Top 10 Container Monitoring Tools for DevOps in 2026
Container monitoring has become a critical component of modern DevOps practices. As organizations increasingly adopt containerized applications and microservices architectures, the need for robust monitoring solutions has never been more pressing. This article explores the top 10 container monitoring tools for DevOps in 2024, providing insights into their features, benefits, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
What is Container Monitoring and Why is it Important for DevOps?
As containerized applications become the backbone of modern infrastructure, reliable container monitoring is crucial, especially with increasing complexity. For DevOps professionals, choosing the right monitoring solution is vital to ensure performance, security, and scalability. Container monitoring involves tracking the performance, health, and resource usage of these applications, offering real-time visibility into the dynamic environments where containers operate.
Container monitoring is important for the following reasons:
- Performance optimization: Containers are lightweight and scalable, but they can face performance issues due to resource constraints. Monitoring tools offer real-time insights, such as CPU, memory usage, and network latency, helping identify slowdowns and areas for optimization.
- Resource management: Efficient resource management is key in containerized systems. Monitoring tools help track resource use, enabling informed scaling decisions. For instance, reducing memory for underutilized containers or increasing resources for those maxing out CPU usage can enhance performance.
- Troubleshooting: Quick troubleshooting is essential in DevOps. Monitoring tools provide logs, analytics, and alerts, helping to quickly identify and resolve issues, like failed deployments or misconfigurations, ensuring high availability.
- Security: Security is critical in dynamic container environments. Monitoring tools continuously track activity and alert to potential risks, like unusual resource usage or network connections, signaling possible security threats. They also monitor configuration changes to maintain compliance with security policies.
Key Metrics Tracked in Container Monitoring
When monitoring containers, several key metrics are crucial for ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and efficiency. They include:
- CPU and memory usage: These fundamental metrics show how much processing power and memory your containers are consuming. Monitoring helps identify if containers have enough resources or if they're overburdened, potentially leading to performance issues. For example, a web server container maxing out CPU during peak traffic may need scaling or code optimization.
- Network throughput and latency: These metrics measure the communication performance between containers and other services. Throughput tracks data movement, while latency measures data travel time. High throughput with low latency indicates a healthy network, essential for responsive applications. Increased latency in a microservice, for instance, can lead to user delays.
- Container health and uptime: These metrics monitor the operational status and availability of containers. Health checks ensure containers are functioning properly, while uptime tracks how long they run without interruption. Frequent crashes and low uptime in a critical service container could lead to disruptions.
- Application response times: This metric reflects how quickly an application responds to user requests, impacting user experience. Response times can be affected by resource limits, network latency, and code efficiency. For example, slow load times in an e-commerce app could hurt user experience and reduce conversions.
- Error rates and log data: These are crucial for identifying and fixing issues. Error rates show how often failures occur, signaling potential problems, while logs provide detailed information for root cause analysis. A spike in error rates after deployment might indicate a bug or misconfiguration.
The Evolution of Container Monitoring in DevOps
Container monitoring evolved with the rise of containerization. As Docker gained popularity in the early 2010s, traditional monitoring tools couldn't keep up with the dynamic nature of containers. Initially, DevOps teams used a mix of available tools and custom scripts, which often lacked the necessary granularity and real-time insights. The shift to microservices architecture further increased monitoring needs, as the number of components to track grew significantly. This required more advanced monitoring systems capable of handling complex service interconnections.
In response, the container monitoring landscape evolved, introducing new technologies tailored to containerized environments and microservices. These tools enhanced visibility, automation, and analytics, focusing on providing actionable insights to optimize performance, ensure reliability, and maintain security in increasingly complex systems.
Current trends in container monitoring include:
- AI-powered analytics: Modern tools are increasingly using AI and machine learning to enhance their capabilities. AI learns the normal behavior of applications and infrastructure to detect anomalies in real-time, identifying potential issues before they escalate, like unusual resource consumption or spikes in network latency.
