Essential Guide to Virtual Machine Monitoring Tools
In today's digital landscape, virtual machines (VMs) form the backbone of many IT infrastructures. These software-based emulations of physical computers offer flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. However, with great power comes great responsibility — and the need for robust monitoring. Virtual machine monitoring is crucial for maintaining optimal performance, ensuring resource efficiency, and preventing potential issues before they impact your operations.
What is Virtual Machine Monitoring?
Virtual machine (VM) monitoring refers to tracking the performance, health, and resource usage of virtual machines in an IT infrastructure. It helps ensure VMs operate efficiently, avoiding issues like bottlenecks, downtime, or performance degradation.
VM monitoring involves collecting data on various metrics such as CPU usage, memory utilization, disk I/O, and network activity. This data helps analyze VM performance under different workloads, ensuring optimal system functioning.
Importance of VM Monitoring in Modern IT Infrastructure
In today's rapidly evolving IT landscape, virtual machines (VMs) play a critical role in supporting scalable, flexible, and efficient infrastructure. With organizations relying heavily on VMs to host applications, manage workloads, and optimize resource use, effective monitoring of these virtual environments has become essential. VM monitoring not only ensures optimal performance and resource utilization but also safeguards against potential issues that could disrupt business operations. Let’s look into the key benefits of VM monitoring:
- Performance Optimization: VM monitoring helps track resource utilization (CPU, memory, disk, network) in real-time. It ensures that VMs are running efficiently and provides insights into performance bottlenecks, enabling timely adjustments to optimize performance.
- Resource Management: VM monitoring allows administrators to allocate resources effectively, ensuring VMs don’t overuse or underuse resources. This helps prevent resource contention, reducing wasted capacity, and optimizing costs.
- Proactive Issue Detection: VM monitoring detects potential issues early, preventing failures and minimizing downtime.
- Cost Management: Tracking resource usage helps control costs by avoiding unnecessary expenditure on underutilized resources.
Key components of VM monitoring
Virtual Machine (VM) monitoring is crucial for ensuring the health, performance, and reliability of virtualized environments. By tracking specific metrics and components, VM monitoring enables IT administrators to detect and resolve issues before they impact user experience or system performance. Here are the key components of effective VM monitoring:
- Performance Monitoring: Tracks real-time performance metrics like CPU, memory, and storage usage. For example, a VM hosting a web server with CPU usage constantly above 90% might need additional resources.
- Resource Utilization: Ensures efficient use of allocated resources. Overuse or underuse of resources can indicate configuration or application issues.
- Availability Monitoring: Monitors the uptime and accessibility of VMs. A critical VM running a database becoming unavailable can result in lost data or service interruptions.
Differences between VM Monitoring and Physical Server Monitoring
Monitoring a virtual machine (VM) environment differs significantly from monitoring physical servers due to the fundamental differences in infrastructure, architecture, and resource management. Virtual machines run as software instances on top of hypervisors, sharing resources with other VMs, while physical servers are standalone systems with direct access to their hardware. This creates distinct monitoring challenges and requirements for each. Let’s look at them in detail:
- Resource Abstraction: Unlike physical servers, VMs operate in a shared environment with abstracted resources. Monitoring must account for this shared usage and ensure all VMs have adequate resources.
- Dynamic Resource Allocation: VMs can be resized or migrated dynamically without downtime, while physical servers require manual changes. Monitoring ensures smooth transitions.
- Snapshots and Cloning: VMs can be cloned or snapshotted quickly. Monitoring ensures that these operations don’t introduce new issues.
Why Virtual Machine Monitoring is Critical
Virtual machine (VM) monitoring is essential for maintaining the efficiency and security of virtualized environments. Virtualization has become a standard in modern IT infrastructures, and monitoring ensures that the systems function as expected. Here are key reasons why virtual machine monitoring is important:
- Optimizes Performance: Monitoring helps track the performance of VMs by analyzing CPU usage, memory consumption, disk I/O, and network traffic. For example, if a VM begins to overuse CPU resources, real-time alerts allow you to act quickly, preventing performance degradation and ensuring applications run efficiently.
- Prevents Resource Bottlenecks and VM sprawl: Without monitoring, it’s easy for virtual environments to suffer from inefficient resource usage, leading to bottlenecks. By monitoring, resource-hogging VMs can be identified and optimized. Additionally, monitoring helps manage VM sprawl, where unused or redundant VMs clutter the environment. Tools can identify underused or idle VMs, enabling better resource allocation or decommissioning, and avoiding unnecessary costs.
- Capacity Planning and Resource Allocation: As workloads grow, it’s crucial to anticipate when resources such as CPU, RAM, or storage need to be scaled. Monitoring provides insights into trends, allowing administrators to plan for future growth and allocate resources accordingly. For instance, if a particular VM consistently reaches 90% memory usage, this indicates a need for memory scaling to maintain stability.
