Pipelines
Rules for transforming logs are configured by creating Logs Processing Pipelines in SigNoz UI.
A pipeline is typically dedicated to a single preprocessing responsibility. For example, extraction of attributes from nginx text logs would happen in its own pipeline, and there would be another pipeline for parsing application logs and yet another for dropping PII fields from log attributes.
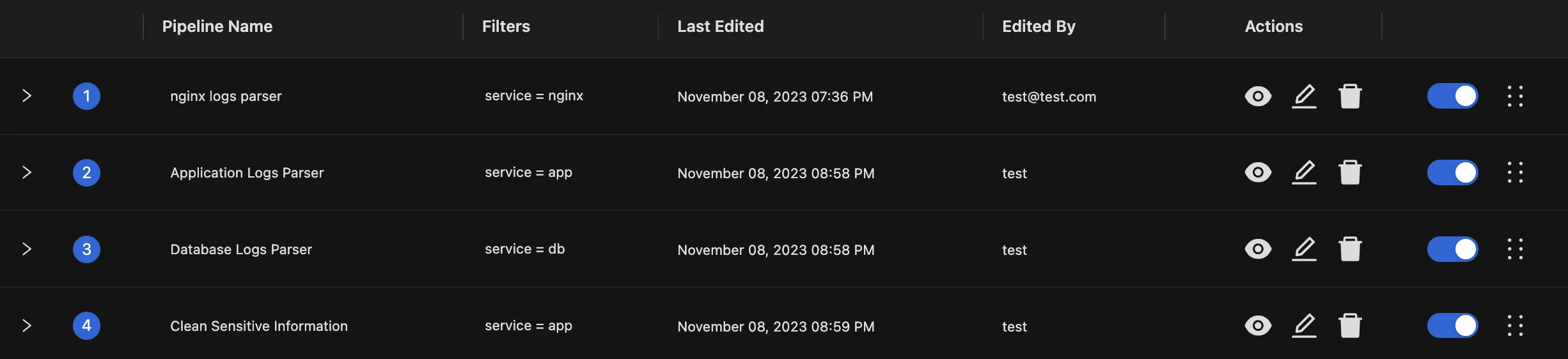
A list of pipelines, each addressing a single responsibility
Logs get preprocessed by passing them through the chain of logs pipelines one by one. If a log matches a pipeline’s filter, it gets processed (transformed) by that pipeline, before moving on to test the log against the next pipeline’s filter and so on.
In the example above, each incoming log would first get tested for "nginx logs parser" pipeline's filter, and if it is a match, it will be transformed by that pipeline. The transformed log will then be tested for a match with the "Application Logs Parser" pipeline, followed by other pipelines in the chain one by one.
Processors
Apart from specifying a filter to identify the logs it can process, a pipeline is composed of a chain of log processors. Each processor takes care of a particular type of log transformation.
When a log matches a pipeline’s filter, it is processed through its chain of processors one by one.
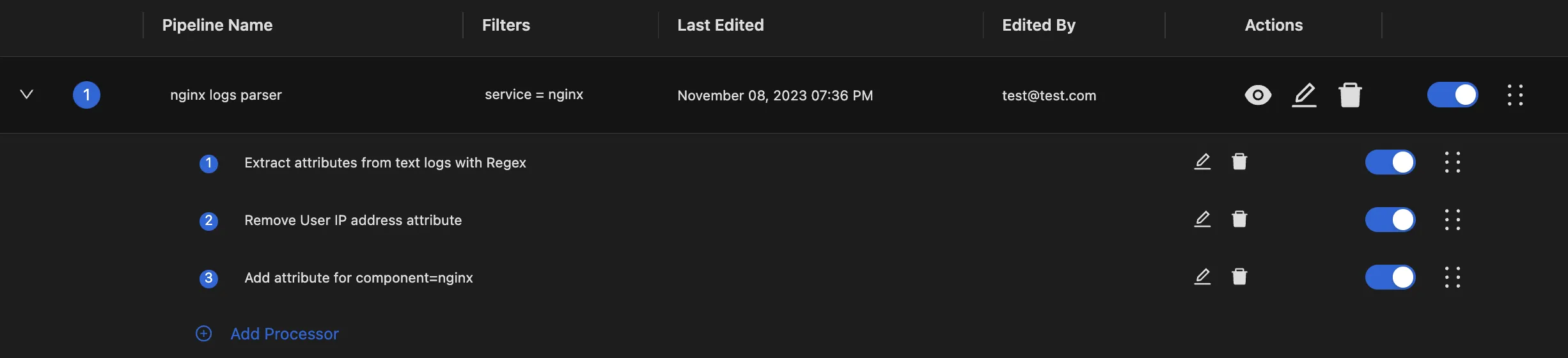
Processors for an Nginx pipeline
SigNoz provides a variety of processors for achieving desired log transformations.