- Unified observability: This trend combines various types of monitoring data—metrics, logs, and traces—into a single view, giving DevOps teams a comprehensive understanding of system health and performance. Metrics provide performance stats, logs offer detailed event records, and traces follow a request's path through multiple services.
- Auto-discovery: Auto-discovery automatically detects and monitors new containers and services as they are deployed, eliminating the need for manual settings. This feature ensures that all components are consistently monitored in dynamic environments where containers are frequently created and terminated.
- Kubernetes-native solutions: These monitoring tools are built to work seamlessly with Kubernetes, addressing its unique challenges. They integrate with Kubernetes APIs to monitor clusters, pods, and services, providing insights into the orchestration layer and helping manage the complexity of containerized applications.
Looking ahead, container monitoring is likely to become even more automated and intelligent, with an increased focus on security monitoring and cross-cloud visibility.
Top 10 Container Monitoring Tools for 2024
Selecting the right container monitoring tool is vital for maintaining a resilient and high-performing infrastructure. Here’s a look at the top 10 container monitoring tools for 2024, each offering unique features and capabilities tailored to different needs:
1. SigNoz
SigNoz is an open-source APM (Application Performance Monitoring) and observability platform tailored for modern DevOps environments:
Key Features:
- End-to-End Distributed Tracing: Provides comprehensive visibility into the journey of requests across your microservices, identifying bottlenecks and performance issues.
- Metrics and Logs Correlation: Merges performance metrics with logs, enabling a deeper understanding of system health and simplifying troubleshooting.
- Native Support for OpenTelemetry: Facilitates seamless integration with OpenTelemetry for standardized and flexible instrumentation across various services.
- Custom Dashboards and Alerts: Offers customizable dashboards to visualize data according to your needs and configurable alerts to notify you of potential issues based on defined criteria.
Pros:
- Easy Setup and Deployment: Designed to be user-friendly with straightforward installation and configuration, which helps in quick onboarding.
