SLO Monitoring - A Guide to Measuring Service Reliability
In today’s fast-paced digital world, service reliability is non-negotiable. Users expect applications to be available, responsive and error-free at all times. How can organizations meet those lofty expectations? SLO monitoring is the answer, a powerful framework for measuring and maintaining service reliability.
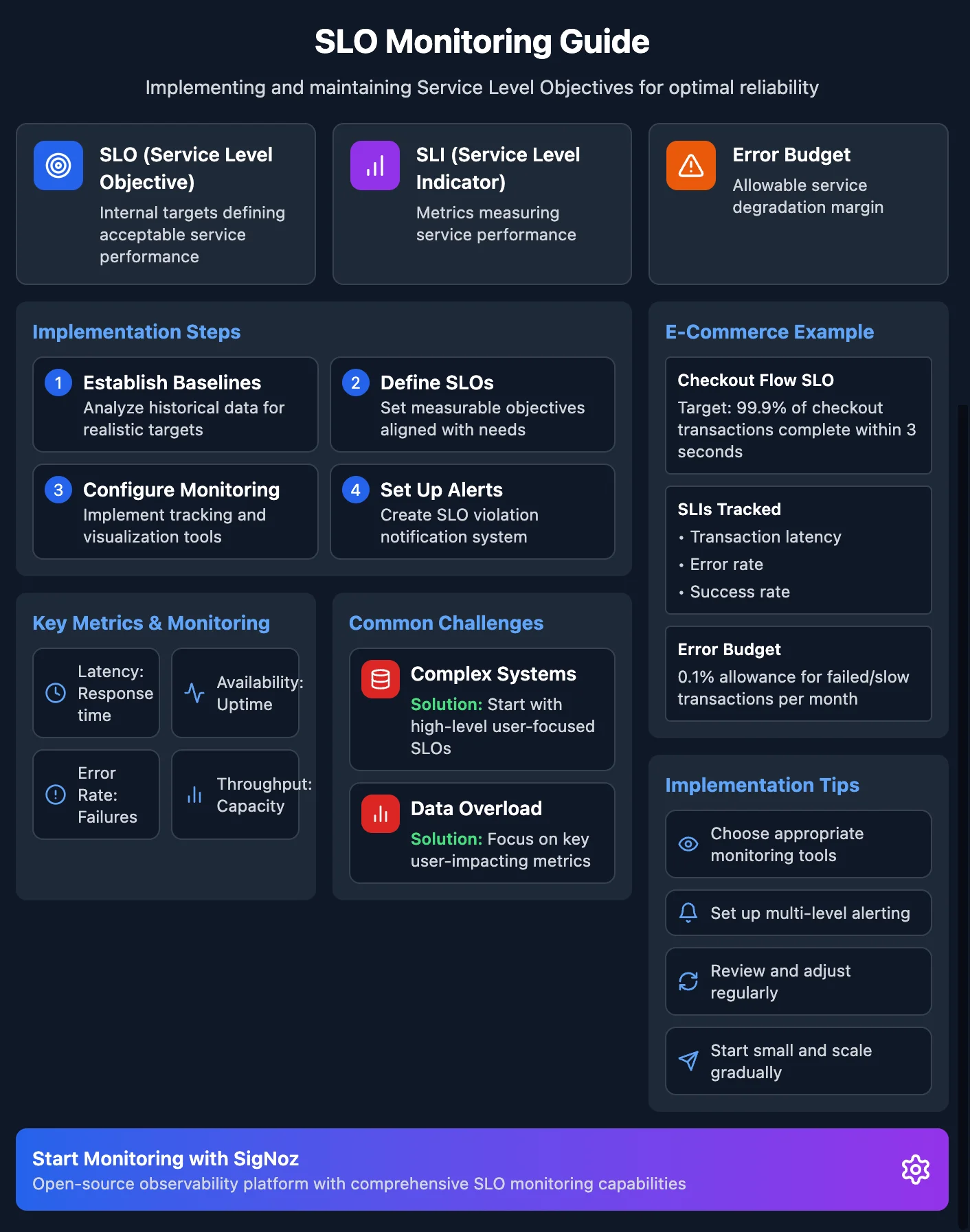
What is SLO Monitoring?
