Tomcat Performance Monitoring with OpenTelemetry - Key Metrics and Setup Guide
Apache Tomcat exposes performance data via JMX (Java Management Extensions), giving you access to thread pool usage, request throughput, session counts, and JVM metrics such as heap memory usage and garbage collection. While built-in tools like the Tomcat Manager and JConsole can display this data in real time, they lack historical retention, alerting, and the ability to correlate metrics with request traces. OpenTelemetry solves this by giving you a single, vendor-neutral pipeline for collecting traces, metrics, and logs from Tomcat. The OpenTelemetry Java agent attaches to Tomcat with zero code changes and exports telemetry directly to your observability backend.
In this guide, we will set up Tomcat performance monitoring using the OpenTelemetry Java agent, build a Dockerized Tomcat application with demo endpoints, instrument it, and verify traces, metrics, and logs flowing into the observability backend.
Prerequisites
Before starting, make sure you have the following ready:
- Docker and Docker Compose are installed on your machine
- A SigNoz account (SigNoz Cloud)
- Basic familiarity with Tomcat (you don't need a running Tomcat instance; we will set one up)
- You will also need Ingestion Key and Ingestion URL from your SigNoz account. For a detailed walkthrough on getting these credentials, see how to get the ingestion key and ingestion url from SigNoz Cloud.
Implementation Roadmap
Setting up Tomcat monitoring with OpenTelemetry involves four steps:
- Create the project structure with a Dockerfile and demo endpoints
- Configure OpenTelemetry environment variables to send telemetry to SigNoz Cloud
- Start the stack with Docker Compose
- Verify data in SigNoz Cloud
The architecture follows the SigNoz Tomcat instrumentation docs. The OpenTelemetry Java agent handles all three signals (traces, metrics, and logs) and exports them directly to SigNoz Cloud via OTLP. Let's walk through each step.
Step 1: Create the Project Structure
Create a project directory with the Dockerfile, demo web application, and supporting files:
mkdir -p tomcat-monitoring/webapps/ROOT
cd tomcat-monitoring
Create Dockerfile
The Dockerfile uses a multi-stage build: an Alpine stage downloads the OpenTelemetry Java agent, and the Tomcat stage copies it in and attaches it via CATALINA_OPTS.
# tomcat-monitoring/Dockerfile
FROM alpine:3.20 AS otel
ARG OTEL_JAVA_AGENT_VERSION=2.13.3
RUN apk add --no-cache curl \
&& mkdir -p /otel \
&& curl -fL "https://github.com/open-telemetry/opentelemetry-java-instrumentation/releases/download/v${OTEL_JAVA_AGENT_VERSION}/opentelemetry-javaagent.jar" \
-o /otel/opentelemetry-javaagent.jar
FROM tomcat:10.1-jdk17-temurin
COPY /otel/opentelemetry-javaagent.jar /opt/otel/opentelemetry-javaagent.jar
COPY webapps/ROOT /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/ROOT
# Attach the OTel Java agent at Tomcat startup.
ENV CATALINA_OPTS="-javaagent:/opt/otel/opentelemetry-javaagent.jar"
The agent version is pinned via a build argument (OTEL_JAVA_AGENT_VERSION=2.13.3). This makes upgrades explicit and reproducible. The agent attaches to Tomcat through the standard -javaagent JVM flag, which Tomcat picks up from CATALINA_OPTS (an environment variable that Tomcat reads at startup to pass extra JVM arguments specifically to the Tomcat process).
Demo Web Application
Create three JSP pages that give you different types of telemetry to verify in SigNoz: normal requests, slow requests, and errors.
