LLMOps - Mastering Large Language Model Operations
LLMOps or Large Language Model Operations, is transforming how businesses maintain and deploy advanced AI models. This developing field addresses the special issues associated with large language models (LLMs), expanding existing MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) approaches to meet the specific needs of AI development. LLMOps covers the complete lifespan of LLMs, from data preparation and model training to deployment and ongoing monitoring.
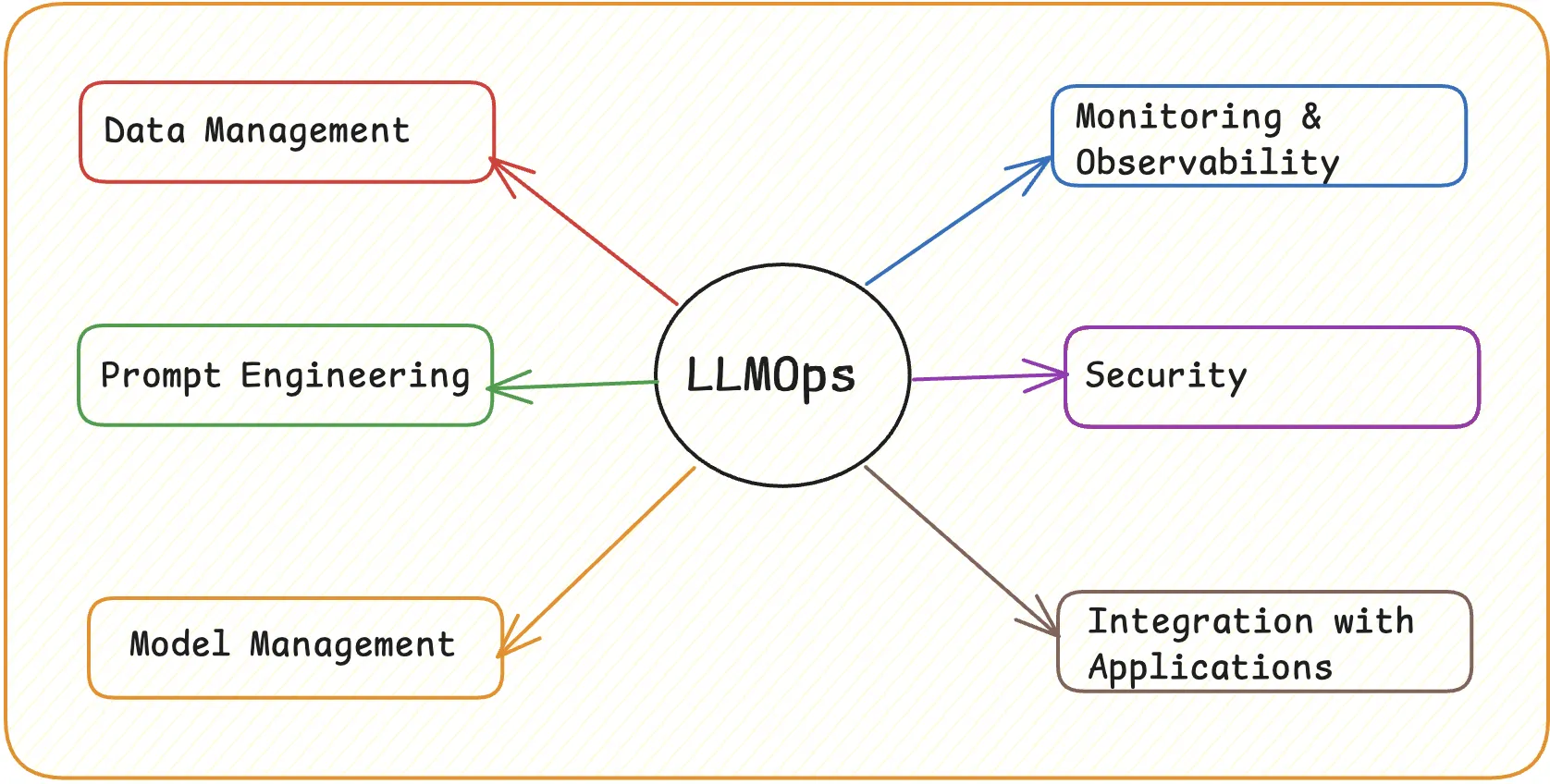
What is LLMOps? Understanding the Basics
LLMOps refers to the operational procedures for managing large language models. It builds on the foundation of MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) but focuses on the special requirements of AI systems driven by LLMs.
