Overview
This document provides a detailed walkthrough on how to send Google Cloud Functions metrics to SigNoz.
Prerequisites
- A Google Cloud account with administrative privileges or Cloud Functions Admin privileges.
- Access to a project in Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- The Google Cloud Functions APIs must be enabled. You can follow this guide to learn how to enable an API in Google Cloud.
Setup
Get started with Cloud Function Configuration
Follow these steps to create the Cloud Function:
Step 1: Go to your GCP console and search for Cloud Functions, go to Functions, and click on CREATE FUNCTION.

Create Cloud Functions
Step 2: Enter the following information to create a Cloud Function:
- Environment: Select "2nd gen."
- Function name: Enter a name for your Cloud Function.
- Region: The default region of your GCP account will be used.
- Trigger: Specify how the Cloud Function will be triggered.
- Trigger Type: Select "HTTPS" to enable triggering the Cloud Function via a URL.
- Authentication: Decide if the invocation needs to be authenticated or unauthenticated. For this demonstration, we have chosen unauthenticated invocation.
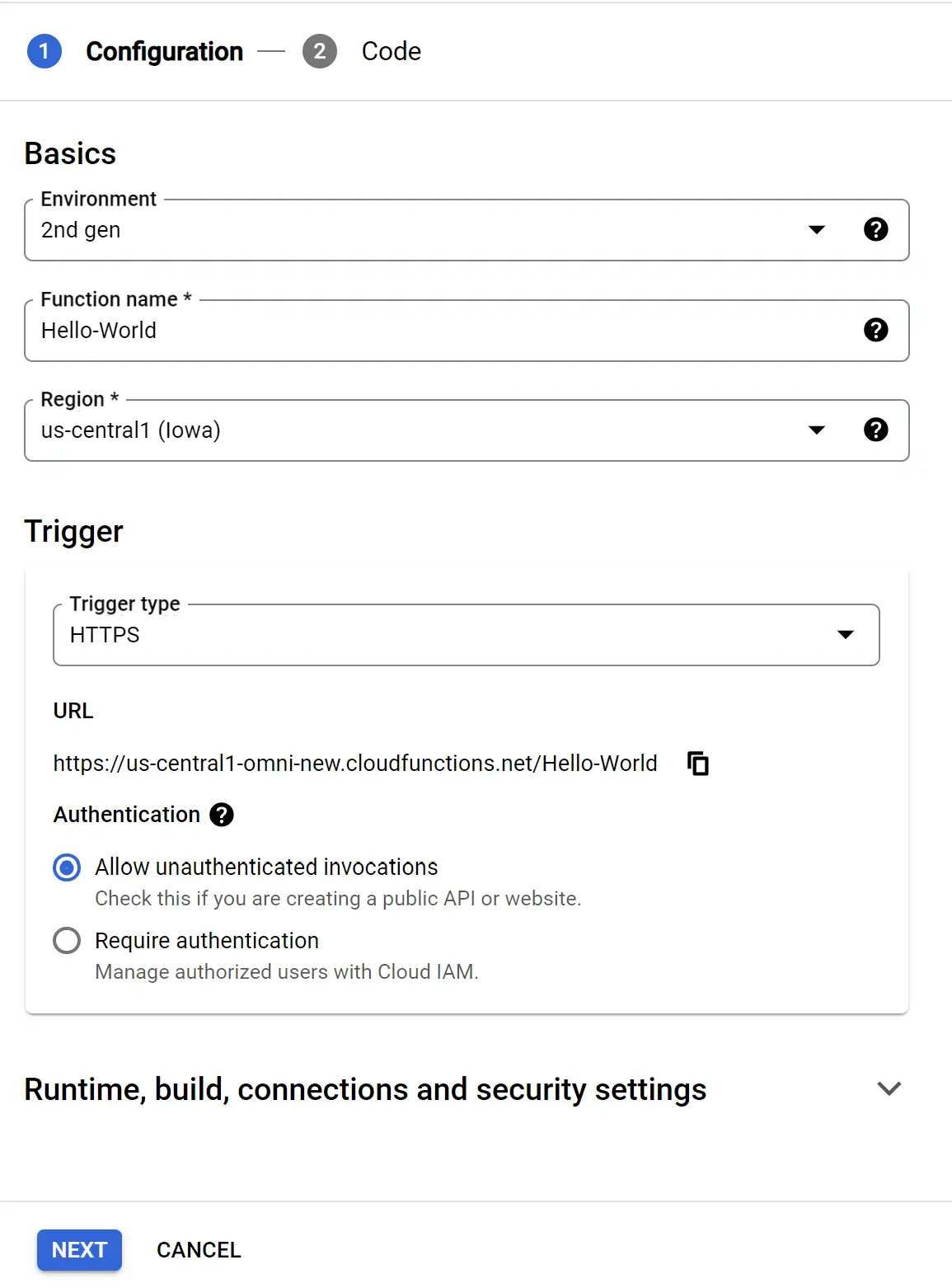
Configure Cloud Function
Step 3: Click on the NEXT button, which will bring us to the page where we can add our code. Here we are using a simple python Hello World! script.
