OpenTelemetry vs. OpenTracing - Decoding the Future of Telemetry Data
OpenTelemetry and OpenTracing are open-source projects used to instrument application code for generating telemetry data. While OpenTelemetry can help you generate logs, metrics, and traces, OpenTracing focuses on generating traces for distributed applications.
If you’re thinking of choosing between OpenTelemetry and OpenTracing, go for OpenTelemetry. OpenTracing is now deprecated, and users of OpenTracing are advised to migrate to OpenTelemetry.
Quick Guide: OpenTelemetry vs OpenTracing
| Feature | OpenTelemetry | OpenTracing |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Traces, Metrics, Logs | Traces only |
| Active Development | Yes | Maintenance mode |
| Language Support | Extensive | Limited |
| Auto-instrumentation | Yes | Limited |
| Ecosystem Compatibility | Broad | Narrow |
| Future-proofing | High | Low |
| Migration Path | N/A | To OpenTelemetry |
| Context Propagation | Advanced | Basic |
| Performance Overhead | Low | Varies |
| Cloud-Native Integration | Strong | Limited |
| Vendor Neutrality | High | Moderate |
| Community Support | Large and growing | Diminishing |
| Backward Compatibility | Yes (with OpenTracing) | N/A |
| Standardization | CNCF graduated project | CNCF archived project |
Before we see the differences between OpenTelemetry and OpenTracing, let’s have a brief overview of what each technology is.
What is OpenTelemetry?
OpenTelemetry is an open-source project under the Cloud Native Computing Foundation(CNCF) that aims to standardize the generation and collection of telemetry data. Telemetry data includes logs, metrics, and traces.
It was formed after the merger of OpenTracing and OpenCensus, two projects with similar goals but different approaches.
OpenTelemetry is a collection of APIs, SDKs, and client libraries used to generate telemetry data from your application code.
The data you collect with OpenTelemetry is vendor-agnostic and can be exported in many formats.
The biggest advantage of using OpenTelemetry is that you have the freedom to choose a backend of your choice. You don’t get locked into a vendor, and engineering teams can get ramped up on a single technology to generate telemetry data.
Which backend analysis tool to choose?
You can try SigNoz, a full stack open-source APM built natively on OpenTelemetry.
To integrate OpenTelemetry with your application code, you can use the OpenTelemetry client libraries of the required programming language. OpenTelemetry also provides a collector known as OTel(OpenTelemetry) collector that can be used to process and export telemetry data in multiple formats.
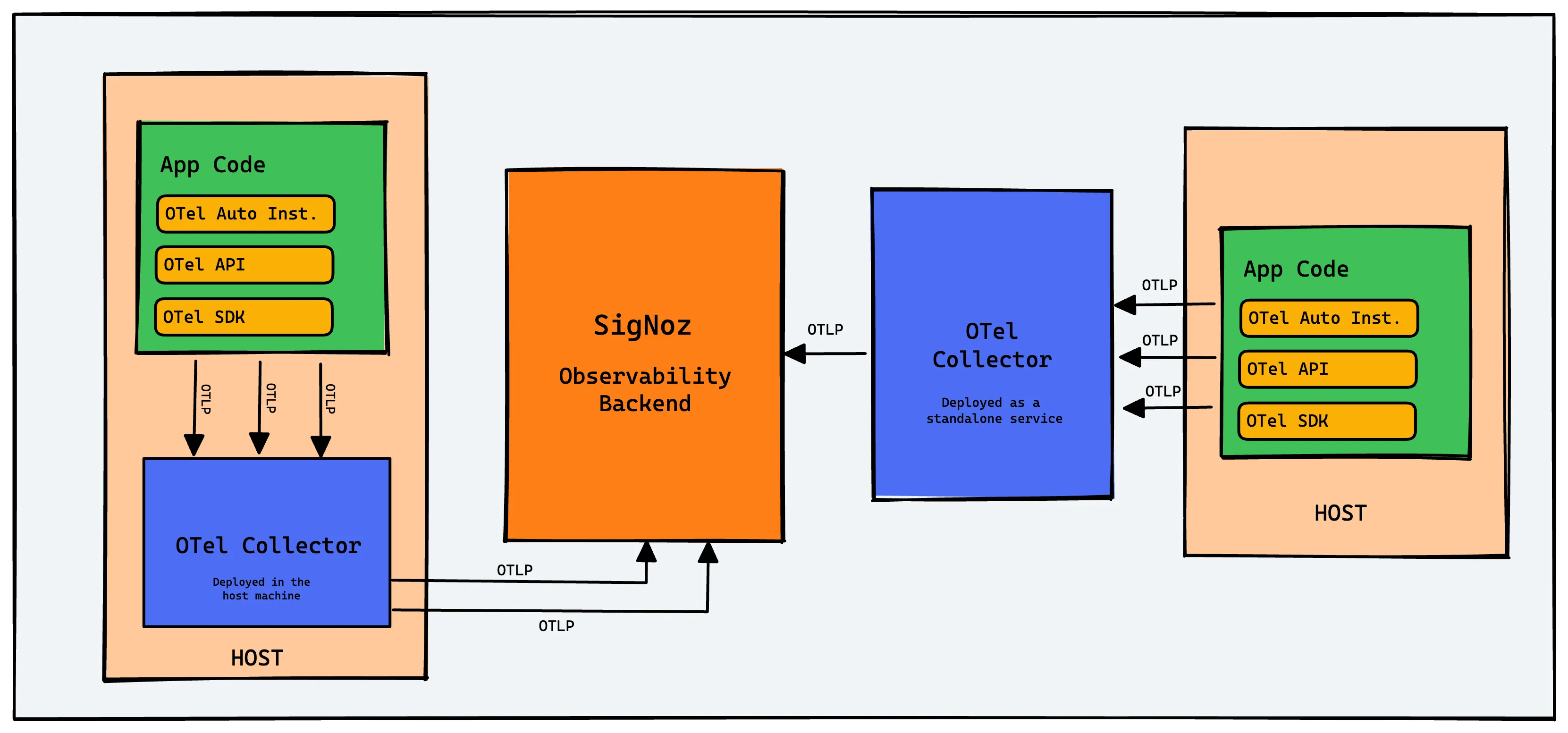
Key components of OpenTelemetry include:
- APIs: Define how to generate and manage telemetry data.