Let us look at some of its main components:
Data Preparation
Data Preparation includes choosing high-quality datasets for training and fine-tuning LLM models. Data quality is essential because it has a direct impact on model performance. Data preparation involves data collection, cleaning, augmentation, and diversity to prevent biases. For example, a diverse set of language styles, themes, and dialects is required in natural language processing to build a strong language model.
Note:
- Data cleaning is a critical step in data preparation that involves identifying and correcting errors or inconsistencies in the dataset.
- Data augmentation involves creating new training examples from the existing dataset to improve the robustness and generalizability of machine learning models.
- Data diversity refers to the inclusion of a wide range of data types, styles, and contexts in the training dataset to ensure the model can generalize well across different scenarios.
Model Training
Optimizing the training process for large-scale language models is a difficult task that requires a huge amount of computational resources and expertise. This includes choosing proper algorithms, modifying hyperparameters, and utilizing distributed computing frameworks to deal with the massive amounts of data and parameters involved. Techniques such as transfer learning and fine-tuning pre-trained models can also be used to boost efficiency and performance.
Deployment
Efficiently integrating LLMs into production contexts involves more than simply using a trained model. It requires a well-planned deployment pipeline that guarantees scalability, dependability, and simplicity of interface with current systems. To handle a large deployment, deployment techniques may involve employing containerization technologies such as Docker, orchestration platforms such as Kubernetes, and serverless architectures.
Monitoring
Continuously monitoring model performance and spotting faults is essential for ensuring the reliability and usefulness of LLMs in production. Monitoring involves tracking multiple performance parameters, detecting data drift, and verifying that model predictions are consistent over time. This can be accomplished via automated monitoring systems that provide real-time insights into model performance and notify teams of any irregularities.
LLMOps play a crucial role in the AI development lifecycle, ensuring that language models are not only powerful but also reliable, scalable, and ethically sound. By implementing robust LLMOps practices, organizations can better manage the complexities associated with large language models and ensure their AI initiatives deliver value effectively and responsibly.
The Evolution from MLOps to LLMOps
While MLOps and LLMOps share common goals, LLMOps addresses challenges that are related to large language models (LLMs). Let us look at some of these challenges and how LLMOps tackles them:
- Scale: LLMs often require massive computational resources for training and inference. Training an LLM can involve processing terabytes of data and utilizing thousands of GPUs over extended periods. This requires complex infrastructure, efficient resource management, and the ability to scale operations seamlessly. LLMOps practices include using distributed training frameworks, optimizing resource utilization, and leveraging cloud-based solutions to handle the scale.
- Complexity: Managing complex model architectures and large parameter spaces is a big problem for LLMs. These models can include billions of parameters, necessitating sophisticated strategies for model optimization, parameter tuning, and performance monitoring. LLMOps uses specific tools and frameworks built to manage this complexity, such as
TensorFlow,PyTorch, and Hugging Face's Transformers library. - Ethical Considerations: When working with LLMs, it is vital to minimize biases and ensure responsible AI use. These models may unintentionally learn and perpetuate biases found in the training data, resulting in ethical and societal difficulties. LLMOps highlights the need for ethical AI approaches, such as bias identification, fairness evaluation, and the establishment of rules for responsible AI use. Ethical LLMOps procedures include regular audits and transparency reports.
- Specialized Tools: Using frameworks built for language model creation is necessary for effective LLMOps. Hugging Face's Transformers, OpenAI's GPT and others offer pre-trained models, fine-tuning capabilities, and other features designed specifically for LLM development. These technologies make it easier to create, train, and deploy big language models.
We can summarize the comparision as:
| Aspect | MLOps | LLMOps |
|---|---|---|
| Scale | Manages computational resources for standard ML models. | Handles massive computational resources for LLMs, involving terabytes of data and thousands of GPUs. |
| Complexity | Focuses on optimizing standard model architectures and parameter tuning. | Manages complex model architectures with billions of parameters, requiring specialized optimization. |
| Ethical Considerations | Addresses biases and fairness in ML models. | Emphasizes minimizing biases in LLMs and ensuring responsible AI use through regular audits. |
| Specialized Tools | Utilizes general ML frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch. | Leverages tools like Hugging Face's Transformers and OpenAI's GPT for specialized LLM development. |
LLMOps highlights the importance of effective governance and compliance management, particularly in issues such as data protection and model explainability. This focus derives from greater scrutiny of AI systems and their potential societal consequences. Implementing LLMOps entails creating clear data handling norms and protocols, assuring model interpretability and transparency, and adhering to legislation like as GDPR and CCPA. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) are both data privacy regulations, but they apply in different regions and have some distinct features.
