Network Observability - Key to Modern IT Performance
Network observability goes beyond merely collecting data on network performance, it provides a comprehensive, it provides a comprehensive understanding of the entire network ecosystem. By leveraging telemetry data from routers, switches, firewalls, servers, and applications, observability tools allow organizations to visualize the intricate interactions within their networks.
This holistic view enables IT professionals to quickly identify and resolve issues before they impact service quality.
What is Network Observability?
Network observability is the ability to gain comprehensive visibility into the internal state of your network by analyzing its outputs. Unlike traditional network monitoring, which limits itself to predefined metrics and alerts, observability takes a more holistic approach.
Network observability enables network administrators and engineers to ask open-ended questions, explore unknown issues, and gain insights that weren’t previously obvious.
Key components of network observability include:

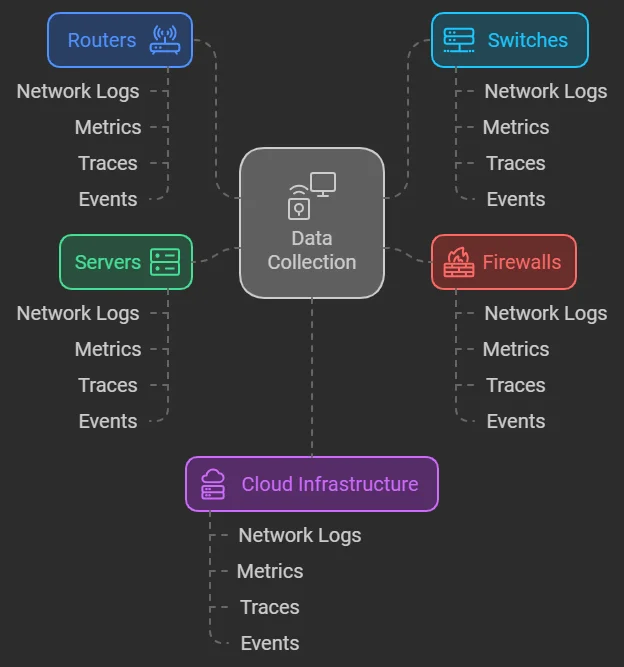
- Analysis: The collected data is processed, correlated, and analyzed to uncover patterns and identify root causes of performance issues. This often involves the use of advanced analytics to detect anomalies.
- Visualization: Dashboards and visual tools are critical for understanding the health of your network at a glance. Well-designed visualisations highlight important trends and issues, making it easier for teams to quickly grasp network conditions.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) play crucial roles in network observability. These technologies enable automated analysis of vast amounts of data, detecting patterns that humans might miss. AI and ML algorithms can predict potential issues, allowing teams to resolve problems before they escalate, thereby reducing downtime and optimizing network performance.
The Evolution of Network Management
The journey from basic network management to modern network observability reflects the increasing complexity of today’s IT infrastructure. Let’s take a brief look at how management has evolved.
| Aspect | Early Network Management | Traditional Monitoring | Modern Network Observability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Basic connectivity checks | Monitoring predefined metrics (e.g., bandwidth, CPU) | Real-time insights and comprehensive visibility |
| Technology Used | Ping tests, basic traffic monitoring | SNMP-based tools | Advanced tools with AI/ML for deeper analysis |
| Metric Scope | Limited to connectivity | Bandwidth, CPU, packet loss | Network behaviour, performance, dependencies |
| Data Insights | Simple, minimal insights | Predefined, lacks contextual data | Correlated, contextual insights across distributed systems |
| Environment Type | Basic local networks | Local networks and data centers | Cloud-native, microservices, hybrid cloud environments |
| Issue Detection | Reactive (based on device failure or downtime) | Reactive (altered after threshold breach) | Proactive 0predictive, real-time issue detection) |
| Scalability | Not scalable | Scales to larger networks but with limitations | Scales to handle complex, distributed environments |
| Real-Time Analysis | Not available | Limited | Real-time, with predictive analytics and anomaly detection |
| Example Use Case | Checking if devices are connected | Monitoring bandwidth usage across routers | Monitoring cloud-based microservices and infrastructure. |
Why Network Observability is Crucial for Modern IT
In the rapidly evolving IT landscape, the complexity of infrastructure has reached unprecedented levels. Organizations are increasingly adopting hybrid cloud and multi-cloud environments, leveraging containerized applications and microservices architectures to stay agile and competitive.
This shift, while offering flexibility and scalability, also introduces a tangled web of interdependencies and challenges that make traditional monitoring tools insufficient.
