Top 8 Sentry Alternatives in 2026: Beyond Error Tracking
TL;DR
- SigNoz: Best for teams that need to correlate errors with traces, logs, and application metrics in one platform. It’s OpenTelemetry-native with usage-based pricing.
- GlitchTip: Best drop-in Sentry replacement, compatible with Sentry SDKs, free to self-host with Docker Compose, and lightweight compared to self-hosted Sentry.
- Raygun: Best for frontend teams that want deployment-to-error correlation, integrated RUM, and error grouping prioritised by user impact.
Sentry is one of the most widely used error tracking tools in software development, catching exceptions, grouping them into issues, and providing stack traces and breadcrumbs to help you diagnose what broke. However, problems tend to emerge once your needs grow beyond that core scope. Sentry bills on usage with monthly quotas per data category (errors, spans, replays, logs). Spikes can quickly consume your monthly quota, and if you enable pay-as-you-go budgets, unexpected spikes can also increase spend. Managing costs requires configuring quota limits, spike protection, and SDK-level sampling.

On top of pricing, there are data concerns too. In January 2024, Sentry proposed updated terms language allowing use of Usage Data and Service Data for analytics and product development (including AI). After customer feedback, Sentry clarified a consent-first approach for identifiable customer data and updated its legal posture so that non-identifying Service Data may be used for product development, while customer authorisation is required to use other Service Data for purposes beyond providing the service. If you're in a regulated industry, review Sentry's current data-processing terms before adopting. And if you're considering self-hosting to avoid these issues, Sentry's self-hosted stack relies on multiple backend services (PostgreSQL, Redis, Kafka, ClickHouse, Relay, and more), making it operationally heavy to maintain.
Beyond cost and compliance, there's a more fundamental limitation. As applications shift toward microservices and distributed architectures, stack traces alone no longer tell the full story. Teams need to correlate exceptions with logs, metrics, and traces to understand what actually went wrong across their entire infrastructure, and that's precisely the gap many of the alternatives in this guide are designed to fill.
Top 8 Sentry Alternatives for 2026
The tools in this list fall into three categories:
- Full Observability Platforms: Tools that go beyond error tracking into logs, metrics, tracing, and application performance monitoring. SigNoz, New Relic, and Datadog fall here.
