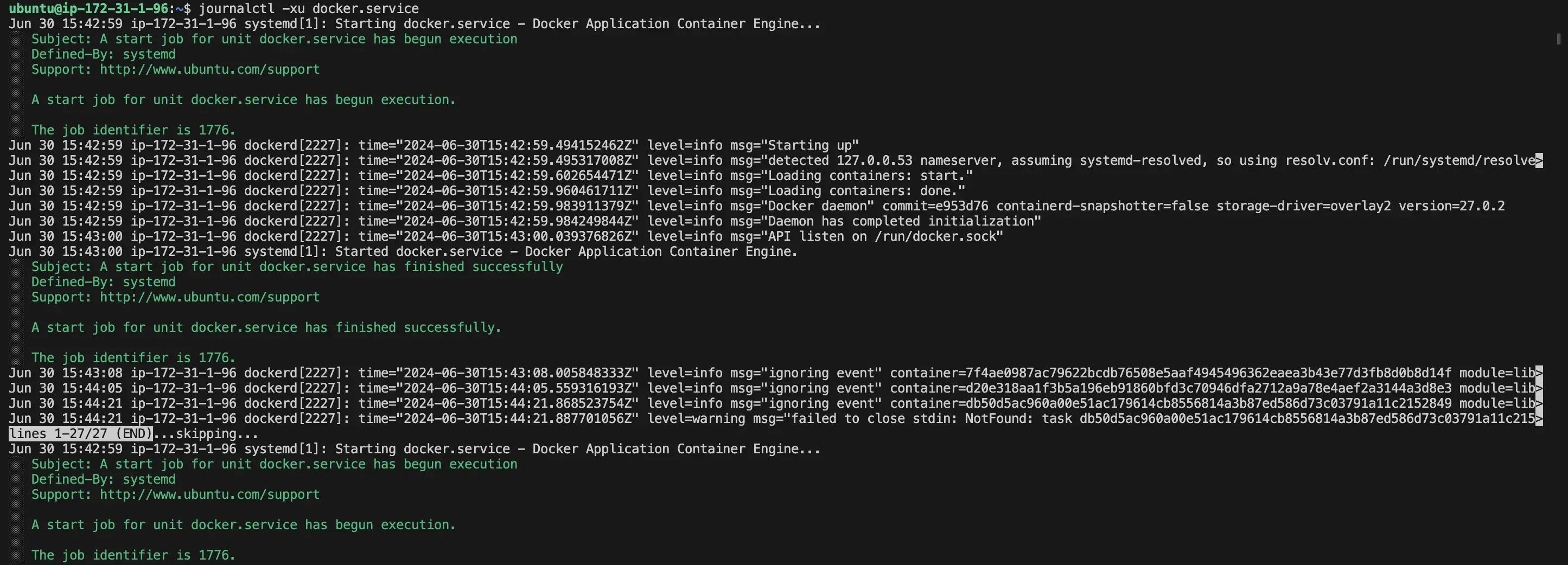
# For systemd-based systems (most modern distributions)
journalctl -xu docker.service
# For older systems
tail -f /var/log/syslog | grep docker
Windows Systems
Docker Desktop on Windows stores logs at:
C:\ProgramData\docker\containers\<container-id>\<container-id>-json.log
With Docker Desktop using WSL2, logs are actually within the WSL2 VM:
\\wsl.localhost\docker-desktop\mnt\docker-desktop-disk\data\docker\containers\<container-id>\<container-id>-json.log
Daemon Logs: Available in Windows Event Viewer under Applications and Services Logs → Docker.