- Enhances Security and Compliance: Monitoring plays a key role in detecting potential security threats. For example, unusual traffic patterns or unauthorized access attempts on VMs can be flagged in real-time, preventing breaches. Additionally, monitoring helps maintain compliance with industry standards by ensuring that VMs adhere to security policies, such as regular patching and appropriate resource configurations.
Essential Features of VM Monitoring Tools
Modern virtual machine (VM) monitoring tools should include several key features to effectively manage and optimize virtualized environments. Here are the essential features that organizations should look for in a VM monitoring tool:
- Real-Time Performance Metrics Tracking: Monitoring tools should provide real-time insights into key performance metrics such as CPU usage, memory utilization, disk I/O, and network throughput. This enables administrators to quickly identify performance bottlenecks and make informed decisions to optimize resources.
- Automated Alerts and Notifications: Automated alerts help prevent critical failures by notifying teams when issues arise. For instance, if a VM's memory usage crosses a certain threshold, the tool will trigger an alert to inform the operations team to take corrective action. This automated response ensures quick issue resolution before downtime impacts services.
- Capacity Planning and Forecasting Capabilities: Capacity planning is essential to anticipate future resource needs. For example, if historical data shows that a VM's disk usage increases by 10% every month, the tool can forecast when more storage will be needed. This helps avoid resource exhaustion and helps plan infrastructure scaling.
- Integration with Broader IT Management Systems: VM monitoring tools should integrate with IT management platforms for unified observability. For instance, when integrated with IT service management tools like ServiceNow, monitoring alerts can automatically generate incident tickets. This reduces manual intervention and streamlines issue resolution processes.
Advanced Monitoring Capabilities
Advanced monitoring capabilities provide crucial insights into the performance and health of systems. Key features include:
- Application-Level Monitoring within VMs: This type of monitoring goes beyond basic resource tracking. It provides application-level visibility, allowing you to track the performance of applications running within VMs. For example, monitoring a Java application running on a VMware VM allows memory usage, response times, and error rates to be tracked directly from the application layer.
- Cross-Platform Support: To accommodate diverse IT environments, monitoring tools should offer cross-platform support, enabling seamless monitoring across various virtualization platforms such as VMware, Hyper-V, and cloud services like Azure and AWS. This ensures a unified view of all VMs, regardless of their underlying infrastructure.
- Historical Data Analysis and Trend Reporting: Advanced monitoring tools should provide robust analytics capabilities, allowing you to generate reports that highlight trends over time and help inform capacity planning and resource allocation decisions.
- Custom Dashboards and Visualization Options: The ability to create custom dashboards tailored to specific monitoring needs enhances monitoring efficiency. These dashboards display key metrics, such as memory consumption, disk usage, or application response times, in an easy-to-understand format.
How to Choose the Right VM Monitoring Tool
Selecting the appropriate VM monitoring tool can significantly impact performance management and resource allocation. Several factors should be considered to make an informed decision.
Assess Specific Needs and Infrastructure
Start by analyzing the organization's infrastructure, including the number of virtual machines, applications, and workloads. Evaluate how the monitoring tool will fit into your existing infrastructure and ensure it provides the necessary features to address your organization’s monitoring objectives.
Evaluate Scalability and Multi-Cloud Support
As infrastructure grows, the monitoring tool should scale accordingly without compromising performance. In a dynamic setup with multi-cloud environments, look for a solution that offers robust multi-cloud support, allowing you to monitor resources across various clouds from a single interface.
Consider Ease of Use and Implementation
A tool that is simple to implement and configure can save time and reduce operational complexity. Look for a VM monitoring solution with an intuitive user interface that is easy to navigate. Additionally, consider the implementation process—tools that require extensive setup or training may delay deployment and impact productivity. A solution that offers quick installation and configuration will save valuable time and resources.
Analyze Cost-Effectiveness and ROI
Balancing costs with functionality is vital. Enterprise-level tools come with advanced features but may be overkill for smaller organizations. For businesses with smaller budgets, free or open-source tools could provide basic monitoring at no cost, with paid add-ons for advanced functionalities.
Best Practices for Effective VM Monitoring
To ensure optimal performance and reliability in virtual machine (VM) environments, implementing best practices for VM monitoring is crucial. Here are some key strategies to consider:
Establish Baseline Performance Metrics:
It is critical to have a clear understanding of what normal performance looks like for a VM. Baseline metrics, such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and disk I/O, serve as reference points to identify anomalies.
Implement Proactive Monitoring and Alerting:
Proactive monitoring helps in identifying potential issues before they escalate into critical problems. Setting up alerts for key performance indicators such as high CPU load, low memory, or unusual network activity ensures quick response to anomalies.