- SDKs: Implement the APIs for various programming languages.
- Collector: Receives, processes, and exports telemetry data.
OpenTelemetry supports three main types of telemetry data:
- Traces: Track the flow of requests through distributed systems.
- Metrics: Measure the performance and behavior of applications.
- Logs: Capture detailed information about events and errors.
What is OpenTracing?
OpenTracing is a vendor-neutral API standard for distributed tracing. It focuses on providing a consistent way to instrument applications for tracing across different languages and platforms.
It is difficult for engineering teams to see how requests are performing across services. And that’s where distributed tracing comes into the picture.
But the problem for large organizations in adopting distributed tracing was the lack of reusable instrumentation for a vast number of open-source frameworks and libraries.
OpenTracing APIs were meant to solve this by developing a common instrumentation API.
The core concepts of OpenTracing include:
- Spans: Represent a unit of work or operation.
- Traces: A collection of spans that form a complete request path.
- Context propagation: Passing trace information across service boundaries.
While OpenTracing excelled at standardizing distributed tracing, it had limitations when addressing broader observability needs. This shortcoming eventually led to its evolution into OpenTelemetry.
OpenTelemetry vs OpenTracing
OpenTelemetry was formed after the merger of OpenTracing and OpenCensus and is currently being actively developed as the single standard for application instrumentation under CNCF. OpenTelemetry combines the functionalities of OpenTracing and OpenCensus and also extends them.
While OpenTelemetry can be your single source for all kinds of telemetry data like logs, metrics, and trace
OpenTracing was focused only on distributed tracing. For users who are using OpenTracing APIs, they can migrate to OpenTelemetry.
For organizations and developers currently on the fence, the choice is clear: OpenTelemetry. Not only does it encompass the functionalities of OpenTracing, but it also offers extended capabilities.
With OpenTracing being deprecated, migrating to OpenTelemetry is the logical step forward. The transition is made easier by OpenTelemetry's active efforts to ensure backward compatibility and its comprehensive approach to telemetry data.
OpenTracing's performance often varied due to diverse implementations, whereas OpenTelemetry was engineered for consistently low overhead across its standardized APIs and SDKs.
OpenTelemetry vs OpenTracing: Feature Comparison
To understand why OpenTelemetry has become the preferred choice, let's compare its features with OpenTracing:
- Scope of telemetry data:
- OpenTelemetry: Covers traces, metrics, and logs.
- OpenTracing: Focuses solely on distributed tracing.
- Language and framework support:
- OpenTelemetry: Offers extensive support for multiple languages and frameworks.
- OpenTracing: Provides support for several languages but with less active development.
- Vendor neutrality and ecosystem compatibility:
- OpenTelemetry: Designed for seamless integration with various backends and tools.
- OpenTracing: Offers vendor neutrality but with a smaller ecosystem.
- Performance and overhead:
- OpenTelemetry: Optimized for minimal performance impact and low overhead.
- OpenTracing: Generally lightweight but may vary depending on implementation.
Data Model and Instrumentation
The data model and instrumentation approaches differ significantly between OpenTelemetry and OpenTracing:
- OpenTelemetry's unified data model:
- Provides a consistent structure for traces, metrics, and logs.
- Enables correlation between different types of telemetry data.
- OpenTracing's tracing-specific model:
- Focuses on span and trace concepts.
- Lacks native support for metrics and logs.
- Instrumentation approaches:
- OpenTelemetry: Offers auto-instrumentation libraries and manual instrumentation APIs.
- OpenTracing: Requires manual instrumentation in most cases.
- Backward compatibility:
- OpenTelemetry: Includes a compatibility layer for OpenTracing, easing migration.