- Drop-in Sentry Replacements (SDK-Compatible): Drop-in alternatives that work with your existing Sentry SDKs. Simply update the server address in your configuration to point to the new tool, and you're done. GlitchTip and Bugsink fall here.
- Focused Error Tracking Platforms: Hosted error monitoring tools with a Sentry-style workflow but different pricing or specialisation. Bugsnag, Raygun, and Rollbar.
In the sections ahead, we review each tool based on what it does well, how it compares to Sentry, and why you should consider it.
Category 1: Full Observability Platforms
These platforms go beyond error tracking by correlating exceptions with logs, metrics, and traces in a single view. They also offer flexibility in where your data resides, whether that's their cloud, yours, or a hybrid setup.
1. SigNoz
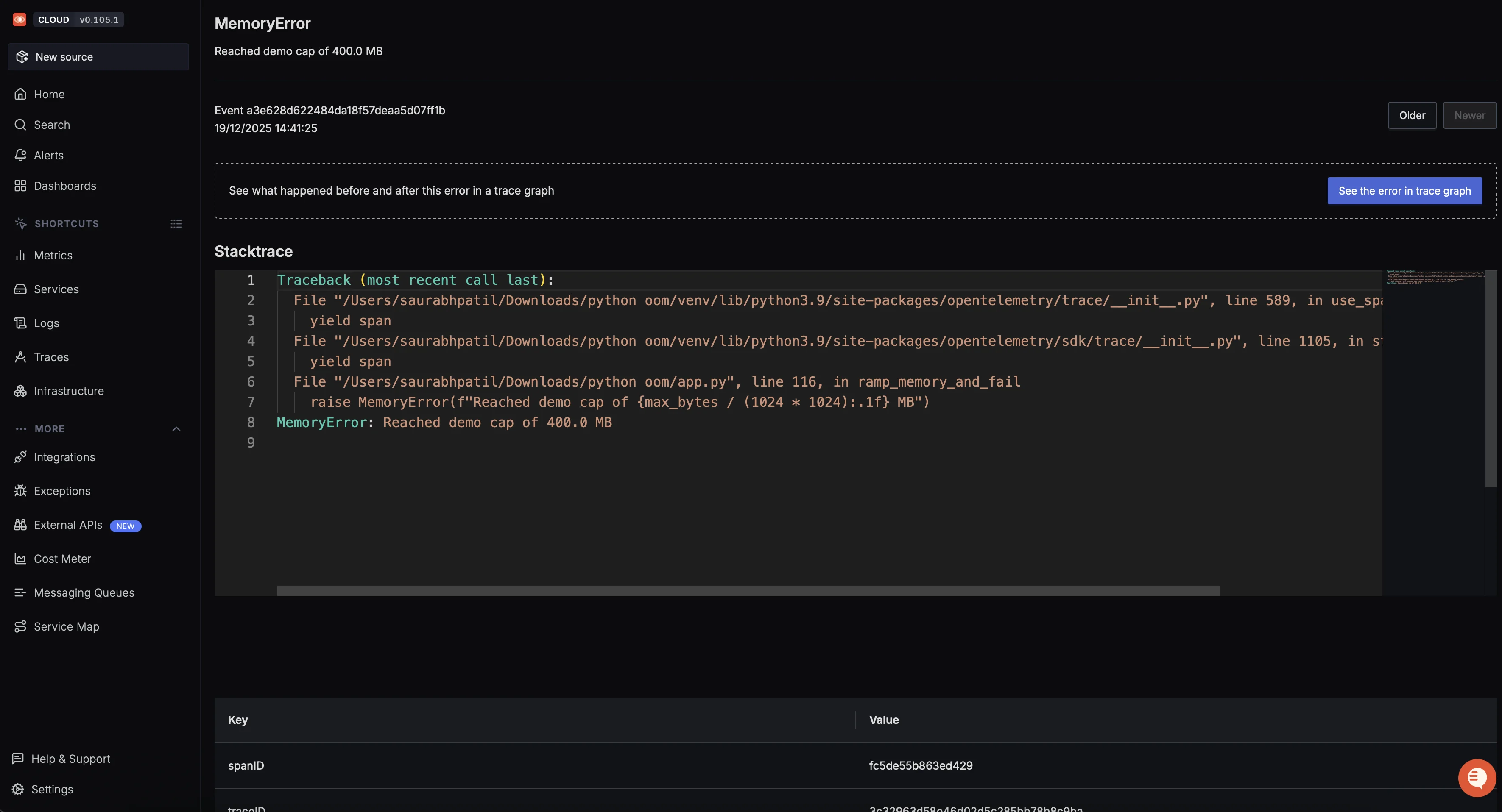
SigNoz is an OpenTelemetry-native observability platform that provides unified error tracking alongside logs, metrics, and distributed traces. You can instrument your application using OpenTelemetry libraries and send the telemetry to SigNoz, which then gives you a correlated view of every exception across your entire stack in one place. Sentry's core instrumentation is via Sentry SDKs, though it also supports OpenTelemetry ingestion (e.g., OTLP) for some telemetry workflows.
SigNoz ties each exception to the trace span that triggered it, plus the related logs and host metrics. When an error occurs, you can see the downstream API call that failed, the database query that timed out, and the application state at the moment of the failure. This correlated debugging is critical for microservices and distributed architectures, where an error in one service is almost always caused by something happening in another. Sentry now offers Logs alongside errors and tracing, but teams that want full application monitoring and broad metrics coverage often still pair Sentry with (or switch to) a dedicated observability platform.
SigNoz is also better suited for monitoring backend applications and complex applications. It provides out-of-the-box visibility into Kubernetes clusters, serverless functions, and messaging queues like Kafka, areas where Sentry has limited coverage. While Sentry provides richer metadata for frontend errors (like session replays and breadcrumbs), it lacks the deep application monitoring that backend and platform teams need.
You can get started in minutes with SigNoz Cloud, which offers a 30-day free trial with full feature access, or self-host with the open-source community edition. For teams with strict data residency requirements, there's also an enterprise self-hosted or BYOC plan.