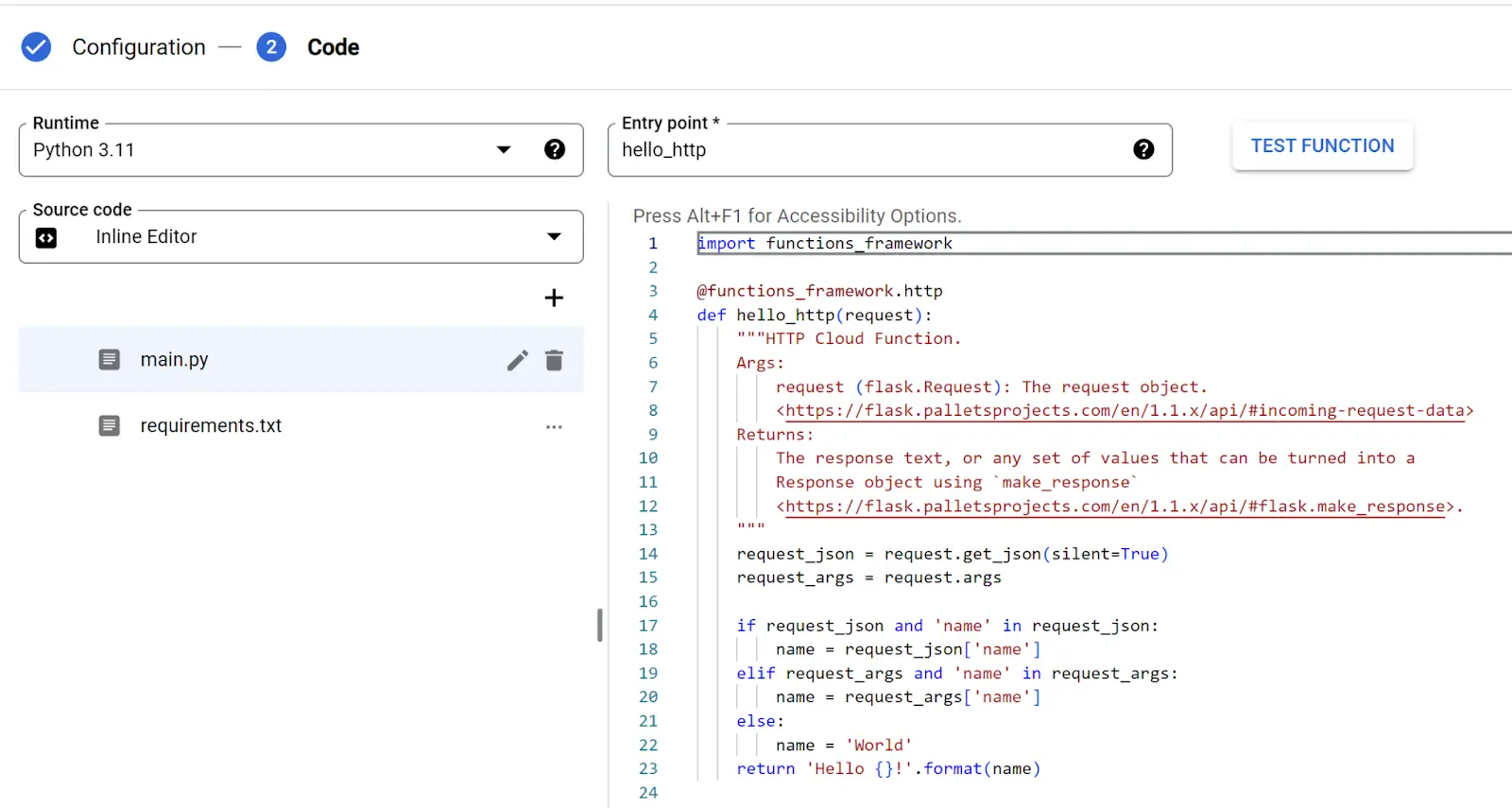
Set entrypoint and source code
Add code to the Google Cloud Function
For this demonstration, we will be using python 3.11.