/webapps/ROOT/index.jsp is the landing page, which generates standard request traces:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Tomcat + OpenTelemetry + SigNoz</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Apache Tomcat Monitoring Demo</h1>
<p>This app is instrumented using the OpenTelemetry Java agent.</p>
<ul>
<li><a href="/slow.jsp?delayMs=500">Slow endpoint (500 ms)</a></li>
<li><a href="/slow.jsp?delayMs=1200">Slow endpoint (1200 ms)</a></li>
<li><a href="/error.jsp">Error endpoint</a></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
/webapps/ROOT/slow.jsp has the sow endpoint that generates traces with configurable latency, useful for testing latency alerts:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/plain; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String delayParam = request.getParameter("delayMs");
int delayMs = 250;
if (delayParam != null) {
try {
delayMs = Integer.parseInt(delayParam);
} catch (NumberFormatException ignored) {
delayMs = 250;
}
}
Thread.sleep(Math.max(delayMs, 0));
out.println("Slept for " + delayMs + " ms");
%>
/webapps/ROOT/error.jsp exposes the error endpoint to generate traces with error status, useful for testing error rate alerts:
<%-- webapps/ROOT/error.jsp --%>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/plain; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
throw new RuntimeException("Intentional demo error for telemetry");
%>
Step 2: Configure OpenTelemetry Environment Variables
The OpenTelemetry Java agent can be configured via environment variables, system properties, or a properties configuration file. The key variables for SigNoz Cloud are OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT and OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS.
Create a .env file to store your SigNoz Cloud credentials:
# tomcat-monitoring/.env
SIGNOZ_INGESTION_ENDPOINT=https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443
SIGNOZ_INGESTION_KEY=<your-ingestion-key>
# Optional overrides
OTEL_SERVICE_NAME=tomcat-monitoring-demo
OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES=deployment.environment=demo,service.version=1.0.0
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL=http/protobuf
Replace <region> with your SigNoz Cloud region (us, in, or eu) and <your-ingestion-key> with your SigNoz ingestion key.
Now create the**docker-compose.yml**file that wires the environment variables to the Tomcat container:
# tomcat-monitoring/docker-compose.yml
services:
tomcat:
build:
context: .
container_name: tomcat-otel-signoz-demo
ports:
- "8080:8080"
environment:
OTEL_SERVICE_NAME: "${OTEL_SERVICE_NAME:-tomcat-monitoring-demo}"
OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES: "${OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES:-deployment.environment=demo,service.version=1.0.0}"
OTEL_TRACES_EXPORTER: "otlp"
OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER: "otlp"
OTEL_LOGS_EXPORTER: "otlp"
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL: "${OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL:-http/protobuf}"
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT: "${SIGNOZ_INGESTION_ENDPOINT}"
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS: "signoz-ingestion-key=${SIGNOZ_INGESTION_KEY}"
The Java agent enables all three signals (traces, metrics, and logs) and sends them directly to SigNoz Cloud.
Your project directory should look like this:
tomcat-monitoring/
├── Dockerfile
├── docker-compose.yml
├── .env
└── webapps/
└── ROOT/
├── index.jsp
├── slow.jsp
└── error.jsp
Step 3: Start the Stack
Build and start the container:
docker compose up --build -d
Verify Tomcat is running:
curl http://localhost:8080
You should see the demo landing page HTML with links to the slow and error endpoints.
Check that the OTel Java agent attached successfully:
docker logs tomcat-otel-signoz-demo 2>&1 | grep -i "opentelemetry"
You should see a line like [otel.javaagent] opentelemetry-javaagent - version: 2.13.3.
Generate Traffic
To produce meaningful telemetry data across all three endpoint types, create a load generation script:
#!/usr/bin/env bash
# tomcat-monitoring/scripts/generate-load.sh
set -euo pipefail
BASE_URL="${1:-http://localhost:8080}"
ROUNDS="${2:-20}"
echo "Generating traffic against ${BASE_URL} for ${ROUNDS} rounds..."
for i in $(seq 1 "${ROUNDS}"); do
curl -fsS "${BASE_URL}/" >/dev/null
curl -fsS "${BASE_URL}/slow.jsp?delayMs=$((200 + (RANDOM % 1000)))" >/dev/null
# Intentionally ignore failures from the error endpoint.
curl -s "${BASE_URL}/error.jsp" >/dev/null || true
done
echo "Done. Check SigNoz Cloud for traces/metrics/logs from service: tomcat-monitoring-demo"
Run it:
chmod +x scripts/generate-load.sh
./scripts/generate-load.sh
This sends 20 rounds of normal, slow (200-1200ms random delay), and error requests.