Why LLMOps Matters: Benefits and Use Cases
Implementing LLMOps provides various benefits to companies working with large language models, which can have a substantial impact on their AI initiatives and overall business results. Let us now take a look at the advantages and real-world applications:
Improved Model Performance: Systematic fine-tuning and optimization of LLMs produces superior results. Organizations may increase the accuracy and relevance of their AI applications by regularly monitoring and refining the models. To achieve optimal performance approaches such as hyperparameter adjustments, gradient accumulation, and regular retraining with updated data sets are used.
Example: In a customer service chatbot, regular fine-tuning based on user interactions helps the bot understand and respond more accurately to customer queries, enhancing the overall customer experience.
Enhanced Scalability: LLMOps methods enable the efficient deployment of LLMs across several applications. Organizations may deploy LLMs at scale by leveraging containerization, orchestration tools such as Kubernetes, and scalable cloud infrastructure, guaranteeing they can manage large numbers of requests while providing constant performance.
Example: In e-commerce, using LLMs to power personalized recommendation systems assures that the system can scale to handle millions of users while providing real-time suggestions.
Better Governance: Compliance with AI legislation and ethical principles is easier to manage using LLMOps. This includes putting in place data privacy controls, making sure model decisions are transparent, and assessing models regularly for biases and ethical considerations.
Example: In healthcare, employing LLMOps to comply with HIPAA rules ensures that patient data is managed securely and that models used to make diagnosis or treatment recommendations are transparent and objective.
Faster Time-to-Market: LLMOps streamline procedures, accelerating the development of AI-powered solutions. Organizations can shorten the time it takes to transition from model development to production by automating workflows, defining best practices, and using continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
Example: In content production, utilizing LLMOps enables quick development and deployment of AI models that produce and summarize material for marketing campaigns, significantly reducing the time required to launch new content initiatives.
Real-World Applications of LLMOps
LLMOps allow for the effective deployment of language models in numerous areas, revolutionizing how enterprises use AI to improve their operations and services:
- Customer Service: You can enable intelligent chatbots and virtual assistants to understand and respond to consumer requests in real-time which can increase customer happiness while lowering operational costs.
- Content Creation: Writing and summarizing text for marketing or publishing, allowing content teams to create high-quality content quickly and efficiently.
- Language Services: Improving translation and localization skills, enabling firms to operate in various languages and reach a worldwide audience.
- E-commerce: Creating tailored product recommendation systems, enhancing user experience, and increasing revenues by recommending relevant products based on user behaviour.
How to Implement LLMOps: Best Practices and Strategies
Implementing LLMOps efficiently necessitates a systematic approach and adherence to best practices. Let us look at some of the crucial strategies for success:
Establish a Robust Data Pipeline:
- Data Collection: Continuously collect data from many sources relevant to your use case. Ensure that the data is high-quality, accurate, and up-to-date. You can use numerous options for pipelines such as Azure DevOps Pipeline and Jenkins for automating data collection processes.
- Data Cleaning: Use automated methods to handle missing values, eliminate duplicates, and fix errors.
- Data Preprocessing: Normalize, tokenize, and encode data as needed for your model. For NLP tasks, text preprocessing techniques like stopword removal and stemming may be used.
Example: You can use Pandas to preprocess data in a text-based dataset. For instance, using the
pandaslibrary in Python, you can remove null values and duplicates with commands likedf.dropna()anddf.drop_duplicates(). Additionally, Azure DevOps Pipeline can be set up to automate the entire data preprocessing workflow, ensuring data is consistently prepared for model training.Implement Version Control:
- Tools Git LFS is used to manage huge files, while DVC is used to version data and models.
- Tracking changes: Ensure that any changes to data, code, and model parameters are tracked (refer to example below). This helps with reproducibility and understanding of model evolution.