SLO monitoring refers to the practice of setting, measuring, and tracking Service Level Objectives (SLOs) for systems, applications, or services. SLOs are specific measurable targets that define the acceptable performance and reliability of service from the user’s perspective. These targets are typically derived from Service Level Indicators (SLIs) such as uptime, latency, or error rates.
- Effective SLO monitoring enables teams to understand how their services perform against predefined expectations, helping to ensure they meet business goals and customer satisfaction.
- By continuously observing these metrics, organizations can proactively identify and address performance issues before they escalate.
Why is SLO Monitoring Important?
SLO monitoring is crucial because it bridges the gap between technical performance and business outcomes. Here are some key reasons why it’s important:
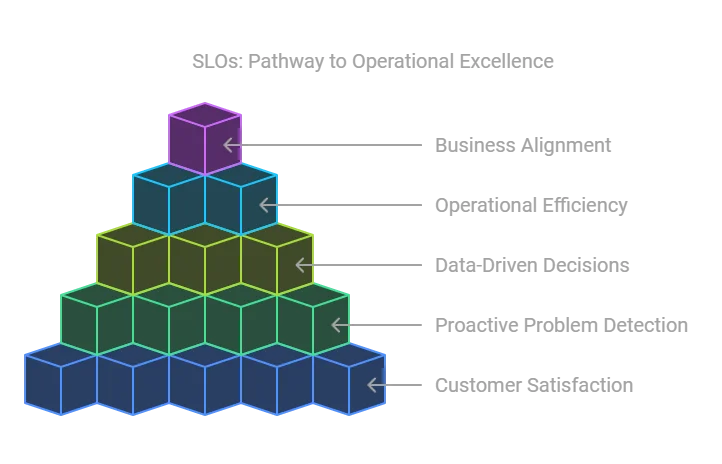
- Customer Satisfaction: SLOs focus on what matters to the end user, ensuring that services meet their expectations for availability and performance.
- Proactive Problem Detection: Monitoring SLOs helps detect and resolve issues before they impact users, minimizing downtime and preserving reputation.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: SLOs provide concrete metrics that guide prioritization of engineering tasks, balancing innovation with reliability.
- Operational Efficiency: Teams can focus on addressing the most critical reliability risks rather than overengineering solutions.
- Alignment with Business Goals: SLO monitoring ties technical performance to organizational objectives, fostering collaboration between engineering and business teams.
Why Should You Care About SLO Monitoring?
SLO monitoring isn’t just a technical practice, it’s a strategic asset for businesses, engineering teams, and decision-makers. Here’s why it matters to you:
- Clear Performance Benchmarks: SLOs set well-defined, measurable targets for service reliability and performance, enabling your team to stay aligned with business and user expectations.
- User-Centric Priorities: By focusing on metrics that impact end-user experiences, such as latency, availability, or error rates, you ensure your efforts directly enhance customer satisfaction.
- Reduced Firefighting: SLO monitoring empowers teams to proactively address issues before they escalate, saving time and resources spent on reactive firefighting.
- Optimized Engineering Efforts: Instead of overengineering or guessing priorities, SLOs guide teams to invest in improvements that deliver maximum impact on user experience and business outcomes.
- Data-Driven Confidence: Having reliable SLO data fosters confidence in your decision-making processes, whether it’s about launching new features, allocation budgets, or scaling infrastructure.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations with robust SLO monitoring gain an edge by delivering consistent, high-quality services and building customer trust and loyalty.
Key Components of Effective SLO Monitoring
To implement effective SLO monitoring, organizations must focus on its foundational components:
- Service Level Indicators (SLIs): These are the measurable metrics that reflect the performance or reliability of a service, such as latency, throughput, or error rates. Choosing the right SLIs is critical to meaningful SLO monitoring.
- Service Level Objectives (SLOs): These are the targets derived from SLIs that define acceptable levels of service. For example, an SLO might state that 99.9% of requests must be served within 200 milliseconds.
