Proactive Monitoring - Prevent Issues Before They Happen
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, system failures and performance issues can spell disaster for businesses. You can't afford to wait for problems to occur before taking action. This is where proactive monitoring comes into play. It's a game-changing approach that allows you to anticipate and prevent issues before they impact your operations. But what exactly is proactive monitoring, and how can you implement it effectively?
What is Proactive Monitoring?
Proactive monitoring refers to a preventive approach to IT system management that focuses on identifying and addressing potential issues before they develop into major problems. This strategy involves continuously tracking key performance metrics, system health indicators, and usage patterns to ensure systems run smoothly and efficiently. By anticipating and mitigating problems early, proactive monitoring helps organizations avoid costly downtime and maintain optimal performance.
Proactive vs. Reactive Monitoring
Proactive and reactive monitoring are two distinct strategies for managing IT systems. Let’s look at the major differences between the two.
| Aspect | Proactive Monitoring | Reactive Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Preventive and anticipatory | Reactive and responsive |
| Data Analysis | Involves real-time data collection, historical trend analysis, and predictive modeling | Limited to real-time data analysis only |
| Response Time | Immediate response through automation or alerting before issues escalate | Response only after an incident occurs, leading to potential downtime |
| Technology Used | Advanced analytics, AI, and machine learning | Basic monitoring tools |
| Impact on Downtime | Significantly reduces downtime by preventing issues | Higher downtime risk due to delayed responses |
| User Experience | Maintains high user satisfaction by ensuring continuous service performance | User experience is affected during incidents or outages |
| IT Team Focus | Frees up resources for innovation by minimizing manual issue handling | IT teams are often occupied with firefighting, reducing time for strategic work |
| Cost Implications | Cost-effective in the long term by preventing major disruptions and optimizing resource allocation | May incur higher costs due to emergency responses, downtime, and possible revenue loss |
While proactive monitoring aims to prevent issues from arising, reactive monitoring involves responding to problems after they have occurred. In a reactive approach, IT teams act when an alert signals an issue, working quickly to diagnose and resolve it. This can result in service disruptions and customer dissatisfaction.
Conversely, proactive monitoring continuously evaluates the system’s performance and stability, using automated tools and intelligent analysis to detect potential warning signs. This allows teams to take preemptive measures, reducing the likelihood of system failures and minimizing the impact of potential disruptions.
Key Components of an Effective Proactive Monitoring System
To be truly effective, a proactive monitoring system should include several essential components:
- Real-time Data Collection: Continuous data collection from various sources, such as servers, applications, and network devices, provides an accurate, up-to-date view of system health.
- Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning: Leveraging analytics tools and machine learning algorithms helps identify trends, anomalies, and early warning signs, allowing teams to make informed decisions.
- Automated Alerts and Notifications: Automated systems should trigger alerts when performance metrics deviate from normal ranges, enabling swift intervention before issues escalate.
- Dashboards and Visualization Tools: Comprehensive dashboards that display system metrics and health statuses offer IT teams an at-a-glance view of critical information, facilitating quick analysis.
- Scalable Architecture: A scalable framework ensures that the monitoring solution can grow with the business and handle larger data volumes as needed.
Benefits of Implementing Proactive Monitoring in Business Operations
The implementation of proactive monitoring offers numerous advantages for businesses:
- Reduced Downtime: By identifying and addressing issues early, proactive monitoring significantly reduces unplanned outages, keeping services operational and ensuring high availability.
- Improved User Experience: Proactively maintained systems deliver consistent performance, leading to greater customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Enhanced Security: Early detection of anomalies can indicate potential security threats, enabling timely action to safeguard systems and data.
- Cost Savings: Preventing issues before they escalate helps reduce the expenses associated with emergency fixes, data recovery, and lost productivity.
- Better Resource Management: Proactive monitoring allows IT teams to optimize resource allocation, ensuring that personnel focus on strategic initiatives rather than emergency response efforts.
Overall, proactive monitoring is a vital part of modern IT system management, enabling businesses to stay ahead of potential problems, streamline operations, and enhance system reliability.
The Evolution from Reactive to Proactive Monitoring
In the rapidly advancing IT landscape, monitoring practices have undergone a significant transformation, evolving from reactive approaches to proactive strategies. This shift has been driven by the need for enhanced reliability, efficiency, and customer satisfaction in modern systems.
