APM Metrics: All You Need to Know
What are APM Metrics?
APM (Application Performance Monitoring) metrics are quantifiable measurements that track your application's response times, error rates, throughput, and resource consumption to ensure optimal performance, reliability, and user experience.
When something goes wrong in this intricate web, APM metrics become your diagnostic tools for rapid problem identification and resolution.
The difference between a minor hiccup and a costly outage often comes down to how quickly you can answer three fundamental questions:
- Is my application working properly? (Availability and error rates)
- How fast is it responding? (Performance and latency)
- What's the user experience like? (User satisfaction metrics)
Analogy:
Think of your application like a patient in a hospital. Just as doctors rely on vital signs: heart rate, blood pressure, temperature to assess human health, Application Performance Monitoring (APM) uses metrics to assess application health.
But here's where the analogy gets interesting: while human vital signs are relatively straightforward to measure, modern applications are like complex organisms with thousands of interconnected systems. A single user request might travel through multiple services, databases, caches, and third-party APIs before returning a response.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore 15+ essential APM metrics and when to use what metric to help you build robust application monitoring that prevents incidents before they impact users.
Core APM Metrics: The Essential 15+ Indicators
Understanding APM metrics is like learning to read your application's vital signs. Each metric tells part of the story, but together they provide a complete picture of your application's health. Let's examine the metrics that form the foundation of effective application performance monitoring, organized by category for maximum impact.
Performance Metrics: Understanding Speed and Responsiveness
Performance metrics answer the fundamental question "How fast is my application?" But as we'll discover, measuring performance isn't as simple as timing how long requests take.
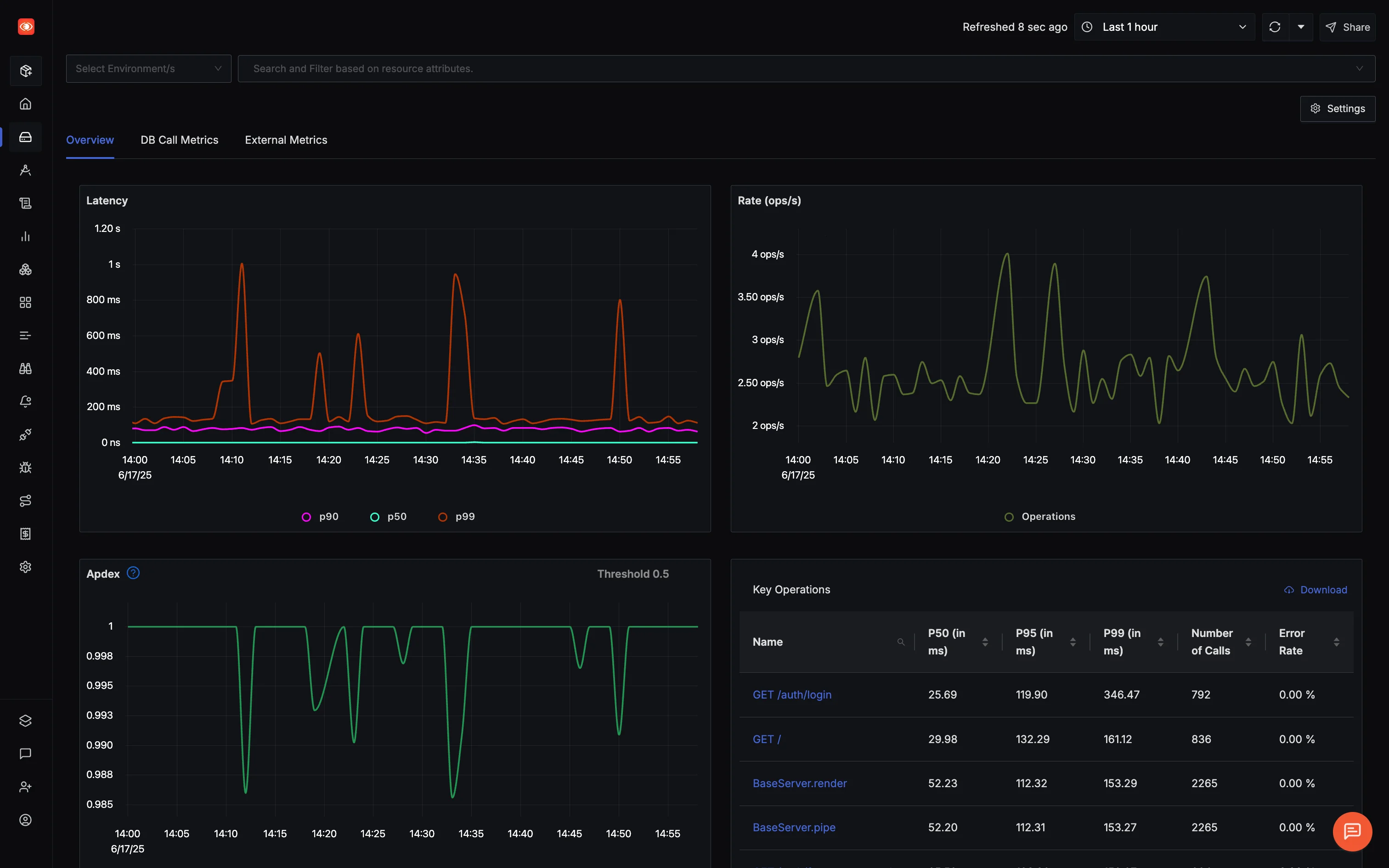
Response Time/Latency: Beyond Simple Averages
Response time measures the complete duration from when your application receives a request until it sends the final response byte back to the client. This seems straightforward, but there's a critical nuance that catches many teams off guard.
