Overview
This documentation provides a step-by-step guide to setting up web vitals monitoring with OpenTelemetry traces on SigNoz.
Already sending frontend traces?
If you've followed the Sending Traces from your frontend application guide, you can skip Steps 1 and 2 below as your instrumentation file is already set up. Jump straight to Step 3 to add web vitals capture to your existing setup.
Prerequisites
- SigNoz Cloud or self-hosted account
- A web application from where you want to send web vitals
Setup
Step 1: Install dependencies
npm install web-vitals
npm install @opentelemetry/api
npm install @opentelemetry/sdk-trace-web
npm install @opentelemetry/instrumentation
npm install @opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-http
npm install @opentelemetry/context-zone
npm install @opentelemetry/resources
npm install ua-parser-js
yarn add web-vitals
yarn add @opentelemetry/api
yarn add @opentelemetry/sdk-trace-web
yarn add @opentelemetry/instrumentation
yarn add @opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-http
yarn add @opentelemetry/context-zone
yarn add @opentelemetry/resources
yarn add ua-parser-js
Read more about the dependencies
web-vitals: Core library for measuring and reporting web vitals metrics (LCP, INP, CLS, TTFB, FCP)@opentelemetry/api: Provides the core OpenTelemetry API for creating traces and spans@opentelemetry/sdk-trace-web: Web-specific implementation of OpenTelemetry tracing for browser environments@opentelemetry/instrumentation: Base package for OpenTelemetry instrumentation capabilities@opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-http: Exports traces to OpenTelemetry Protocol (OTLP) over HTTP@opentelemetry/context-zone: Manages context propagation using browser's Zone.js for async operations@opentelemetry/resources: Defines service metadata and attributes for your applicationua-parser-js: Parses user agent strings to extract browser, device, and OS information for RUM features
Step 2: Create an instrumentation file
The instrumentation file is required to setup the OTLPTraceExporter and WebTracerProvider which are used to capture web vitals as traces within your application and export them to your collector.
import { OTLPTraceExporter } from '@opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-http';
import {
WebTracerProvider,
BatchSpanProcessor,
} from '@opentelemetry/sdk-trace-web';
import { ZoneContextManager } from '@opentelemetry/context-zone';
import { resourceFromAttributes } from '@opentelemetry/resources';
const exporter = new OTLPTraceExporter({
// For the self-hosted version, please use the collector url instead.
url: `https://ingest.<INGESTION_REGION>.signoz.cloud:443/v1/traces`,
headers: {
// Optional for the self-hosted version
'signoz-ingestion-key': '<INGESTION_KEY>',
},
});
const provider = new WebTracerProvider({
resource: resourceFromAttributes({
'service.name': '<SERVICE_NAME>',
}),
spanProcessors: [new BatchSpanProcessor(exporter)],
});
provider.register({
contextManager: new ZoneContextManager(),
});
- Set the
<INGESTION_REGION>to match your SigNoz Cloud region - Replace
<INGESTION_KEY>with your SigNoz ingestion key <SERVICE_NAME>is the name of your service
import { OTLPTraceExporter } from '@opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-http';
import {
WebTracerProvider,
BatchSpanProcessor,
} from '@opentelemetry/sdk-trace-web';
import { ZoneContextManager } from '@opentelemetry/context-zone';
import { resourceFromAttributes } from '@opentelemetry/resources';
const exporter = new OTLPTraceExporter({
// For the self-hosted version, please use the collector url instead.
url: `https://ingest.<INGESTION_REGION>.signoz.cloud:443/v1/traces`,
headers: {
// Optional for the self-hosted version
'signoz-ingestion-key': '<INGESTION_KEY>',
},
});
const provider = new WebTracerProvider({
resource: resourceFromAttributes({
'service.name': '<SERVICE_NAME>',
}),
spanProcessors: [new BatchSpanProcessor(exporter)],
});
provider.register({
contextManager: new ZoneContextManager(),
});
- Set the
<INGESTION_REGION>to match your SigNoz Cloud region - Replace
<INGESTION_KEY>with your SigNoz ingestion key <SERVICE_NAME>is the name of your service
For self-hosted deployments, add the following CORS configuration to your OpenTelemetry Collector config file to allow browser requests from your frontend domain. Also, update the endpoint and remove the ingestion key header as shown in Cloud → Self-Hosted.
receivers:
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4317
http:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4318
cors:
allowed_origins:
- <YOUR_FRONTEND_URL>
allowed_headers: ['*']
This configures the OTel Collector to export traces to SigNoz Cloud using the OTLP/HTTP protocol. Read more about OTel Collector configuration here.