2. New Relic
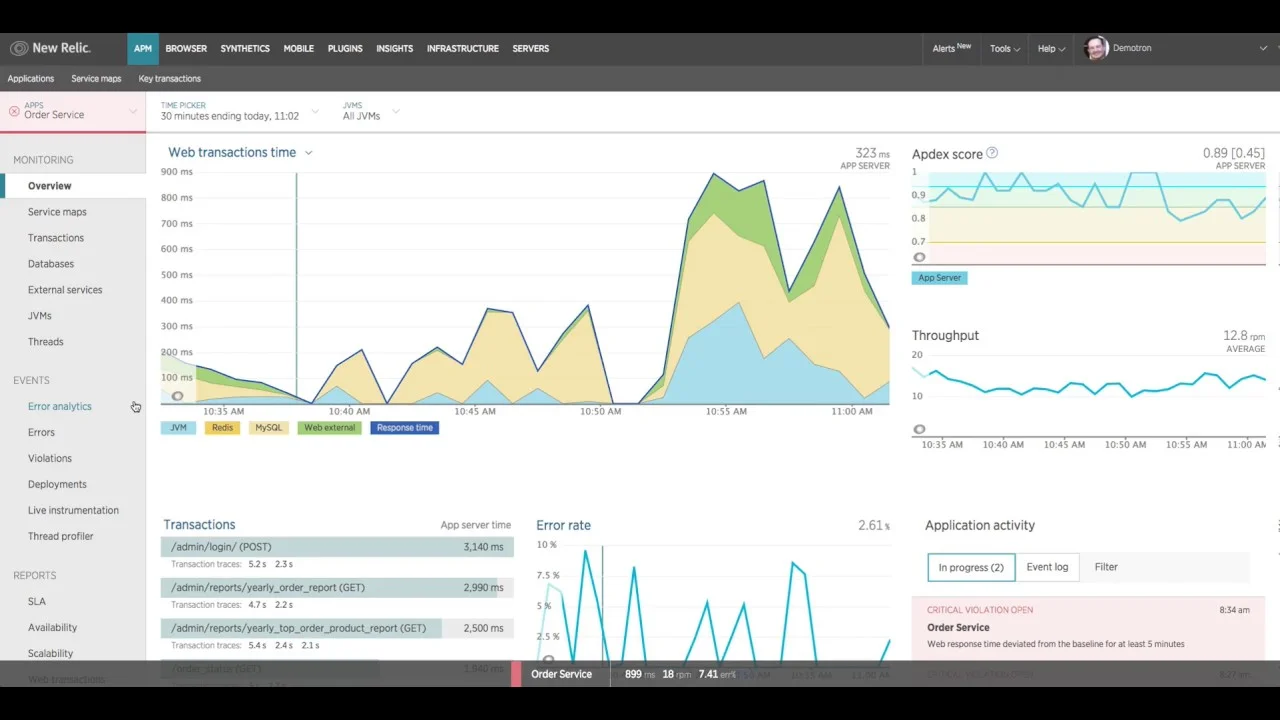
New Relic is an enterprise observability platform that combines APM, error tracking, log management, infrastructure monitoring, and real user monitoring under one roof. Unlike Sentry, which focuses on catching exceptions via SDKs, New Relic provides full-stack visibility, tying errors to the application traces, infrastructure metrics, and deployment events that caused them.
New Relic's error tracking is embedded within its broader APM experience. When an error occurs, you see the full transaction trace, the host-level metrics at that moment, and any related logs, giving you more context than Sentry's stack-trace-and-breadcrumb approach. New Relic also includes AI-powered anomaly detection and 700+ integrations for monitoring databases, cloud services, and third-party APIs. Teams often choose New Relic over Sentry when they need a single platform that covers both error tracking and infrastructure-level observability without stitching together multiple tools.
3. Datadog
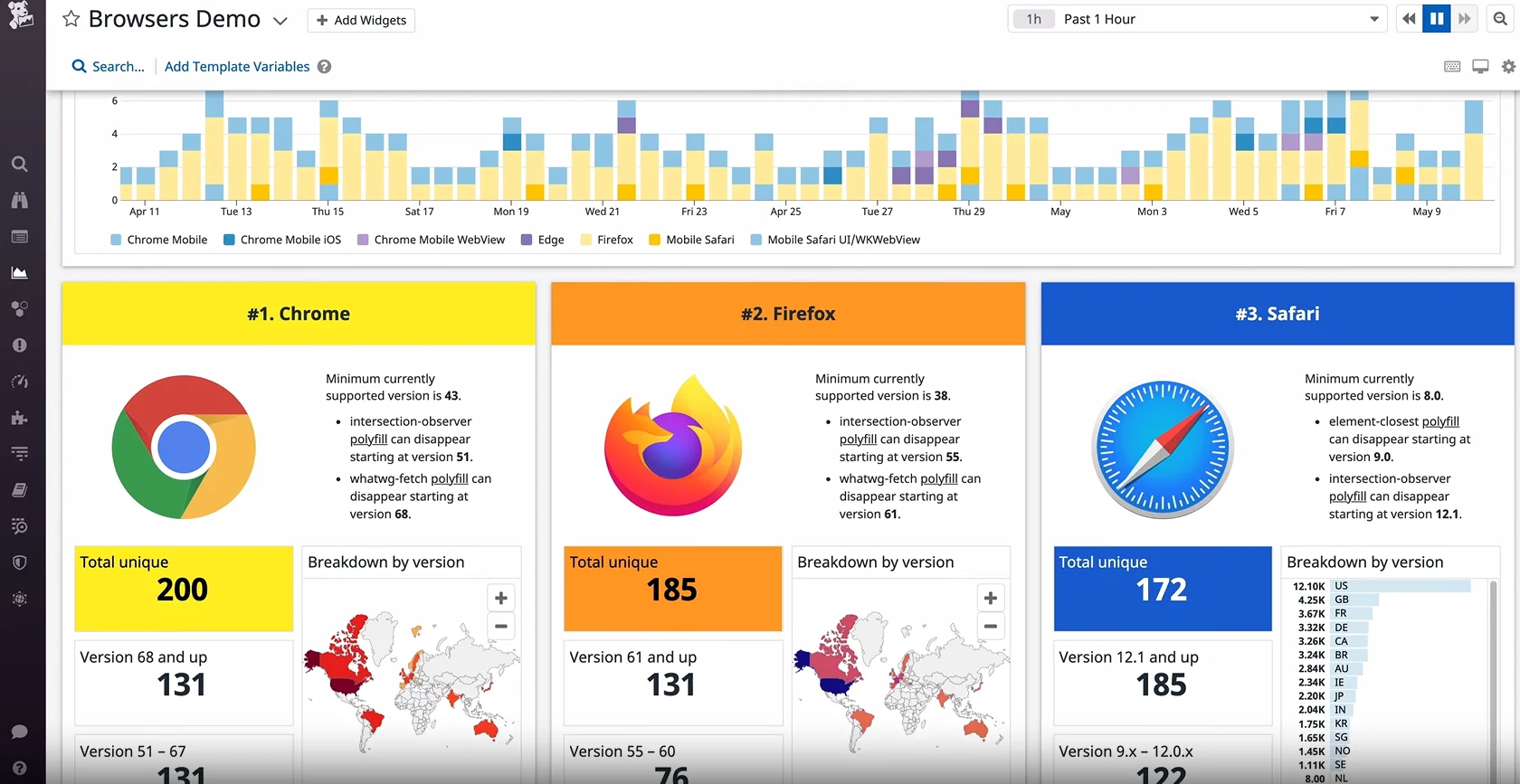
Datadog is an enterprise observability platform that consolidates infrastructure monitoring, APM, log management, error tracking, and security into a single product. With 1,000+ integrations and automatic service mapping across microservices, it provides a level of infrastructure visibility that Sentry simply doesn't offer.