Here is the complete code for the main.py file, along with a summary of its functionality.
import functions_framework
@functions_framework.http
def hello_http(request):
"""HTTP Cloud Function.
Args:
request (flask.Request): The request object.
<https://flask.palletsprojects.com/en/1.1.x/api/#incoming-request-data>
Returns:
The response text, or any set of values that can be turned into a
Response object using `make_response`
<https://flask.palletsprojects.com/en/1.1.x/api/#flask.make_response>.
"""
request_json = request.get_json(silent=True)
request_args = request.args
if request_json and 'name' in request_json:
name = request_json['name']
elif request_args and 'name' in request_args:
name = request_args['name']
else:
name = 'World'
return 'Hello {}!'.format(name)
Import the Framework: The
functions_frameworkmodule is imported to handle HTTP requests.Define the Function: The
hello_httpfunction is defined to process HTTP requests. This function is triggered whenever the Cloud Function receives an HTTP request.Handle the Request:
- The function checks if the incoming request contains JSON data (
request_json). - It also checks for URL query parameters (
request_args).
- The function checks if the incoming request contains JSON data (
Determine the Name to Greet:
- If the JSON body contains a key
name, it uses its value. - If the query parameters contain a key
name, it uses its value. - If neither is provided, it defaults to 'World'.
- If the JSON body contains a key
Return the Response:
- The function returns a greeting message: 'Hello {name}!', where '{name}'' is replaced with the determined name.
Testing your cloud function
Step 1: After completing the deployment, navigate to the TRIGGER section to obtain the URL to invoke the function.
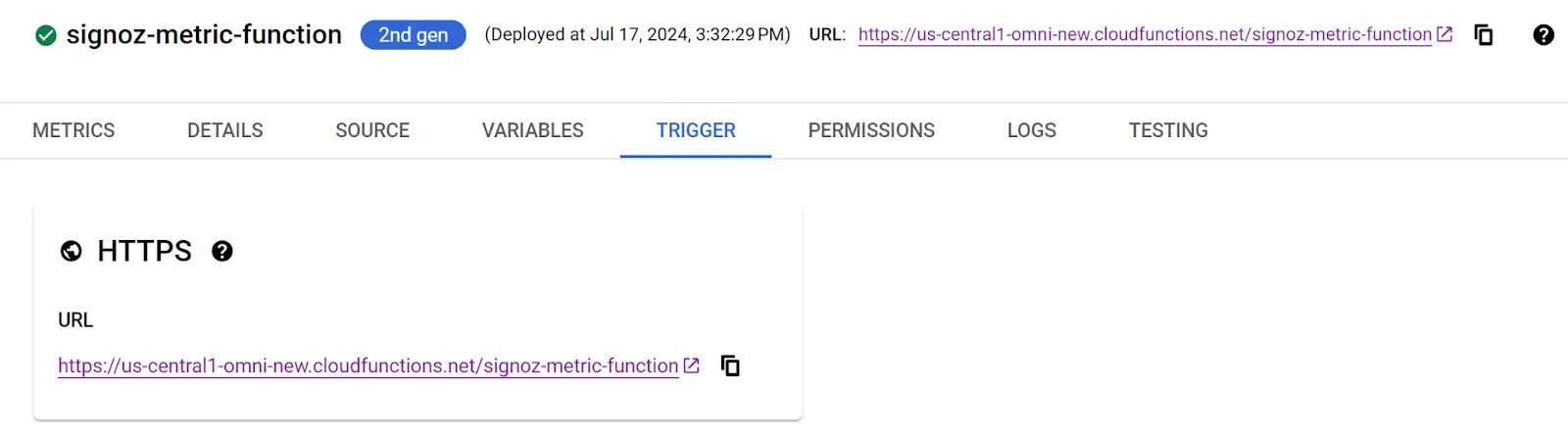
Deploying Cloud Function
Step 2: Hit the URL that you have obtained, and you should see the function output.