Regular Review and Optimize Monitoring Strategies:
Monitoring strategies should evolve with changes in the infrastructure and application workloads. Reviewing data trends regularly helps in adjusting thresholds and monitoring scope.
Leverage Automation for Routine Monitoring Tasks:
Utilize automation to streamline routine monitoring tasks, such as data collection, report generation, and alert management. Automating repetitive monitoring tasks can save time and reduce the risk of human error. Implementing scripts or utilizing built-in automation features within monitoring tools can significantly improve efficiency.
Common Challenges in VM Monitoring and How to Overcome Them
Virtual machine (VM) monitoring can present several challenges, especially in complex environments. Addressing these issues requires a clear understanding of how to manage resources, ensure performance, and maintain visibility across different infrastructures.
Dealing with VM Sprawl and Resource Overprovisioning:
VM sprawl happens when there are too many VMs running unnecessarily, often leading to overprovisioning of resources. This can result in wasted capacity, increased costs, and management complexity. Implementing automation to enforce policies can help limit sprawl and ensure that resources are allocated according to actual demand. Regular audits and consolidation of underutilized VMs also help control sprawl.
Managing Performance in Dynamic, Scalable Environments:
Maintaining consistent performance becomes a challenge as VMs scale up or down in cloud environments. Monitoring CPU, memory, and disk I/O is essential to identify potential bottlenecks. Real-time performance metrics enable timely adjustments. For instance, auto-scaling can be configured based on workload thresholds, ensuring optimal resource allocation without manual intervention.
Ensuring Visibility Across Hybrid and Multi-cloud Setups:
In hybrid and multi-cloud environments, gaining visibility into the performance and health of VMs across different platforms can be difficult. Centralized monitoring solutions allow teams to track VMs across multiple clouds in one dashboard. These tools collect logs, performance data, and security metrics, providing a comprehensive view. Integrating monitoring across cloud and on-premises environments ensures consistency in performance tracking.
Balancing Monitoring Granularity with System Overhead:
Monitoring too many metrics can introduce overhead, while too few may result in blind spots. It's essential to strike a balance by identifying critical performance indicators without overloading the system. For example, monitoring memory and CPU usage every few seconds might create excessive data storage and processing needs. Instead, setting up threshold-based alerts, where notifications trigger only when certain limits are breached, can minimize system impact while maintaining effective monitoring.
Leveraging SigNoz for Comprehensive VM Monitoring
SigNoz is a full-stack open-source Application Performance Monitoring (APM) solution that provides a modern, unified approach to VM monitoring. By integrating metrics, logs, and traces into a single platform, SigNoz offers extensive visibility into your virtual environments, making it ideal for end-to-end monitoring of your virtual machines.
Key Features of SigNoz for VM Monitoring
Real-Time Performance Tracking: SigNoz enables continuous tracking of VM performance across multiple virtualization platforms, allowing you to monitor CPU usage, memory, disk I/O, and network bandwidth in real time.