Datadog's error tracking is part of a much larger platform, so you can correlate frontend exceptions with backend traces, infrastructure metrics, and deployment events. Watchdog AI detects anomalies that would slip past Sentry's threshold-based alerts. The tradeoff is cost and complexity. Datadog is significantly more expensive than Sentry, with per-host pricing plus usage-based add-ons, and the learning curve is steeper. It's a better choice for enterprise teams that want everything consolidated and have the budget to support it.
Category 2: Drop-in Sentry Replacements (SDK-Compatible)
These tools are directly compatible with Sentry's SDKs and DSN format, so migration is as simple as changing the server address in your existing configuration. They prioritise lightweight self-hosting and operational simplicity over Sentry's broader feature set.
4. GlitchTip
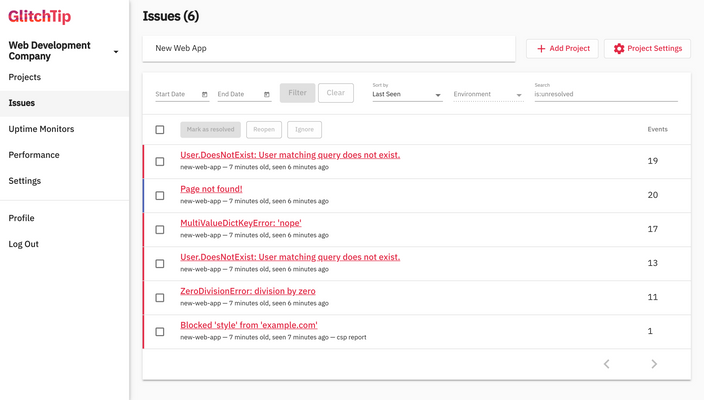
GlitchTip is an open-source error tracking tool that's directly compatible with Sentry's SDKs and DSN format. If you're currently using Sentry and want to switch without re-instrumenting your codebase, GlitchTip is the closest drop-in replacement available. You self-host it with Docker Compose, change the DSN in your existing Sentry SDK configuration, and you're done.
GlitchTip covers error tracking, performance monitoring, and uptime monitoring out of the box, but it doesn't try to be a full observability platform. That's what keeps it lightweight compared to Sentry's multi-service self-hosted stack. It's free to self-host, or you can opt for a hosted plan if you'd rather not manage infrastructure. It supports many Sentry SDKs because it implements the same event protocol.