Step 3: Capture and export Web Vitals
Use the web-vitals library to capture key performance metrics like CLS, INP, LCP, TTFB, and FCP. These are captured through callback functions that you define and exported as traces.
import { onFCP, onINP, onTTFB, onLCP, onCLS, type Metric } from 'web-vitals';
import { trace, context, type Context } from '@opentelemetry/api';
import { hrTime } from '@opentelemetry/core';
const webVitalsTracer = trace.getTracer('web-vitals-instrumentation');
let webVitalsContext: Context | null = null;
let isContextCreated = false;
function createWebVitalsContext() {
if (!isContextCreated) {
const parentSpan = webVitalsTracer.startSpan('web-vitals');
webVitalsContext = trace.setSpan(context.active(), parentSpan);
parentSpan.end();
isContextCreated = true;
}
return webVitalsContext;
}
function createWebVitalsSpan(metric: Metric) {
const ctx = createWebVitalsContext();
if (!ctx) {
console.warn('Web vitals context not available for:', metric.name);
return;
}
const now = hrTime();
const webVitalsSpan = webVitalsTracer.startSpan(
metric.name,
{ startTime: now },
ctx
);
webVitalsSpan.setAttributes({
'web_vital.name': metric.name,
'web_vital.id': metric.id,
'web_vital.navigationType': metric.navigationType,
'web_vital.delta': metric.delta,
'web_vital.rating': metric.rating,
'web_vital.value': metric.value,
'url.full': window.location.href,
'page.title': document.title,
});
webVitalsSpan.end();
return webVitalsSpan;
}
createWebVitalsContext();
onFCP(metric => {
createWebVitalsSpan(metric);
});
onINP(metric => {
createWebVitalsSpan(metric);
});
onTTFB(metric => {
createWebVitalsSpan(metric);
});
onLCP(metric => {
createWebVitalsSpan(metric);
});
onCLS(metric => {
createWebVitalsSpan(metric);
});
import { onFCP, onINP, onTTFB, onLCP, onCLS } from 'web-vitals';
import { trace, context } from '@opentelemetry/api';
import { hrTime } from '@opentelemetry/core';
const webVitalsTracer = trace.getTracer('web-vitals-instrumentation');
let webVitalsContext = null;
let isContextCreated = false;
function createWebVitalsContext() {
if (!isContextCreated) {
const parentSpan = webVitalsTracer.startSpan('web-vitals');
webVitalsContext = trace.setSpan(context.active(), parentSpan);
parentSpan.end();
isContextCreated = true;
}
return webVitalsContext;
}
function createWebVitalsSpan(metric) {
const ctx = createWebVitalsContext();
if (!ctx) {
console.warn('Web vitals context not available for:', metric.name);
return;
}
const now = hrTime();
const webVitalsSpan = webVitalsTracer.startSpan(
metric.name,
{ startTime: now },
ctx
);
webVitalsSpan.setAttributes({
'web_vital.name': metric.name,
'web_vital.id': metric.id,
'web_vital.navigationType': metric.navigationType,
'web_vital.delta': metric.delta,
'web_vital.rating': metric.rating,
'web_vital.value': metric.value,
'url.full': window.location.href,
'page.title': document.title,
});
webVitalsSpan.end();
return webVitalsSpan;
}
createWebVitalsContext();
onFCP(metric => {
createWebVitalsSpan(metric);
});
onINP(metric => {
createWebVitalsSpan(metric);
});
onTTFB(metric => {
createWebVitalsSpan(metric);
});
onLCP(metric => {
createWebVitalsSpan(metric);
});
onCLS(metric => {
createWebVitalsSpan(metric);
});
Validate
The captured web vitals can be viewed in the Traces Explorer. Each web-vital trace contains the 5 web vitals as child spans.