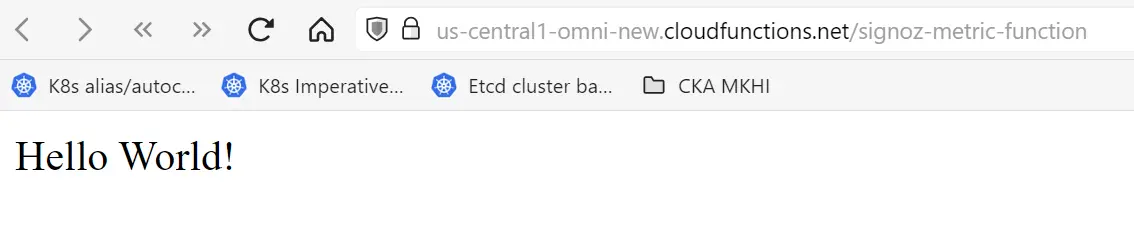
Trigger Cloud function.
Deploy OpenTelemetry to scrape the metrics from Google Cloud Monitoring
Step 1: Install and configure OpenTelemetry for scraping the metrics from Google Cloud Monitoring. Follow OpenTelemetry Binary Usage in Virtual Machine guide for detailed instructions.
Note that googlecloudmonitoring receiver is supported only from version 0.112.0 and above of opentelemetry-collector. So, ensure you download and use the appropriate release.
Step 2: Create config.yaml.
Under the googlecloudmonitoring receiver, you need to specify the metrics that you want to capture in the metrics_list. You can include all the metrics that you would like to capture for Cloud Function, see the available metrics for Cloud Function.
Here is the config.yaml file for capturing Cloud Function metrics:
receivers:
googlecloudmonitoring:
collection_interval: 5m # Can be specified in seconds (s), minutes (m), or hours (h)
project_id: my-project-id
metrics_list:
- metric_name: "cloudfunctions.googleapis.com/function/execution_count"
- metric_name: "cloudfunctions.googleapis.com/function/execution_times"
- metric_name: "cloudfunctions.googleapis.com/function/instance_count"
- metric_name: "cloudfunctions.googleapis.com/function/network_egress"
- metric_name: "cloudfunctions.googleapis.com/function/user_memory_bytes"
- metric_name: "cloudfunctions.googleapis.com/function/active_instances"
processors:
resource/env:
attributes:
- key: deployment.environment