- OpenTracing: No direct compatibility with OpenTelemetry.
Why Choose OpenTelemetry over OpenTracing?
Several factors make OpenTelemetry a more attractive choice for modern observability needs:
- Comprehensive observability: OpenTelemetry's support for traces, metrics, and logs provides a complete picture of your system's health and performance.
- Future-proofing: As the successor to OpenTracing, OpenTelemetry benefits from ongoing development and community support.
- Broader ecosystem: OpenTelemetry's wide adoption means better integration with cloud-native tools and services.
- Simplified instrumentation: Auto-instrumentation capabilities reduce the effort required to implement observability in your applications.
Migrating from OpenTracing to OpenTelemetry
If you're currently using OpenTracing, here's a step-by-step guide to migrate to OpenTelemetry:
- Assess your current OpenTracing implementation:
- Identify all instrumented components.
- Document custom instrumentation and integrations.
- Plan your migration strategy:
- Decide between a gradual or all-at-once approach.
- Set up a testing environment to validate the migration.
- Install OpenTelemetry dependencies:
- Add OpenTelemetry SDK and API libraries to your project.
- Include the OpenTracing shim for backward compatibility.
- Update your instrumentation:
- Replace OpenTracing imports with OpenTelemetry equivalents.
- Modify custom instrumentation to use OpenTelemetry APIs.
- Configure the OpenTelemetry SDK:
- Set up exporters for your chosen backend.
- Adjust sampling and other SDK settings as needed.
- Test and validate:
- Ensure all traces are correctly captured and exported.
- Compare performance metrics before and after migration.
- Gradually remove OpenTracing dependencies:
- Once confident in the migration, remove OpenTracing libraries.
- Update any remaining OpenTracing-specific code.
Common challenges in migration include:
- Adapting custom instrumentation to OpenTelemetry concepts.
- Ensuring consistent context propagation across services.
- Managing differences in configuration between OpenTracing and OpenTelemetry.
To overcome these challenges:
- Leverage the OpenTracing shim to maintain compatibility during transition.
- Use OpenTelemetry's extensive documentation and community resources.
- Consider a phased approach, migrating one service or component at a time.
Here is a guide from the official documentation of OpenTelemetry on How to Migrate from OpenTracing to OpenTelemetry.
Implementing OpenTelemetry with SigNoz
SigNoz is an open-source application performance monitoring (APM) tool that works seamlessly with OpenTelemetry. It provides a powerful platform for visualizing and analyzing your telemetry data.
Key benefits of using SigNoz with OpenTelemetry include:
- Full-stack observability: Monitor your entire application stack with traces, metrics, and logs.
- Custom dashboards: Create tailored views of your system's performance.
- Alerting: Set up intelligent alerts based on your telemetry data.
- Cost-effective: As an open-source solution, SigNoz can significantly reduce your observability costs.
To get started with SigNoz:
- Install SigNoz using Docker or Kubernetes or SetUp a cloud account.
- Configure your OpenTelemetry SDK to export data to SigNoz.
- Start exploring your application's performance data through the SigNoz UI.
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Key Takeaways
- OpenTelemetry offers a more comprehensive observability solution compared to OpenTracing.
- While OpenTracing focuses solely on tracing, OpenTelemetry supports traces, metrics, and logs.
- Migrating from OpenTracing to OpenTelemetry is recommended and supported through compatibility layers.
- OpenTelemetry provides better vendor neutrality and future-proofing for your observability needs.
- SigNoz offers a powerful, open-source platform for leveraging OpenTelemetry data.
FAQs
Is OpenTelemetry compatible with OpenTracing?
OpenTelemetry is backwards compatible with OpenTracing using software bridges. For example, the OpenTracing bridge will take any OpenTelemetry tracer and convert it into an OpenTracing tracer.
Does Jaeger use OpenTelemetry?
Yes, Jaeger has robust and mature support for OpenTelemetry. It can directly ingest telemetry data via the OpenTelemetry Protocol (OTLP), making it a popular backend for OpenTelemetry traces. While development is continuous, its OpenTelemetry libraries and integration are stable and widely used.
Is OpenTracing still actively maintained?
While OpenTracing is still maintained, active development has shifted to OpenTelemetry. The OpenTracing project is in maintenance mode, with efforts focused on supporting migration to OpenTelemetry.
Can I use OpenTracing and OpenTelemetry in the same project?
Yes, you can use both in the same project during migration. OpenTelemetry provides a compatibility layer that allows you to use OpenTracing APIs with OpenTelemetry implementation.
What are the main benefits of switching from OpenTracing to OpenTelemetry?
The main benefits include comprehensive observability (traces, metrics, and logs), broader ecosystem support, and future-proofing your observability strategy.
How does OpenTelemetry improve upon OpenTracing's limitations?
OpenTelemetry addresses OpenTracing's limitations by providing a unified approach to observability, supporting multiple telemetry types, and offering better integration with modern cloud-native architectures.