Example: You can use DVC to track data and model versions. For example, setting up DVC in a project involves initializing DVC with
dvc init, then adding data files withdvc add <file>. These files can be pushed to remote storage, ensuring all data changes are versioned alongside code in Git.Automate Testing and Evaluation:
- Testing Frameworks: Develop through test cases using frameworks like
pytestto evaluate model performance, fairness, and safety. - Continuous Integration: Integrate automated tests into your CI/CD pipeline to ensure that models meet performance standards before deployment. It is crucial to differentiate between unit testing and integration testing. Integration testing ensures different components of your system work together, while unit testing focuses on individual components.
Example: You can write a simple
pytestfunction to test model accuracy.def test_model_accuracy(): model = load_model('path_to_model') test_data = load_data('path_to_test_data') accuracy = evaluate_model(model, test_data) assert accuracy > 0.85- Testing Frameworks: Develop through test cases using frameworks like
Deploy a Monitoring System:
- Platforms: Use platforms like SigNoz for real-time monitoring of model performance, drift detection, and alerting.
- Custom Metrics: Define and track custom metrics specific to your model's performance and operational health.
Example: You can set up SigNoz for monitoring. Integrating SigNoz involves setting up the platform to collect metrics from your application. For instance, you can configure SigNoz to monitor your LLM's API endpoints, tracking metrics such as response time and error rates. Custom metrics can include specific indicators like model prediction confidence levels or data processing throughput, tailored to reflect the unique performance aspects of your language model. For more details, click here.
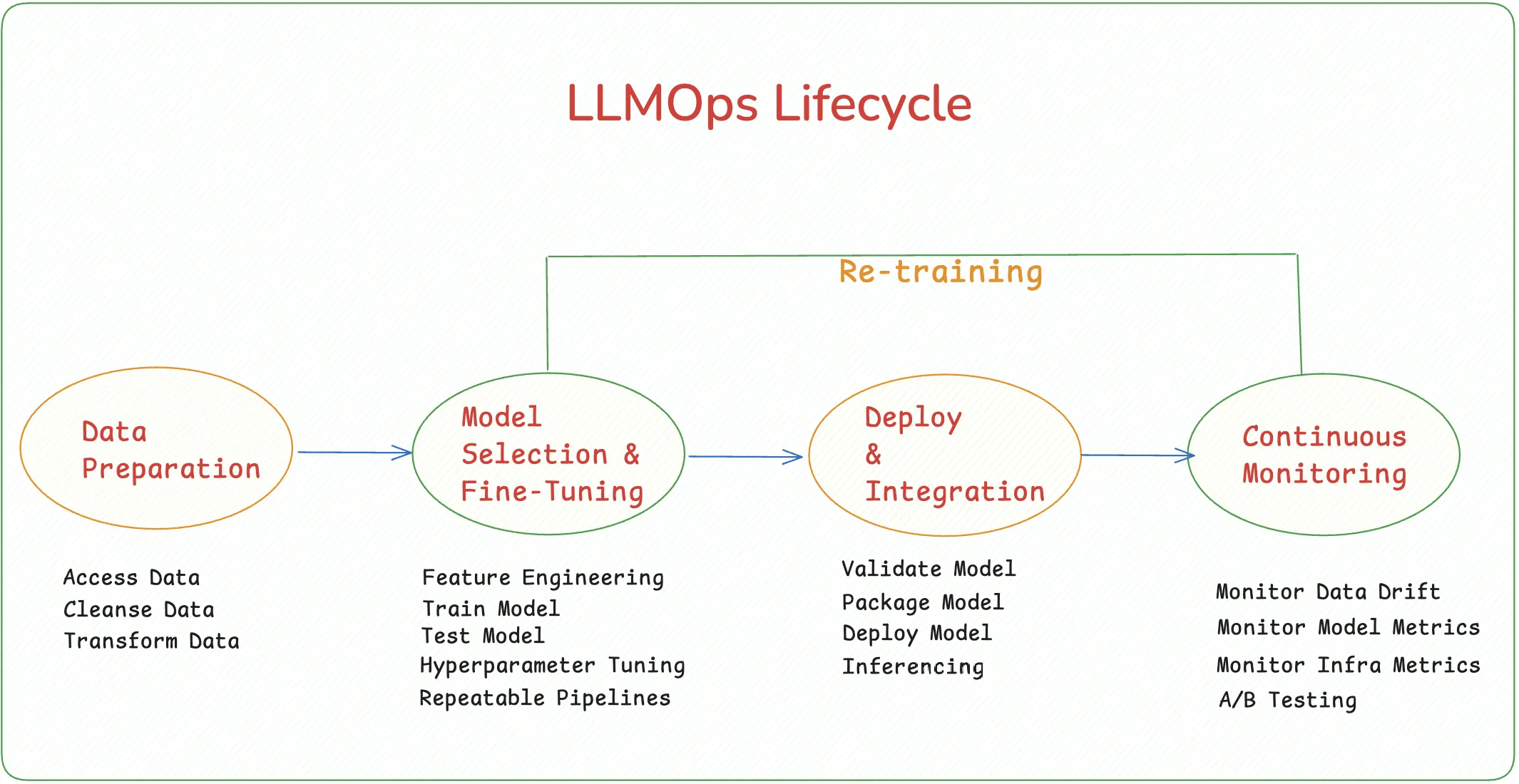
Key Stages in the LLMOps Lifecycle
The LLMOps lifecycle consists of several critical stages to ensure effective model management and deployment:
- Data Preparation: Ensure diversity and address biases in the administration of high-quality datasets. This includes gathering, sanitizing, and preparing data.
