What are SysLog formats? How to use them?
Syslog is a standard for message logging that allows devices such as routers, switches, and servers to send event messages to a central log server. The messages sent by these devices are known as syslog messages and include information such as the date, time, device hostname, and message content.

Syslog was originally developed as a part of the BSD operating system, but many other operating systems and network devices have since adopted it. It is used to track system events, security alerts, and other important messages, and it provides a central location for storing and managing log data.
Before we dig deeper into Syslog formats, let’s learn more about Syslogs.
What is Syslog protocol?
Syslog messages are typically sent using the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) and are received by a syslog server, which can then process and store the messages as needed. The syslog protocol includes a set of rules and conventions for formatting and transmitting syslog messages, and these rules are followed by devices and servers that use syslog. It defines the structure and content of syslog messages, as well as the rules for sending and receiving them.
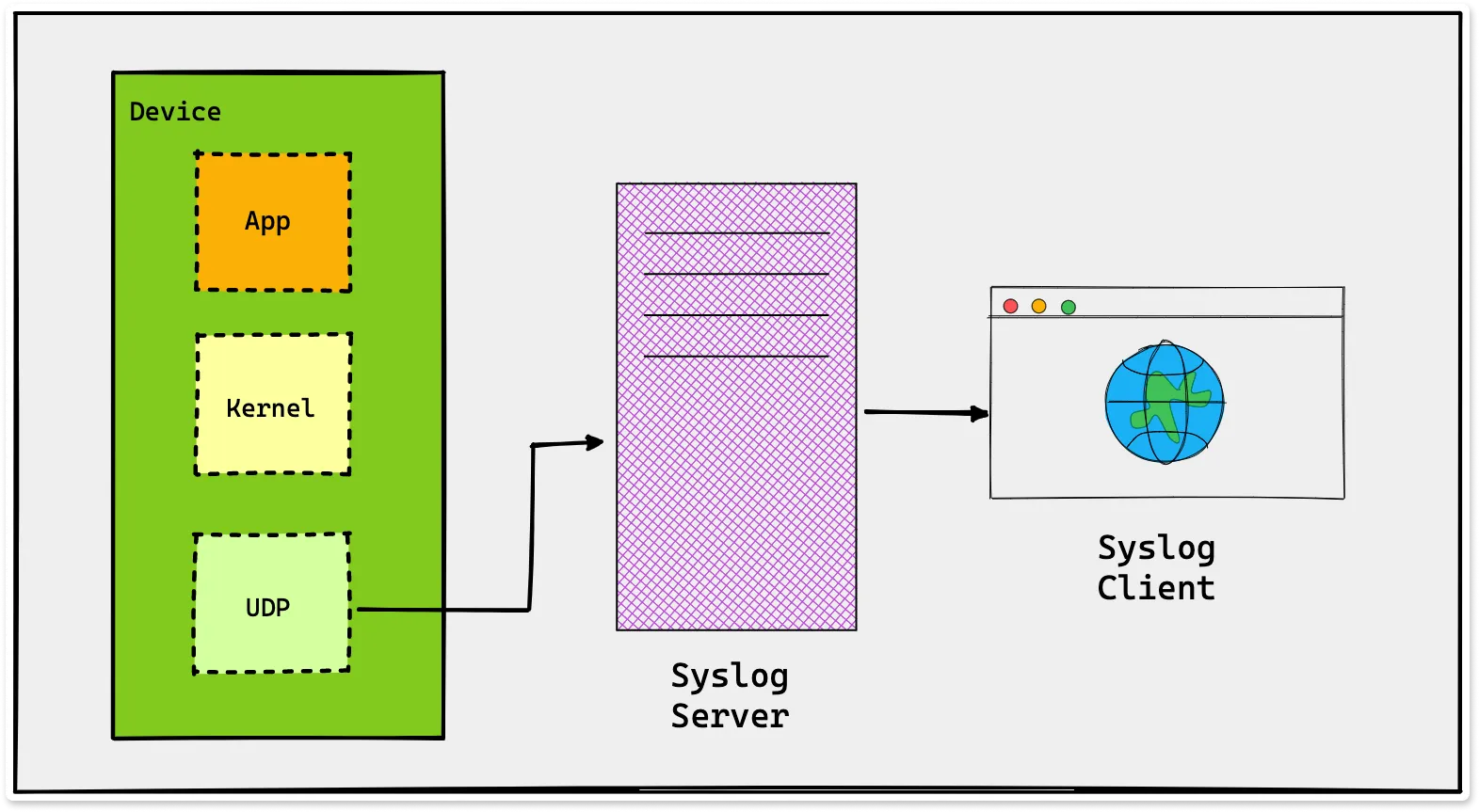
In the diagram shown above, Device is a network device that generates syslog messages. These messages are generated by applications and the kernel running on the device, and are passed to the UDP layer for transmission. The syslog server receives the messages and processes them as needed. The syslog client can then retrieve and view the log messages stored on the syslog server.