Most engineers instinctively reach for average response time as their primary metric. This intuition makes sense, after all, we use averages everywhere in daily life. However, averages can be dangerously misleading when it comes to user experience. Here's a real-world example that illustrates why:
Your API endpoint serves 1,000 requests with these response times:
- 900 requests: 50ms each
- 80 requests: 100ms each
- 15 requests: 500ms each
- 5 requests: 5,000ms each (database timeouts)
The calculations reveal the problem:
- Average: 115ms
- P50 (Median): 50ms
- P95: 100ms
- P99: 500ms
The average (115ms) is heavily skewed by just 5 slow requests, making it unrepresentative of what most users actually experience. Meanwhile, P50 shows that half your users experience 50ms response times or better, a much more accurate picture of typical performance.
This is where percentiles become invaluable. P95 tells you that 95% of your users experience 100ms or better response times, while P99 reveals those outlier cases that might indicate serious issues. Those 5 slow requests in our example? They represent real users waiting 5 seconds for a response—users who are likely to abandon your application.
Explore how different response times impact performance metrics in real-time. Rapidly click the client below to send requests and watch how P50, P95, P99, and average metrics respond differently:
Throughput: Measuring Your Application's Capacity
While response time tells you how fast individual requests are processed, throughput reveals how much work your application can handle overall. Throughput measures your application's capacity: how many requests it processes per unit time, typically expressed as requests per second (RPS) or transactions per minute (TPM).
Throughput becomes particularly interesting when viewed alongside response time because they often tell a story together. Healthy systems typically maintain consistent throughput with stable response times. However, when systems approach their limits, you'll observe a telling pattern.
Understanding the Relationship Between Throughput and Response Time:
Consider this progression during a traffic spike:
Time 10:00: 1000 req/min, 200ms avg response
Time 10:05: 800 req/min, 500ms avg response
Time 10:10: 600 req/min, 1000ms avg response
Notice the inverse relationship? As response times increase, throughput actually decreases despite steady incoming demand. This pattern signals that your system has reached capacity limits, requests are taking longer to process, which means fewer can be completed in any given time window.
This throughput degradation often indicates resource saturation. Your application might be waiting for database connections, struggling with high CPU usage, or hitting memory limits. The beauty of monitoring throughput alongside response time is that it helps you distinguish between genuine performance issues and simple load variations.
Time to First Byte (TTFB): The Foundation of User Experience
Time to First Byte represents the initial response your server provides to a client request. While it might seem like a technical detail, TTFB significantly impacts user perception because it determines how quickly browsers can begin rendering content.
TTFB encompasses several sequential steps, each contributing to the total time:
- DNS Resolution: 20-120ms (varies by caching)
- TCP Connection: 50-200ms (depends on geographic distance)
- SSL Handshake: 100-300ms (HTTPS connections)
- Server Processing: 50-500ms+ (varies by complexity)
Understanding these components helps you optimize systematically. For example, if your server processing time is excellent (50ms) but overall TTFB is poor (800ms), the issue likely lies in network or connection overhead rather than your application code.
Reliability Metrics: Building Trust Through Consistency
Performance metrics tell you how fast your application runs, but reliability metrics tell you whether it runs at all. These metrics directly impact user trust and business outcomes.
