This guide shows you how to instrument your Go application with OpenTelemetry and send traces to SigNoz. Instrument your Go services with the OpenTelemetry Go SDK and send traces to SigNoz Cloud or a self-hosted collector.
Prerequisites
- Go 1.21 or later
- A SigNoz Cloud account or self-hosted SigNoz instance
- Your application code
Send traces to SigNoz
Step 1. Set environment variables
Set the following environment variables to configure the OpenTelemetry exporter:
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT="https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443"
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS="signoz-ingestion-key=<your-ingestion-key>"
export OTEL_SERVICE_NAME="<service-name>"
Verify these values:
<region>: Your SigNoz Cloud region<your-ingestion-key>: Your SigNoz ingestion key<service-name>: A descriptive name for your service (e.g.,payment-service)
Step 1. Set environment variables
Add these environment variables to your deployment manifest:
env:
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT
value: 'https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443'
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS
value: 'signoz-ingestion-key=<your-ingestion-key>'
- name: OTEL_SERVICE_NAME
value: '<service-name>'
Verify these values:
<region>: Your SigNoz Cloud region<your-ingestion-key>: Your SigNoz ingestion key<service-name>: A descriptive name for your service (e.g.,payment-service)
Step 1. Set environment variables (PowerShell)
$env:OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT = "https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443"
$env:OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS = "signoz-ingestion-key=<your-ingestion-key>"
$env:OTEL_SERVICE_NAME = "<service-name>"
Verify these values:
<region>: Your SigNoz Cloud region<your-ingestion-key>: Your SigNoz ingestion key<service-name>: A descriptive name for your service
Step 1. Set environment variables in Dockerfile
Add environment variables to your Dockerfile:
FROM golang:1.21-alpine AS builder
WORKDIR /app
COPY go.mod go.sum ./
RUN go mod download
COPY . .
RUN go build -o main .
FROM alpine:latest
WORKDIR /app
COPY /app/main .
# Set OpenTelemetry environment variables
ENV OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT="https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443"
ENV OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS="signoz-ingestion-key=<your-ingestion-key>"
ENV OTEL_SERVICE_NAME="<service-name>"
CMD ["./main"]
Or pass them at runtime using docker run:
docker run -e OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT="https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443" \
-e OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS="signoz-ingestion-key=<your-ingestion-key>" \
-e OTEL_SERVICE_NAME="<service-name>" \
your-image:latest
Verify these values:
<region>: Your SigNoz Cloud region<your-ingestion-key>: Your SigNoz ingestion key<service-name>: A descriptive name for your service (e.g.,payment-service)
Step 2. Install OpenTelemetry packages
Run the following command in your project directory:
go get \
go.opentelemetry.io/otel \
go.opentelemetry.io/otel/sdk \
go.opentelemetry.io/otel/exporters/otlp/otlptrace/otlptracegrpc \
go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/net/http/otelhttp
Step 3. Create the tracer initialization
Create a file named tracing.go in your project:
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/exporters/otlp/otlptrace/otlptracegrpc"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/propagation"
"go.opentelemetry.io/otel/sdk/resource"
sdktrace "go.opentelemetry.io/otel/sdk/trace"
semconv "go.opentelemetry.io/otel/semconv/v1.21.0"
)
func initTracer(ctx context.Context) (func(context.Context) error, error) {
// Reads OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT and OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS from environment
exporter, err := otlptracegrpc.New(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Reads OTEL_SERVICE_NAME from environment and adds host/process/OS attributes
res, err := resource.New(ctx,
resource.WithFromEnv(),
resource.WithHost(),
resource.WithOS(),
resource.WithProcess(),
)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
tp := sdktrace.NewTracerProvider(
sdktrace.WithBatcher(exporter),
sdktrace.WithResource(res),
)
// Makes the tracer available to instrumentation libraries
otel.SetTracerProvider(tp)
// Propagates trace context across service boundaries using W3C standards
otel.SetTextMapPropagator(propagation.NewCompositeTextMapPropagator(
propagation.TraceContext{},
propagation.Baggage{},
))
return tp.Shutdown, nil
}
Step 4. Instrument your application
Here's a complete example using net/http with automatic instrumentation:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"os/signal"
"go.opentelemetry.io/contrib/instrumentation/net/http/otelhttp"
)
func main() {
ctx, cancel := signal.NotifyContext(context.Background(), os.Interrupt)
defer cancel()
shutdown, err := initTracer(ctx)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to initialize tracer: %v", err)
}
defer shutdown(ctx)
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprint(w, "Hello from instrumented server!")
