Prerequisites
- Node.js version 18 or higher
- An instance of SigNoz (either Cloud or Self-Hosted)
- An existing Node.js application
Send logs to SigNoz
This guide will walk you through instrumenting your Node.js application to send logs from the default console logger to SigNoz using the OpenTelemetry (OTel) SDK.
Step 1: Install dependencies
Install the required OpenTelemetry packages:
npm install --save @opentelemetry/api-logs \
@opentelemetry/sdk-logs \
@opentelemetry/exporter-logs-otlp-http \
@opentelemetry/resources \
@opentelemetry/semantic-conventions \
express
npm install --save @opentelemetry/api-logs \
@opentelemetry/sdk-logs \
@opentelemetry/exporter-logs-otlp-http \
@opentelemetry/resources \
@opentelemetry/semantic-conventions \
express \
typescript \
ts-node \
@types/node \
@types/express
yarn add @opentelemetry/api-logs \
@opentelemetry/sdk-logs \
@opentelemetry/exporter-logs-otlp-http \
@opentelemetry/resources \
@opentelemetry/semantic-conventions \
express
yarn add @opentelemetry/api-logs \
@opentelemetry/sdk-logs \
@opentelemetry/exporter-logs-otlp-http \
@opentelemetry/resources \
@opentelemetry/semantic-conventions \
express \
typescript \
ts-node \
@types/node \
@types/express
Step 2: Set environment variables
Set the following environment variables to configure the OpenTelemetry exporter:
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT="https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443"
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS="signoz-ingestion-key=<your-ingestion-key>"
export OTEL_SERVICE_NAME="nodejs-console-app"
Verify these values:
<region>: Your SigNoz Cloud region.<your-ingestion-key>: Your SigNoz ingestion key.
If using a local OTel Collector (VM), use:
export OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT="http://localhost:4318"
# Do not set OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS
Add these environment variables to your deployment manifest:
env:
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT
value: 'https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443'
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS
value: 'signoz-ingestion-key=<your-ingestion-key>'
- name: OTEL_SERVICE_NAME
value: 'nodejs-console-app'
Verify these values:
<region>: Your SigNoz Cloud region.<your-ingestion-key>: Your SigNoz ingestion key.
Avoiding Duplicate Logs
If using the k8s-infra chart (which auto-collects container logs), disable log collection for this application to prevent duplicates.
Create a Dockerfile in your project root:
FROM node:20-alpine
WORKDIR /app
# Copy package files
COPY package*.json ./
# Install dependencies
RUN npm install
# Copy instrumentation files and application code
COPY logger.js ./
COPY console-instrumentation.js ./
COPY . .
# Set OpenTelemetry environment variables
ENV OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT="https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443"
ENV OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS="signoz-ingestion-key=<your-ingestion-key>"
ENV OTEL_SERVICE_NAME="nodejs-console-app"
# Expose application port
EXPOSE 3000
# Start the application
CMD ["node", "index.js"]
Build and run the container:
# Build the image
docker build -t nodejs-console-app .
# Run the container
docker run -p 3000:3000 nodejs-console-app
Replace the placeholders in the Dockerfile:
<region>: Your SigNoz Cloud region.<your-ingestion-key>: Ingestion key for your SigNoz Cloud, see Ingestion Keys.
Set environment variables in PowerShell:
$env:OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT = "https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443"
$env:OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS = "signoz-ingestion-key=<your-ingestion-key>"
$env:OTEL_SERVICE_NAME = "nodejs-console-app"
Replace the placeholders:
<region>: Your SigNoz Cloud region.<your-ingestion-key>: Ingestion key for your SigNoz Cloud, see Ingestion Keys.