- Model Selection and Fine-Tuning: Select suitable pre-trained models and develop them further to meet particular needs. Hyperparameter tweaking, transfer learning, and iteration based on performance measurements are some methods for fine-tuning.
- Deployment and Integration: Integrate with current systems to serve models in production environments with efficiency. This entails containerization using deployment frameworks such as Docker, or TensorFlow Serving.
- Continuous Monitoring and Retraining: To preserve accuracy, regularly assess model performance and retrain as necessary. The use of broad monitoring and alerting systems ensures timely detection of performance degradation.
Overcoming Challenges in LLMOps Implementation
There are certain challenges involved in implementing LLMOps, but these can be successfully handled with the appropriate tactics and resources:
High Computational Requirements:
- Scalable Infrastructure: To train and operate large language models, invest in high-performance processing resources, such as GPUs and TPUs.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: Make use of cloud computing platforms like as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, which provide services specifically tailored for AI workloads and scalable infrastructure.
Example: Using SageMaker and EC2 to set up an AWS training environment. AWS SageMaker offers fully managed services for training and deploying machine learning models at scale. By setting up training jobs on EC2 instances with powerful GPUs, you can utilize SageMaker's distributed training capabilities to handle large datasets and complex models efficiently. This setup enables automatic scaling, spot instance usage for cost efficiency, and integration with other AWS services for a seamless workflow.
Complex Versioning:
- Experiment Tracking: Make sure all versions of experiments, models, and datasets are documented by using tools like MLflow or Weights & Biases.
- Version Control Systems: Use Git LFS or DVC to version big model files and datasets.
Example: Using MLflow to track experiments. MLflow provides a centralized repository to track experiments, recording parameters, metrics, artifacts, and models. When you are training a large language model, you can use MLflow as MLflow logs each experiment's configurations and outcomes which enables reproducibility and easy comparison of different model versions. This systematic tracking helps in fine-tuning models and ensures that the best-performing model configurations are identified and can be reproduced reliably.
Data Privacy and Security:
- Data Protection Measures: Encrypt sensitive data and use access controls and anonymization methods to keep it safe over the lifecycle of the LLM.
- Accordance: Make sure that data privacy laws such as the CCPA and GDPR are followed.
Example: Data encryption before storage. Implementing data encryption before storage involves using encryption algorithms to convert sensitive data into unreadable formats, ensuring that unauthorized users cannot access the original information. For instance, you can use AWS Key Management Service (KMS) to encrypt data stored in S3 buckets provides an additional layer of security.
Ethical Considerations:
- Bias Mitigation: Put frameworks and instruments in place to evaluate and lessen biases in models and training data. To ensure impartiality, evaluate and update datasets regularly.
- Responsible AI: Create guidelines and procedures that support openness, responsibility, and moral application of AI.
Example: Model fairness evaluation with Fairlearn. Fairlearn is an open-source toolkit that helps assess and remove unfairness in machine learning models. By integrating Fairlearn into your workflow, you can analyze your model's predictions across different demographic groups to identify potential biases. For example, after training a language model, you can use Fairlearn to evaluate its performance on subsets of data representing different genders or ethnicities. The toolkit provides metrics and visualizations to understand disparities and offers algorithms to adjust the model, promoting fairness and reducing bias.