- Error Budgets: This represents the allowable level of service degradation within a specific time period. Error budgets provide a structured way to balance reliability with innovation, helping teams decide when to prioritize reliability work over new features.
- Monitoring Tools: Tools like SigNoz, Prometheus, or Grafana are essential for collecting and visualizing data related to SLIs. These tools help automate tracking and alerting based on SLO thresholds.
- Dashboards and Alerts: Comprehensive dashboards provide centralized visibility into SLO compliance. Coupled with alerting systems, they notify teams when performance approaches or exceeds acceptable thresholds, enabling swift responses.
Choosing the Right SLIs for Your Service
When selecting SLIs (Service Level Indicators), focus on metrics directly affecting the user experience and system performance.
- Latency: Measures how quickly your service responds to user requests. The lower the latency, the better the user experience.
- Availability: Tracks whether your service is up and accessible. High availability ensures users can rely on your service.
- Error Rate: Monitors how often requests or operations fail. A low error rate reflects a reliable service.
- Throughput: It Evaluates how much load your system can handle. Higher throughput indicates better performance under demand.
How to Implement SLO Monitoring in Your Organization
Implementing SLO monitoring is a strategic process that requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide to get started:
- Establish Baselines:
- Analyze historical data to understand your current performance metrics.
- Identify trends, patterns, and areas of improvement to set realistic, achievable targets.
- Example: Review your past three months’ uptime and downtime logs to determine your current availability rate (e.g., 99.7%) as a starting point.
- Define SLOs:
- Collaborate with stakeholders to set measurable, user-focused objectives that align with business goals.
- Ensure SLOs are specific, actionable, and relevant to your customer’s experiences.
- Example: If your e-commerce platform needs to ensure fast checkout times, define an SLO such as “95% of checkout transactions must be completed within 2 months.”
- Choose SLIs:
- Select metrics (SLIs) that directly reflect user experience, such as latency, error rate, throughput, or availability.
- Ensure SLIs are meaningful and quantifiable, avoiding metrics that don’t provide actionable insights.
- Example: For a video streaming service, choose the buffering rate (e.g., “less than 0.5% of streamed video segments experience buffering”) as a critical SLI.
- Set Up Monitoring:
- Implement robust monitoring tools that collect, process, and visualize SLI data in real-time.
- Integrate these tools with dashboards for easy tracking of SLO compliance.
- Example: Use a tool like SigNoz or Prometheus to monitor application response times and visualize the percentage of requests meeting your SLO in a dashboard.
- Create Alerts:
- Configure alerts to notify teams when an SLO is at risk of being violated.
- Use actionable thresholds to avoid alert fatigue, such as “Trigger an alert if error rate exceeds 1% for 10 consecutive minutes.”
- Ensure alerts are routed to the appropriate teams for quick resolution.
- Example: For an online payment system, create an alert: “Trigger an incident if payment failure rates exceed 2% for more than 5 minutes.”
- Review and Iterate:
- Regularly evaluate your SLOs to ensure they remain relevant as your system and user needs evolve.
- Use insights from SLO compliance reports to refine objectives and optimize your processes.
- Example: After a product update, review the SLO for login success rates and adjust if new features affect user authentication speed.
Best Practices for SLO Monitoring
Implementing SLO monitoring effectively requires adherence to proven strategies:
- Define Meaningful SLIs and SLOs: Focus on metrics that truly impact user’s experience. Avoid vanity metrics and ensure SLOs align with user needs and business objectives.
- Involve Stakeholders: Collaborate with both technical and business teams to set realistic and meaningful objectives. This ensures alignment and buy-in across the organization.
- Leverage Error Budgets: Use error budgets as a tool to balance reliability and feature development. When error budgets are exhausted, prioritize reliability tasks until the service stabilizes.
- Automate Monitoring and Reporting: Implementing automated systems to track SLI performance, generate reports, and send alerts. This reduces manual overhead and ensures timely detection of issues.
- Iterate and Improve: Regularly review and adjust SLOs based on user feedback, service evolution, and changing business priorities.