macOS Systems
Docker Desktop runs containers inside a Linux VM. Logs are within:
~/Library/Containers/com.docker.docker/Data/log/vm/
Accessing VM logs:
# Docker daemon logs
tail -f ~/Library/Containers/com.docker.docker/Data/log/vm/dockerd.log
# Container runtime logs
tail -f ~/Library/Containers/com.docker.docker/Data/log/vm/containerd.log
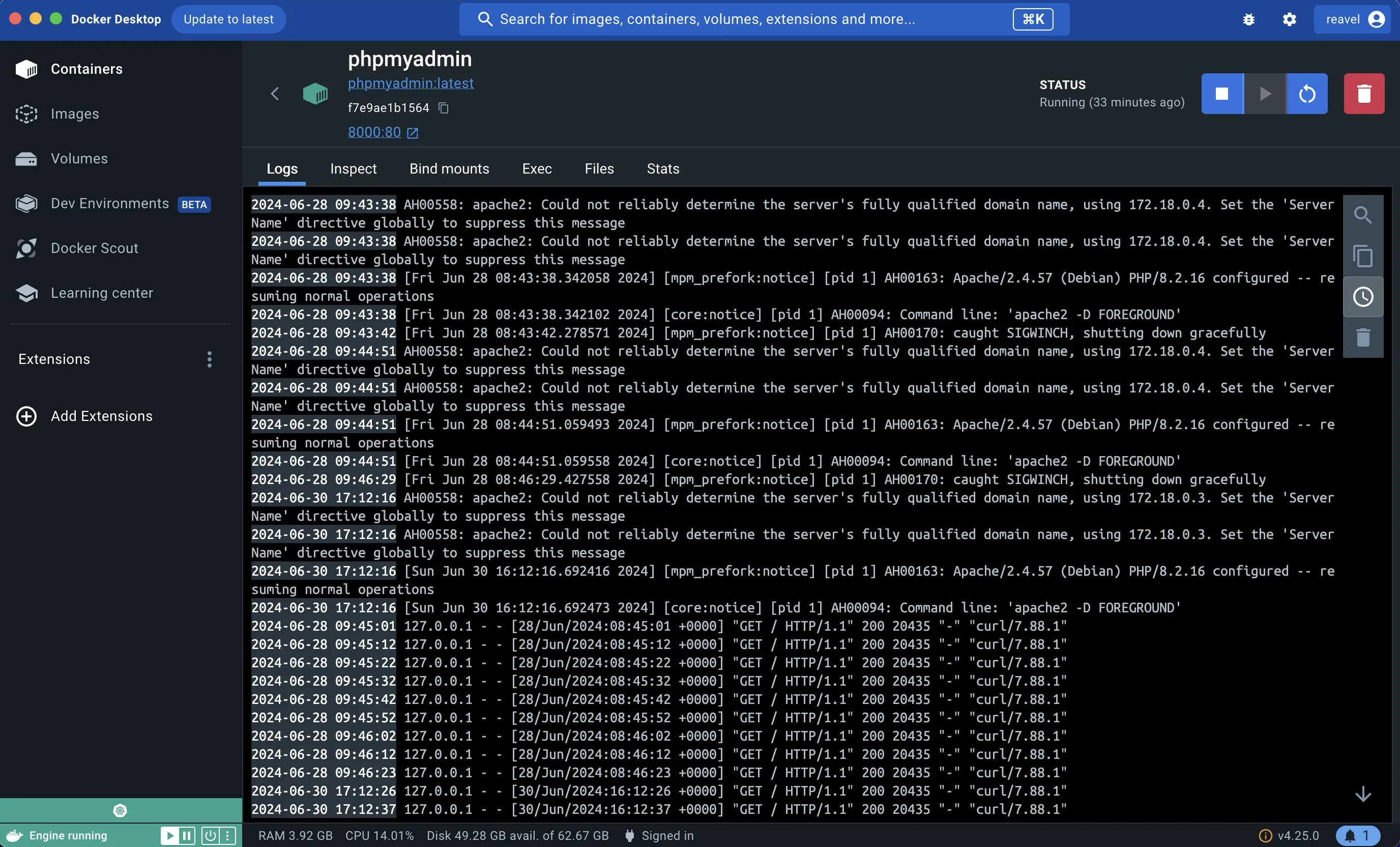
Docker Desktop UI Access: You can also access container logs through the Docker Desktop interface:
Mastering the Docker Logs Command
While direct file access works, the docker logs command provides consistent functionality across platforms:
Essential Usage Patterns
# View all logs
docker logs <container-name>
# Real-time monitoring
docker logs -f <container-name>
# Show recent entries
docker logs --tail 100 <container-name>
# Time-based filtering
docker logs --since 1h <container-name>
docker logs --since 2025-07-23T10:00:00 <container-name>
# Combine filters
docker logs -f --tail 50 --since 30m <container-name>
Advanced Filtering
# Time range filtering
docker logs --since 2025-07-23T10:00:00 --until 2025-07-23T11:00:00 <container-name>
# Include timestamps
docker logs -t <container-name>
# Show additional metadata
docker logs --details <container-name>
Managing Log File Growth
Uncontrolled log growth is a common production issue. Docker doesn't rotate logs by default, so they can consume all available disk space.