Step 3: Configure OpenTelemetry Logger
Create a new file called logger.js or logger.ts in your project root. This file reads the configuration from the environment variables set in the previous step.
const {
LoggerProvider,
BatchLogRecordProcessor,
} = require("@opentelemetry/sdk-logs");
const { OTLPLogExporter } = require("@opentelemetry/exporter-logs-otlp-http");
const { resourceFromAttributes } = require("@opentelemetry/resources");
const { ATTR_SERVICE_NAME } = require("@opentelemetry/semantic-conventions");
// Create a resource with your service information
const resource = resourceFromAttributes({
[ATTR_SERVICE_NAME]: process.env.OTEL_SERVICE_NAME || "nodejs-console-app",
});
// Configure the OTLP exporter
// It automatically reads OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT and OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS
const logExporter = new OTLPLogExporter({});
// Create and configure the logger provider
const loggerProvider = new LoggerProvider({
resource,
processors: [new BatchLogRecordProcessor(logExporter)], // Configure batch processor
});
module.exports = loggerProvider;
import {
LoggerProvider,
BatchLogRecordProcessor,
} from "@opentelemetry/sdk-logs";
import { OTLPLogExporter } from "@opentelemetry/exporter-logs-otlp-http";
import { resourceFromAttributes } from "@opentelemetry/resources";
import { ATTR_SERVICE_NAME } from "@opentelemetry/semantic-conventions";
// Create a resource with your service information
const resource = resourceFromAttributes({
[ATTR_SERVICE_NAME]: process.env.OTEL_SERVICE_NAME || "nodejs-console-app",
});
// Configure the OTLP exporter
// It automatically reads OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT and OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS
const logExporter = new OTLPLogExporter({});
// Create and configure the logger provider
const loggerProvider = new LoggerProvider({
resource,
processors: [new BatchLogRecordProcessor(logExporter)], // Configure batch processor
});
export default loggerProvider;
Step 4: Instrument the Default Console Logger
Create a new file called console-instrumentation.js or console-instrumentation.ts in your project root. This file wraps the default console methods to send logs to OpenTelemetry:
require("@opentelemetry/api-logs");
const loggerProvider = require("./logger");