5. Bugsink
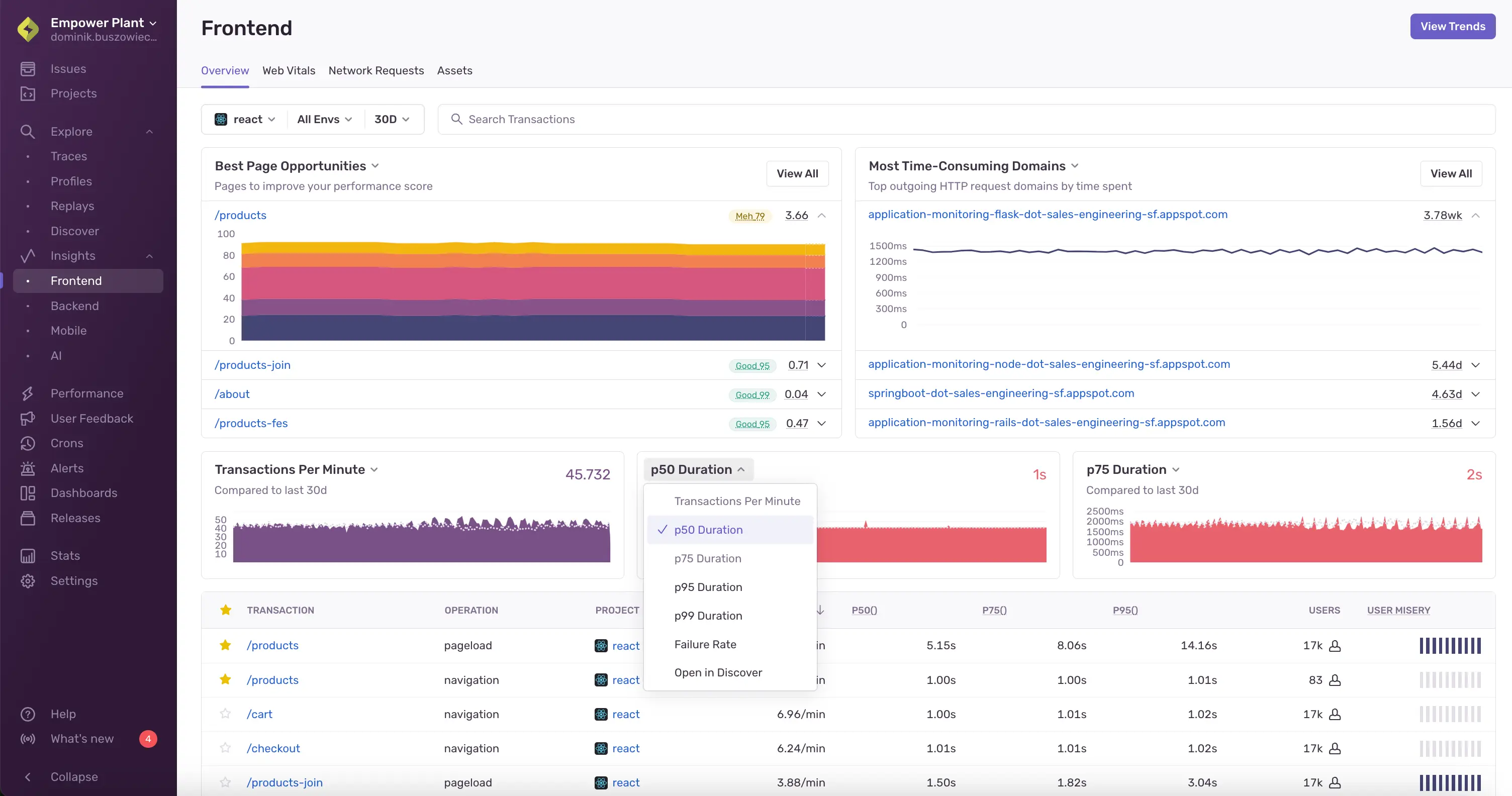
Bugsink is a lightweight, self-hosted, Sentry-SDK-compatible error tracker designed to minimise operational dependencies. It runs on minimal hardware, making it ideal for small teams or solo developers who want error tracking without operational overhead. Like GlitchTip, it accepts events from any Sentry SDK, so you switch by just changing your DSN.
Bugsink focuses on the core error tracking workflow: receiving events, grouping them, and letting you browse and manage issues. There's no performance monitoring or uptime tracking. Bugsink is source-available under the PolyForm Shield license (generally "use, but don't compete"). Self-hosting for internal use avoids vendor usage-based overages, but review the license terms if your use case involves offering it as a service. It's a solid option if you want data residency control and don't want to run Sentry's full self-hosted stack.
Category 3: Focused Error Tracking Platforms
These tools focus specifically on catching, grouping, and alerting on errors with a workflow similar to Sentry. They differentiate through pricing models, platform specialisations, or tighter integrations with specific ecosystems like mobile or CI/CD.