- Cost-Effective: Being an open-source tool, it provides a budget-friendly option for startups and smaller teams without compromising on essential monitoring features.
- Active Development and Community Support: Benefits from ongoing enhancements and a growing community, which can offer help and resources as the tool evolves.
Cons:
- Newer Platform with Evolving Features: As a relatively new entrant, it may still be developing some features and could lack the maturity found in more established tools.
- Limited Enterprise-Level Support: It may not provide the extensive support and dedicated services that larger organizations might require, potentially making it less suitable for enterprise-level deployments.
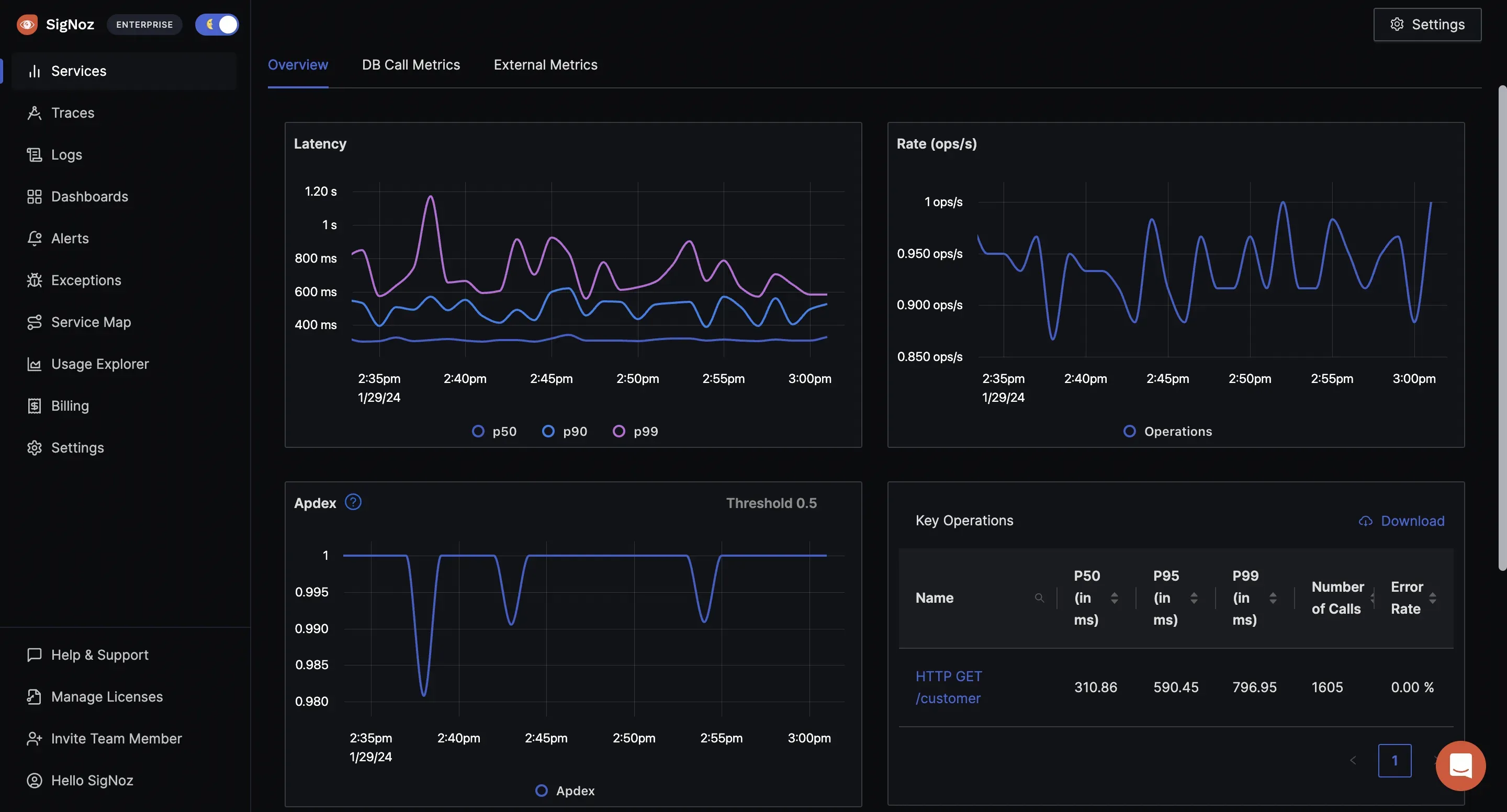
To learn more about SigNoz.
2. Prometheus & Grafana
Prometheus and Grafana together create a robust open-source solution for container monitoring:
Prometheus: A time-series database that specializes in metrics collection and alerting. It efficiently stores and queries metrics data over time, providing insights into system performance and health.
Grafana: A visualization tool that works with Prometheus to build dynamic, interactive dashboards. It turns raw metrics into comprehensible visualizations, allowing for easier monitoring and analysis.
Key Features:
- Pull-Based Metrics Collection: Prometheus scrapes metrics from configured endpoints at specified intervals, ensuring up-to-date data.
- Powerful Query Language (PromQL): Allows for complex queries and aggregations of time-series data, giving in-depth insights into system performance.
- Alerting Rules: Supports defining alerting rules based on metric thresholds, with flexible notification options to keep teams informed.
- Wide Range of Exporters: Provides exporters for various systems and services, enabling comprehensive metrics collection from diverse sources.
Pros:
- Highly Scalable and Reliable: Designed to handle large volumes of metrics data and scale with growing infrastructures.
- Strong Community Support: Benefits from an extensive ecosystem and active community, offering numerous plugins and integrations.
- Native Kubernetes Integration: Integrates seamlessly with Kubernetes, simplifying container and orchestration monitoring.
Cons:
- Steep Learning Curve: Advanced features and PromQL can be complex to master, requiring a deeper understanding of the system.
- Requires Additional Tools for Log Management: Prometheus focuses on metrics, so additional tools are needed for comprehensive log management and analysis.
