When Does DynamoDB Throttle Request - Understanding When and Why It Happens
DynamoDB is Amazon's NoSQL database service and it is known for its scalability and reliable performance. However, like every other system, it has some limitations. When these restrictions are surpassed, DynamoDB implements a precaution known as throttling.
In this article, you learn about DynamoDB throttling, and how it affects your application and its working. You also learn how to control or prevent DynamoDB throttling.
What is DynamoDB Throttling?
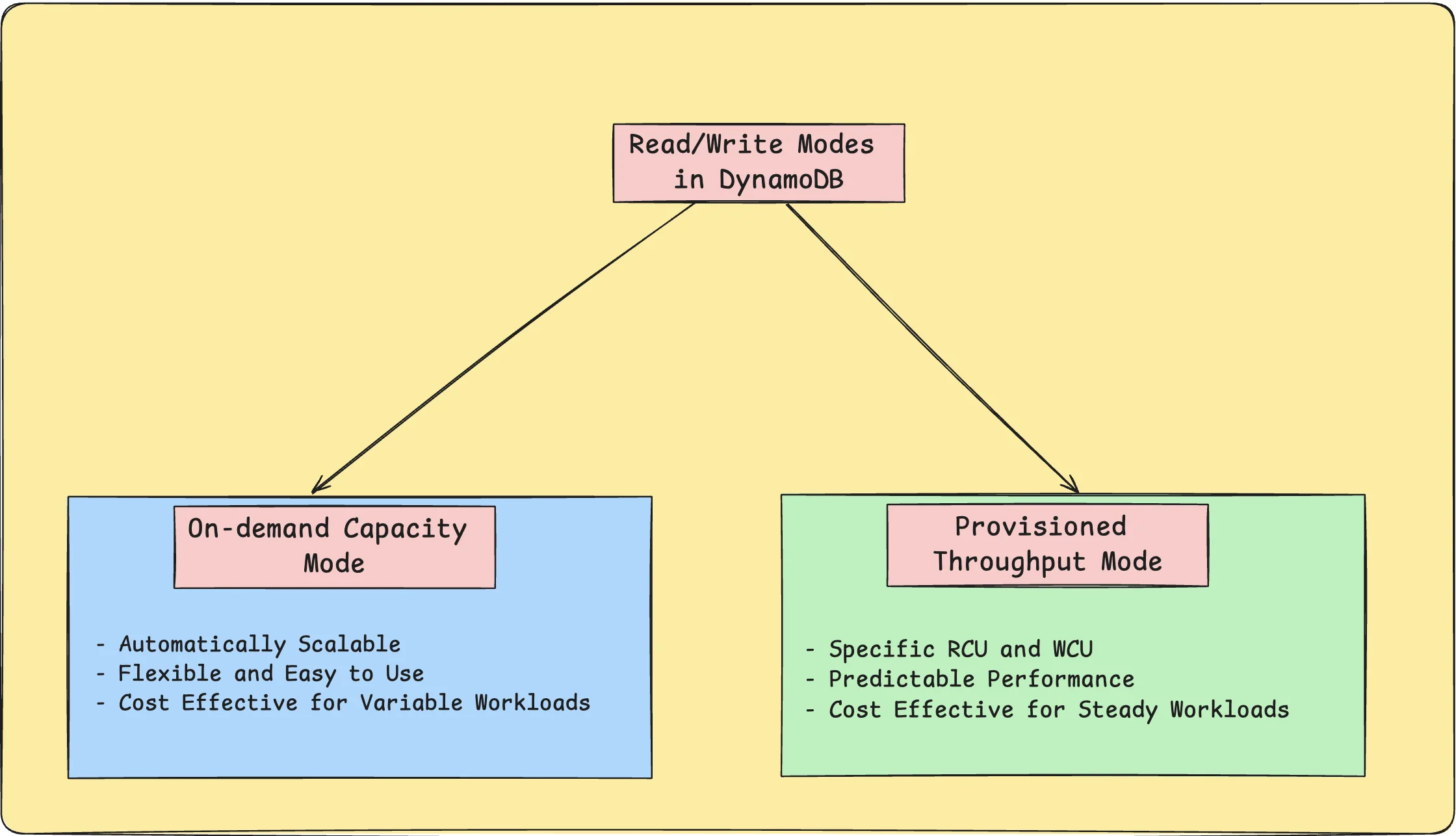
DynamoDB throttling is a safety mechanism that restricts the number of requests to a table or partition if they exceed the maximum capacity. This behaviour relates to DynamoDB's two capacity modes:
- Provisioned throughput mode: In Provisioned throughput mode, you manually set the read and write capacity units (RCUs and WCUs) that your table can handle per second. Throttling occurs when the predefined boundaries are exceeded. For example, if your table is supplied with 50 write capacity units and you attempt to make 70 write requests per second, 20 of them will be throttled.