Network observability emerges as a vital solution, offering comprehensive visibility across your entire infrastructure. Here’s why it is essential for modern IT operations:
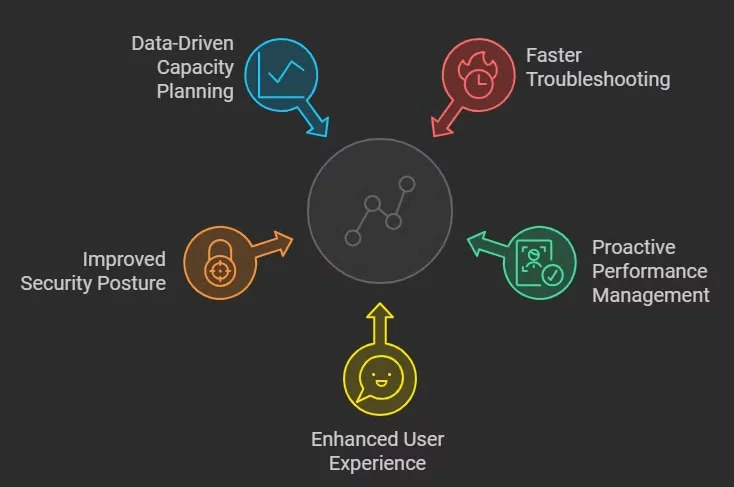
- Faster Troubleshooting: In complex environments, identifying the root cause of issues can be daunting. Network observability enhances your ability to detect and diagnose problems swiftly, significantly reducing Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR). With actionable insights, IT teams can quickly pinpoint the origins of slowdowns or outages, effectively minimizing downtime.
- Proactive Performance Management: By continuously monitoring network performance, observability enables organizations to identify potential issues before they affect users. This proactive approach helps maintain optimal service levels and enhances overall user satisfaction.
- Enhanced User Experience: Network observability ensures that all services operate at peak performance, directly contributing to seamless user experiences. By optimising application delivery and network reliability, businesses can foster higher customer retention and satisfaction.
- Improved Security Posture: With the rise in cyber threats, network observability plays a critical role in security management. It facilitates the detection of anomalies that may indicate security breaches or vulnerabilities, allowing for timely interventions to safeguard sensitive data.
- Data-Driven Capacity Planning: Organizations can make informed decisions regarding network resources by leveraging the insights gained from observability tools. This capability supports effective planning and resource allocation, ensuring that infrastructure can adapt to changing demands.
Key Components of Network Observability
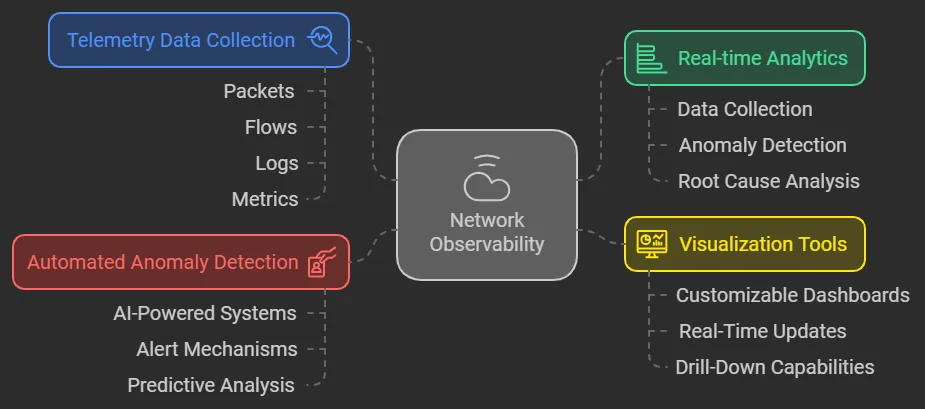
Understanding the key components of network observability is essential for organizations aiming to enhance their IT infrastructure performance and reliability. By leveraging these components, businesses can gain comprehensive insights into their network operations, enabling proactive management and optimization. Here are the fundamental elements of network observability.
- Telemetry Data Collection:
- Packets: Capture detailed data about network traffic, providing insights into individual data transmissions.
- Flows: Aggregated traffic information that summarizes data movement across the network, helping identify patterns and trends.
- Logs: Record events from network devices and applications, offering a historical view that aids in troubleshooting and compliance.
- Metrics: Provided quantitative network performance measurements, such as latency, bandwidth utilization, and error rates, essential for assessing overall health.
- Real-time Analytics:
- Data Collection: Integrates information from various sources to create a cohesive understanding of network behaviour.