Step 4: Verify in SigNoz
Navigate to theServicestab (under APM) in your SigNoz dashboard. You should see tomcat-monitoring-demo listed with the automatically generated RED metrics (Rate, Errors, Duration).
Click on tomcat-monitoring-demo to view
Application Metrics: Request rate, average latency, error percentage, and p99 latency
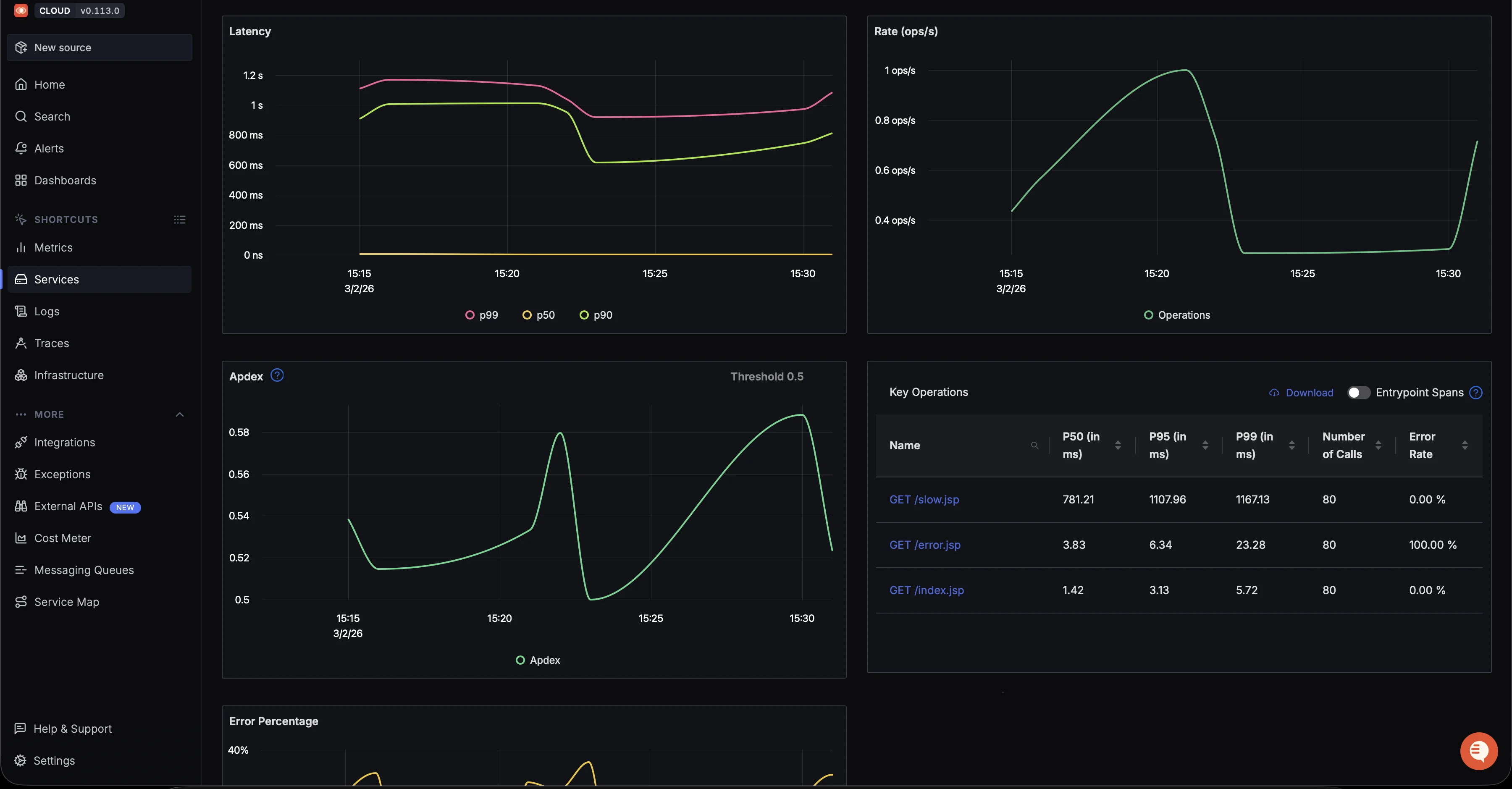
Tomcat demo service RED metrics and per-endpoint breakdown. This gives you a high-level view of request rate, latency distribution, and error percentage for your Tomcat service.