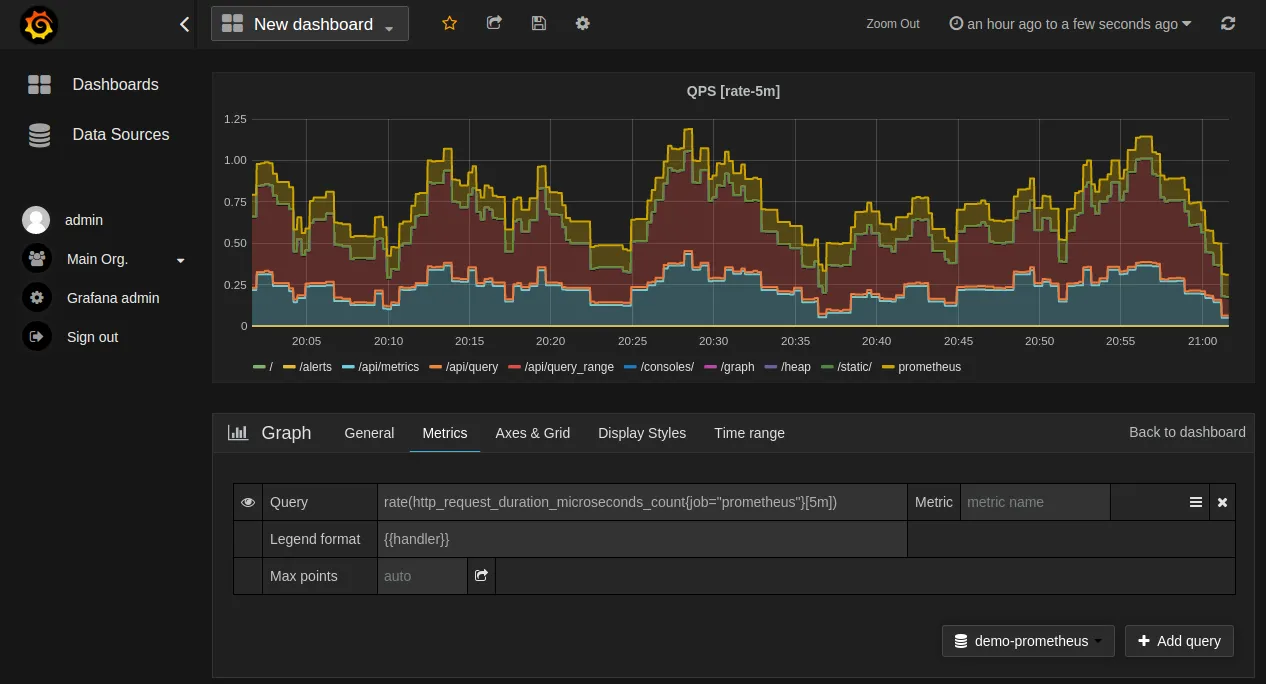
3. Datadog
Datadog is a versatile cloud-based monitoring platform designed to support complex containerized environments:
Key Features:
- Automatic Discovery and Monitoring: Detects and monitors containers automatically as they are deployed, simplifying management.
- Real-Time Performance Tracking: Provides continuous visibility into the performance of both hosts and containers, helping to identify issues promptly.
- Advanced Anomaly Detection: Utilizes machine learning to identify unusual patterns and potential issues before they affect performance.
- Customizable Dashboards and Alerts: Allows users to create tailored dashboards and configure alerts to focus on the most critical metrics.
Pros:
- User-Friendly Interface: Offers an intuitive and easy-to-navigate interface, making it accessible for teams of all sizes.
- Extensive Integration Options: Integrates with a wide array of third-party tools and services, providing a comprehensive monitoring solution.
- Strong Collaboration Features: Facilitates teamwork with features like shared dashboards and integrated communication tools.
Cons:
- Can Be Expensive: Pricing can be high for large-scale or enterprise-level deployments, potentially making it less suitable for smaller teams or budgets.
- Occasional Data Lag: Some users have reported delays in data visibility, which can affect real-time monitoring effectiveness.