The syslog protocol includes several message formats, including the original BSD syslog format, the newer IETF syslog format, and the extended IETF syslog format. It also defines a set of message priorities and severities that can be used to classify syslog messages based on their importance.
In addition to its use as a logging system, syslog can also be used to forward messages to other servers or devices for further processing or analysis. This allows organizations to centralize their log data and make it easier to manage and analyze.
What are Syslog formats?
There are several different syslog message formats in use. Depending on your use-case, you can choose one to support your needs. Below are some examples of Syslog formats:
The original BSD syslog format, which has the following structure:
<priority>timestamp hostname: message
The priority field is a numerical value that indicates the severity and importance of the message. The timestamp is the date and time when the message was generated, and the hostname is the name of the device that generated the message. The message itself follows the colon.
The newer IETF syslog format, which has the following structure:
timestamp hostname process[pid]: message
In this format, the timestamp and hostname fields have the same meanings as in the BSD syslog format. The process field indicates the name of the process that generated the message, and the pid field indicates the process ID. The message itself follows the colon.
The extended IETF syslog format, which includes additional fields such as the message ID, structured data, and a message header:
timestamp hostname process[pid]: message header message
In this format, the timestamp, hostname, process, and pid fields have the same meanings as in the IETF syslog format. The message header field is a brief summary of the message, and the message field contains the full message content.
In addition to these formats, there are also custom syslog formats that specific vendors have developed for use with their products. These formats may include additional fields or structures beyond the standard syslog formats and may be used to convey specific types of information or to support specific features of the vendor's products.
How to use Syslog formats?
To use Syslog formats, devices and systems typically include a Syslog daemon (also known as a syslogd) that is responsible for generating and sending Syslog messages. The Syslog is configured to use a specific Syslog format and to send messages to a designated Syslog server.
The Syslog server receives the messages and processes them as needed, typically storing them in a central log repository for later analysis.
Analyzing Syslog with Open Source Log Management Tool
In production environments, you need to have a centralized logging system in order to effectively use logs for debugging and troubleshooting purposes. SigNoz, an open source APM provides log analytics as one of its features.
SigNoz is a full-stack open source APM that you can use as an alternative to Loki and Elasticsearch. SigNoz uses a columnar database ClickHouse to store logs, which is very efficient at ingesting and storing logs data. Columnar databases like ClickHouse are very effective in storing log data and making it available for analysis.