value: prod
action: upsert
batch: {}
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: "ingest.{region}.signoz.cloud:443"
tls:
insecure: false
headers:
"signoz-ingestion-key": "<your-ingestion-key>"
service:
pipelines:
metrics:
receivers: [googlecloudmonitoring]
processors: [resource/env,batch]
exporters: [otlp]
Depending on the choice of your region for SigNoz cloud, the otlp endpoint will vary according to this table.
| Region | Endpoint |
|---|---|
| US | ingest.us.signoz.cloud:443 |
| IN | ingest.in.signoz.cloud:443 |
| EU | ingest.eu.signoz.cloud:443 |
After successful configuration start the OTel Collector using following command:
./otelcol-contrib --config ./config.yaml &> otelcol-output.log & echo "$!" > otel-pid
Step 3: If the configurations are configured correctly, you can see the output logs from OpenTelemtry as follows:
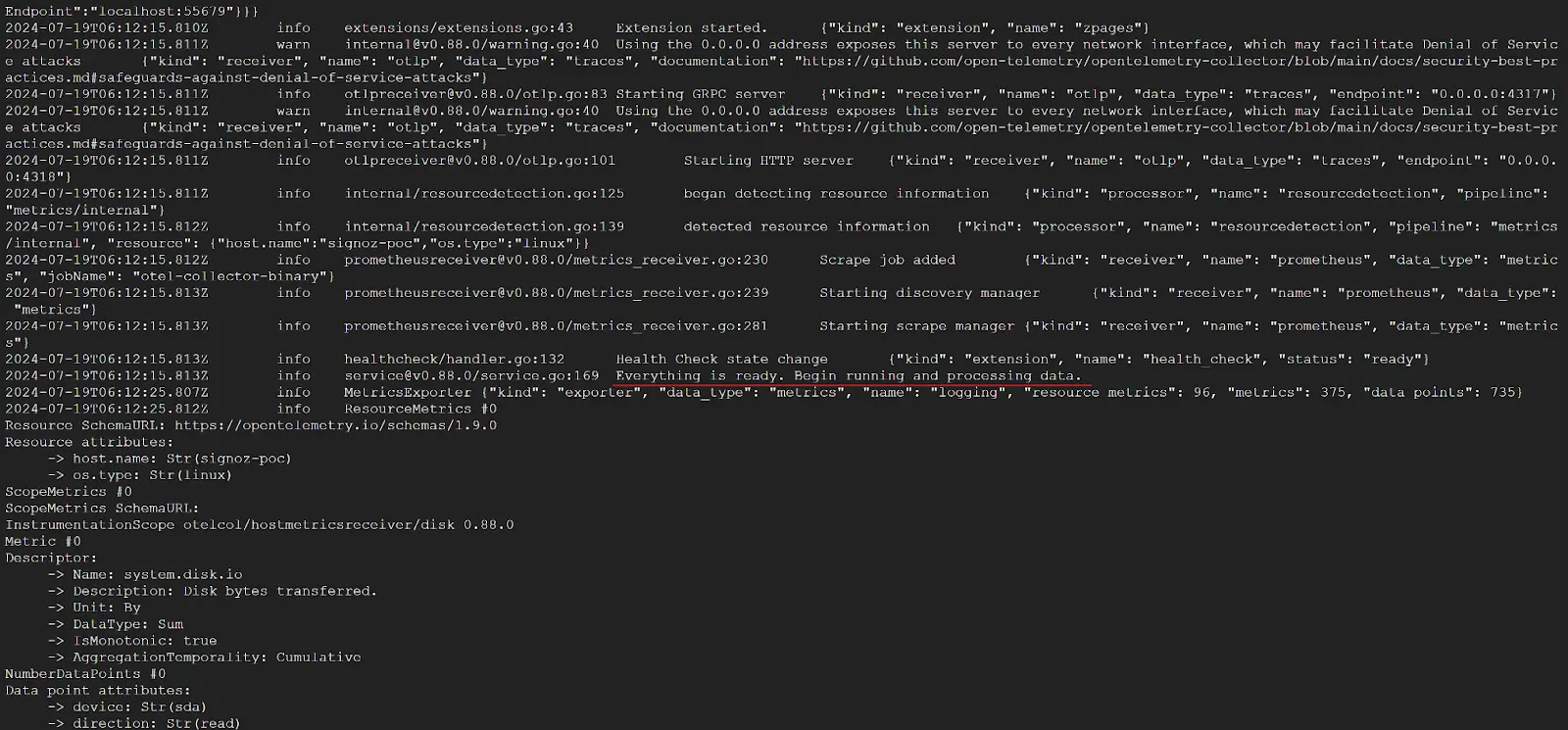
Viewing OTel Collector Logs
Send and Visualize the metrics obtained by OpenTelemetry in SigNoz
Step 1: Go to the SigNoz Cloud URL and head over to the dashboard.
Step 2: If not already created, create a new dashboard. You can create the dashboard and multiple panel under it by following the instructions here.
Step 3: While creating the panel, select metric for Cloud Function.
All metrics starting with cloudfunctions_googleapis_com_ have been collected from Cloud Function.
For example, cloudfunctions_googleapis_com_function_execution_times is one of the metrics which is collected.