Error Rates: Your Application's Health Indicator
Error rates serve as your application's immune system indicator: they show how often things go wrong and help you maintain service quality. Error rates measure the percentage of failed requests out of total requests, providing a clear picture of application reliability.
Understanding different error categories helps you prioritize responses and identify root causes:
Error Categories:
- HTTP 4xx errors: Client-side issues (400 Bad Request, 404 Not Found)
- HTTP 5xx errors: Server-side issues (500 Internal Server Error, 503 Service Unavailable)
- Application-specific errors: Business logic failures, validation errors
The distinction matters because each category requires different response strategies. A spike in 404 errors might indicate broken links or changed URLs (potentially fixed with redirects), while 500 errors suggest server problems requiring immediate technical attention.
Availability/Uptime: The Foundation of Service Reliability
Availability measures the percentage of time your application is operational and accessible to users. While conceptually simple, availability measurement reveals interesting complexities that affect how you architect and monitor systems.
The basic calculation: (Total time - Downtime) / Total time × 100
This straightforward formula becomes nuanced when you consider what "downtime" means. Is it when your servers are down? When users can't log in? When critical features are broken but the site loads? Your definition of availability should align with user expectations and business requirements.
The "Nines" Explained:
- 99% availability = 87.6 hours downtime per year
- 99.9% availability = 8.76 hours downtime per year
- 99.99% availability = 52.6 minutes downtime per year
- 99.999% availability = 5.26 minutes downtime per year
Each additional "nine" represents roughly a 10x reduction in allowable downtime and often a significant increase in infrastructure costs and complexity. Most applications target 99.9% availability as the sweet spot between cost and reliability.
User Experience Metrics: Connecting Technical Performance to Business Impact
Technical metrics tell you what's happening in your systems, but user experience metrics tell you what's happening to your business. These metrics bridge the gap between technical performance and user satisfaction.
Apdex Score: Quantifying User Satisfaction
Apdex (Application Performance Index) transforms raw performance data into user satisfaction scores, providing a business-friendly view of technical performance. This metric converts response time measurements into a 0-1 scale that directly correlates with user experience quality.
The beauty of Apdex lies in its recognition that users have different tolerance levels for response times. Rather than treating all response times equally, Apdex categorizes user experience into three distinct zones:
Formula: (Satisfied + (Tolerating × 0.5)) / Total Samples
Categories:
- Satisfied: Response time ≤ T (your defined threshold)
- Tolerating: T < Response time ≤ 4T
- Frustrated: Response time > 4T
Real Example: E-commerce checkout with 1,000 transactions, threshold T = 2 seconds:
- 700 transactions ≤ 2 seconds (Satisfied)
- 200 transactions 2-8 seconds (Tolerating)
- 100 transactions > 8 seconds (Frustrated)
Apdex = (700 + (200 × 0.5)) / 1000 = 0.8
This score (0.8) immediately tells you that 80% of your users had a good experience, with the remaining 20% experiencing some level of performance frustration.
The critical decision in Apdex implementation is setting the threshold (T). This shouldn't be an arbitrary technical decision, it should be based on user behavior research and business requirements. For the checkout example, if user studies show 85% abandon after 4 seconds, setting T = 2 seconds ensures you maintain good satisfaction scores.
Page Load Time Components: Understanding the Complete User Journey
Page load time represents the complete user experience from clicking a link to seeing a fully interactive page. Breaking this down into components helps you identify specific optimization opportunities and understand where performance bottlenecks occur.
Understanding each component's contribution reveals where to focus optimization efforts:
- DNS Lookup: 20-120ms
- TCP Connection: 50-200ms
- SSL Handshake: 100-300ms
- Time to First Byte: 200-500ms
- Content Download: 100-500ms
- DOM Processing: 50-200ms
- Rendering: 100-300ms
Modern web performance focuses on specific milestones that correlate with user perception:
Core Web Vitals (2025 Standards):
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): < 2.5 seconds
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): < 200ms (replaced FID in 2024)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): < 0.1
- Time to Interactive (TTI): < 5 seconds
These metrics matter because they align with user psychology. Users form first impressions within milliseconds of page load beginning (FCP), judge content quality when main content loads (LCP), and expect full interactivity within reasonable timeframes (TTI).
Infrastructure Metrics: The Foundation Supporting Everything Else
While application metrics tell you what users experience, infrastructure metrics tell you why they experience it. These metrics help identify resource constraints that impact application performance.