Traces: Click any trace to see the span waterfall. You should see spans for
GET /,GET /slow.jsp, andGET /error.jsp.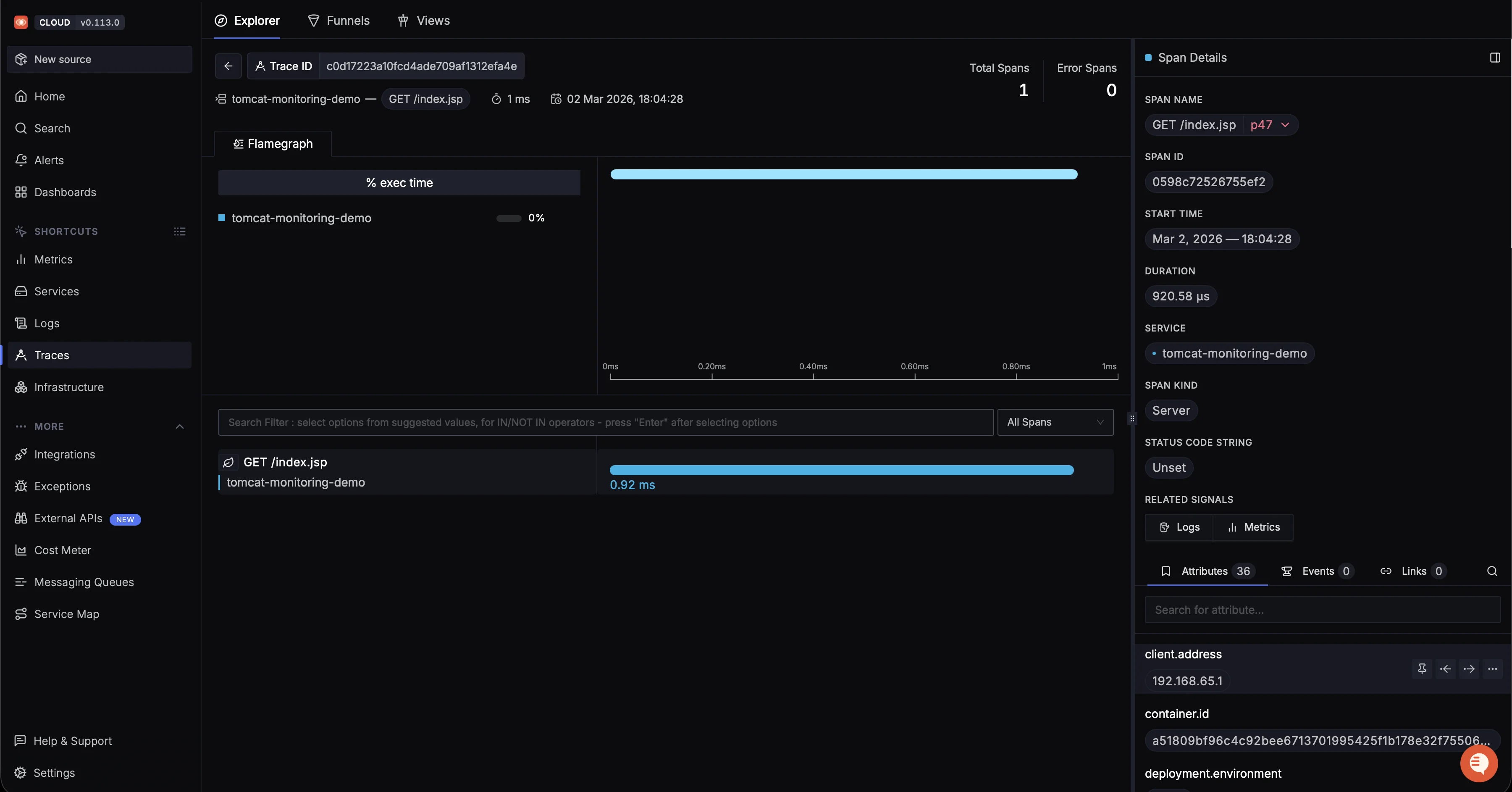
Detailed span view for a Tomcat request with execution time and attributes. Each span represents a single HTTP request handled by Tomcat, including slow and error endpoints.