- On-demand capacity mode: In On-demand capacity mode, DynamoDB dynamically adapts its capacity according to the workload, but it has some limitations. The on-demand mode is more adaptable than the provisioned throughput mode. It can dynamically assign capacity based on the traffic. However, in case of abrupt traffic surges such as a spike that exceeds double the previous high in a short period can still result in throttling.
Throttling helps to keep your table and the underlying infrastructure stable by preventing the overconsumption of resources. So, when a request is throttled, DynamoDB returns a ProvisionedThroughputExceededException which indicates that the request has exceeded the allocated capacity. This error prevents your table from being overloaded and disturbing other users or workloads.
Why DynamoDB Throttles Requests
You can use DynamoDB throttling as a resource protection for the following reasons:
- Throttling ensures that no single table monopolizes resources and also protects it from potentially degrading performance for other users.
- By limiting excess usage, DynamoDB ensures that latency and throughput for requests to your table stay consistent.
- Throttling also acts as a reminder for users to reconsider their application designs. It minimizes queries and makes better use of the available capacity.
When Does DynamoDB Throttle Requests?
DynamoDB throttles requests when traffic exceeds the available capacity or resource use becomes wasteful. Some of the major scenarios when throttling typically occurs:
- In provisioned mode, DynamoDB throttles requests that exceed the specified read or write capacity units. For example, if you allot 100 read capacity units but you are performing 150 read requests in one second then 50 of them will be throttled.
- Even in on-demand mode, if traffic unexpectedly exceeds double the previous peak within 30 minutes, DynamoDB may throttle some queries. This usually happens when there is an unexpected rise, such as a viral event or a marketing campaign spike.
- If your data is unevenly spread across partitions, one or more partitions may become a hot partition. A hot partition receives significantly more traffic than others then it leads to exceeding the allowable throughput and resulting in throttling for requests addressed at that partition.
- Queries that are not well-optimized may utilize more read or write capacity than necessary. For example, a full table scan or an ineffective filter expression can waste a high number of read capacity units which can result in throttling.
Common Scenarios Leading to Throttling
Throttling often occurs when the number of requests surpasses the table's provisioned or on-demand capacity. Some of the most common scenarios that lead to throttling:
- Batch operations, such as
BatchGetItemandBatchWriteItem, allow you to read or write several things at once. These batch operations can improve throughput but these large batch activities can quickly consume more capacity than expected especially if the batch size is not regulated. When the provisioned limits are surpassed, the system may immediately throttle. - If your application is experiencing an unexpected traffic spike for example, during a product launch, marketing campaign, or seasonal surge and there is insufficient capacity then DynamoDB may restrict your queries. This is particularly challenging if your capacity estimates do not account for peak demand patterns.
- When partition keys are unevenly distributed then some partitions may receive an unusually high number of requests, resulting in hot partitions. This happens when you use sequential keys (such as timestamps) if your data model isn't built to distribute traffic evenly across partitions.
- DynamoDB automatically responds to traffic spikes in the on-demand mode. However, in very unpredictable or irregular workloads where traffic varies greatly; it can cause temporary capacity deficiencies, resulting in throttling during periods of unexpected increases.