- Anomaly Detection: Utilizes AI and ML algorithms to identify unusual patterns that may indicate performance issues or security threats.
- Root Cause Analysis: Facilitates quick identification of underlying issues, allowing IT teams to address problems efficiently.
- Visualization Tools:
- Customizable Dashboards: Tailor visual interfaces for different stakeholders, ensuring relevant information is easily accessible.
- Real-Time Updates: Provide immediate insights into network status and performance metrics, aiding in timely decision-making.
- Drill-Down Capabilities: Allow users to explore data in detail, enhancing the ability to diagnose specific issues.
- Automated Anomaly Detection:
- AI-Powered Systems: Learn normal behaviour patterns within the network, enabling rapid identification of derivations.
- Alert Mechanisms: Trigger notifications for any anomalies detected, ensuring that IT teams can respond swiftly to potential issues.
- Predictive Analysis: Forecast future problems based on historical data trends, allowing for proactive adjustments before issues escalate.
How to Implement Network Observability
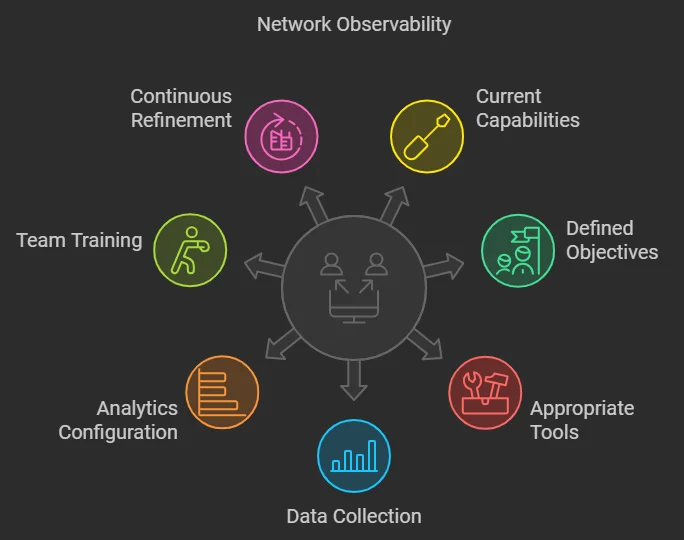
Implementing network observability is essential for organizations aiming to enhance their network performance and reliability. Here’s a streamlined, step-by-step guide to effectively implement network observability:
- Assess Current Capabilities: To effectively implement network observability, organizations must first assess their current capabilities. This involves:
- Evaluate Existing Tools: Conduct a thorough audit of your current monitoring and observability tools. Assess their effectiveness in providing visibility across your network.
- Identify Gaps: Look for areas lacking visibility, such as blind spots in network traffic, under-monitored applications, or sufficient data collection methods. This assessment will help you understand where improvements are necessary.
- Define Objectives: Once the current capabilities are assessed, organizations should define clear objectives for their network observability efforts.
- Determine Insights Needed: Clearly outline the specific insights you require from your network observability efforts. This could include performance metrics, user experience indicators, or security threat detection.
- Set Clear Goals: Establish measurable objectives, such as reducing Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR) by a certain percentage, improving application response times, or enhancing overall user satisfaction.
- Select Appropriate Tools: The right tools are critical for effective network observability.
- Choose the Right Platforms: Research and select observability tools that fit your organization’s needs. Look for platforms that offer compatibility with your existing technology stack and can scale as your infrastructure grows.
- Consider Features: Evaluate features such as data visualization capabilities, real-time analytics, machine learning for anomaly detection, and ease of integration with other systems.
- Implement Data Collection: Effective data collection is foundational to successful observability.
- Deploy Agents and Collectors: Install agents on critical devices and applications to gather telemetry data effectively. Ensure that data collection covers all aspects of your network, including cloud environments, on-premises systems, and hybrid setups.
- Ensure Comprehensive Coverage: Map out all critical systems and services to ensure no essential components are left unmonitored.
- Configure Analytics and Alerting: Setting up analytics and alerting mechanisms is vital for proactive network management.
- Set Up Dashboards: Create customizable dashboards tailored to different teams (e.g., IT operations, security, development) to provide relevant insights at a glance. Dashboards should facilitate quick decision-making based on real-time data.
- Define Alert Thresholds: Establish clear thresholds for alerts based on historical performance data and business priorities. Implement escalation procedures to ensure timely responses to critical issues.
- Train Your Team: A well-trained team is essential for maximizing the benefits of observability tools.
- Provide Training Sessions: Organize training workshops for IT staff to familiarize them with the observability tools and best practices for data analysis.