// Get a logger instance
const logger = loggerProvider.getLogger("default", "1.0.0");
// Store original console methods
const originalConsole = {
log: console.log,
info: console.info,
warn: console.warn,
error: console.error,
debug: console.debug,
};
// Map severity levels
const SeverityNumber = {
DEBUG: 5,
INFO: 9,
WARN: 13,
ERROR: 17,
};
// Override console methods
console.log = function (...args) {
const message = args
.map((arg) => (typeof arg === "object" ? JSON.stringify(arg) : String(arg)))
.join(" ");
logger.emit({
severityNumber: SeverityNumber.INFO,
severityText: "INFO",
body: message,
attributes: {},
});
originalConsole.log.apply(console, args);
};
console.info = function (...args) {
const message = args
.map((arg) => (typeof arg === "object" ? JSON.stringify(arg) : String(arg)))
.join(" ");
logger.emit({
severityNumber: SeverityNumber.INFO,
severityText: "INFO",
body: message,
attributes: {},
});
originalConsole.info.apply(console, args);
};
console.warn = function (...args) {
const message = args
.map((arg) => (typeof arg === "object" ? JSON.stringify(arg) : String(arg)))
.join(" ");
logger.emit({
severityNumber: SeverityNumber.WARN,
severityText: "WARN",
body: message,
attributes: {},
});
originalConsole.warn.apply(console, args);
};
console.error = function (...args) {
const message = args
.map((arg) => (typeof arg === "object" ? JSON.stringify(arg) : String(arg)))
.join(" ");
logger.emit({
severityNumber: SeverityNumber.ERROR,
severityText: "ERROR",
body: message,
attributes: {},
});
originalConsole.error.apply(console, args);
};
console.debug = function (...args) {
const message = args
.map((arg) => (typeof arg === "object" ? JSON.stringify(arg) : String(arg)))
.join(" ");
logger.emit({
severityNumber: SeverityNumber.DEBUG,
severityText: "DEBUG",
body: message,
attributes: {},
});
originalConsole.debug.apply(console, args);
};
import "@opentelemetry/api-logs";
import loggerProvider from "./logger";
// Get a logger instance
const logger = loggerProvider.getLogger("default", "1.0.0");
// Store original console methods
const originalConsole = {
log: console.log,
info: console.info,
warn: console.warn,
error: console.error,
debug: console.debug,
};
// Map severity levels
const SeverityNumber = {
DEBUG: 5,
INFO: 9,
WARN: 13,
ERROR: 17,
};
// Override console methods