Resource Utilization: Reading Your System's Vital Signs
Resource utilization metrics reveal whether your infrastructure can adequately support your application's demands. Like monitoring a patient's vital signs, these metrics provide early warning signals before problems become critical.
CPU Usage Patterns: CPU utilization follows predictable patterns that help you identify normal vs. problematic behavior:
- < 70%: Healthy utilization with room for spikes
- 70-80%: Monitor closely, consider scaling
- 80-90%: High utilization, scaling recommended
- > 90%: Critical, immediate attention required
However, sustained high CPU usage affects more than just response times. It creates a cascade effect: garbage collection increases in managed languages, context switching overhead grows, and system responsiveness degrades even for simple operations.
Memory Consumption Insights: Memory monitoring requires understanding both current usage and trends over time:
- Track heap vs non-heap usage in managed languages
- Monitor for memory leaks (gradual increase over time)
- Set alerts for sustained usage > 85%
Memory leaks particularly insidious because they appear gradually. A small leak might not cause problems for days or weeks, but eventually leads to OutOfMemory errors and application crashes.
Storage and Network Considerations: Modern applications depend heavily on I/O performance:
Disk I/O Metrics:
- IOPS: Input/output operations per second
- Throughput: MB/s read/write rates
- Queue depth: Pending I/O operations
Network I/O:
- Bandwidth utilization
- Packet loss rates
- Connection counts and limits
Container-Specific Considerations: In Kubernetes environments, monitoring becomes more complex because resources are shared and dynamically allocated.
Advanced APM Metrics for Modern Applications
As applications become more sophisticated, monitoring needs evolve beyond basic performance metrics. Modern applications require deeper insights into database performance, microservices interactions, and distributed system behavior.
Database Performance Metrics: The Hidden Performance Killer
Database performance issues often masquerade as application performance problems. Since most applications depend heavily on data access, database metrics frequently reveal the root cause of user-facing performance issues.
Query Performance Analysis: Understanding database query behavior provides insights that application metrics alone cannot reveal:
- Slow query identification: Track queries exceeding defined thresholds
- Query frequency: Most commonly executed queries
- Query efficiency: Rows examined vs. rows returned ratios
The relationship between these metrics tells important stories. A query that examines 10,000 rows but returns only 10 results might be a candidate for index optimization. Similarly, a simple query that executes thousands of times per minute might benefit more from caching than a complex query that runs once per day.
Connection Management: Database connection pooling affects both performance and resource utilization:
- Pool utilization: Available vs. used connections
- Connection wait time: How long requests wait for available connections
- Connection lifetime: Average connection duration
Connection pool exhaustion often manifests as sudden response time spikes rather than gradual degradation, making these metrics critical for maintaining stable performance.
Lock Analysis and Cache Performance: Database locking and caching significantly impact concurrent request handling:
Lock Analysis:
- Lock contention: Blocking and deadlock frequency
- Lock wait time: Duration requests wait for locks
- Lock escalation: Row locks escalating to table locks
Cache Performance:
- Hit ratio: Percentage of requests served from cache
- Cache efficiency: Memory usage vs. performance gains
- Cache eviction rate: How frequently cache entries are removed
Microservices-Specific Metrics: Navigating Distributed Complexity
Microservices architecture introduces monitoring challenges that don't exist in monolithic applications. Service interdependencies, network communication, and distributed transaction patterns require specialized metrics to maintain visibility across the system.
Service Dependency Health: In microservices architectures, your application's health depends not just on your code, but on the health of every service you depend on:
- Circuit breaker status: Open/closed state of protection mechanisms
- Retry patterns: Frequency and success rates of retry attempts
- Timeout occurrences: Requests failing due to timeout limits
These metrics become especially important during partial system failures. When a downstream service degrades, circuit breakers and retry logic protect your system from cascading failures. Monitoring these patterns helps you understand how failures propagate and how well your resilience mechanisms work.
Inter-Service Communication: Communication between services introduces latency and failure points that don't exist in monolithic applications:
- Service-to-service latency: Response times between internal services
- Message queue depth: Backlog in asynchronous communication
- Load balancing distribution: Traffic distribution across service instances
Service-to-service latency often compounds in unexpected ways. A request that traverses five services might experience the worst-case latency from each service, creating user-facing response times that exceed any single service's performance.
Distributed Transaction Metrics: Managing data consistency across multiple services requires monitoring transaction patterns:
- Transaction success rate: End-to-end transaction completion
- Compensation event frequency: Rollback operations in saga patterns
- Cross-service correlation: Tracking requests across service boundaries
Scenario-Specific Metric Frameworks
Different application architectures benefit from focused monitoring approaches. Rather than trying to monitor everything, these frameworks help you select the most impactful metrics for your specific situation.