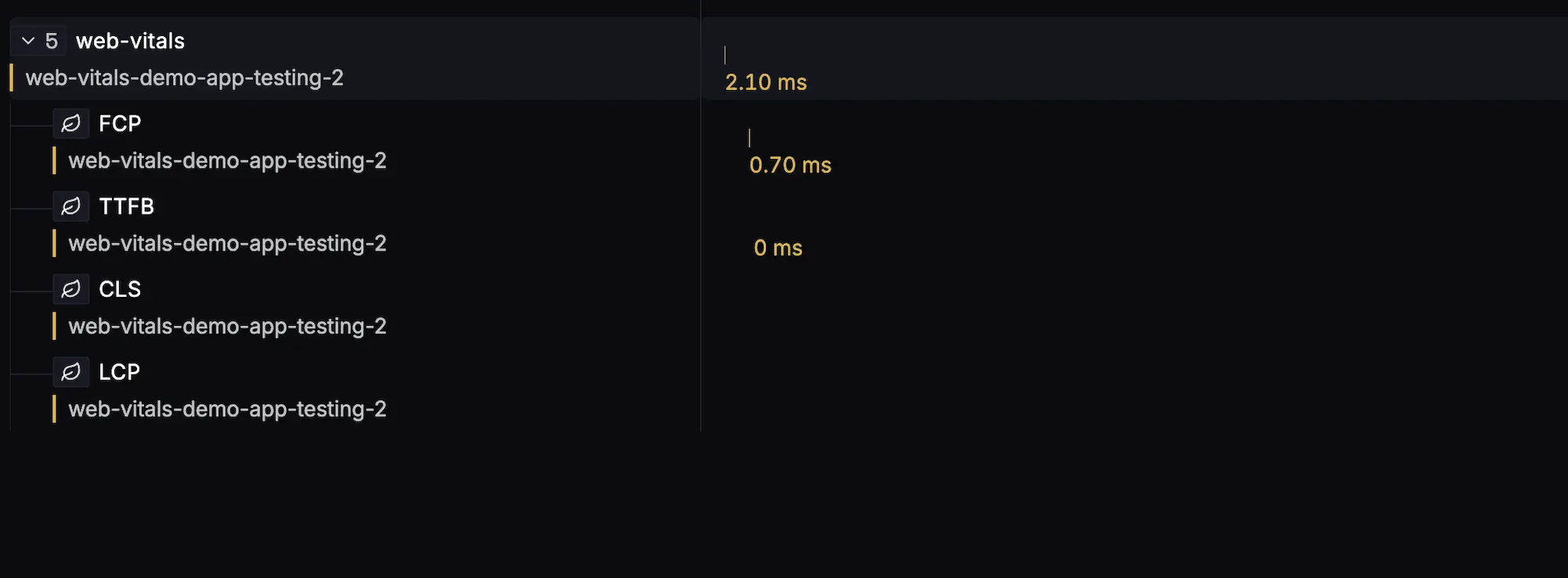
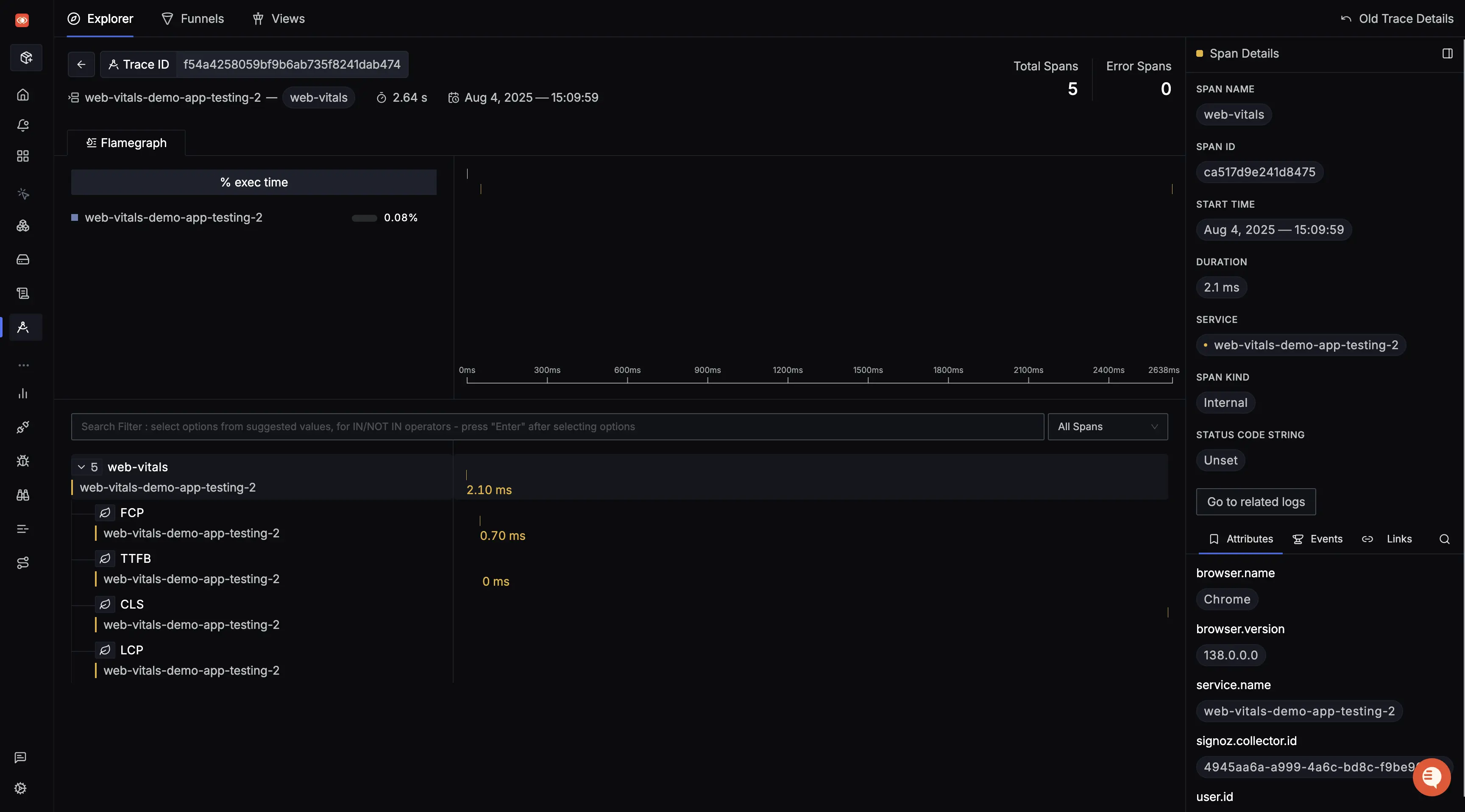
Attaching additional identifiers to your Web Vitals
You can enrich web vitals with additional metadata like browser type, user ID, page URL etc. to enable real user monitoring (RUM)-like insights.
To do so, you need to write a custom implementation of SpanProcessor which will intercept all your exported spans and attach additional attributes to them.
import type { SpanProcessor } from '@opentelemetry/sdk-trace-web';
import { UAParser } from 'ua-parser-js';
export const CONSTANTS = {
USER_ID: 'user.id',
USER_AGENT_ORIGINAL: 'user_agent.original',
USER_AGENT_VERSION: 'user_agent.version',
USER_AGENT_NAME: 'user_agent.name',
};
function getBrowserInfo() {
// You can add your custom browser tracking logic here as well.
// This example uses the ua-parser-js package.
const parser = new UAParser();
const result = parser.getResult();
return {
userAgentOriginal: result.ua || '',
userAgentVersion: result.browser.version || '',
userAgentName: result.browser.name || '',
};
}