- Encourage a Data-Driven Culture: Promote an organizational culture that values data-driven decision-making by sharing success stories and insights gained from observability efforts.
- Continuously Refine: Finally, organizations should commit to continuously refining their observability strategy
- Regularly Review Strategy: Schedule periodic reviews of your observability strategy to assess its effectiveness. Gather feedback from stakeholders and make necessary adjustments based on evolving business needs.
- Stay Updated: Keep abreast of new features, industry trends, and best practices in network observability to continuously enhance your approach.
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
Implementing network observability isn't without its hurdles. Here are some common challenges and strategies to overcome them:
- Data Volume Management: The sheer volume of telemetry data generated by network devices can overwhelm storage and processing capabilities, making it difficult to extract meaningful insights.
- Implement Efficient Storage Solutions: Use scalable storage solutions that can handle large volumes of telemetry data without compromising performance.
- Establish Retention Policies: Define retention policies that balance the need for historical data with storage costs.
- Integration Difficulties: Integrating new observability tools with existing IT systems can be complex, leading to compatibility and operational disruptions.
- Select Tools with Robust APIs: Choose observability platforms that offer strong APIs and pre-built integrations with other tools in your tech stack to facilitate seamless connectivity.
- Conduct Pilot Tests: Run pilot tests for new tools before full-scale implementation to identify integration challenges early on.
- Addressing Privacy Concerns: Collecting and analyzing telemetry data raises privacy and compliance issues, particularly regarding sensitive information.
- Enforce Data Governance Policies: Develop comprehensive data governance policies that outline how telemetry data will be collected, stored, and used while ensuring compliance with regulations (e.g., GDPR).
- Utilize Anonymization Techniques: Run pilot tests for new tools before full-scale implementation to identify integration challenges early on.
- Cultural Resistance: Resistance from team members who are accustomed to traditional monitoring methods can hinder the adoption of new observability practices.
- Demonstrate Quick Wins: Showcase early successes from observability initiatives to build confidence among stakeholders.
- Communicate ROI Clearly: Present clear metrics demonstrating the return on investment from improved network performance and reduced downtime.
Leveraging SigNoz for Network Observability
SigNoz, an open-source observability platform, offers a powerful solution for gaining comprehensive insights into your network’s performance, security, and overall health. By integrating SigNoz into your IT infrastructure, you can unlock a wealth of benefits that will transform the way you manage and optimize your network.
Key Features for Network Observability:
- End-to-End Tracing: SigNoz provides powerful distributed tracing capabilities that allow you to follow the path of requests as they flow through your network.
- This end-to-end visibility helps you identify bottlenecks, understand dependencies between services, and quickly pinpoint the root cause of performance issues.
- Metrics collection and visualization: SigNoz collects a wide range of network metrics, including throughput, latency, error rates, and more.
- The platform offers customizable dashboards and visualisations that make it easy to monitor critical performance indicators and spot trends or anomalies.
- Log Management and Analysis: SigNoz integrates log management functionality, enabling you to collect, store, and analyze logs from various network devices and applications.
- The advanced log querying capabilities allow you to quickly filter, search, and correlate log data to troubleshoot problems and gain deeper insights.
- AI-Powered Anomaly Detection: SigNoz leverages machine learning algorithms to automatically detect anomalies in network behaviour.
- The platform establishes baselines for normal performance and sends alerts when deviations occur, allowing you to proactively address potential issues before they impact users or services.
Benefits of Using SigNoz for Network Observability:
- Faster Troubleshooting: SigNoz’s comprehensive visibility and powerful analytics capabilities enable you to quickly identify and resolve network issues, reducing Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR).
- Improved Performance: By continuously monitoring network performance and identifying bottlenecks, SigNoz helps you optimize network resources and ensure optimal performance for critical applications and services.
- Enhanced Security: SigNoz’s anomaly detection features can help you identify potential security threats, such as unauthorized access attempts or suspicious traffic patterns, allowing you to take proactive measures to protect your network.
- Cost Optimization: SigNoz’s open-source nature and flexible pricing model make it a cost-effective alternative to proprietary network observability solutions. The platform’s scalability also allows you to optimize costs by right-sizing your observability infrastructure.
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Whether you choose the cloud or self-hosted option, SigNoz provides the tools you need to gain deep insights into your network's behaviour. SigNoz is a comprehensive choice for organizations looking to enhance their network observability capabilities and drive better business outcomes.
Future Trends in Network Observability
The field of network observability is undergoing rapid transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving business needs. Here are some key trends to watch for as we move forward:
- AIOps Integration: The integration of Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations (AIOps) will become increasingly prevalent.