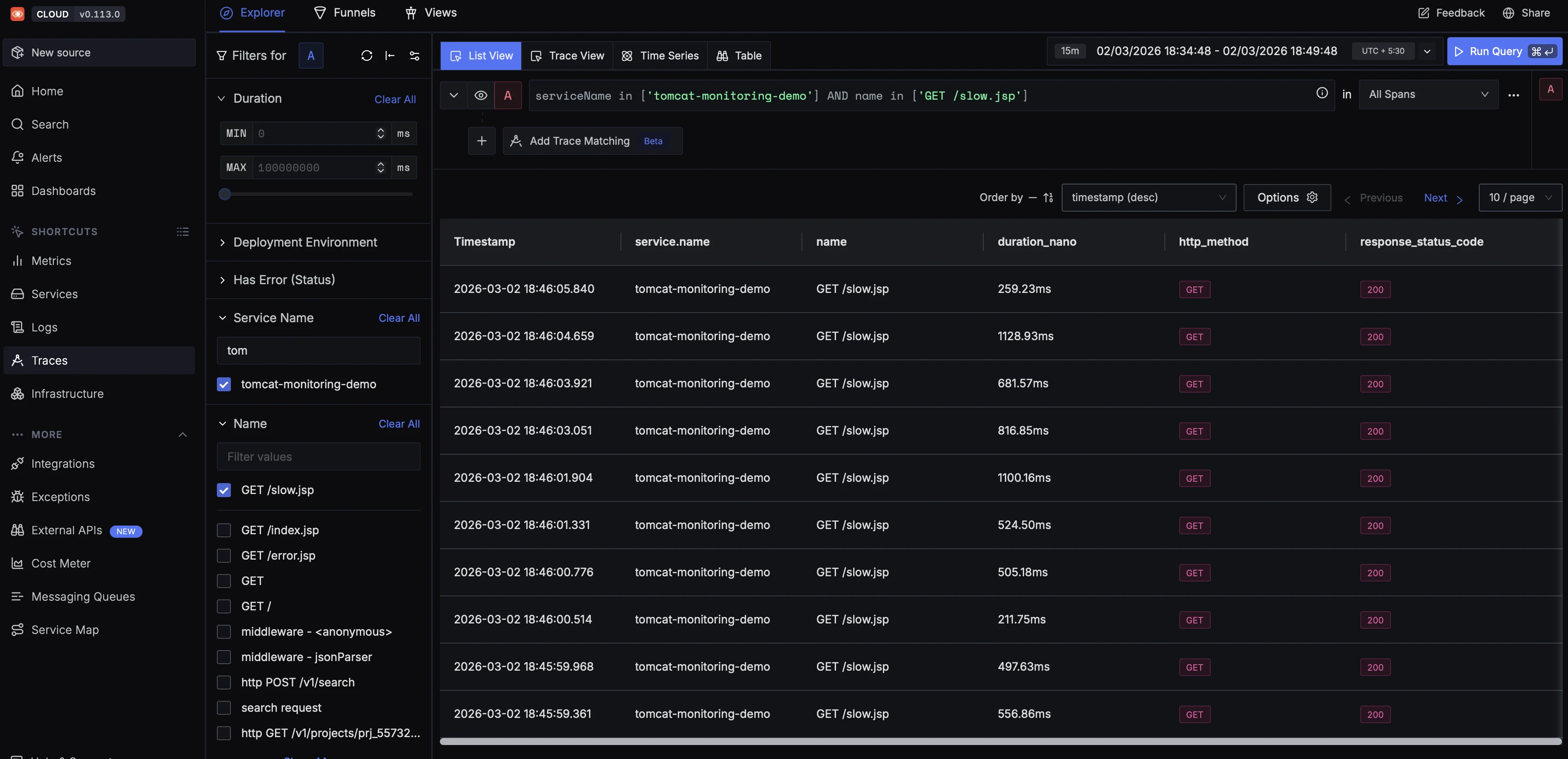
If you want a broader view, switch to the Traces tab to see all captured requests.