function getUserId() {
// You can add your custom user ID tracking logic here as well.
// This example uses localStorage.
const userId = localStorage.getItem('userId');
return {
userId: userId || '',
};
}
const CustomSpanProcessor: SpanProcessor = {
onStart: span => {
const userData = getUserId();
const browserInfo = getBrowserInfo();
span.setAttribute(CONSTANTS.USER_ID, userData.userId);
span.setAttribute(
CONSTANTS.USER_AGENT_ORIGINAL,
browserInfo.userAgentOriginal
);
span.setAttribute(
CONSTANTS.USER_AGENT_VERSION,
browserInfo.userAgentVersion
);
span.setAttribute(CONSTANTS.USER_AGENT_NAME, browserInfo.userAgentName);
},
onEnd: () => Promise.resolve(),
forceFlush: () => Promise.resolve(),
shutdown: () => Promise.resolve(),
};
export default CustomSpanProcessor;
import { UAParser } from 'ua-parser-js';
export const CONSTANTS = {
USER_ID: 'user.id',
USER_AGENT_ORIGINAL: 'user_agent.original',
USER_AGENT_VERSION: 'user_agent.version',
USER_AGENT_NAME: 'user_agent.name',
};
function getBrowserInfo() {
// You can add your custom browser tracking logic here as well.