- This trend will enable predictive insights, automated remediation of issues, and enhanced decision-making processes, allowing organizations to respond to network anomalies with greater speed and efficiency.
- Intent-Based Networking (IBN): Intent-Based Networking (IBN) is a modern approach to network management that leverages artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and orchestration to automate the configuration and management of networks based on high-level business intents.
- By automating routine tasks and configurations, IBM reduces the workload on network administrators, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives rather than manual management.
- Insights gained from continuous analytics help organizations make informed decisions about network performance and resource allocation.
- Edge Computing Observability: As edge computing grows, observability solutions will expand their capabilities to monitor these distributed environments effectively.
- This includes providing visibility into devices and applications located at the network edge, which is critical for real-time data processing and decision-making.
- Unified Observability: There will be a significant shift towards unified observability platforms that integrate network, application, and infrastructure monitoring. This trend aims to provide a comprehensive view of the entire IT ecosystem, enabling organizations to correlate data across different domains for better insights and faster troubleshooting.
- Open Standards: Initiatives like OpenTelemetry will drive the adoption of open standards in observability data collection and analysis.
- This trend will facilitate interoperability between different observability tools and promote a more collaborative ecosystem, allowing organizations to choose best-of-breed solutions without vendor lock-in.
- Proactive Performance Management: Organizations will adopt more proactive strategies for performance management, and utilize observability insights to anticipate issues before they escalate into significant problems.
- This trend emphasizes the importance of continuous monitoring and analysis in maintaining optimal network performance.
- Expansion of Multi-Cloud Observability: As organizations adopt multi-cloud strategies, there will be a growing need for observability solutions that provide visibility across various cloud platforms.
- This trend will help organizations manage complex cloud environments effectively while ensuring consistent performance and security.
Key Takeaways
- Network observability provides comprehensive visibility into the behaviour, performance, and health of complex IT infrastructures, enabling organizations to understand intricate interactions within their networks.
- Unlike traditional monitoring, network observability allows for proactive management by identifying potential issues before they impact users, thus enhancing overall network reliability and performance.
- Successfully implementing network observability necessitates a strategic approach that includes assessing current capabilities, defining objectives, selecting appropriate tools, and training teams.
- SigNoz stands out as a robust open-source platform for network observability, offering features like end-to-end tracing, metrics visualization, log management, and AI-powered anomaly detection.
- The evolution of network observability is leaning towards AI-driven solutions that provide predictive insights and automated responses to enhance operational efficiency and security.
FAQs
What's the difference between network monitoring and network observability?
| Aspect | Network Monitoring | Network Observability |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Narrow, specific metrics and device health | Wide, comprehensive view of network health and behaviour |
| Data Collected | Basic, uptime, bandwidth, device availability | Comprehensive, logs, metrics, traces, flows and telemetry |
| Alerts | Predefined rules based on thresholds | Predefined and AI-driven anomaly detection |
| Contextual Understanding | Limited context, often reactive | Holistic understanding of network state and performance |
| Use Cases | Monitoring for uptime and performance metrics | Root cause analysis, performance optimization anomaly detection |
How does network observability improve IT performance?
- Faster Troubleshooting: Network observability provides deep visibility, enabling IT teams to quickly identify and resolve performance issues.
- Proactive Issue Prevention: By continuously monitoring network behaviours, observability tools detect anomalies and potential problems before they impact users.
- Enhanced User Experience: Maintaining optimal network performance ensures a seamless user experience, improving customer satisfaction and productivity.
- Data-Driven Capacity Planning: Insights from observability solutions help IT teams make informed decisions about network resources, optimizing costs and performance.
What are the key features to look for in a network observability tool?
- Comprehensive Data Collection: Ability to collect metrics, logs, traces, and flow data from various network components.
- Advanced Analytics: Powerful analytics and machine learning capabilities for identifying patterns, anomalies, and root causes.
- Customizable Visualizations: Intuitive dashboards and reports tailored to different stakeholder’s needs.
- Proactive Alerting: AI-powered anomaly detection and alerting to notify teams of potential issues.
- Scalability: Ability to handle the growing complexity and scale of modern network environments.
Can network observability help with cloud migration and management?
- Visibility During Migration: Observability tools provide insights into application dependencies and performance impacts, enabling cloud migration.
- Monitoring Hybrid Environments: Ongoing visibility into cloud-based and on-premises infrastructure ensures optimal performance post-migration.
- Compatibility with Cloud-Native Technologies: Observability solutions should support the monitoring of modern, dynamic cloud environments and architectures.