Finally, move to the Logs tab to inspect correlated application logs.
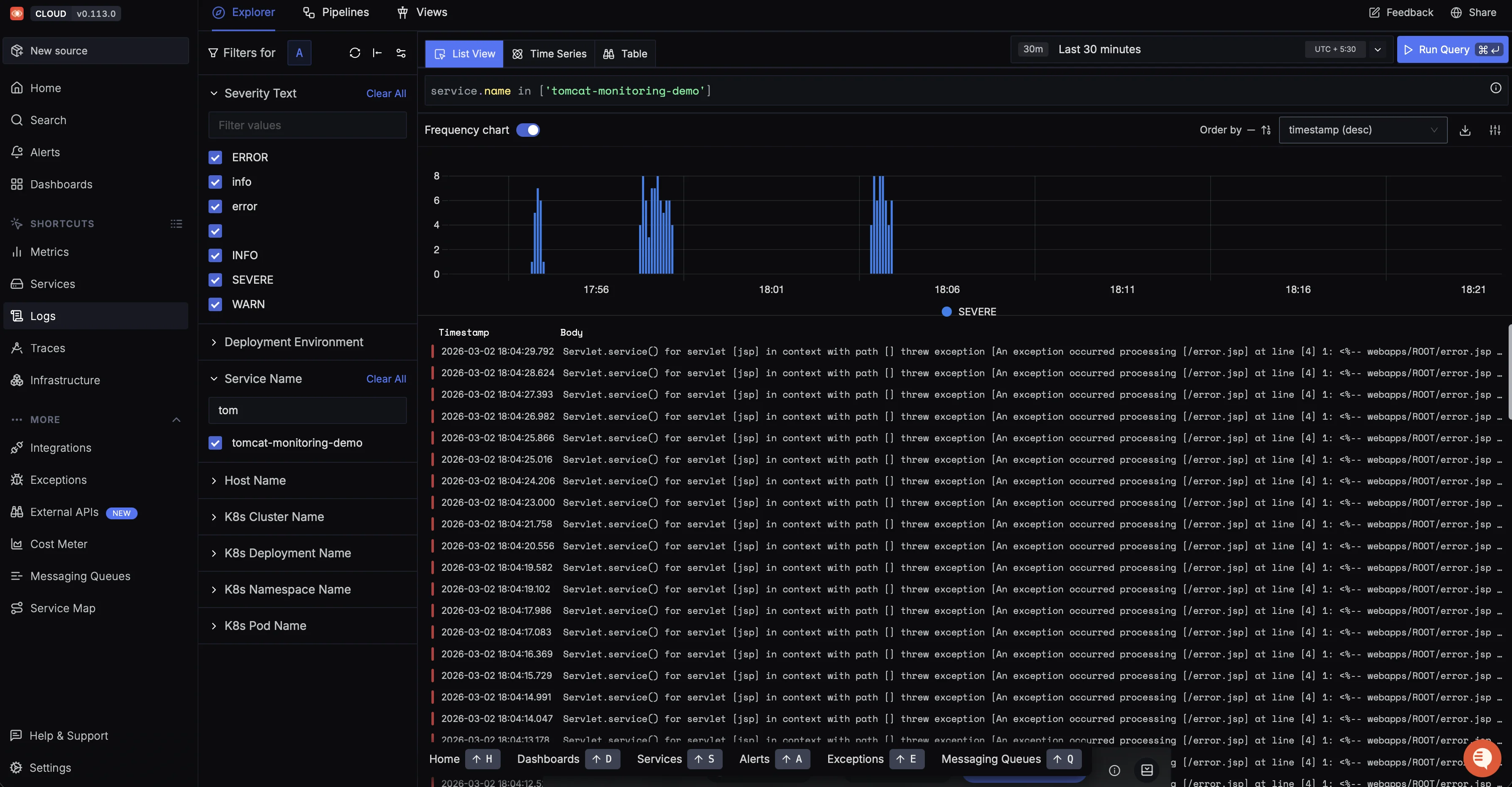
Apache Tomcat Performance Key Metrics
Now that data is flowing, here are the metrics that matter most. The OpenTelemetry Java agent exports JVM runtime metrics automatically when OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER=otlp is set. You can use these metric names directly in the SigNozMetrics→Query Builderto create dashboard panels.