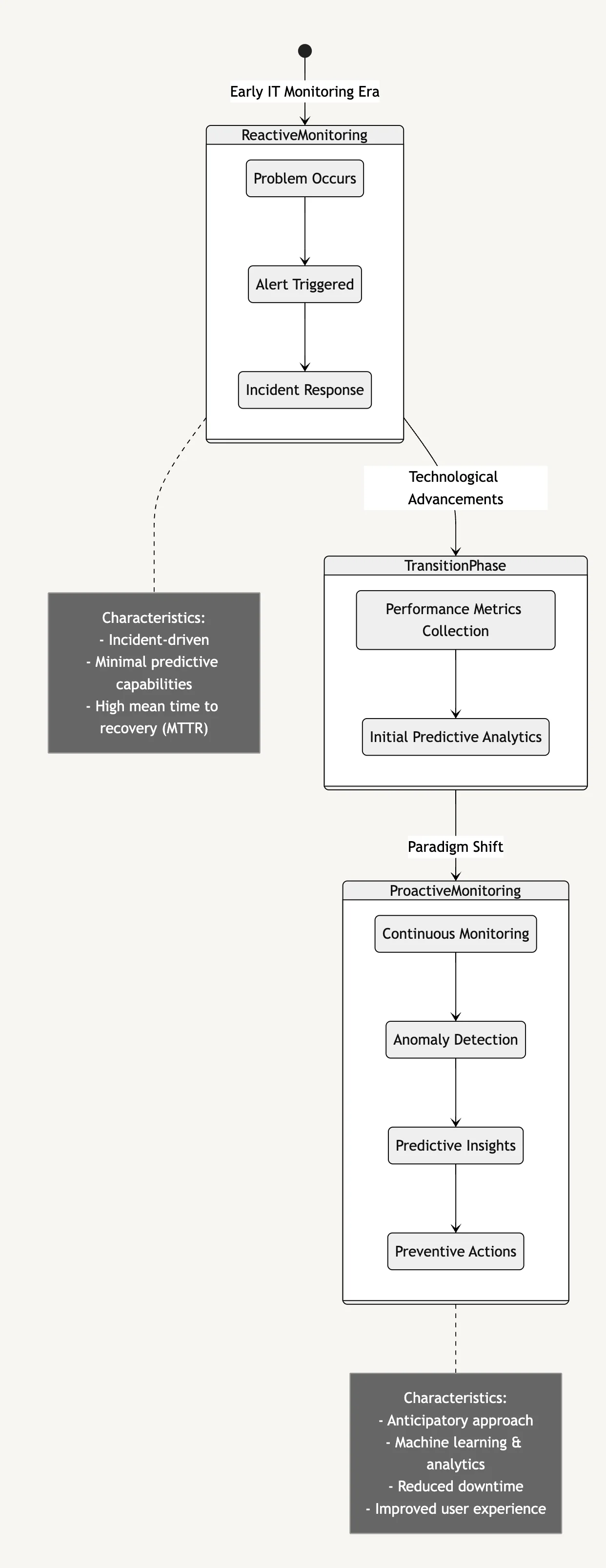
Technological advancements and shift in mindset from firefighting to prevention: Technological advancements have gradually enabled a shift from reactive to proactive monitoring. Modern observability platforms, enhanced with machine learning and real-time analytics, empower organizations to anticipate potential issues before they disrupt operations. Proactive monitoring encompasses the continuous analysis of performance metrics, historical data trends, and anomaly detection to preempt failures. This shift reflects a broader change in IT strategy—moving from a “firefighting” mode to a preventive and resilience-focused mindset.
Impact on business continuity and customer satisfaction The adoption of proactive monitoring has far-reaching benefits for business continuity and customer satisfaction. Organizations that anticipate issues before they escalate can maintain higher service reliability, reduce downtime, and deliver a seamless user experience.
SigNoz, an open-source observability tool, exemplifies this evolution. By offering features like distributed tracing, detailed performance insights, and alerting capabilities, SigNoz supports proactive monitoring. It enables teams to visualize and address potential performance bottlenecks in their distributed systems, thus preventing outages and optimizing system health.
Why is Proactive Monitoring Critical for Modern Businesses?
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, proactive monitoring has emerged as an indispensable component for organizations seeking to maintain seamless operations and stay competitive. Here’s why proactive monitoring is critical for modern businesses:
Reduction of Downtime and Associated Costs
Unplanned downtime can have significant financial and reputational repercussions. Proactive monitoring mitigates these risks by enabling IT teams to detect and address potential issues before they escalate into full-scale outages.