Monitoring and Observability in LLMOps with SigNoz
Sustaining the performance and dependability of LLMs in production requires effective monitoring. SigNoz, an open-source observability platform, provides AI and ML systems with strong characteristics like:
- Distributed Tracing: In applications driven by LLM, monitor requests throughout microservices. This aids in comprehending the request flow and locating bottlenecks.
- Custom Dashboards: Showcase important indicators related to the effectiveness of language models. Dashboards shed light on the behaviour of models and the state of operations.
- Alerting: Configure alerts to be notified proactively when there may be problems or a decline in performance. Alerts guarantee that any irregularities are dealt with right away.
- Full Stack Observability: Gain comprehensive visibility across the entire stack, from infrastructure to applications and LLMs. This holistic view helps in identifying and resolving issues at any layer, ensuring seamless operations.
Setting Up SigNoz for LLM Monitoring
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
To configure SigNoz for LLM monitoring:
- Define Custom Metrics: Keep an eye on LLM-specific metrics such as error rates, token usage, and inference time.
- Build Dashboards: Construct visual aids that offer information about resource usage and model performance.
- Set Up Alerts: Establish guidelines to quickly alert teams to abnormalities or performance problems.
Through the resolution of these issues and the utilization of monitoring instruments such as SigNoz, companies may guarantee that their lifecycle managers (LLMs) function effectively and dependably, yielding the intended results in real-world settings.
Interested in doing LLM monitoring with SigNoz? Refer SigNoz’s official doc on LLM Monitoring for complete guide.
For framework- and provider-specific setups, see the docs for OpenAI, Anthropic, LangChain/LangGraph, and LlamaIndex.
Future Trends in LLMOps
The need for increasingly advanced AI systems and technical developments is driving the ongoing evolution of the LLMOps area. Among the major new developments in LLMOps are the following:
More Automation:
- Tools Powered by AI: utilizing AI to automate several model deployment, management, and optimization processes. This covers maintenance duties, deployment pipelines, and automated hyperparameter tweaking.
Example: Automating model tuning and selection with AutoML frameworks.
Community-Based Education:
- Confidentiality-Boosting Methods: By using federated learning, localized data may be used to train models across dispersed devices or servers. This method lowers the chance of data breaches while improving privacy.
Example: Simple Flower-based federated learning configuration.
Specialized Hardware:
- AI-specific Chips: Development and application of specialized hardware to boost the effectiveness and performance of huge language models, such as TPUs and AI accelerators. These processors are made to manage the computing demands of AI workloads more efficiently.
Example: Making effective use of TPUs in TensorFlow to train models.
Industry-Specific Platforms:
- Tailored LLMOps Solutions: Creating tools and platforms that are suited to particular industries, like the legal, finance, and healthcare fields. These technologies enable more efficient language model deployment and management by addressing the particular needs and legal restrictions of each business.
Example: Setting up a healthcare data LLMOps pipeline tailored to the sector.
Key Takeaways
- LLMOps is essential for efficiently managing the lifecycle of large language models, assuring their dependability and performance.
- LLMOps implementation results in faster development cycles, improved model performance, and scalability.
- Creating strong data pipelines, putting version control in place, automating testing, and thorough monitoring are important best practices.
- Addressing complicated problems, high computational requirements, data protection, and ethical issues are necessary to overcome LLMOps obstacles.
- Tools such as SigNoz are essential to guarantee the effectiveness and dependability of LLMs in production settings.
FAQs
What's the difference between LLMOps and traditional MLOps?
LLMOps focuses specifically on the unique challenges of large language models, such as massive computational requirements and complex ethical considerations. Traditional MLOps covers a broader range of machine learning models and may not address LLM-specific issues.
How does LLMOps help in managing ethical concerns with AI?
LLMOps incorporates processes for bias detection, fairness assessment, and transparency in model decisions. It emphasizes responsible AI development practices throughout the lifecycle of language models.
What are the essential tools needed to get started with LLMOps?
Key tools include version control systems (e.g., Git LFS), experiment tracking platforms (e.g., MLflow), containerization technologies (e.g., Docker), and monitoring solutions (e.g., SigNoz).
How often should LLMs be retrained or fine-tuned in an LLMOps framework?
The frequency of retraining depends on factors like data drift, task complexity, and performance requirements. Generally, continuous monitoring helps determine when retraining is necessary, which could be weekly, monthly, or quarterly.