Here is the sample dashboard for Cloud Function:
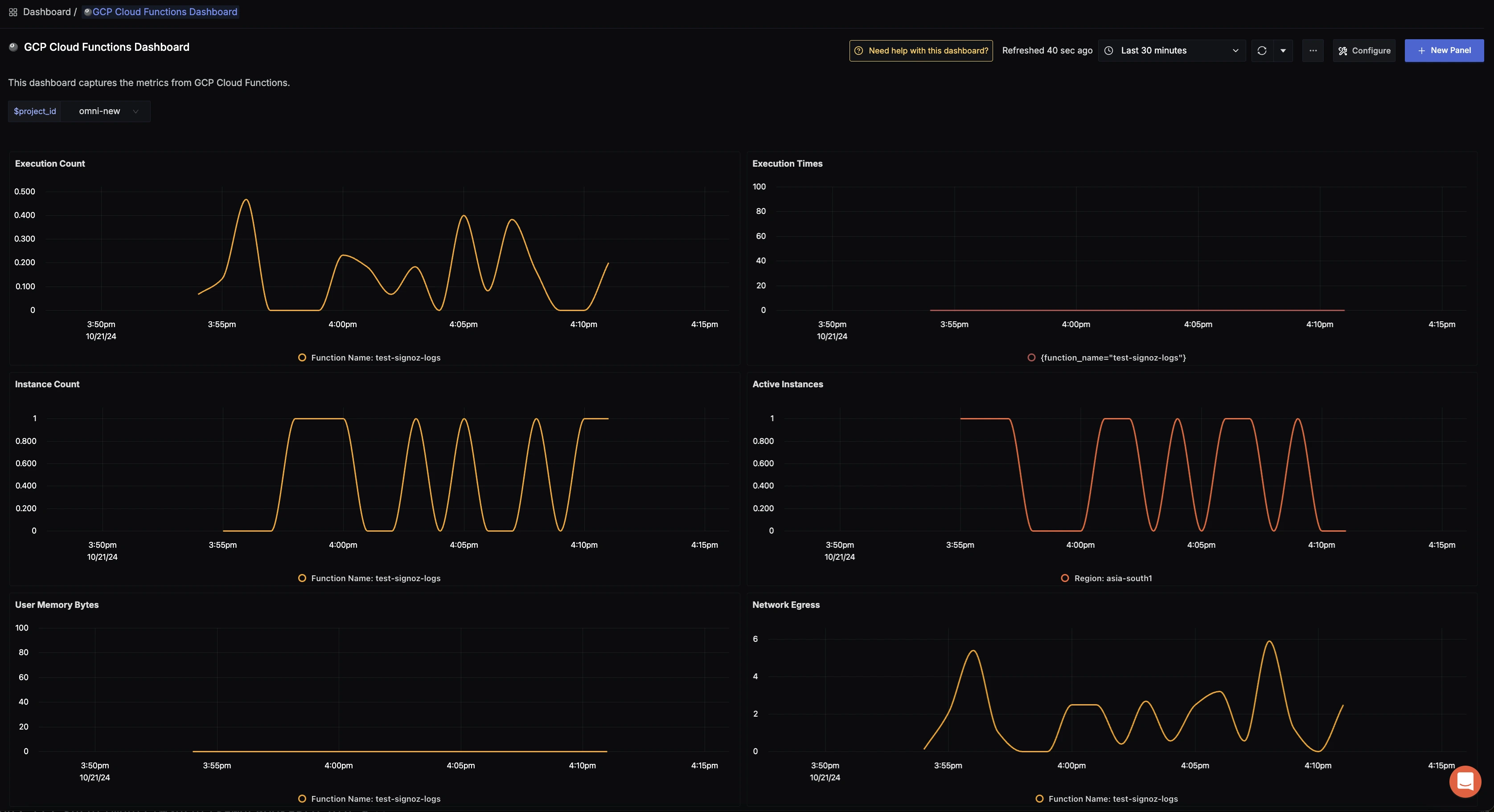
GCP Cloud Function dashboard
Troubleshooting
If you run into any problems while setting up monitoring for your Cloud Function's metrics with SigNoz, consider these troubleshooting steps:
- Verify Configuration: Double-check your
config.yamlfile to ensure all settings, including the ingestion key and endpoint, are correct. - Review Logs: Look at the logs of both your Cloud Function and the OpenTelemetry Collector to identify any error messages or warnings that might provide insights into what’s going wrong.
- Update Dependencies: Ensure all relevant packages and dependencies are up-to-date to avoid compatibility issues.
- Consult Documentation: Review the SigNoz and OpenTelemetry documentation for any additional troubleshooting of the common issues.s
Prerequisites
- A Google Cloud account with administrative privileges or Cloud Functions Admin privileges.
- Access to a project in Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- The Google Cloud Functions APIs must be enabled. You can follow this guide to learn how to enable an API in Google Cloud.
Setup
Get started with Cloud Function Configuration
Follow these steps to create the Cloud Function:
Step 1: Go to your GCP console and search for Cloud Functions, go to Functions, and click on CREATE FUNCTION.

Create Cloud Functions
Step 2: Enter the following information to create a Cloud Function:
- Environment: Select "2nd gen."