Google SRE Golden Signals: Comprehensive System Health
Google's Site Reliability Engineering team developed the Four Golden Signals framework based on operating some of the world's largest distributed systems. This framework provides comprehensive coverage while remaining manageable for large-scale operations.
The beauty of the Golden Signals lies in their completeness, they answer the fundamental questions about any service:
1. Latency: Time to serve requests (distinguish successful vs. failed request latency) This matters because failed requests often complete faster than successful ones (failing fast), which can skew your understanding of user experience.
2. Traffic: Demand on your system (requests per second, transactions per minute)
Traffic measurement helps you understand load patterns and capacity requirements.
3. Errors: Rate of failed requests (explicit failures + implicit failures) Error tracking should include both obvious failures (HTTP 500 errors) and subtle failures (incorrect results, timeouts).
4. Saturation: How "full" your service is (resource utilization and queue depth) Saturation indicates how close your system is to hitting capacity limits.
When to use Golden Signals:
- Large-scale web applications
- Microservices architectures
- Systems with high request volumes
- Applications requiring comprehensive health overview
RED Method for Request-Driven Applications
The RED method focuses specifically on request-centric metrics, making it ideal for applications where user requests drive all important business functionality.
Rate: Requests per second your service handles
Errors: Number or percentage of failed requests
Duration: Response time distribution (use percentiles, not averages)
RED works particularly well because it aligns with how users experience your application. Users care about whether their requests succeed (Errors), how long requests take (Duration), and whether your system can handle their traffic levels (Rate).
When to use RED Method:
- RESTful APIs and web services
- Request-response pattern applications
- Service-oriented architectures
- Applications where user-facing requests are primary concern
USE Method for Infrastructure Focus
The USE method provides systematic resource analysis, making it invaluable for infrastructure bottleneck identification and capacity planning.
Utilization: Percentage of time resource is busy
Saturation: Amount of work resource cannot service (queued)
Errors: Error events occurring at the resource level
USE excels at helping you systematically examine every resource in your system. By checking utilization, saturation, and errors for each resource, you can methodically identify bottlenecks.
When to use USE Method:
- Infrastructure bottleneck identification
- Capacity planning activities
- Performance optimization efforts
- Resource-constrained environments
SLIs, SLOs, and Error Budgets in Practice
Service Level Indicators (SLIs), Service Level Objectives (SLOs), and error budgets represent the evolution from reactive monitoring to proactive reliability management. They transform APM metrics from technical measurements into business-aligned reliability targets.
Service Level Indicators (SLIs): Measuring What Matters to Users
SLIs bridge the gap between technical metrics and user experience by measuring specific, user-relevant characteristics of service behavior.
Good SLI Characteristics: Effective SLIs share several important qualities:
- User-centric: Reflects actual user experience, not internal technical details
- Measurable: Can be reliably collected and calculated from your systems
- Attributable: Can be tied to specific service components for debugging
- Proportional: Changes meaningfully with service quality improvements or degradation
Common SLI Types:
Request/Response SLIs:
Availability = (Successful requests / Total requests) × 100
Latency = (Requests completed within 200ms / Total requests) × 100
Quality = (Requests producing correct output / Total requests) × 100
Data Processing SLIs:
- Freshness: How up-to-date processed data is
- Coverage: Proportion of data successfully processed
- Correctness: Proportion of data processed without errors
The key insight is that SLIs should measure outcomes that directly matter to users, not internal technical metrics that might not correlate with user experience.
Service Level Objectives (SLOs): Setting Reliability Targets
SLOs combine SLIs with target values and time windows to create concrete reliability commitments. They answer the question: "How reliable should our service be?"
SLO Components: Every well-formed SLO includes four essential elements:
- SLI: What you're measuring
- Target: The threshold for acceptable performance
- Time Window: Period over which target applies
- Consequences: Actions when SLO is missed
Example SLOs:
- "99.9% of requests will complete successfully over a rolling 30-day window"
- "95% of API requests will complete within 200ms over a rolling 7-day window"
- "99.5% of data processing jobs will complete without errors monthly"
SLO Setting Best Practices: Setting effective SLOs requires balancing user expectations, technical capabilities, and business requirements:
- Start conservative: Begin with achievable targets based on current performance
- Align with business needs: Balance reliability requirements with development velocity
- Use error budgets: Track remaining failure allowance to guide decisions
- Regular review: Adjust SLOs based on user feedback and business changes
Error Budgets and Policy: Making Reliability Decisions Data-Driven
Error budgets quantify acceptable failure levels, enabling teams to make data-driven decisions about the trade-off between reliability and feature development velocity.