Configuring Log Rotation
Global configuration in /etc/docker/daemon.json:
{
"log-driver": "json-file",
"log-opts": {
"max-size": "10m",
"max-file": "3",
"compress": "true"
}
}
Per-container rotation:
docker run --log-opt max-size=50m --log-opt max-file=5 nginx
Docker Compose setup:
services:
web:
image: nginx
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-size: "10m"
max-file: "3"
compress: "true"
Emergency Cleanup
When logs have already consumed too much space:
# Find largest log files
find /var/lib/docker/containers/ -name "*json.log" -exec du -h {} \; | sort -hr
# Truncate logs for running containers (use carefully)
sudo truncate -s 0 /var/lib/docker/containers/*/*-json.log
# Remove logs for stopped containers
docker container prune
Production Logging Strategies
Alternative Logging Drivers
Local Driver (Recommended): Provides automatic rotation and compression:
{
"log-driver": "local",
"log-opts": {
"max-size": "10m",
"max-file": "5",
"compress": "true"
}
}
Syslog Driver: Forward logs to centralized syslog servers:
docker run --log-driver=syslog \
--log-opt syslog-address=tcp://logs.example.com:514 \
--log-opt tag="{{.ImageName}}" \
nginx
Journald Driver: Integrate with systemd journal:
{
"log-driver": "journald",
"log-opts": {
"tag": "{{.ImageName}}/{{.Name}}"
}
}
View with: journalctl -u docker CONTAINER_NAME=myapp
Centralized Logging Architecture
For production environments, implement centralized logging:
- Direct Forwarding: Use logging drivers to send logs directly to centralized systems
- Agent-Based Collection: Deploy log collectors like Fluentd or Fluent Bit
- Sidecar Pattern: Run dedicated logging containers
Security considerations:
docker run --log-driver=syslog \
--log-opt syslog-address=tcp+tls://secure-logs.example.com:6514 \
--log-opt syslog-tls-ca-cert=/path/to/ca.pem \
myapp
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Permission Denied Errors
# Add user to docker group
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
# Or use sudo for direct file access
sudo docker logs <container-name>
Missing Logs
Check logging driver configuration:
# Inspect container logging setup
docker inspect <container-name> | grep -A 10 "LogConfig"
# Verify daemon logging settings
docker info | grep "Logging Driver"
Monitoring Log Sizes