Example: Imagine an e-commerce platform experiencing a spike in traffic during a flash sale. Without proactive monitoring, a sudden server overload could crash the website, resulting in lost sales and frustrated customers. Proactive monitoring detects traffic surges early, enabling the system to auto-scale resources and prevent downtime.
Improvement in Overall System Performance and Reliability
Proactive monitoring ensures that potential bottlenecks or performance dips are identified early, facilitating timely interventions. This approach leads to a more stable and robust IT environment, where resources are optimized, and disruptions are minimized.
Example: A logistics company tracks database query performance through proactive monitoring. By identifying slow-running queries, the IT team optimizes them before they affect delivery tracking systems, ensuring smooth operations during peak shipping periods.
Enhanced User Experience and Customer Satisfaction
User experience is heavily influenced by system responsiveness and availability. Proactive monitoring helps maintain high levels of system performance, directly contributing to faster load times and seamless interactions for end-users.
Example: A streaming platform monitors buffering times and server latency. If latency increases, the system automatically switches to alternative servers, ensuring uninterrupted streaming for users and retaining customer loyalty.
Competitive Advantage through Consistent Service Delivery
In a market of evolving customer expectations, businesses must stand out through reliable service delivery. Proactive monitoring helps maintain continuous operations and adapt to challenges swiftly, reducing service disruptions and positioning the company as dependable and forward-thinking.
Example: A financial services firm relies on proactive monitoring to detect unusual transaction patterns in real time. By resolving potential issues instantly, the firm assures customers of secure and uninterrupted services, setting itself apart in the highly competitive fintech sector.
How Does Proactive Monitoring Work?
Proactive monitoring is an approach centered around continuous oversight of an organization’s IT infrastructure to anticipate and prevent potential issues. It relies on several key mechanisms:
- Continuous Data Collection and Analysis: Data is gathered from servers, applications, and network components in real time, providing a comprehensive view of system health.
- Utilization of Machine Learning and AI: Advanced algorithms analyze historical and current data to detect patterns and anomalies that could signal impending issues.
- Real-Time Alerting Systems: When potential risks are identified, the system triggers alerts to relevant teams, allowing for quick interventions.
- Automated Response Mechanisms: Routine problems can be addressed through automated scripts or tools, reducing the need for manual intervention and ensuring rapid resolution.
Key Technologies Enabling Proactive Monitoring
Several advanced technologies empower proactive monitoring to function effectively:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): These algorithms facilitate the identification of subtle trends and deviations from the norm, enabling predictive capabilities.
- Predictive Analytics Tools: These tools leverage data modeling to forecast possible future system failures and recommend preemptive measures.
- Synthetic Monitoring Techniques: Simulated user interactions are used to test applications and services from different geographical points, ensuring consistent performance and identifying issues before actual users are impacted.
- AIOps Platforms: By integrating AI-driven insights, AIOps platforms streamline operations by correlating data from various sources, automating responses, and providing comprehensive monitoring for complex environments.
Proactive monitoring, empowered by these technologies, ensures that businesses can minimize risks, optimize performance, and maintain uninterrupted service.
Best Practices for Implementing Proactive Monitoring
Implementing proactive monitoring requires a strategic approach to ensure potential issues are identified and addressed before they affect system performance or user experience. These best practices, supported by real-world examples, provide a roadmap for achieving effective monitoring.
Establishing Baseline Performance Metrics
To implement proactive monitoring effectively, begin by defining baseline performance metrics that capture the normal behavior of your systems. For example:
- Web Traffic: An e-commerce platform might expect an average of 500 concurrent users during business hours and a spike to 1,500 users during flash sales.
- Database Queries: A database might handle around 10,000 queries per hour under normal conditions.
Once these baselines are established, deviations like a sudden drop in web traffic or unusually high query latencies can be flagged as potential issues. Regularly revisit these metrics to account for changes, such as infrastructure upgrades or seasonal business trends.
Setting Up Comprehensive Monitoring Across All Systems
Proactive monitoring must cover all layers of the IT environment to provide a unified view. Here are some examples:
- A logistics company might monitor server CPU usage, API response times, and delivery app performance. A slowdown in API response times could indicate a database bottleneck, allowing teams to address it before it impacts delivery tracking.