})
// Wrap with otelhttp middleware for automatic instrumentation
handler := otelhttp.NewHandler(mux, "my-service")
log.Println("Server starting on :8080")
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", handler))
}
Library instrumentation
Choose your Go framework or library to add automatic instrumentation without leaving this page. Use the categories below to pick a specific integration.
Databases & Caches
GORM
This guide shows you how to add OpenTelemetry instrumentation to GORM. Complete the core Go instrumentation setup first.
Install GORM OpenTelemetry plugin
go get gorm.io/gorm
go get gorm.io/plugin/opentelemetry/tracing
Configure GORM with tracing
import (
"gorm.io/driver/postgres"
"gorm.io/gorm"
"gorm.io/plugin/opentelemetry/tracing"
)
func initDB() (*gorm.DB, error) {
dsn := "host=localhost user=postgres password=secret dbname=myapp port=5432"
db, err := gorm.Open(postgres.Open(dsn), &gorm.Config{})
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
// Add OpenTelemetry tracing plugin to instrument all operations
if err := db.Use(tracing.NewPlugin()); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return db, nil
}
// Use WithContext to propagate trace context
db.WithContext(ctx).Where("id = ?", userID).First(&user)
Tested with:
- Go 1.25.1
- OpenTelemetry Go SDK v1.38.0
- gorm.io/gorm v1.31.1
- gorm.io/plugin/opentelemetry v0.1.16
Validate
After running your instrumented application, verify traces appear in SigNoz:
- Generate some traffic by making requests to your application.
- Open SigNoz and navigate to Traces.
- Click Refresh and look for new trace entries from your application.
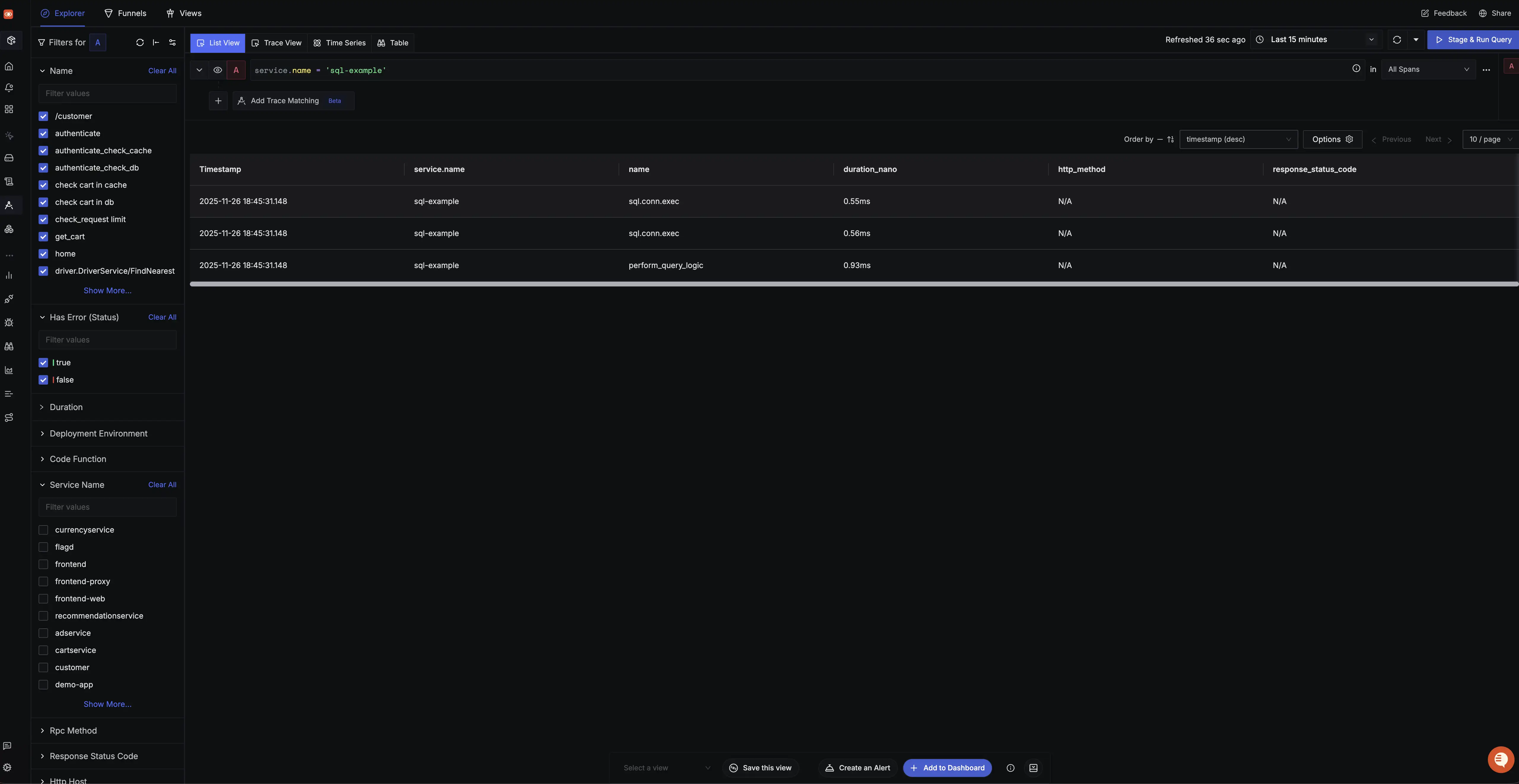
- Click on any trace to view detailed span information and timing.

Troubleshooting
Why don't traces appear in SigNoz?
Check environment variables are set:
echo $OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT
echo $OTEL_SERVICE_NAME
Verify network connectivity:
# For SigNoz Cloud
curl -v https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443/v1/traces
Why do OTLP exports fail with connection refused?
- VM: Verify the endpoint URL and that your firewall allows outbound HTTPS
- Kubernetes: Ensure the OTel Collector service is running and accessible
- Self-hosted: Confirm the collector is listening on the expected port
Why do spans go missing for specific requests?
Ensure you're using instrumented versions of HTTP clients and database drivers. Check if you have not set a sampling rate type which might affect sending spans or span rate.
Setup OpenTelemetry Collector (Optional)
What is the OpenTelemetry Collector?
Think of the OTel Collector as a middleman between your app and SigNoz. Instead of your application sending data directly to SigNoz, it sends everything to the Collector first, which then forwards it along.
Why use it?
- Cleaning up data — Filter out noisy traces you don't care about, or remove sensitive info before it leaves your servers.
- Keeping your app lightweight — Let the Collector handle batching, retries, and compression instead of your application code.
- Adding context automatically — The Collector can tag your data with useful info like which Kubernetes pod or cloud region it came from.
- Future flexibility — Want to send data to multiple backends later? The Collector makes that easy without changing your app.
See Switch from direct export to Collector for step-by-step instructions to convert your setup.
For more details, see Why use the OpenTelemetry Collector? and the Collector configuration guide.
Next steps
- Send logs from your Go application using popular logging libraries: Logrus, Zap, or Zerolog
- Correlate traces with logs to accelerate triage across signals
- Set up alerts for your Go application
- Create dashboards to visualize metrics
- Need to create custom spans or add attributes yourself? Use the Manual Instrumentation in Go guide once the base setup is in place.