Why Does DynamoDB Implement Throttling?
DynamoDB's throttling technique is intended to achieve many aims. Throttling ensures both system stability and equitable resource allocation. DynamoDB implements throttling for the following reasons:
- DynamoDB is a shared service. Throttling ensures that no single table or job monopolizes resources and it allows all users to share the system's capacity.
- Throttling protects DynamoDB's overall performance by preventing excessive requests from degrading performance across other tables or applications. Without throttling, a poorly managed workload may influence the performance of other users who share the infrastructure.
- Throttling ensures consistent table performance by imposing capacity limitations. It ensures that your key processes have continuous throughput, preventing database overloads.
- Throttling also motivates developers to use more efficient data models, capacity planning, and retry methods. It encourages customers to optimize their queries, partition keys, and workload allocation, creating a more efficient and scalable application design.
How to Identify DynamoDB Throttling Issues
Identifying throttling issues early is important to ensure the smooth performance of your application. Several tools and metrics are provided by DynamoDB to help you spot throttling before it becomes a problem:
- Amazon CloudWatch's
ThrottledRequestsmetric records the number of throttled requests. Monitoring this indicator lets you identify if your table is consistently exceeding its capacity constraints, allowing you to take action before its performance degrades. - Look for problem codes like
ProvisionedThroughputExceededExceptionin your application logs. These errors indicate that your queries are being throttled because of exceeding capacity restrictions. Integrating log monitoring technologies like SigNoz can help you receive real-time notifications when throttling happens. - AWS X-Ray is a distributed tracing tool that can help you find performance issues like throttling. You can trace the flow of requests through your system to determine where delays or failures due to throttling may occur.
- Set up custom alerts in CloudWatch to alert you when throttling happens. You can set alarms to go off when the
ThrottledRequestsstatistic exceeds a specific level thus it allows you to take proactive steps to fix the problem.
Strategies to Prevent DynamoDB Throttling
Some of the key strategies that you can use to prevent throttling:
- It is critical to estimate and provision an appropriate number of read and write capacity units (RCUs/WCUs). You can use previous traffic data to predict future peaks and ensure your table can manage the predicted load. In provisioned mode, exceeding capacity will result in throttling.
- When throttling occurs, you can set up a retry system with exponential backoff. This strategy retries failed requests at increasing intervals and it gives the table time to recover and lowers the possibility of overloading the system again.
- Enable DynamoDB Auto Scaling, which will automatically modify the provided capacity based on actual traffic patterns. This helps to eliminate manual intervention while also ensuring that your table can scale up or down as needed and thus it prevents throttling during unexpected traffic spikes.
- Efficient data modelling is critical for spreading workload evenly across partitions. You can use partition keys that evenly distribute traffic, eliminate hot partitions, and optimize your query patterns to use the least amount of capacity.
Best Practices for Capacity Management
Effective capacity management is very crucial to prevent throttling and optimize costs in DynamoDB. Some of the best practices for capacity management:
- DynamoDB workloads evolve with time, and so should your capacity. You should periodically monitor your table's usage patterns and adjust the supplied capacity as needed. By monitoring historical traffic statistics and projecting growth, you can ensure that your table is always ready for peak demand without incurring excessive costs.
- If your workload is consistent and predictable then you can think about using DynamoDB's reserved capacity. This enables you to lock in reduced rates by committing to a specific capacity level for one or three years, resulting in significant cost savings over on-demand pricing. Reserved capacity allows you to handle consistent demand efficiently without worrying about unexpected cost surges of electricity.
- Implementing a caching layer can help to reduce read demand on DynamoDB. DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX) is a fully managed in-memory caching service that is created exclusively for DynamoDB and can significantly accelerate read operations while reducing the requirement for a large provisioned read capacity.
- When dealing with high-volume writes, it's critical to spread the load across different partition keys to avoid hot partitions. Write sharding is a technique in which you tweak your partition key scheme to distribute writes more equally. For example, you can add a random suffix to your partition keys to spread writes across different partitions and reduce the possibility of throttling.