- Ensure Observability: Invest in robust observability systems that provide deep insights into system behaviour, helping diagnose and resolve issues efficiently.
- Foster a Culture of Accountability: Encourage teams to take ownership of SLOs and use them as a framework for continuous improvement. Celebrate success when targets are met and analyze failures to drive learning.
Challenges in SLO Monitoring and How to Overcome Them
SLO monitoring presents various challenges that can hinder its effectiveness, but these challenges can be addressed with structured and thoughtful approaches:
Complex Systems: In environments like microservices architectures, services are often interconnected and dependent on one another. This interdependency makes it challenging to define SLOs that capture the overall user experience while accounting for the contributions of multiple components.
Solution: Begin by defining high-level SLOs that reflect the end user’s experience, such as application response time or availability. Gradually work your way down to individual components, breaking down the broader SLOs into sub-objectives that measure the contributions of each service. This layered approach ensures clarity while tackling the complexity of interconnected systems.
Data Overload: Modern systems generate an overwhelming amount of metrics and logs, making it difficult to identify which data points are relevant for meaningful SLO monitoring. This overload often leads to confusion and inefficiency in monitoring efforts.
Solution: Narrow the focus to a small, carefully chosen set of Service Level Indicators (SLIs) that directly impact the user’s experience. Prioritize metrics such as latency, error rates, and availability, and use these as the foundation for your SLOs. By concentrating on the metrics that truly matter, you avoid unnecessary noise and ensure actionable insights.
Stakeholder Alignment: Conflicting priorities between different teams, such as engineering, operations, and business stakeholders, can make it challenging to define SLOs that are both realistic and aligned with overall objectives. These misalignments can slow down the SLO implementation process and lead to dissatisfaction.
Solution: Establish an inclusive process for SLO creation by involving representatives from all relevant teams. Facilitate open discussions to understand each team’s needs and constraints, and tie the SLOs to clear business outcomes. When SLOs are framed as essential to achieving organizational goals, it becomes easier to gain buy-in and foster collaboration.
Unrealistic Targets: Overly ambitious SLOs, whether due to lack of experience or external pressure, can lead to unsustainable workloads, team burnout, and disappointment when targets are consistently missed. Unrealistic objectives also risk demotivating teams and harming the overall reliability strategy.
Solution: Rely on historical performance data, system behaviour patterns, and industry standards to set realistic and achievable SLO targets. Start with conservative objectives and iterate based on continuous monitoring and feedback. This adaptive approach allows teams to improve gradually while maintaining morale and a sense of accomplishment.
Leveraging SLO Monitoring for Continuous Improvement
SLO monitoring transcends the basic objective of maintaining service performance, it serves as a strategic framework to propel continuous improvement across technical, operational, and cultural dimensions of your organization. By integrating SLO monitoring into your processes, you can unlock actionable insights that drive better decisions and outcomes.
- Identify and Address Technical Debt: SLO data provides a clear picture of where systems are underperforming or approaching the limits of reliability. This information allows teams to prioritize technical debt that directly impacts user experience, ensuring reliability efforts are focused where they matter most.
- Optimize Capacity Planning and Resource Allocation: Trends observed in SLO data can offer predictive insights into future resource requirements. For example, analyzing patterns in latency or throughput can guide infrastructure scaling decisions, ensuring adequate capacity to meet growing user demands while avoiding unnecessary expenditure.
- Foster a Reliability-Focused Culture: By embedding SLOs into your organization’s development and operations processes, you create a culture that values reliability and accountability. Teams begin to view SLOs as shared goals, aligning their efforts to consistently deliver high-quality user experiences.
- Enable Data-Driven Trade-Offs: Clear, measurable SLOs empower teams to make informed decisions about balancing reliability with feature development and cost management. For instance, understanding your error budget allows you to weigh the risks of deploying new features against the potential impact on system reliability.
- Facilitate Iterative Improvements: SLO monitoring isn’t a one-time exercise, it’s an ongoing process. Regularly reviewing and refining SLOs based on user feedback and evolving business priorities ensures that your services continually adapt and improve.