- Function name: Enter a name for your Cloud Function.
- Region: The default region of your GCP account will be used.
- Trigger: Specify how the Cloud Function will be triggered.
- Trigger Type: Select "HTTPS" to enable triggering the Cloud Function via a URL.
- Authentication: Decide if the invocation needs to be authenticated or unauthenticated. For this demonstration, we have chosen unauthenticated invocation.

Configure Cloud Function
Step 3: Click on the NEXT button, which will bring us to the page where we can add our code. Here we are using a simple python Hello World! script.

Set entrypoint and source code
Add code to the Google Cloud Function
For this demonstration, we will be using python 3.11.
Here is the complete code for the main.py file, along with a summary of its functionality.
import functions_framework
@functions_framework.http
def hello_http(request):
"""HTTP Cloud Function.
Args:
request (flask.Request): The request object.
<https://flask.palletsprojects.com/en/1.1.x/api/#incoming-request-data>
Returns:
The response text, or any set of values that can be turned into a
Response object using `make_response`
<https://flask.palletsprojects.com/en/1.1.x/api/#flask.make_response>.
"""
request_json = request.get_json(silent=True)
request_args = request.args
if request_json and 'name' in request_json:
name = request_json['name']
elif request_args and 'name' in request_args:
name = request_args['name']
else:
name = 'World'
return 'Hello {}!'.format(name)
Import the Framework: The
functions_frameworkmodule is imported to handle HTTP requests.Define the Function: The
hello_httpfunction is defined to process HTTP requests. This function is triggered whenever the Cloud Function receives an HTTP request.Handle the Request:
- The function checks if the incoming request contains JSON data (
request_json). - It also checks for URL query parameters (
request_args).
- The function checks if the incoming request contains JSON data (
Determine the Name to Greet:
- If the JSON body contains a key
name, it uses its value. - If the query parameters contain a key
name, it uses its value. - If neither is provided, it defaults to 'World'.
- If the JSON body contains a key
Return the Response:
- The function returns a greeting message: 'Hello {name}!', where '{name}' is replaced with the determined name.
Testing your Cloud Function
Step 1: After completing the deployment, navigate to the TRIGGER section to obtain the URL to invoke the function.

Deploying Cloud Function
Step 2: Hit the URL that you have obtained, and you should see the function output.

Trigger Cloud function.
Deploying a Self-Hosted SigNoz in a Docker container
Step 1: The deployment process of the Self-Hosted SigNoz can be found in official documentation.
Step 2: Make sure all the containers are running in a Healthy state.
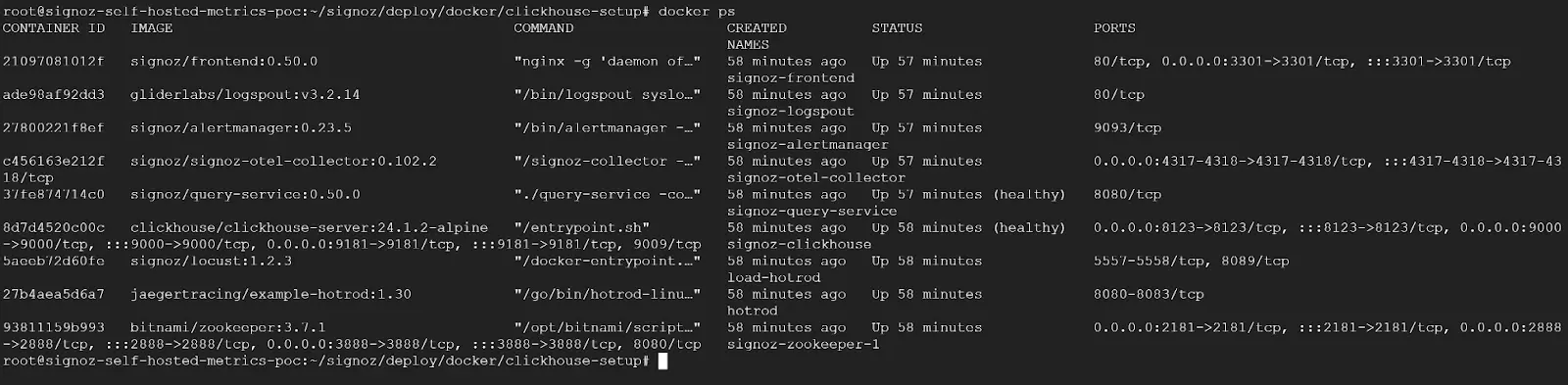
SigNoz Self-Hosted using Docker.