Monitoring DynamoDB Performance with SigNoz
Monitoring DynamoDB performance is crucial for detecting bottlenecks, such as throttling, and guaranteeing a smooth operation. SigNoz provides a comprehensive solution for real-time performance monitoring, allowing you to track DynamoDB metrics and optimize database administration. Some of the ways how SigNoz can help you:
SigNoz offers real-time monitoring of DynamoDB metrics such as
ThrottledRequests, read and write latencies, and capacity use. This type of visibility enables you to identify possible problems before they impact your application's performance.SigNoz allows you to design customizable dashboards that are tailored to your individual monitoring needs. You can view important DynamoDB metrics in a single place which makes it simple to discover trends, bottlenecks, and areas for optimization.
Create proactive alerts in SigNoz to advise you of throttling events or other performance issues. You can set thresholds for specific metrics, such as high request latencies or excessive throttled requests, to ensure that issues are detected in real time.
Actionable Tip
Regularly review your SigNoz dashboards and alerts to stay on top of your DynamoDB’s performance. Early detection and intervention can prevent throttling from affecting your application.
Get Started with SigNoz: To begin using SigNoz for monitoring your DynamoDB performance, visit SigNoz and follow the setup instructions to integrate with your DynamoDB instances.
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Troubleshooting DynamoDB Throttling Issues
When DynamoDB throttling occurs, quick troubleshooting is essential to restore smooth operation. Some of the steps you can follow to address throttling effectively:
- Begin by reviewing your CloudWatch metrics, specifically
ConsumedReadCapacityUnitsandConsumedWriteCapacityUnits. These will show you how near your consumption is to your provisioned capacity. - Use DynamoDB's partition-level metrics to identify the hot partitions that are receiving unusual access. The uneven distribution of traffic between partitions is a common source of throttling. So, identifying and resolving these hot partitions can greatly reduce throttling problems.
- Check your query patterns for ineffectiveness. You should avoid performing extensive scans and ensure that you are retrieving only the necessary data. Consider indexing frequently used features to boost performance and reduce capacity use.
Key Takeaways
- DynamoDB throttles requests to ensure system stability, fairness, and equal resource allocation for all users.
- Throttling occurs when your application exceeds its provisioned capacity or encounters unexpected traffic surges, particularly in on-demand mode.
- Effective capacity planning, well-designed data models, and efficient queries are critical strategies for preventing throttling.
- Monitoring solutions such as SigNoz provide real-time visibility into performance and can help you avoid throttling by allowing you to establish proactive alarms.
FAQs
How quickly does DynamoDB respond to throttling conditions?
DynamoDB responds to throttling situations extremely instantly. DynamoDB throttles request in real time once they exceed the provisioned throughput restrictions. This fast response contributes to the overall stability of the system.
Can throttling occur in DynamoDB on-demand capacity mode?
Yes, throttling is possible even in on-demand capacity mode. While on-demand mode automatically adapts to manage most traffic fluctuations, it still has limitations based on prior peak traffic volumes. If your traffic unexpectedly exceeds those limits, throttling may occur to protect the system.
What's the difference between provisioned throughput exceeded and throttling errors?
Throttling causes an error message stating "provisioned throughput exceeded". Throttling is DynamoDB's response when your request exceeds the provided or on-demand capacity, whereas an error message indicates that your request could not be completed owing to the exceeded limitations. Throttling is the system's response, while error is the symptom you see in your application.
How can I estimate the right capacity for my DynamoDB table to avoid throttling?
To determine the appropriate capacity for your DynamoDB table:
- You can examine your application's read and write patterns, determining how frequently and in what volumes data is accessed.
- You can determine the necessary read and write capacity units depending on the size of the items being read or written and the frequency of access.
- You can use DynamoDB's capacity calculator to project your capacity requirements precisely.
- You can implement DynamoDB Auto Scaling to dynamically alter capacity in response to traffic changes.
- You can review your capacity utilization regularly and update your estimations as your application evolves.