6. Bugsnag
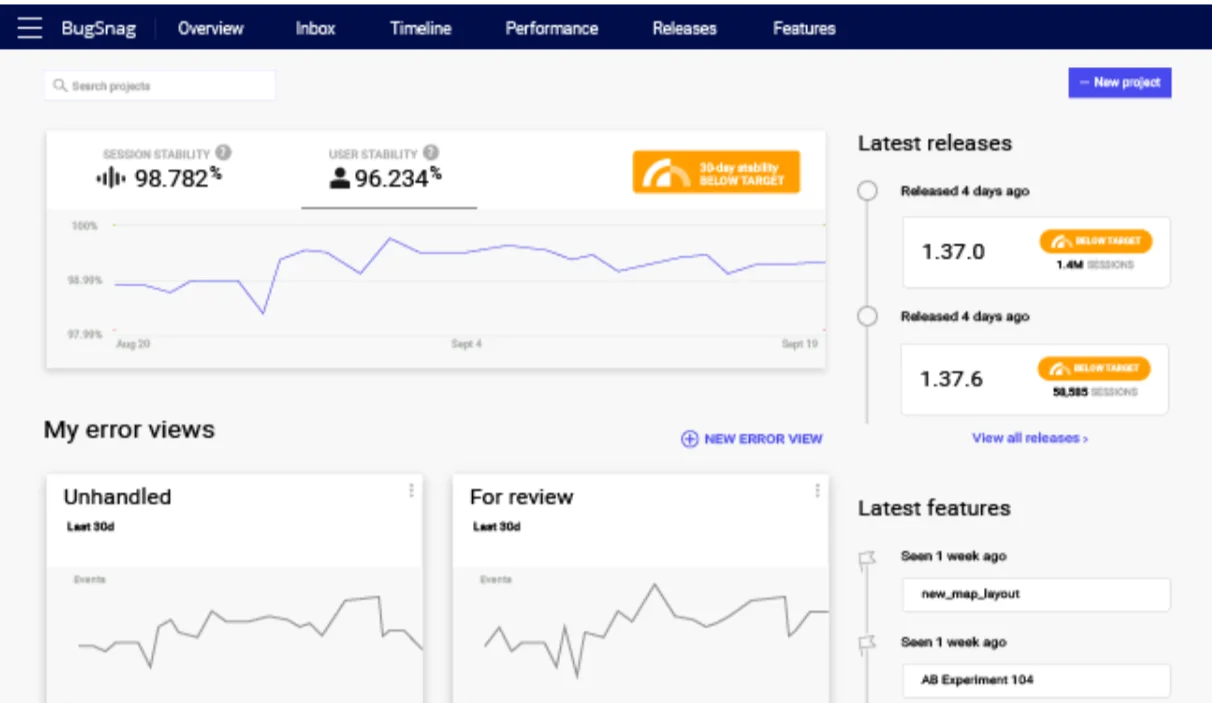
Bugsnag is an error and performance monitoring platform with strong mobile crash reporting and broader support across many application types. While Sentry supports mobile SDKs, Bugsnag provides deeper mobile-specific data, including Application Not Responding (ANR) events, Out of Memory (OOM) crashes, and the ability to filter errors by OS version, browser version, device/server environment, and any custom metadata you choose to capture.
Bugsnag's stability score gives product managers a single metric to track release health and decide whether to ship new features or fix bugs. You can correlate crashes with specific A/B test variants and track stability per release, which is more granular than what Sentry offers for mobile. Bugsnag integrates with Jira, Slack, and GitHub and supports breadcrumb collection to diagnose issues in context.