JVM Metrics (Exported by Java Agent)
| Metric | Description | What to Watch For |
|---|---|---|
jvm.memory.used{jvm.memory.type="heap"} | Current heap memory usage in bytes | Baseline climbing toward 90%+ of max after full GC cycles indicates a memory leak |
jvm.memory.committed{jvm.memory.type="heap"} | Heap memory committed by the JVM | Should stay well below jvm.memory.max |
jvm.memory.limit{jvm.memory.type="heap"} | Maximum heap memory available | Use with jvm.memory.used to calculate utilization percentage |
jvm.memory.used{jvm.memory.type="nonheap"} | Non-heap memory (metaspace, code cache) | Steady growth may indicate classloader leaks |
jvm.thread.count | Current number of live JVM threads | A sustained climb without traffic increase suggests thread leaks |
jvm.gc.duration.sum | Cumulative GC pause time | Use rate(jvm.gc.duration.sum[5m]) to track GC overhead; pauses above 200ms cause request timeouts |
jvm.gc.duration.count | Number of GC events | Sudden spikes in GC frequency often precede OOM errors |
jvm.class.loaded | Number of currently loaded classes | Should stabilize after startup; continuous growth indicates classloader leaks |
Dashboards and Alerts
SigNoz provides a built-in RED metrics dashboard (Rate, Errors, Duration) out of the box for any service instrumented with the OpenTelemetry Java agent. You can find this under the Services tab → click on tomcat-monitoring-demo to see request rate, error percentage, and latency percentiles without any manual configuration.
If you want to create custom dashboards for JVM metrics or Tomcat-specific panels, follow the SigNoz dashboard creation guide.
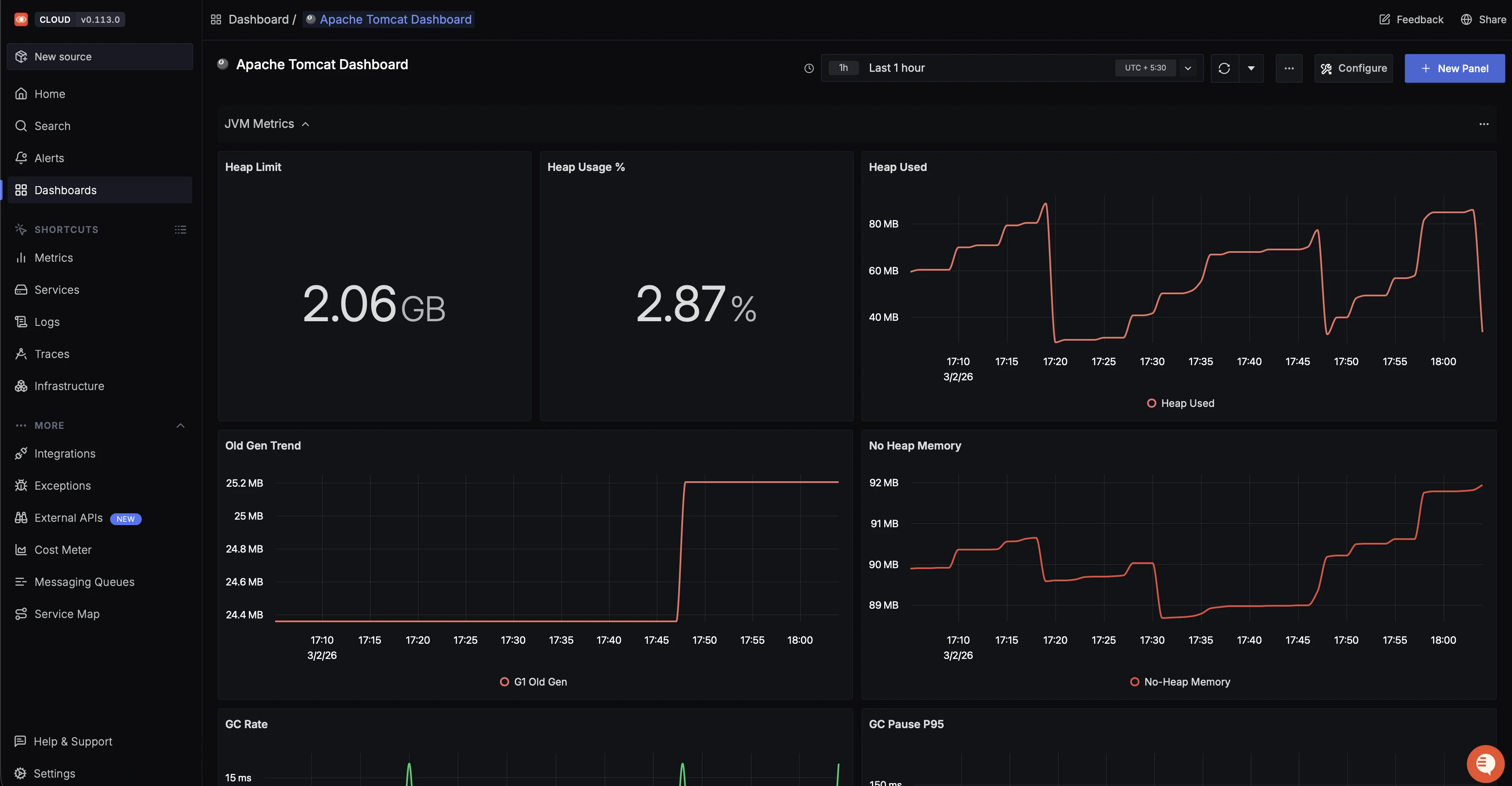
SigNoz also supports threshold-based alerts on any metric. For Tomcat monitoring, configure alerts for these conditions:
| Condition | Threshold | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Error rate spike | error_rate > 5% for 3 min | Critical |