Proactive monitoring script:
#!/bin/bash
find /var/lib/docker/containers/ -name "*json.log" | \
while read log; do
size=$(du -h "$log" | cut -f1)
container=$(echo "$log" | cut -d'/' -f5 | cut -c1-12)
echo "Container: $container - Log size: $size"
done | sort -k4 -hr
Advanced Docker Log Management with SigNoz
While direct log access works for debugging, production environments need scalable log management. SigNoz provides comprehensive Docker log observability that goes beyond basic file viewing.
Key Capabilities for Docker Environments
Unified Log Collection: SigNoz uses OpenTelemetry collectors to aggregate logs from multiple Docker containers with automatic labeling and metadata enrichment.
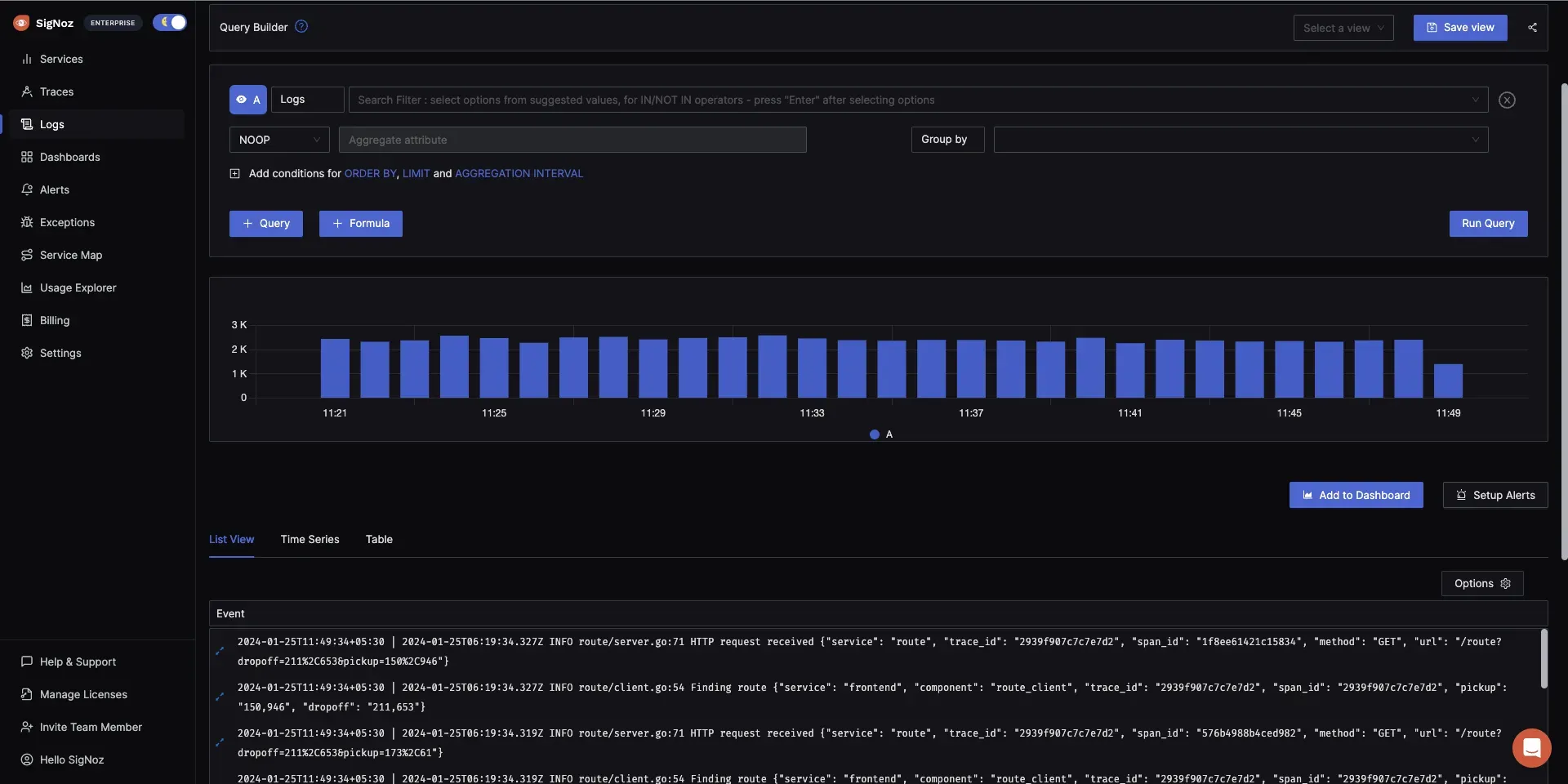
Real-time Analysis: Advanced log querying capabilities with structured filtering, search builders, and JSON views for efficient troubleshooting.
Integration Benefits:
- Pre-configured setup with ready-to-use
docker-compose.yamlfiles - Enhanced log organization using logspout-signoz for automatic service labeling
- Correlation with metrics and traces for complete container observability
- Efficient storage using ClickHouse columnar database
Production Features:
- Live tail logging across multiple containers
- Custom dashboards for Docker log analytics
- Anomaly detection for proactive issue identification
- Advanced retention and archiving policies
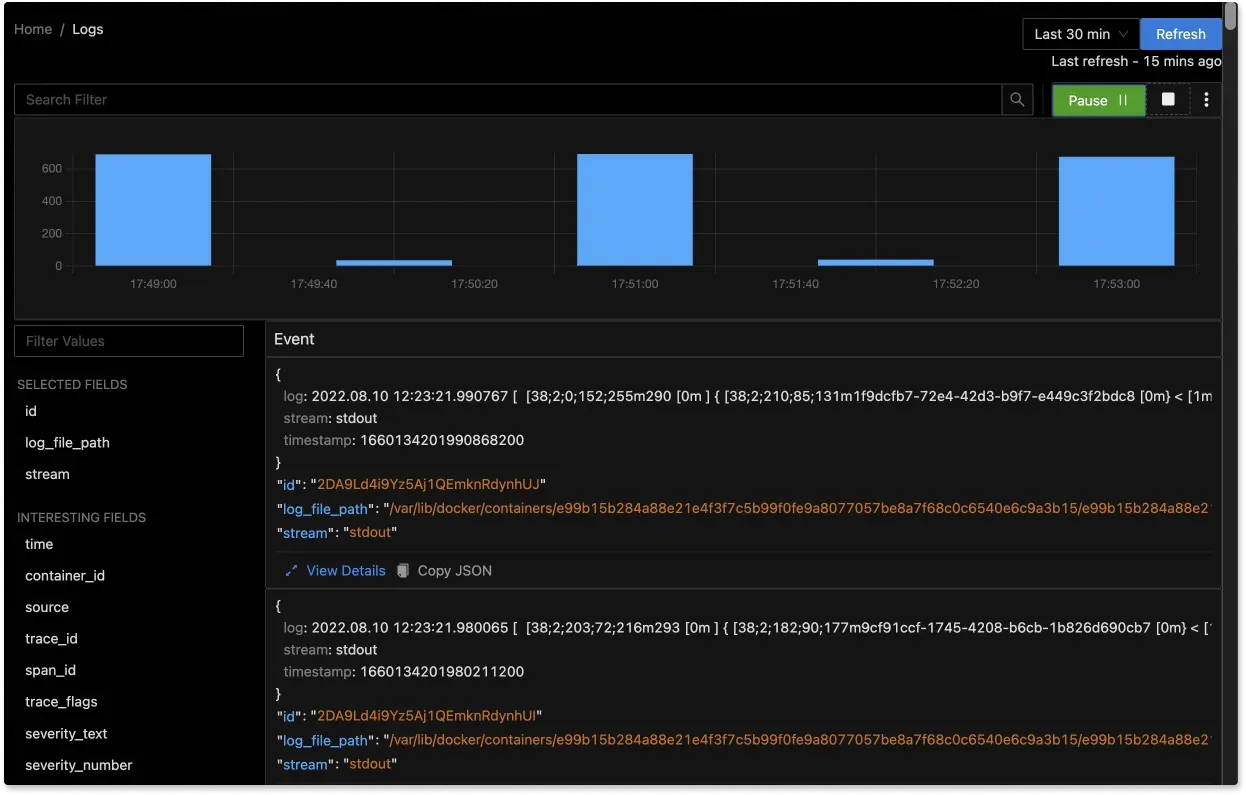
Advanced Filtering and Search:
Setup Process
SigNoz simplifies Docker log collection through:
- Environment configuration with
OTEL_COLLECTOR_ENDPOINTand ingestion keys - Automated collection via OpenTelemetry receivers
- Enhanced metadata through logspout-signoz integration
You can get started by following the Docker logs collection guide in the SigNoz documentation.
Getting Started with SigNoz
You can choose between various deployment options in SigNoz. The easiest way to get started with SigNoz is SigNoz cloud. We offer a 30-day free trial account with access to all features.
Those who have data privacy concerns and can't send their data outside their infrastructure can sign up for either enterprise self-hosted or BYOC offering.
Those who have the expertise to manage SigNoz themselves or just want to start with a free self-hosted option can use our community edition.