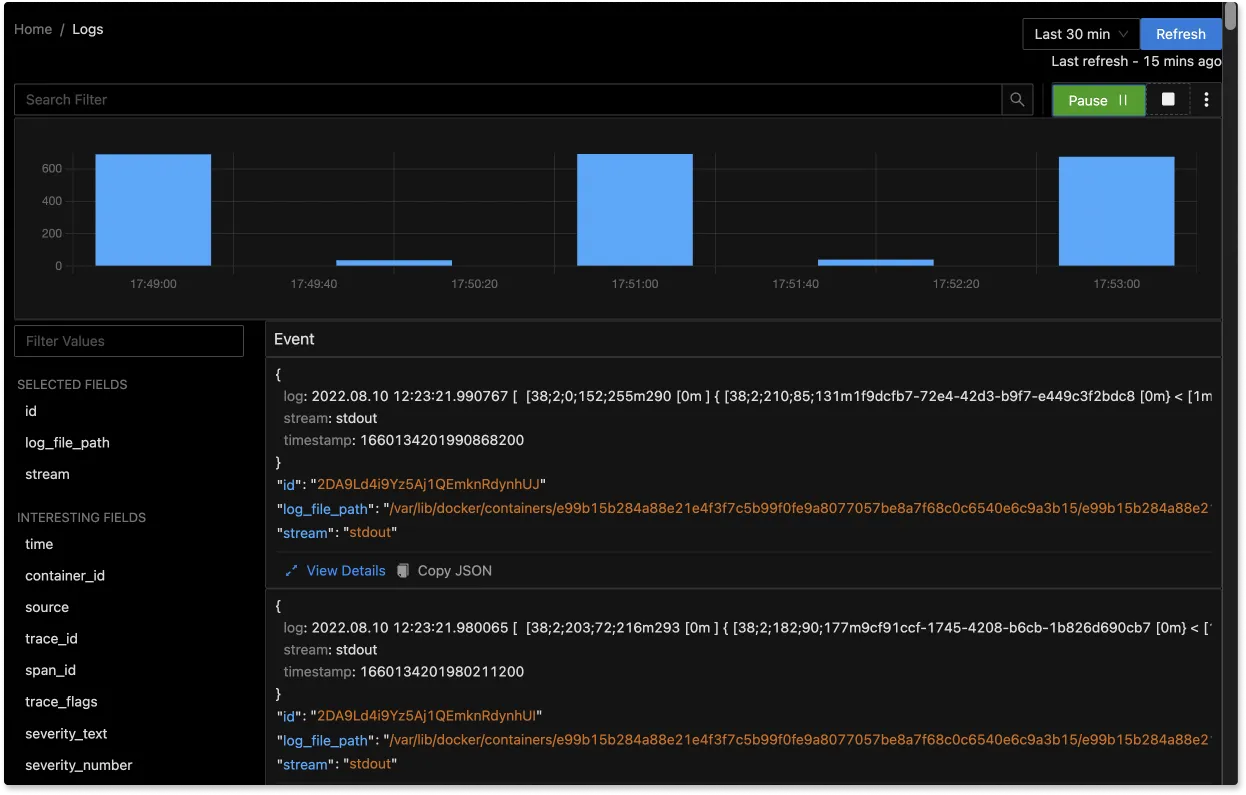
The logs tab in SigNoz has advanced features like a log query builder, search across multiple fields, structured table view, JSON view, etc.
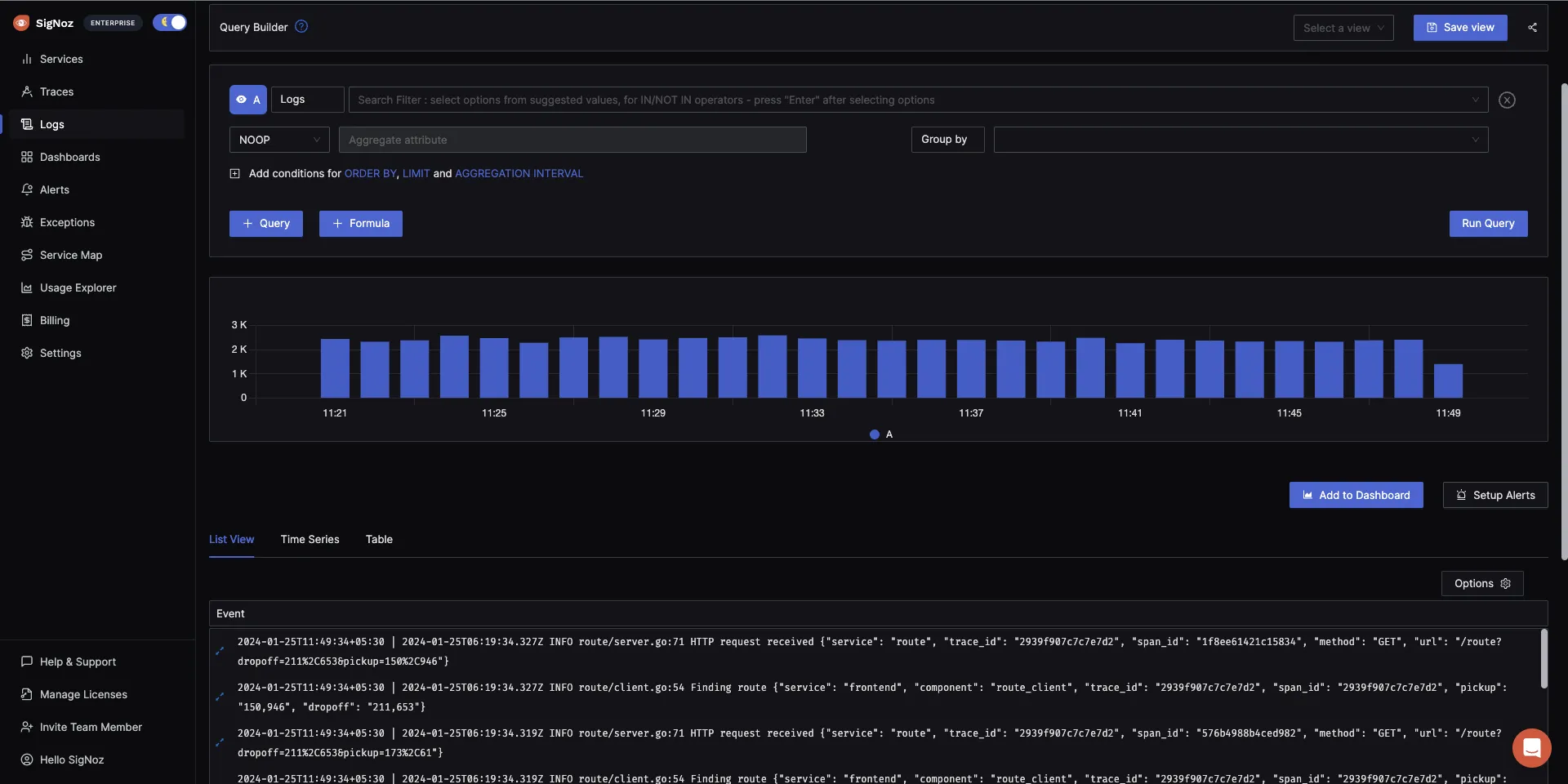
You can also view logs in real time with live tail logging.