Note that googlecloudmonitoring receiver is supported only from version 0.112.0 and above of opentelemetry-collector. So, ensure you download and use the appropriate release.
The self-hosted SigNoz setup also includes the OTel collector in the bundle. Docker will deploy the OTel collector beside SigNoz as a container. The same OTel collector can be used to directly receive any signals, otherwise, if one more OTel Collector is required for a more granular collection, we can add an additional independent OTel collector, see Using Central OTel collector in between tab.
Apart from using the native OTel collector present in the docker from the previous method, we can also deploy an additional independent OTel collector which can act as an additional collector in this setup for more granular metrics collection.
Step 1: Install and configure OpenTelemetry to scrape the metrics from Google Cloud Monitoring. Add the following code block to the OpenTelemetry configuration file. Under exporters, we should have an exporter pointing to our SigNoz self-host setup. For example, in the below snippet, the endpoint-ip would be the address of the VM in which the SigNoz self-host setup is present.
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: "<endpoint-ip>:4317"
tls:
insecure: true
debug:
verbosity: normal
Step 2: After successful configuration, start the OTel service.
Please make appropriate changes to the networking connections (adding network to security groups, opening ports, etc.) on your VMs as per your setup.
Configuring config.yaml
Here is the config.yaml file for capturing Cloud Function metrics:
receivers:
googlecloudmonitoring:
collection_interval: 5m # Can be specified in seconds (s), minutes (m), or hours (h)
project_id: my-project-id
metrics_list:
- metric_name: "cloudfunctions.googleapis.com/function/execution_count"
- metric_name: "cloudfunctions.googleapis.com/function/execution_times"
- metric_name: "cloudfunctions.googleapis.com/function/instance_count"
- metric_name: "cloudfunctions.googleapis.com/function/network_egress"
- metric_name: "cloudfunctions.googleapis.com/function/user_memory_bytes"
- metric_name: "cloudfunctions.googleapis.com/function/active_instances"
processors:
resource/env:
attributes:
- key: deployment.environment
value: prod
action: upsert
batch: {}
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: "<endpoint-ip>:4317"
tls:
insecure: true
debug:
verbosity: normal
service:
pipelines:
metrics:
receivers: [googlecloudmonitoring]
processors: [resource/env,batch]
exporters: [otlp]
You can include all the metrics that you would like to capture for Cloud Function, see the available metrics for Cloud Function.
If the configurations are configured correctly, you can see the output logs from OpenTelemtry as follows:

Viewing OTel Collector Logs
Visualize the metrics in Self-Hosted SigNoz
Step 1: Go to your Self-Hosted SigNoz UI, and navigate to the Self-Hosted SigNoz dashboard. Click on the Dashboards section to view the metrics. Create a new dashboard (If not already present ). The default Self-Hosted SigNoz dashboard endpoint would be http://<Self-Hosted SigNoz-host-ip>:3301, however, the URL can be different based on how you have set up the infrastructure.
Step 2: If not already created, create a new dashboard. You can create the dashboard and multiple panel under it by following the instructions here.
Step 3: While creating the panel, select metric for Cloud Function.
All metrics starting with cloudfunctions_googleapis_com_ have been collected from Cloud Function.
For example, cloudfunctions_googleapis_com_function_execution_times is one of the metrics which is collected.
Here is the sample dashboard for Cloud Function:

GCP Cloud Function dashboard
Troubleshooting
If you run into any problems while setting up monitoring for your Cloud Function's metrics with SigNoz, consider these troubleshooting steps:
- Verify Configuration: Double-check your
config.yamlfile to ensure all settings, including the ingestion key and endpoint, are correct. - Verify Docker container logs: Check if all the containers are running properly, and not unexpectedly crashed.
- Review Logs: Look at the logs of both your Cloud Function and the OpenTelemetry Collector to identify any error messages or warnings that might provide insights into what’s going wrong.
- Update Dependencies: Ensure all relevant packages and dependencies are up-to-date to avoid compatibility issues.
- Consult Documentation: Review the SigNoz and OpenTelemetry documentation for any additional troubleshooting of the common issues.