Hope we answered all your questions regarding Docker logs location. If you have more questions, feel free to use the SigNoz AI chatbot, or join our slack community.
Key Takeaways
- Platform locations vary:
/var/lib/docker/containers/(Linux),C:\ProgramData\docker\containers(Windows), Docker VM (macOS) - Use
docker logscommand for consistent cross-platform access - Implement log rotation to prevent disk space issues (
max-size,max-fileoptions) - Consider centralized logging solutions for production scalability
- Monitor log sizes proactively with automated scripts and alerts
Understanding these fundamentals ensures effective container log management across development and production environments.
FAQs
Where can I find docker logs?
Docker logs are stored in /var/lib/docker/containers/<container-id>/<container-id>-json.log on Linux and C:\ProgramData\docker\containers\<container-id>\<container-id>-json.log on Windows. Use docker logs <container-name> for cross-platform access.
Where does a container store logs?
Containers output to stdout/stderr streams, which are captured by the Docker daemon and stored on the host filesystem using the configured logging driver. Containers themselves don't store logs internally.
How to check docker logs live?
Use docker logs -f <container-name> to follow logs in real-time, similar to tail -f for regular files.
How to reduce docker logs?
Configure log rotation with max-size and max-file options in your logging driver configuration. Set global defaults in /etc/docker/daemon.json or per-container options during docker run.
Are docker logs persistent?
Docker logs persist on the host filesystem as long as the container exists. They remain available after container stops but are removed when the container is deleted with docker rm.
How do I find the full container ID?
Use docker ps -q --no-trunc for all full container IDs, or docker inspect --format '{{.Id}}' <container-name> for a specific container.
What is the command for docker logs tail?
Use docker logs --tail <number> <container-name> to view the last N lines, for example: docker logs --tail 100 myapp.
Where are docker images stored?
Docker images are stored in /var/lib/docker/image/ on Linux and C:\ProgramData\docker\ on Windows, separate from container logs.