SLO Monitoring with SigNoz: A Practical Approach
SigNoz, an open-source observability platform, makes SLO monitoring accessible and efficient. Follow these steps to set up SLO tracking with SigNoz.
Sign Up for SigNoz Cloud or Self-Host
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.

You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Access SigNoz and Choose Infrastructure Monitoring
Once you have access to SigNoz, navigate to the Get Started section.
Select Infrastructure Monitoring as your monitoring category.
Choose your data sources (e.g., Host Metrics for monitoring server resources).
Proceed by selecting your host machine for deployment.
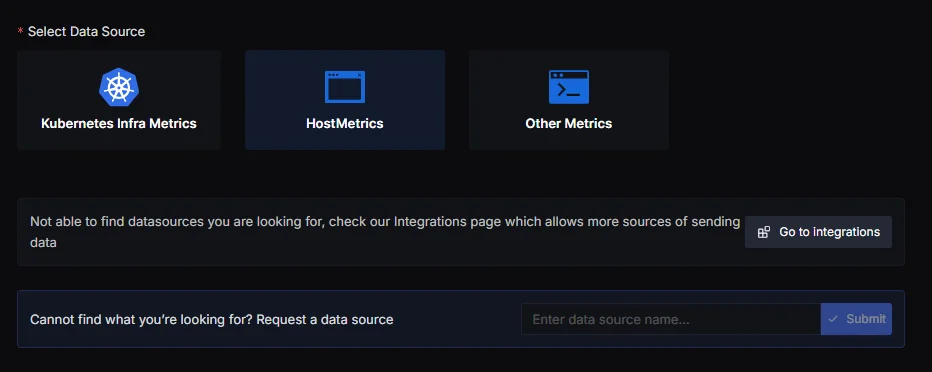
Select the Appropriate Data Source for Implementing SLO Monitoring
Install and Configure the OpenTelemetry Agent
- Follow the provided instructions to install the OpenTelemetry (Otel) agent on your host machine.
- Run the necessary commands to configure the Otel agent to send telemetry data (like metrics and logs) to your SigNoz instance.
- Ensure the data pipeline is correctly set up by verifying incoming metrics in SigNoz.
Build and Import Dashboards
- After successful setup, navigate to Dashboards on the SigNoz homepage and select Import JSON. (You can find Dashboard’s JSON Templates here)
- Upload your desired dashboard configuration file.
- Once imported, choose the relevant hostname (e.g., your VM or server name) to visualize metrics.
- View key infrastructure metrics, including CPU usage, memory consumption, system load averages, and network activity.
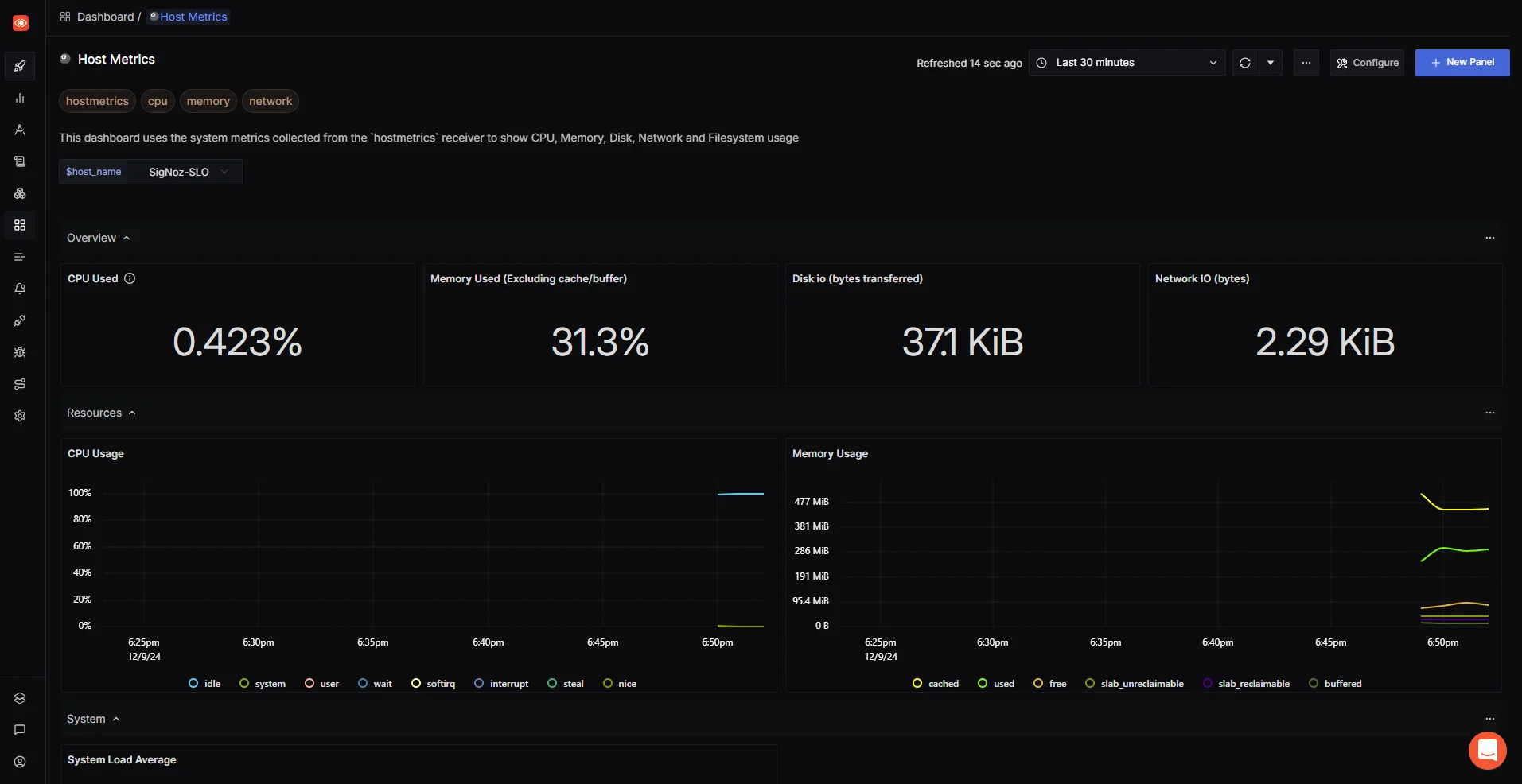
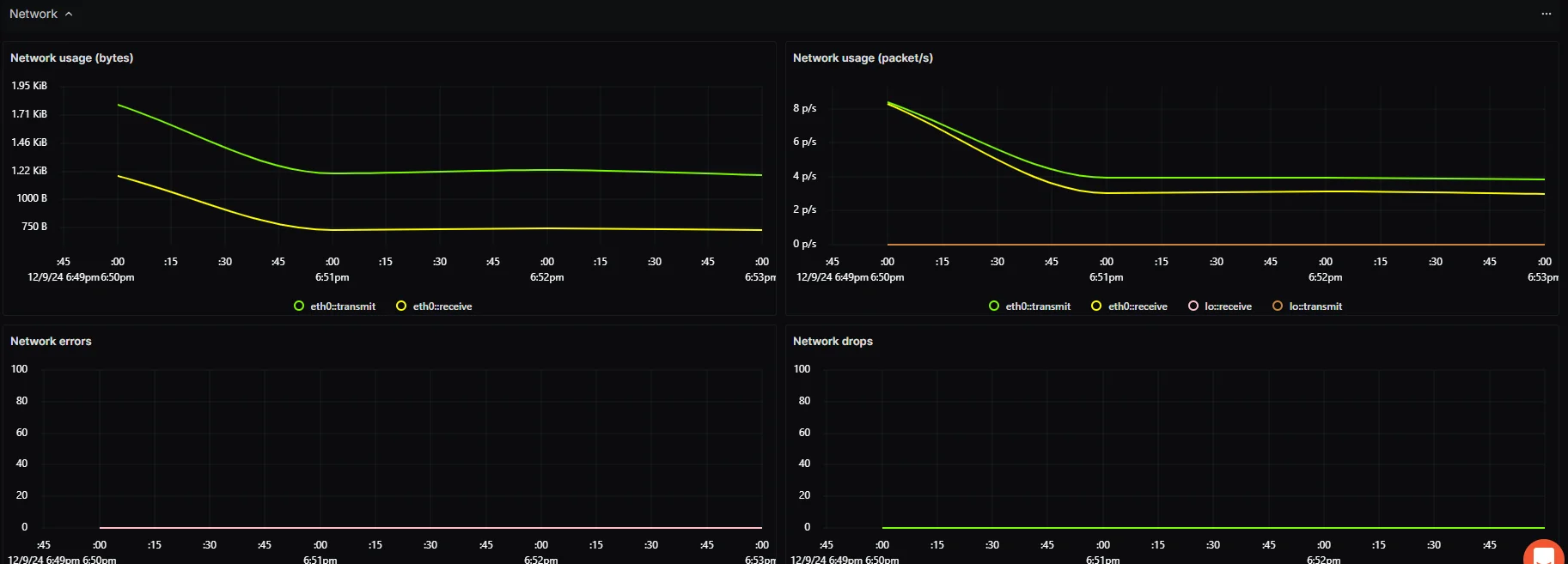
- Set Up Alerts for SLO Monitoring
- Create multi-level actionable alerts in SigNoz to monitor SLO compliance effectively.