7. Raygun
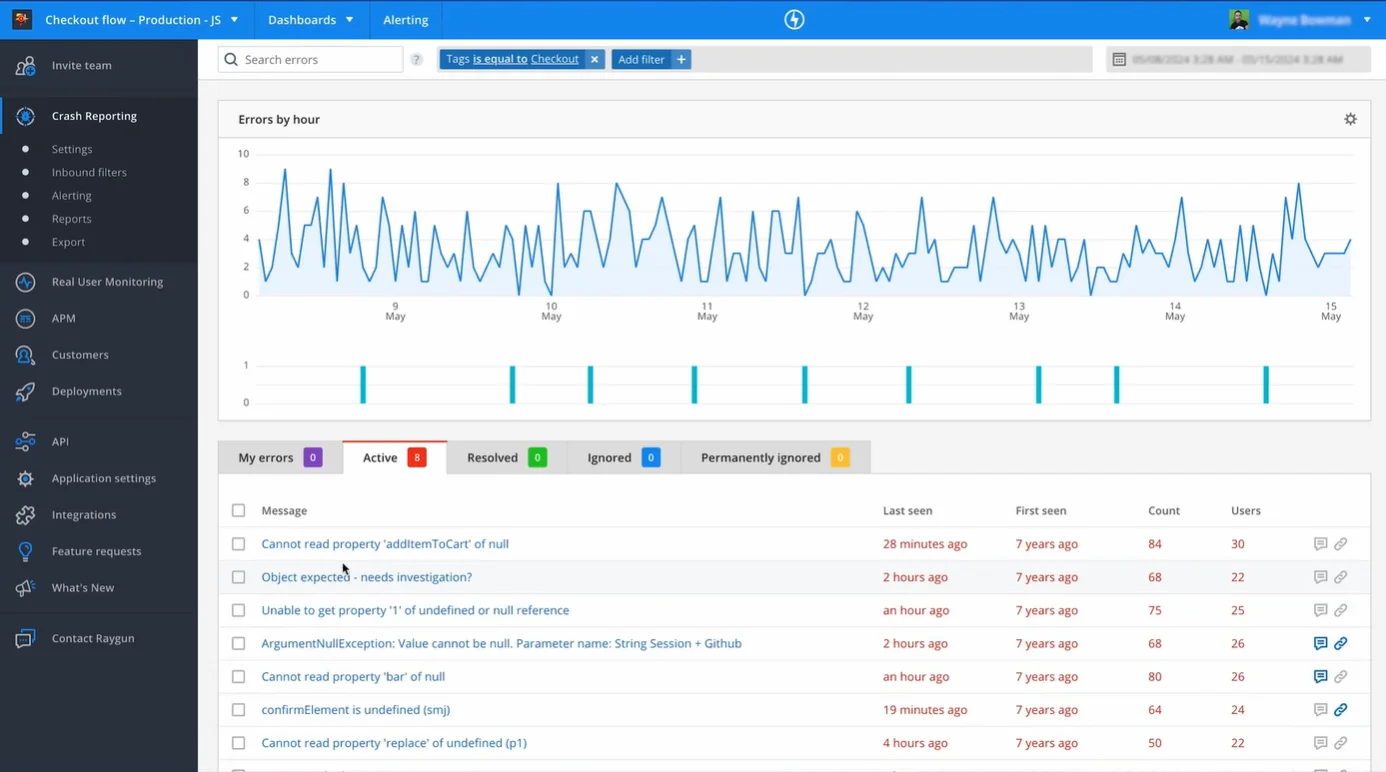
Raygun provides error tracking, real user monitoring (RUM), and application performance monitoring in one product. It's particularly strong in the .NET ecosystem but also supports JavaScript, Java, iOS, and Android. What sets Raygun apart from Sentry is its deployment tracking, which correlates error spikes with specific code deploys and helps you decide whether to roll back when a release introduces regressions.
Raygun's RUM capabilities are more deeply integrated than Sentry's, with P99 latency visuals that show how different users experience page loads across browsers, devices, and global locations. Error grouping is prioritised based on user impact rather than raw count, which helps teams focus on the issues that matter most.
8. Rollbar
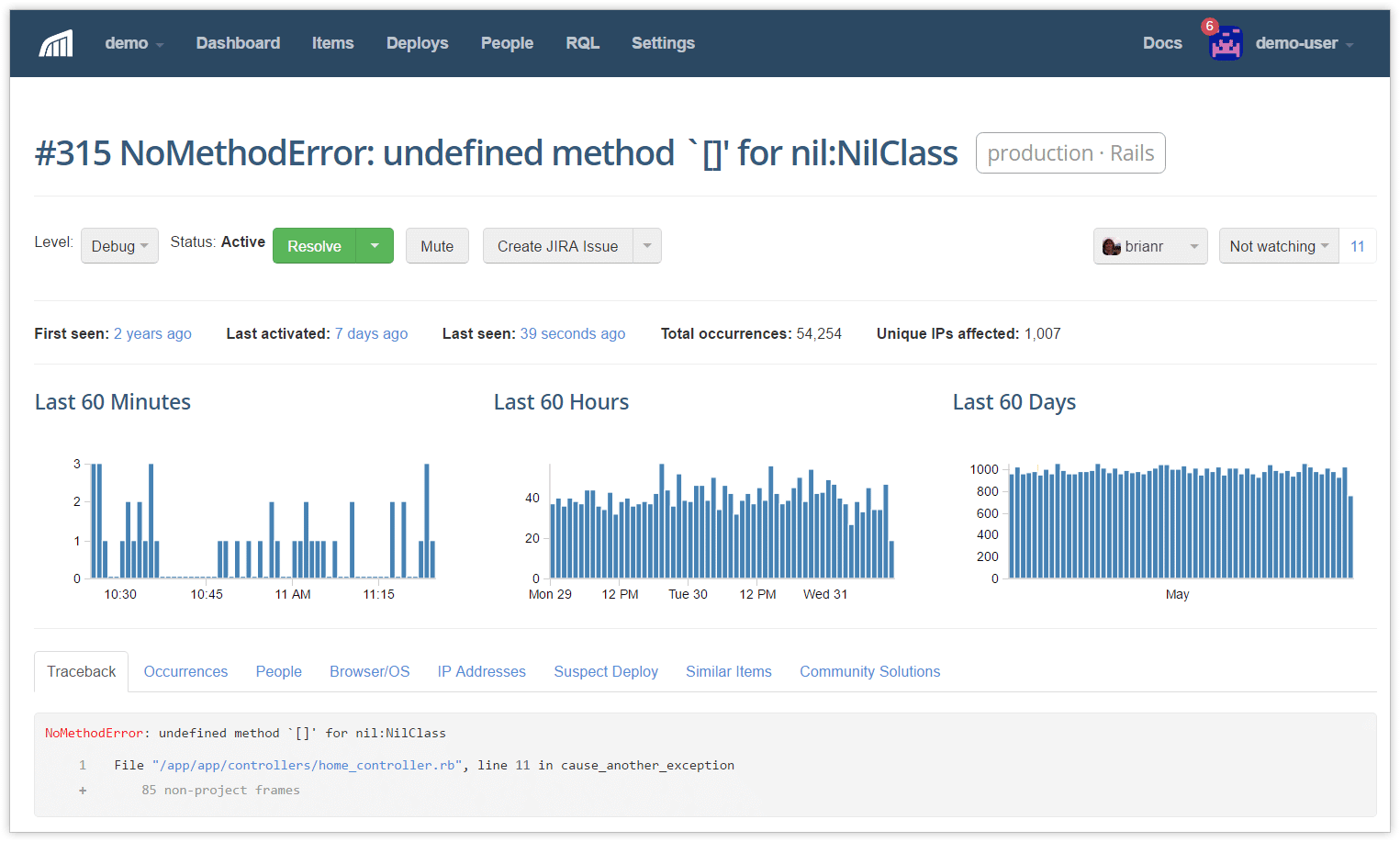
Rollbar is a lightweight error monitoring tool built for development teams that want fast, actionable error alerts without the overhead of a full observability platform. It automatically groups errors using fingerprinting algorithms to reduce noise, so instead of 10,000 duplicate alerts after a deployment, you see one grouped issue with context.
Rollbar integrates directly into your CI/CD pipeline, correlating errors with specific deploys, commits, and pull requests. It supports many popular languages and frameworks and includes "people tracking" to see which users are affected by specific errors. Compared to Sentry, Rollbar stays focused on doing error tracking well with minimal setup, without trying to expand into APM or infrastructure monitoring.
Summary: Top 8 Sentry Alternatives
| Tool | Key Differentiators vs Sentry |
|---|---|