// This example uses the ua-parser-js package.
const parser = new UAParser();
const result = parser.getResult();
return {
userAgentOriginal: result.ua || '',
userAgentVersion: result.browser.version || '',
userAgentName: result.browser.name || '',
};
}
function getUserId() {
// You can add your custom user ID tracking logic here as well.
// This example uses localStorage.
const userId = localStorage.getItem('userId');
return {
userId: userId || '',
};
}
const CustomSpanProcessor = {
onStart: span => {
const userData = getUserId();
const browserInfo = getBrowserInfo();
span.setAttribute(CONSTANTS.USER_ID, userData.userId);
span.setAttribute(
CONSTANTS.USER_AGENT_ORIGINAL,
browserInfo.userAgentOriginal
);
span.setAttribute(
CONSTANTS.USER_AGENT_VERSION,
browserInfo.userAgentVersion
);
span.setAttribute(CONSTANTS.USER_AGENT_NAME, browserInfo.userAgentName);
},
onEnd: () => Promise.resolve(),
forceFlush: () => Promise.resolve(),
shutdown: () => Promise.resolve(),
};
export default CustomSpanProcessor;
Update your instrumentation file to include this processor.
const provider = new WebTracerProvider({
resource: resourceFromAttributes({
'service.name': '<SERVICE_NAME>',
}),
spanProcessors: [new BatchSpanProcessor(exporter), CustomSpanProcessor],
})
Now every span exported will include these additional contextual attributes.
Setup Dashboard and alerts
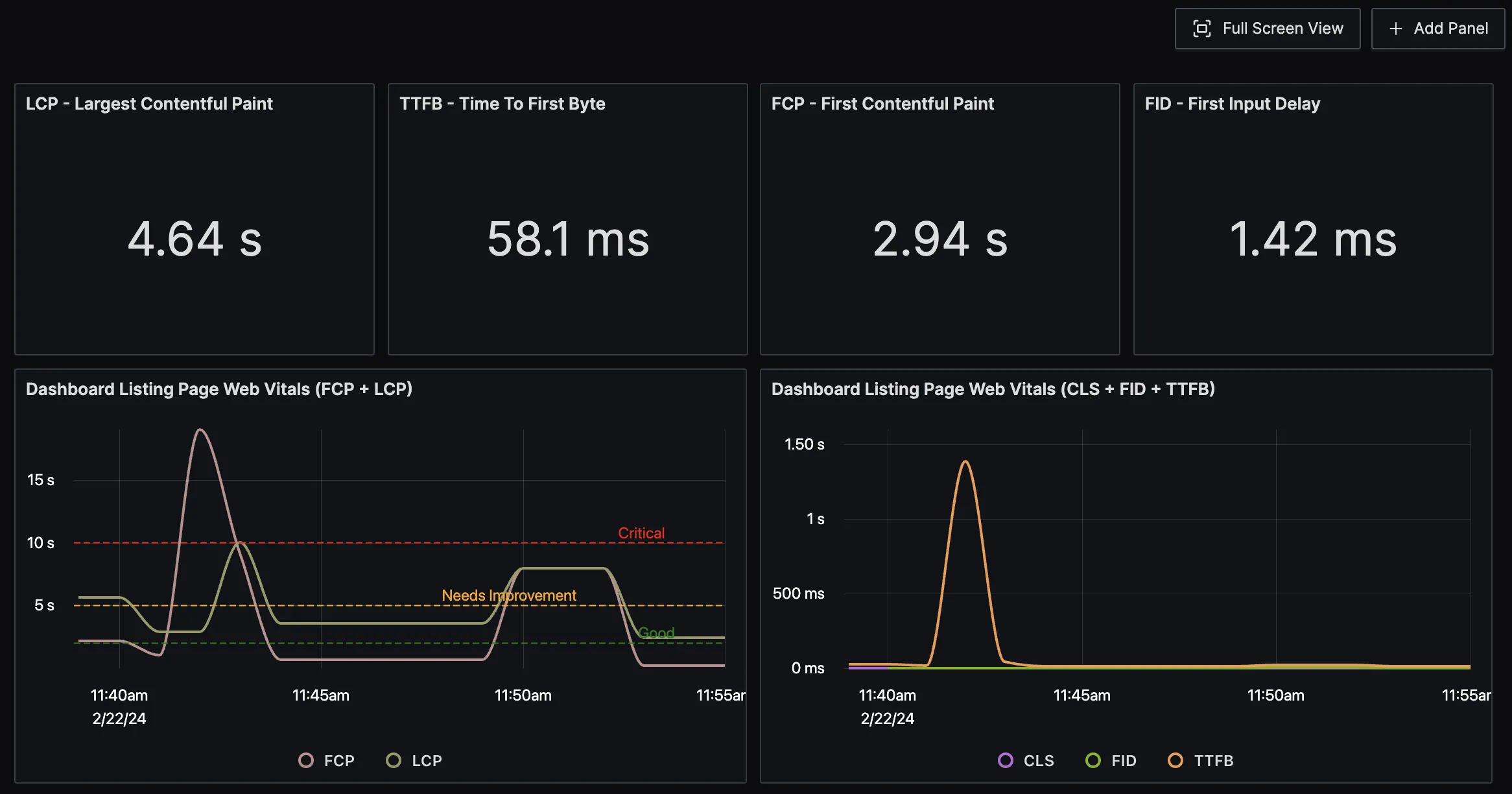
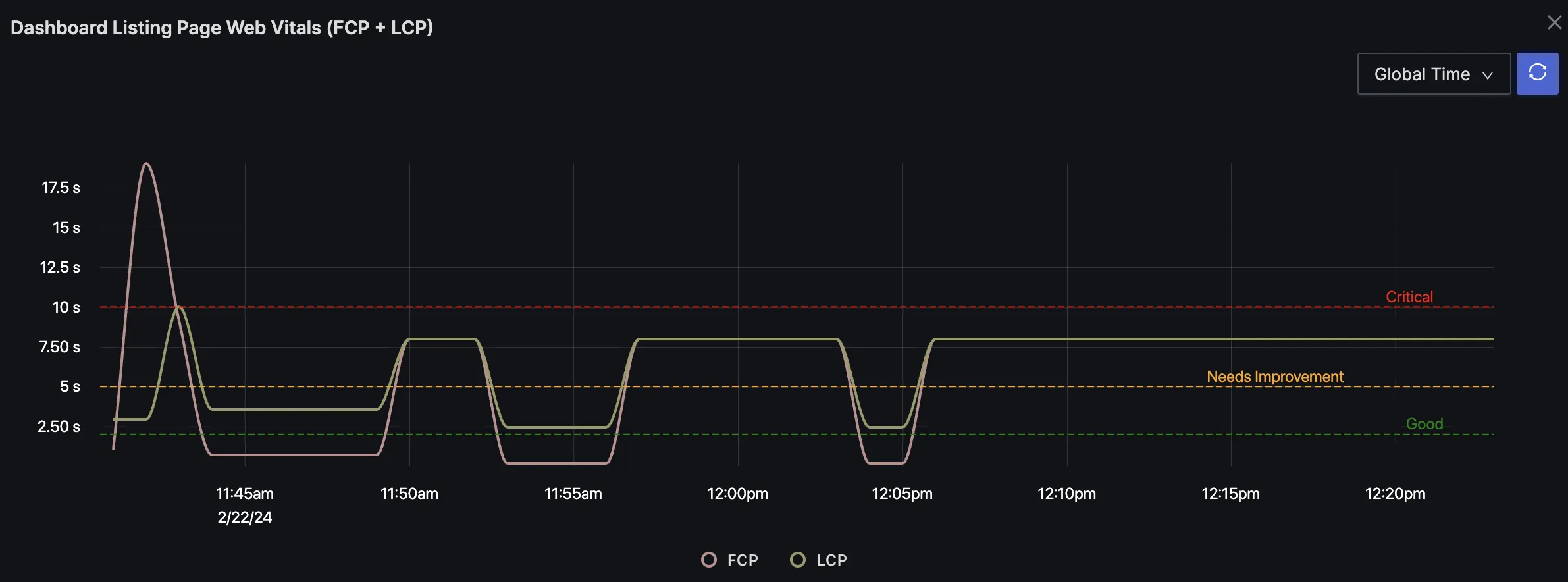
SigNoz charts support thresholds with color coding. For example, the graph below shows three thresholds for good, needs improvement, and critical levels.
Out of Box Dashboard
You can import our out-of-the-box Dashboard for web vitals monitoring
Demo Application
We have set up a Demo React application that demonstrates monitoring Core Web Vitals with traces using OpenTelemetry and sending them to SigNoz.