- Refer to the official SigNoz alert setup documentation for detailed instructions on configuring and refining alerts tailored to your SLOs.
- Analyze Trends and Optimize for Continuous Improvement
- Continously refine your SLOs by identifying areas for improvement in service delivery.
- Iterate and Automate
- As your system evolves, revisit your SLOs, refine alert thresholds, and adapt dashboards to reflect changing business priorities.
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Key Takeaways
- SLO monitoring bridges the gap between technical metrics and user experience, ensuring services meet reliability standards that matter most to customers.
- Selecting meaningful SLIs and setting realistic SLOs aligned with user expectations and business goals is fundamental to success.
- Error budget acts as a guide to balance innovation and reliability, helping teams prioritize tasks effectively without overengineering.
- Automated tools like SigNoz simplifies monitoring and alerting, offering centralized visibility into SLO complaints for proactive issue resolution.
- Regular review and iteration of SLOs ensure they evolve with changing system demands, user needs, and business objectives.
- SLO monitoring fosters a culture of accountability by aligning technical and business teams toward shared reliability goals.
- A comprehensive observability system complements SLO monitoring, enabling deeper insights into system behavior and performance optimization.
FAQs
What's the difference between SLOs, SLAs, and SLIs?
| Term | Definition | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| SLO (Service Level Objective) | Internal targets for service performance and reliability | Sets benchmarks to maintain operational excellence and monitor performance goals. |