console.log = function (...args: any[]) {
const message = args
.map((arg) => (typeof arg === "object" ? JSON.stringify(arg) : String(arg)))
.join(" ");
logger.emit({
severityNumber: SeverityNumber.INFO,
severityText: "INFO",
body: message,
attributes: {},
});
originalConsole.log.apply(console, args);
};
console.info = function (...args: any[]) {
const message = args
.map((arg) => (typeof arg === "object" ? JSON.stringify(arg) : String(arg)))
.join(" ");
logger.emit({
severityNumber: SeverityNumber.INFO,
severityText: "INFO",
body: message,
attributes: {},
});
originalConsole.info.apply(console, args);
};
console.warn = function (...args: any[]) {
const message = args
.map((arg) => (typeof arg === "object" ? JSON.stringify(arg) : String(arg)))
.join(" ");
logger.emit({
severityNumber: SeverityNumber.WARN,
severityText: "WARN",
body: message,
attributes: {},
});
originalConsole.warn.apply(console, args);
};
console.error = function (...args: any[]) {
const message = args
.map((arg) => (typeof arg === "object" ? JSON.stringify(arg) : String(arg)))
.join(" ");
logger.emit({
severityNumber: SeverityNumber.ERROR,
severityText: "ERROR",
body: message,
attributes: {},
});
originalConsole.error.apply(console, args);
};
console.debug = function (...args: any[]) {
const message = args
.map((arg) => (typeof arg === "object" ? JSON.stringify(arg) : String(arg)))
.join(" ");
logger.emit({
severityNumber: SeverityNumber.DEBUG,
severityText: "DEBUG",
body: message,
attributes: {},
});
originalConsole.debug.apply(console, args);
};
Step 5: Initialize Instrumentation in Your Application
Import the instrumentation at the very top of your main application file (e.g., index.js or index.ts):
// This must be the first import
require('./console-instrumentation')
// Your application code follows
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
console.log('Application started')
console.error('This is an error message')
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.info('Server listening on port 3000')
})
// This must be the first import
import './console-instrumentation';
// Your application code follows
import express from 'express';
const app = express();
console.log('Application started');
console.error('This is an error message');
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.info('Server listening on port 3000');