4. Dynatrace
Dynatrace provides an advanced, AI-driven monitoring solution designed for comprehensive application performance management:
Key Features:
- Automatic Discovery and Mapping: Automatically identifies and maps container dependencies, providing a clear view of how containers interact within the environment.
- Root Cause Analysis: Utilizes AI to quickly identify and diagnose the root causes of performance issues, streamlining troubleshooting.
- AI-Assisted Performance Optimization: Leverages artificial intelligence to optimize performance and predict potential issues before they impact the system.
- Scalable for Enterprises: Designed to scale efficiently, making it suitable for large organizations with complex infrastructure.
Pros:
- Powerful AI Capabilities: Advanced AI algorithms enhance problem detection and offer actionable insights for improving performance.
- Comprehensive Visibility: Provides extensive visibility into every layer of the application stack, from the infrastructure to the end-user experience.
- Strong Security and Compliance: Includes robust security features and compliance support, addressing enterprise-grade requirements.
Cons:
- Complex Pricing Structure: The pricing model can be intricate, which may make it challenging to estimate costs accurately.
- Resource-Intensive: The platform's comprehensive features and AI capabilities may require significant resources, potentially impacting performance.
5. Sematext
Sematext offers an integrated solution for both monitoring and log management, catering to a variety of deployment needs:
Key Features:
- Real-Time Metrics and Logs Correlation: Provides simultaneous analysis of metrics and logs, helping teams gain a comprehensive view of system performance.
- Custom Dashboards and Alerting: Allows for the creation of personalized dashboards and alerts tailored to specific needs and performance thresholds.
- Support for Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Environments: Versatile enough to handle monitoring across various cloud platforms and hybrid setups.
- Container-Specific Performance Metrics: Includes features designed to monitor the performance of containerized applications.
Pros:
- Intuitive User Interface: User-friendly design which makes it easy to navigate and configure, reducing the learning curve.
- Flexible Deployment Options: Can be deployed either in the cloud or on-premises, offering flexibility based on organizational needs.
- Competitive Pricing: Offers cost-effective solutions particularly suited for small to medium-sized teams.
Cons:
- Limited Advanced Analytics: It may lack some of the more sophisticated analytical capabilities found in other, more established tools.
- Smaller Community: It has a smaller user community compared to some of the more widely adopted monitoring solutions, which can affect the availability of support and resources.
6. New Relic
New Relic delivers an all-encompassing observability platform with robust capabilities for container monitoring:
Key Features:
- Full-Stack Observability: Provides comprehensive monitoring across metrics, events, logs, and traces, offering a unified view of your entire system.
- AI-Powered Anomaly Detection: Utilizes artificial intelligence to identify unusual patterns and potential issues automatically.
- Custom Dashboards and Reporting: Allows for tailored dashboard creation and detailed reporting to meet specific monitoring needs.
- Extensive Integration Ecosystem: Supports a wide range of integrations, facilitating seamless connectivity with various tools and services.
Pros:
- User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive design that simplifies navigation and management.
- Strong Data Visualization Capabilities: Advanced visualization tools for clearer insights and better decision-making.
- Robust APM Features: Comprehensive application performance monitoring (APM) that enhances visibility into application performance.
Cons:
- Complex Pricing Structure: Pricing can be intricate and may become costly depending on the scale of deployment.
- Steep Learning Curve: Some users may find the platform challenging to master initially, particularly when configuring advanced features.
7. Elastic Observability
Elastic Observability, integrated within the Elastic Stack, offers comprehensive container monitoring along with log management and application performance monitoring (APM):
Key Features:
- Centralized Logging and Metrics Collection: Aggregates logs and metrics into a unified view for easier management and analysis.
- Machine Learning-Powered Anomaly Detection: Uses machine learning algorithms to automatically identify unusual patterns and potential issues.
- Customizable Kibana Dashboards: Provides rich, customizable dashboards through Kibana for tailored data visualization.
- Distributed Tracing Support: Enables tracing across distributed systems to diagnose performance issues and understand system dependencies.
Pros:
- Seamless Integration: Works smoothly with other Elastic Stack components, enhancing overall observability.