- In a SaaS application, monitor both server health and end-user experience metrics, such as page load times. If servers show 100% uptime but users face long load times, you may need to optimize content delivery or caching mechanisms.
Using integrated tools like Datadog, SigNoz, or Prometheus, teams can prevent blind spots and ensure early detection of issues across systems.
Developing and Refining Alert Thresholds
Setting customized alert thresholds minimizes noise and focuses attention on actionable issues. For example:
- Network Latency: Alert if latency exceeds 200ms for more than 5 minutes, rather than triggering alerts for every minor spike.
- Disk Usage: Alert if disk usage exceeds 85% over a sustained period, avoiding false alarms caused by temporary backups.
Historical data plays a vital role here. For instance, if your web server always experiences a minor load increase during lunch hours, configure alerts to trigger only when the increase is outside the expected range. Regularly adjust thresholds based on infrastructure changes or new applications.
Creating a Culture of Proactive Problem-Solving Within IT Teams
Fostering a proactive mindset in IT teams ensures smoother operations and quicker resolutions:
- Example: During a routine monitoring review, a team notices occasional slowdowns in API performance during peak hours. Instead of waiting for the problem to escalate, they scale up resources or introduce request throttling to manage the load proactively.
- Training and Collaboration: Provide workshops on using AI-based monitoring tools like Dynatrace or SigNoz. Encourage collaboration between DevOps, security, and development teams to anticipate and resolve issues before they affect users.
Adopting a learn and adapt culture helps teams prevent recurring problems and continuously improve their monitoring strategies.
Proactive Monitoring with SigNoz: A Practical Approach
SigNoz is an open-source observability tool that provides full visibility into your applications, infrastructure, and microservices. It enables real-time monitoring, helping teams proactively identify and resolve performance issues before they impact users. SigNoz supports both cloud and on-premise environments, making it a versatile tool for modern infrastructures.
Key Features of SigNoz That Enable Proactive Monitoring
- Distributed Tracing: Track requests across microservices to pinpoint performance bottlenecks and optimize system flow.
- Real-Time Metrics: Monitor system health indicators like CPU usage and request rates to detect anomalies.
- Custom Dashboards: Visualize system performance with customizable graphs and charts.
- Alerts and Notifications: Set up alerts for critical thresholds to take action before issues escalate.
- Scalability: SigNoz can handle large-scale infrastructures with ease, whether in the cloud or on-premise.
- Open-Source Flexibility: Fully customizable, allowing integration with other observability tools.
Getting Started with SigNoz
- Install: Use Docker, Kubernetes, or a binary for easy setup.
- Configure: Set up SigNoz to capture traces and metrics from your applications.
- Create Dashboards: Build custom dashboards to track relevant metrics and set alert rules.
- Analyze: Leverage insights to proactively address issues and optimize performance.
Benefits of Using SigNoz for Both Cloud and Open-Source Environments
- Cost-Effective: Being open-source, SigNoz is free to use and customizable.
- Cloud & Hybrid Support: Works seamlessly with cloud services like AWS, GCP, Azure, and on-prem setups.
- Scalability: Handles large-scale infrastructure, growing with your business.
- Real-Time Insights: Provides continuous performance monitoring, enabling proactive issue resolution.
- Simplified Troubleshooting: Distributed tracing helps identify the root cause of issues faster.
- Community Support: Leverage community-driven resources or paid support options.
Overcoming Challenges in Proactive Monitoring
While proactive monitoring offers significant benefits, it also comes with its own set of challenges. Here's how the information can be represented in a table for better readability:
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| False Positives and Alert Fatigue | Overly sensitive monitoring systems can generate excessive alerts, causing important notifications to be overlooked. | Regularly refine alert thresholds and use intelligent alert grouping to minimize noise. |
| Performance Impact | Intensive monitoring can degrade system performance if not implemented carefully. | Use lightweight monitoring agents and optimize data collection frequency to reduce overhead. |
| Data Privacy and Security | Collecting system data raises concerns about unauthorized access and compliance with regulations. | Implement strong data encryption, access controls, and compliance measures to secure data. |
| Integration Complexity | Integrating proactive monitoring with existing workflows and tools can be difficult. | Opt for solutions with robust API support and pre-built integrations with popular DevOps tools. |
| Skill Gap | Specialized skills in data analysis and machine learning are often required for effective monitoring. | Provide training for your team or leverage managed monitoring services to bridge the expertise gap. |
False Positives and Alert Fatigue: Overly sensitive monitoring systems can lead to a flood of alerts, many of which may be false positives. This can lead to alert fatigue, where important notifications are missed or ignored.