Error Budget Calculation:
Error Budget = (100% - SLO Target) × Time Window
Example: (100% - 99.9%) × 30 days = 0.1% × 30 days = 43.2 minutes downtime allowed
This calculation makes the abstract concept of "99.9% reliability" concrete: you have 43.2 minutes of downtime budget per month. This budget can be spent on planned maintenance, incident response, or risky deployments.
Error Budget Policy Framework: Error budget policies provide clear guidance for decision-making:
- Budget remaining > 50%: Normal development pace, feature releases approved
- Budget remaining 10-50%: Increased caution, additional testing required
- Budget remaining < 10%: Focus on reliability, halt risky deployments
- Budget exhausted: Incident response mode, only critical fixes allowed
Quick Start with SigNoz: Out of the box APM Implementation
SigNoz offers an excellent starting point for implementing comprehensive APM without the complexity and cost concerns of enterprise solutions.
Why SigNoz for Modern APM
OpenTelemetry Native: Future-proof your monitoring investment with vendor-neutral instrumentation that works with any backend.
Unified Observability: Metrics, traces, and logs in a single platform eliminate tool sprawl and correlation challenges common with mixed-vendor solutions.
Cost Transparency: No surprise billing or complex pricing models—understand your costs upfront.
Community-Driven Development: Active open-source community ensures rapid feature development and bug fixes.
SigNoz Cloud Setup (Recommended)
The fastest way to get started with comprehensive APM is using SigNoz's managed cloud service:
1. Sign up for SigNoz Cloud at signoz.io/teams for a 30-day free trial. Pricing starts at $19/month for startups (50% discount) and $49/month for standard plans.
2. Instrument your application using OpenTelemetry auto-instrumentation:
To instrument your application with OpenTelemetry and send data to SigNoz, follow the instructions for your programming language or framework below.
- JavaScript
- Python
- Java
- For additional languages and frameworks, see the complete instrumentation documentation.
3. View your data: Within minutes, you'll see service maps, performance metrics, and distributed traces in the SigNoz dashboard.
Get Started with SigNoz
You can choose between various deployment options in SigNoz. The easiest way to get started with SigNoz is SigNoz cloud. We offer a 30-day free trial account with access to all features.
Those who have data privacy concerns and can't send their data outside their infrastructure can sign up for either enterprise self-hosted or BYOC offering.
Those who have the expertise to manage SigNoz themselves or just want to start with a free self-hosted option can use our community edition.
Conclusion
APM metrics serve as your application's vital signs, providing the visibility needed to maintain optimal performance in increasingly complex distributed systems. The key to successful APM implementation lies not in collecting every possible metric, but in focusing on measurements that directly impact user experience and business outcomes.
Here is a quick reference to the APM metrics we covered in this guide:
APM Metrics Quick Reference
Performance Metrics
- Response Time/Latency - P50, P95, P99 percentiles
- Throughput - Requests per second/minute
- Time to First Byte (TTFB) - Initial server response time
Reliability Metrics
- Error Rates - Failed request percentages
- Availability/Uptime - Service operational time
User Experience Metrics
- Apdex Score - User satisfaction index
- Page Load Time - Core Web Vitals (LCP, INP, CLS)
Infrastructure Metrics
- Resource Utilization - CPU, memory, disk, network usage
Database Performance Metrics
- Query Performance - Slow queries, execution frequency
- Connection Pool Health - Pool utilization and wait times
- Cache Hit Ratios - Database and application cache performance
Microservices Metrics
- Service Dependencies - Circuit breaker status, retry patterns
- Inter-Service Communication - Service-to-service latency
- Distributed Transactions - Cross-service transaction success rates
Start with basic monitoring of your most critical user journeys, establish performance baselines, and continuously refine your approach based on real-world operational experience.
Your applications' reliability and your users' trust depends on the insights that only proper monitoring can provide.
Hope we answered all your questions regarding APM metrics. If you have more questions, feel free to use the SigNoz AI chatbot, or join our slack community.
You can also subscribe to our newsletter for insights from observability nerds at SigNoz, get open source, OpenTelemetry, and devtool building stories straight to your inbox.