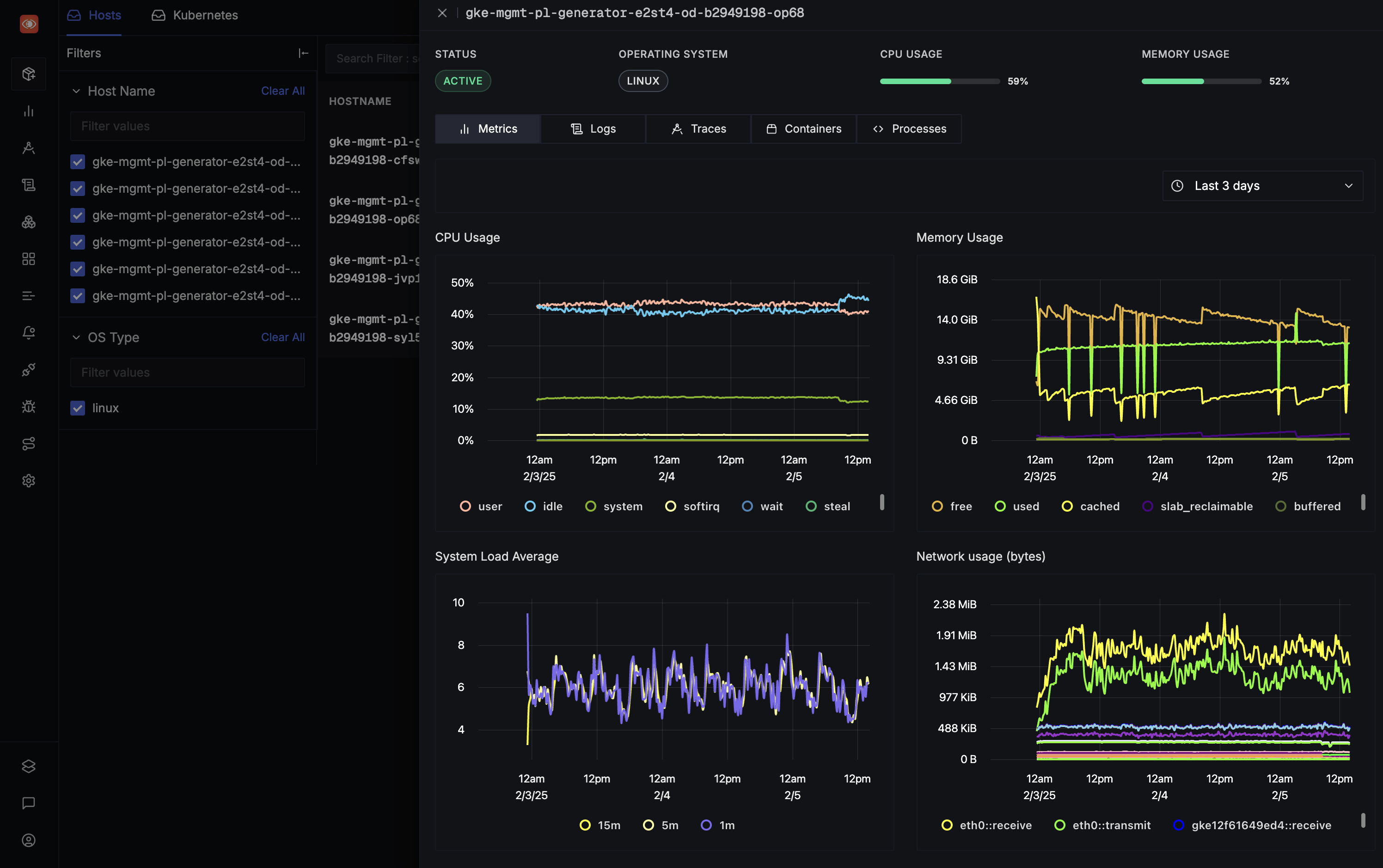
Infrastructure Monitoring in SigNoz Customizable Dashboards: SigNoz provides flexible dashboards that are fully customizable, offering at-a-glance insights to monitor key performance metrics, identify trends, and respond to issues quickly.
Advanced Alerting and Integrations: SigNoz supports alerting capabilities to help you stay informed about critical performance issues. You can configure alerts to integrate with popular communication tools like Slack, email, and PagerDuty, ensuring that you receive notifications as soon as thresholds are crossed.
Support for Cloud and On-Premises VM Monitoring: SigNoz is compatible with cloud-native environments as well as on-premises infrastructure, providing comprehensive monitoring solutions regardless of where your VMs are hosted.
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
For comprehensive guidance on monitoring metrics for VMs like Azure virtual machines, refer to the documentation on Azure VM Metrics Monitoring. This resource offers step-by-step instructions and best practices for effectively tracking performance and optimizing resource allocation within Azure's virtual machine environment.
Future Trends in Virtual Machine Monitoring
The landscape of VM monitoring is evolving rapidly. Keep an eye on these emerging trends:
- AI-driven Analytics: Machine learning algorithms will provide more accurate predictions and anomaly detection.
- Unified Monitoring: Expect tighter integration between VM, container, and microservices monitoring.
- Automated Remediation: Self-healing capabilities will become more sophisticated, reducing manual intervention.
- Focus on User Experience: VM monitoring will increasingly tie back to end-user experience metrics.
Key Takeaways
- Virtual machine monitoring is essential for maintaining performance, efficiency, and security in virtualized environments.
- Choose monitoring tools that offer real-time metrics, automated alerts, and capacity planning features.
- Implement best practices like establishing baselines and leveraging automation for effective monitoring.
- Consider modern solutions like SigNoz for comprehensive VM monitoring across diverse environments.
- Stay informed about emerging trends to future-proof your VM monitoring strategy.
FAQs
What metrics are most important in VM monitoring?
Key metrics include CPU usage, memory utilization, disk I/O, network performance, and application response times. The importance of each metric may vary depending on your specific workloads and applications.
How often should I review my VM monitoring data?
While real-time monitoring is crucial for immediate issue detection, conducting thorough reviews of your VM performance data at least weekly is recommended. This allows you to identify trends and make proactive adjustments.
Can VM monitoring tools help with cost optimization?
Yes, VM monitoring tools can significantly aid in cost optimization. By identifying underutilized resources, these tools help you right-size your VMs and prevent unnecessary spending on excess capacity.
How does VM monitoring differ in cloud vs. on-premises environments?
Cloud environments often provide built-in monitoring tools and may require monitoring of additional metrics like cost and usage against quota limits. On-premises environments typically offer more control over the monitoring infrastructure but may require more setup and maintenance.