| SigNoz | Correlates errors with traces, logs, and metrics in one platform. OpenTelemetry-native with no vendor lock-in. Per-GB pricing instead of per-event. Open source and simple to self-host. |
| New Relic | Full-stack APM with error tracking embedded in transaction traces. AI-powered anomaly detection, 700+ integrations, and infrastructure-level context beyond Sentry's scope. |
| Datadog | 1,000+ integrations, automatic service mapping, and Watchdog AI anomaly detection. Enterprise-grade but significantly more expensive with per-host pricing. |
| GlitchTip | Compatible with many Sentry SDKs and DSN format. Free to self-host with Docker Compose. Covers error tracking, performance, and uptime monitoring. |
| Bugsink | Lightweight, minimal-dependency Sentry replacement. Accepts Sentry SDK events. Source-available under PolyForm Shield. |
| Bugsnag | Deeper mobile crash analytics (ANR, OOM), stability score for release health, and A/B test variant correlation. |
| Raygun | Deployment-to-error correlation for regression identification, integrated RUM with P99 latency visuals, and user-impact-based error prioritization. |
| Rollbar | Fingerprint-based error grouping for noise reduction, CI/CD pipeline integration, and "people tracking" for affected users. |
Getting Started with SigNoz
You can choose between various deployment options in SigNoz. The easiest way to get started with SigNoz is SigNoz Cloud. We offer a 30-day free trial account with access to all features.
Those with data privacy concerns who can’t send their data outside their infrastructure can sign up for either the enterprise self-hosted or BYOC offering.
Those with the expertise to manage SigNoz themselves, or who want to start with a free, self-hosted option, can use our community edition.