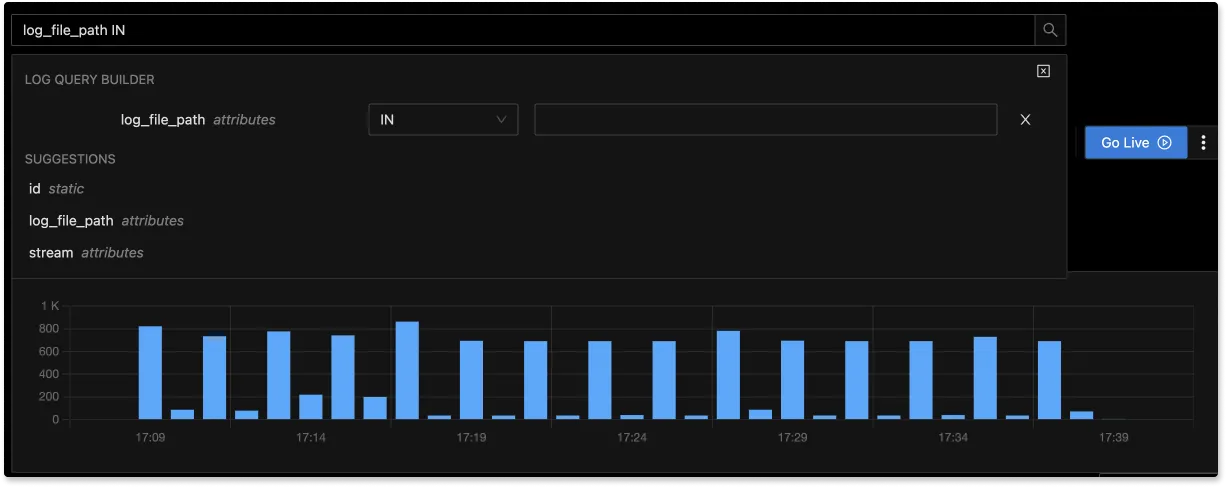
With advanced Log Query Builder, you can filter out logs quickly with a mix and match of fields.
Getting started with SigNoz
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Related Posts