});
Step 6: Run Your Application
Run your application:
node index.js
npx ts-node index.ts
Validate Logs
Captured logs can be viewed in the Logs Explorer section.
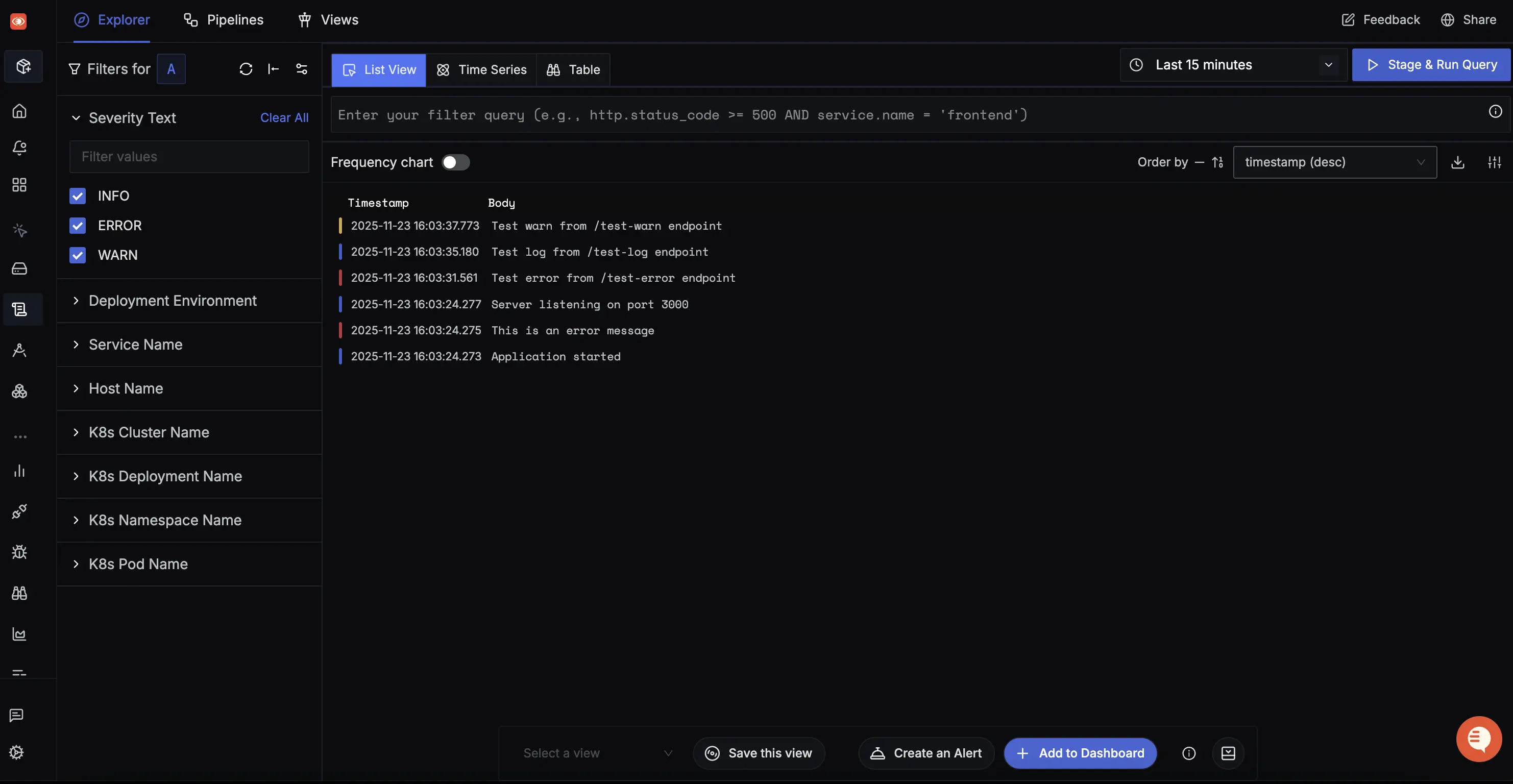
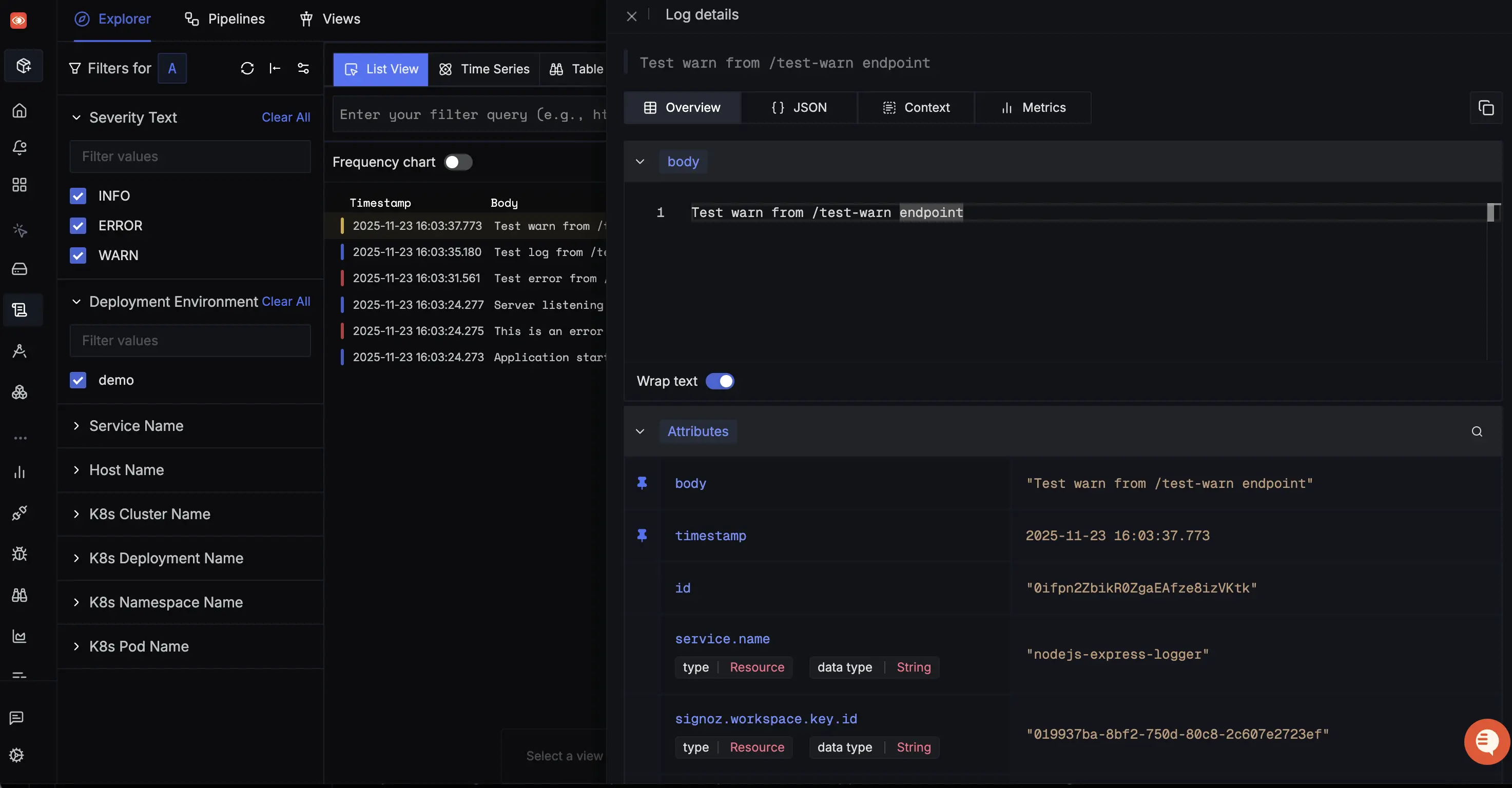
Setup OpenTelemetry Collector (Optional)
What is the OpenTelemetry Collector?
Think of the OTel Collector as a middleman between your app and SigNoz. Instead of your application sending data directly to SigNoz, it sends everything to the Collector first, which then forwards it along.
Why use it?
- Cleaning up data — Filter out noisy traces you don't care about, or remove sensitive info before it leaves your servers.
- Keeping your app lightweight — Let the Collector handle batching, retries, and compression instead of your application code.
- Adding context automatically — The Collector can tag your data with useful info like which Kubernetes pod or cloud region it came from.
- Future flexibility — Want to send data to multiple backends later? The Collector makes that easy without changing your app.
See Switch from direct export to Collector for step-by-step instructions to convert your setup.
For more details, see Why use the OpenTelemetry Collector? and the Collector configuration guide.
Troubleshooting
Why do I see "404 Not Found" errors?
This usually happens if the endpoint URL is incorrect.
- Cloud:
https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443 - Self-Hosted:
http://localhost:4318
Why are my logs not appearing in SigNoz?
- Check if the application started successfully and is actually generating logs.
- Verify your
<region>and<your-ingestion-key>are correct. - If using
console.log, ensureconsole-instrumentation.jsis required before any other code in your application.
Next Steps
- Complete your observability setup by sending traces and metrics from your Node.js application.
- Send Logs from Node.js Pino Logger to SigNoz
- Send Logs from Node.js Winston Logger to SigNoz
- Log Query/Filtering guides
- Alerts setup for logs
Get Help
If you need help with the steps in this topic, please reach out to us on SigNoz Community Slack.
If you are a SigNoz Cloud user, please use in product chat support located at the bottom right corner of your SigNoz instance or contact us at cloud-support@signoz.io.