- Powerful Search and Analysis: Advanced search and analysis capabilities for in-depth data exploration.
- Flexible Deployment Options: Offers various deployment choices, including cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments.
Cons:
- Resource-Intensive: Can be demanding on resources, particularly in large-scale deployments.
- Requires Expertise: Setting up and maintaining the platform effectively often requires specialized knowledge and skills.
8. Instana
Instana provides automated Application Performance Monitoring (APM) specifically designed for microservices and containerized applications:
Key Features:
- Automatic Discovery and Mapping: Automatically identifies and maps containerized environments and their interactions.
- Real-Time Performance Monitoring: Continuously tracks performance metrics and application health in real-time.
- AI-Assisted Root Cause Analysis: Uses artificial intelligence to quickly identify the root cause of performance issues.
- Kubernetes-Native Monitoring: Tailored support for monitoring Kubernetes environments, providing visibility into containerized microservices.
Pros:
- Minimal Configuration: Requires little setup, making it easy to deploy and start monitoring.
- Strong Support for Modern Architectures: Well-suited for complex, modern microservices architectures.
- Intuitive User Interface: Offers a user-friendly interface that simplifies navigating and interpreting monitoring data.
Cons:
- Limited Customization: Fewer customization options compared to some other tools, which may limit flexibility.
- Focus on APM: Primarily targets APM, so additional tools might be necessary for a full-spectrum monitoring solution.
9. Splunk
Splunk offers a comprehensive platform for monitoring, logging, and security analytics:
Key Features:
- Real-Time Data Ingestion and Analysis: Captures and processes data in real-time for immediate insights.
- Machine Learning-Powered Insights: Utilizes machine learning to identify patterns and anomalies in data.
- Customizable Dashboards and Alerts: Allows the creation of tailored dashboards and alert configurations.
- Extensive Third-Party Integrations: Supports integration with a wide range of other tools and systems.
Pros:
- Powerful Search and Analytics: Provides advanced search capabilities and in-depth analytics.
- Strong Security and Compliance: Offers robust security features and helps meet compliance requirements.
- Scalable for Large Enterprises: Suitable for large-scale deployments with extensive data needs.
Cons:
- Can Be Expensive: Costs can add up significantly with high data volumes and extensive usage.
- Steep Learning Curve: Advanced features and configurations can be complex to learn and implement.
10. Zabbix
Zabbix is an open-source monitoring solution with strong support for containers:
Key Features:
- Agentless Monitoring of Containers: Monitors container environments without requiring agents on each container.
- Customizable Templates and Dashboards: Offers the ability to create and modify templates and dashboards to fit specific needs.
- Scalable Architecture: Designed to handle large-scale deployments effectively.
- Extensive Alerting Options: Provides a wide range of alerting configurations and notifications.
Pros:
- No Licensing Costs: Free to use, with no licensing fees.
- Flexible and Highly Customizable: Allows extensive customization to meet various monitoring needs.
- Strong Community Support: Supported by an active community, offering resources and assistance.
Cons:
- User Interface Can Feel Dated: The interface may appear less modern compared to some newer tools.
- Setup and Configuration Can Be Complex: Initial setup and configuration can be challenging and time-consuming.
Key Features to Look for in Container Monitoring Tools
When choosing a container monitoring tool, consider these essential features:
- Real-time metrics: Ensure that the tool delivers real-time information on CPU, memory, and network performance. This enables you to swiftly detect and rectify problems before they worsen, with minimum delay and impact on performance.
- Automated discovery: Look for tools that automatically detect and monitor new containers and services as they are deployed, especially in dynamic environments like Kubernetes.
- Customizable dashboards: Opt for tools that allow you to create personalized dashboards, focusing on the metrics most relevant to your team’s needs.
- Alerting and notifications: Choose a tool with customizable alerts and notifications across multiple channels (e.g., email, SMS, Slack), ensuring your team can respond quickly to issues.
- Integration with orchestration tools: Ensure the tool has native integration with container orchestration platforms like Kubernetes, enabling seamless monitoring of containers as they are managed and scaled.