| SLA (Service Level Agreement) | Contractual commitments made to customers about service performance. | Protects customer interests by legally defining the minimum acceptable level of service. |
| SLI (Service Level Indicator) | Specific metrics used to measure and evaluate SLOs and SLAs. | Provides measurable data points, such as latency, uptime, or error rates, to assess service levels. |
How often should we review and update our SLOs?
Review SLOs at least quarterly. However, you may need to update them more frequently during periods of rapid growth, new feature rollouts, or changes in user expectations. Regular reviews ensure alignment with evolving business needs and customer requirements.
Can SLO monitoring be applied to all types of services?
Yes, SLO monitoring can be applied to a wide range of services, including:
- User-Facing Applications: To ensure responsiveness and availability for end users.
- Internal APIs: To guarantee seamless integrations between systems.
- Infrastructure Components: To maintain the reliability of the foundational elements of your services.
The key is identifying relevant SLIs that align with the service’s nature and user experience.
How do error budgets relate to SLO monitoring?
Error budgets are the permissible amount of unreliability within your SLO. They play a critical role in balancing innovation and reliability.
- If your error budget is underutilized, you can confidently focus on feature development or experiments.
- If your error budget is exhausted, it signals a need to prioritize stability and fix reliability issues before proceeding with new development.
Error budgets provide actionable insights to maintain a balance between delivering new capabilities and ensuring a dependable service.