Solution: Regularly refine your alert thresholds and use intelligent alert grouping to reduce noise.
Performance Impact: Intensive monitoring can itself impact system performance if not implemented carefully.
Solution: Use lightweight monitoring agents and optimize data collection frequency.
Data Privacy and Security: Collecting comprehensive system data raises concerns about data privacy and security.
Solution: Implement strong data encryption, access controls, and compliance measures in your monitoring setup.
Integration Complexity: Integrating proactive monitoring into existing workflows and tools can be challenging.
Solution: Choose monitoring solutions with robust API support and pre-built integrations with popular DevOps tools.
Skill Gap: Effective proactive monitoring often requires specialized skills in data analysis and machine learning.
Solution: Invest in training for your team or consider managed monitoring services.
Future Trends in Proactive Monitoring
As technology evolves, proactive monitoring is poised to become even more sophisticated, leveraging emerging tools and methodologies to address increasingly complex challenges.
Integration of IoT Devices in Monitoring Ecosystems
As IoT devices proliferate, integrating them into proactive monitoring systems will become increasingly important. Real-time data from IoT devices can provide valuable insights into system health, enabling organizations to anticipate potential issues before they affect operations.
Advanced Predictive Capabilities Through Deep Learning
Deep learning algorithms are set to enhance predictive monitoring by identifying complex patterns and anomalies that traditional methods might miss. This will allow businesses to detect subtle, hard-to-predict issues and take preventive measures more effectively.
Expansion of Proactive Monitoring to Business Processes
Proactive monitoring will extend beyond IT systems to encompass broader business processes. By monitoring key business metrics and workflows, organizations can identify potential disruptions or inefficiencies, enabling proactive interventions to optimize operations and maintain smooth business continuity.
Increased Automation in Issue Resolution
Automation will continue to play a key role in proactive monitoring, with systems automatically responding to certain triggers and resolving common issues without human intervention. This will reduce the workload on IT teams and ensure faster response times, ultimately improving system uptime and efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Proactive monitoring is a preventive approach that identifies and addresses potential issues before they impact your business.
- Implementing proactive monitoring leads to reduced downtime, improved system reliability, and enhanced user satisfaction.
- Key technologies enabling proactive monitoring include AI, machine learning, and predictive analytics.
- Best practices include establishing baselines, comprehensive monitoring, and fostering a proactive culture within your organization.
- Tools like SigNoz offer practical solutions for implementing proactive monitoring in both cloud and open-source environments.
- While challenges exist, such as alert fatigue and integration complexity, they can be overcome with the right strategies.
- The future of proactive monitoring points towards more autonomous, AI-driven operations and expanded scope beyond traditional IT systems.
FAQs
What's the difference between proactive and reactive monitoring?
Proactive monitoring focuses on preventing issues before they occur by analyzing trends and predicting potential problems. Reactive monitoring, on the other hand, involves responding to issues after they've already impacted your systems.
| Aspect | Proactive Monitoring | Reactive Monitoring |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Anticipates issues before they occur | Responds to issues after they have occurred |
| Approach | Continuous monitoring and preventive actions | Incident-driven responses and troubleshooting |
| Goals | Maintain optimal performance and prevent downtime | Quickly resolve issues to minimize impact |
| Resource Allocation | Requires ongoing maintenance and updates | Involves emergency responses and repair activities |
How does proactive monitoring improve system reliability?
Proactive monitoring improves system reliability by identifying potential issues early, allowing for preventive maintenance and optimizations. This approach reduces unexpected downtime and maintains consistent performance.
Can small businesses benefit from proactive monitoring?
Yes, small businesses can benefit significantly from proactive monitoring. While the scale might be smaller, preventing downtime and ensuring optimal performance is crucial for businesses of all sizes. Many monitoring solutions offer scalable options suitable for small to medium enterprises.
What are the first steps to implement proactive monitoring in an organization?
To start implementing proactive monitoring:
- Assess your current IT infrastructure and identify critical systems.
- Define key performance indicators (KPIs) and establish baseline metrics.
- Choose a monitoring solution that fits your needs and budget.
- Begin with monitoring your most critical systems and gradually expand coverage.
- Train your team on the new tools and processes, emphasizing the importance of a proactive mindset.