- Distributed tracing: For microservices, look for tools that offer distributed tracing to track requests across services, helping to identify bottlenecks and performance issues.
- Log management: Select a tool with built-in log management, allowing you to correlate logs with metrics and traces for better visibility and troubleshooting.
- Scalability: Ensure the monitoring solution can scale with your infrastructure, handling increasing data volumes and complexity without sacrificing performance.
- API and extensibility: Choose a tool with a robust API for integration with other tools, custom metric intake, and data export, allowing you to tailor the solution to your needs.
- Security features: Look for integrated security monitoring, including anomaly detection and compliance reporting, to protect your containerized environment from threats.
By focusing on these key features, you can select a container monitoring tool that meets your current needs, scales with your infrastructure, and adapts to future challenges.
How to Choose the Right Container Monitoring Tool for Your DevOps Team
Selecting the right container monitoring tool involves considering your organization's specific needs:
- Assess your infrastructure: Understand your current setup, including the number of containers, orchestration systems (like Kubernetes), and cloud environments. This will help you determine the complexity of the monitoring tool you need.
- Define your monitoring goals: Identify what you need to monitor—CPU, memory, network traffic, error rates, etc. Prioritize whether you need immediate alerts, long-term trends, or security monitoring, guiding your choice toward a tool that excels in those areas.
- Evaluate ease of use: Choose a tool that matches your team’s technical skills. Some tools are more complex, while others are user-friendly, so select one that minimizes the learning curve and avoids deployment delays.
- Check integration capabilities: Ensure the tool integrates smoothly with your existing DevOps stack, including CI/CD pipelines and incident management. Look for tools with robust APIs for custom integrations.
- Consider scalability: Pick a solution that can grow with your deployment. It should handle more containers and data as needed, and be cost-effective at scale. Look for real-world examples of how the tool performs in large-scale environments.
- Analyze pricing models: Review the cost structure of each tool, considering both initial and ongoing expenses. Make sure the pricing aligns with your budget and future growth plans.
- Test before committing: Use free trials or demos to see how the tool works in your environment. If possible, run a pilot with a few tools to compare their performance and fit with your needs.
- Review community and support: For open-source tools, check the community activity—forums, plugins, and peer support. For commercial tools, evaluate the quality of customer support, including response times and available services.
By taking these variables into account, you can select a container monitoring solution that meets your present requirements while also scaling to accommodate future expansion, improving system stability and efficiency.
Best Practices for Implementing Container Monitoring in DevOps
To fully harness the benefits of container monitoring, it’s important to follow a set of best practices that ensure your system is both effective and resilient:
- Define Clear Objectives: Start by establishing precise goals for your monitoring plan. Determine what success looks like—whether it's less downtime, better performance, or more security. Clear objectives assist in aligning your monitoring approach with your organization's needs.
- Ensure Comprehensive Instrumentation: Monitor all key components of your containerized applications, including containers, underlying architecture, and dependencies. This thorough approach ensures that no critical data is missed.
- Utilize a Combination of Metrics, Logs, and Traces: Use the "three pillars" of observability—metrics, logs, and traces—to fully understand your system’s health. Metrics offer performance data, logs provide detailed event histories, and traces reveal request flow through your system. Together, these elements give a comprehensive view of your containerized environment.
- Configure Meaningful Alerts: Set up alerts that are specific, actionable, and aligned with your objectives. Avoid generic alerts that may cause alert fatigue. Instead, focus on alerts that indicate critical issues requiring immediate attention, helping your team respond effectively.
- Automate Routine Monitoring Tasks: Wherever possible, automate common monitoring activities and answers. Automation can handle monotonous duties such as log rotation, metric-based scaling, and initiating self-healing procedures, allowing your team to focus on more important responsibilities.
- Continuously Review and Optimize: Evaluate your monitoring plan regularly to ensure that it continues to be effective as your environment changes. This might include upgrading your instrumentation, improving alerts, or incorporating new technologies to handle growing challenges.