| Request latency P95 | > 2000ms for 5 min | Warning |
| Heap memory pressure | heap_used / heap_max > 0.9 after GC | Warning |
| Thread pool saturation | busy_threads / max_threads > 0.85 for 5 min | Warning |
| Active sessions growing | delta(active_sessions[1h]) > 500 without traffic increase | Info |
For instructions on configuring notification channels (Slack, email, PagerDuty), see the SigNoz alerts documentation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is my Tomcat server running out of memory (Heap)?
This is usually due to improper heap size settings or a memory leak in the application. Monitoring tools focus on JVM Garbage Collection (GC) activity to assess whether memory is reclaimed efficiently.
How much overhead does the Java agent add?
The Overhead varies by workload and configuration. Benchmark in staging, then reduce cost/overhead using sampling and by disabling unnecessary instrumentations.
How do I monitor multiple Tomcat instances?
Each Tomcat instance runs its own Java agent and exports directly to SigNoz Cloud. Use OTEL_SERVICE_NAME and OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES to distinguish between instances:
# Instance 1
OTEL_SERVICE_NAME: "tomcat-app-1"
OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES: "deployment.environment=production,host.name=server-1"
# Instance 2
OTEL_SERVICE_NAME: "tomcat-app-2"
OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES: "deployment.environment=production,host.name=server-2"
What are the most important Tomcat metrics to track?
If you're setting up a dashboard, these are the "Golden Signals":
- **Request Latency:**Average processing time per request.
- **Error Counts:**Tracking 4xx and 5xx HTTP status codes.
- **Throughput:**Requests per second (RPS).
- JVM Metrics: Heap usage, non-heap usage, and GC overhead.