- Foster a Culture of Observability: Ensure your team actively uses monitoring data. Encourage regular use of insights from dashboards and alerts to inform decisions and improve processes.
- Implement Data Retention Policies: Balance historical data retention with storage costs and compliance needs. Set retention periods that meet operational and legal requirements while managing storage efficiently.
- Leverage Machine Learning: Enhance monitoring with AI and machine learning to detect anomalies and predict issues before they escalate, enabling proactive management.
- Ensure Security and Compliance: Integrate security monitoring with your overall container monitoring approach. This involves monitoring security-related events, ensuring adherence to industry standards, and responding quickly to any identified risks.
By sticking to these best practices, DevOps teams can build a strong and effective container monitoring system that increases performance, reliability, and operational efficiency across their environments.
Key Takeaways
- Container monitoring is essential to ensure the smooth and reliable operation of containerized applications, helping to identify and resolve issues before they impact performance.
- The container monitoring solution you choose should be tailored to your organization's unique needs, such as the nature of your infrastructure, the size of your operations, and your team's technical competence. Different tools provide varied features and degrees of support, so assess them based on your specific needs.
- Achieve full visibility by using metrics, logs, and distributed tracing—metrics for performance data, logs for detailed system records, and tracing for understanding system interactions.
- Treat container monitoring as an ongoing process. Regularly update strategies to adapt to infrastructure changes and new best practices for long-term DevOps success.
- Balance cost and functionality when selecting a tool, from open-source options to premium services, ensuring scalability as your needs grow.
- Effective container monitoring is a continuous activity, rather than a one-time setup. Regularly review and adjust your monitoring strategies to keep up with changes in your infrastructure, evolving best practices, and new insights. Continuous improvement is critical for long-term success in the DevOps context.
- A strong community and robust support can enhance a monitoring tool’s effectiveness, providing valuable assistance and continuous improvements.
FAQs
What's the difference between container monitoring and traditional application monitoring?
Container monitoring is essential because it focuses on the transient and dynamic nature of containerized environments, tracking metrics like container health, resource usage, and orchestration data across distributed systems. In contrast, traditional application monitoring centers on static, long-running processes, focusing on metrics like CPU and memory usage in more stable environments. Traditional monitoring tools often miss the rapid changes and short-lived states typical in containerized systems, making container-specific monitoring crucial for modern DevOps practices.
How does container monitoring integrate with CI/CD pipelines?
Container monitoring tools seamlessly integrate with CI/CD pipelines by:
- Providing feedback during testing: They deliver real-time insights on application performance during the testing phases, enabling early detection of issues before deployment.
- Automating monitoring setup: Upon deployment, these tools automatically configure monitoring for new containers, ensuring immediate visibility without manual intervention.
- Triggering alerts or rollbacks: Based on performance metrics collected after deployment, the tools can trigger alerts or even initiate automated rollbacks if critical thresholds are breached, maintaining system stability.
- Optimizing applications: Continuous feedback from monitoring tools helps teams identify performance bottlenecks and optimize containerized applications in subsequent iterations, ensuring ongoing improvements.
Can open-source tools like Prometheus compete with commercial container monitoring solutions?
Yes, open-source tools like Prometheus can effectively compete with commercial container monitoring solutions. Prometheus offers scalability, a powerful query language (PromQL), a large ecosystem, and strong community support, making it ideal for customization and Kubernetes integration.
On the other hand, commercial solutions often provide broader out-of-the-box capabilities, quicker setup, and specialized support, which can be crucial for teams seeking rapid deployment and ongoing maintenance without managing the complexities of open-source tools. The choice between open-source and commercial solutions depends on your team's specific needs, technical skills, and available resources.
How does container monitoring help in capacity planning and resource optimization?
Container monitoring offers crucial insights into resource usage, enabling teams to:
- Spot over-provisioned or under-utilized resources
- Forecast future needs using historical data and trends
- Optimize container sizing and resource allocation
- Make data-driven decisions for scaling infrastructure or applications
These insights empower DevOps teams to maximize resource efficiency and enhance capacity planning.
