Troubleshooting RabbitMQ - How to Fix Mnesia Table Errors
RabbitMQ is a powerful message broker that relies on Mnesia, a distributed database management system, for storing its metadata. Mnesia is designed for high availability and fault tolerance, enabling data to be replicated across multiple nodes in a cluster. When you encounter the error "Error while waiting for Mnesia tables" in RabbitMQ, it can bring your messaging system to a halt. This issue often leaves system administrators and developers scratching their heads, wondering how to restore their RabbitMQ instance to a functional state. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the causes of this error, provide step-by-step troubleshooting techniques, and offer strategies to prevent future occurrences — ensuring your RabbitMQ deployment remains robust and reliable.
Understanding RabbitMQ and Mnesia Tables
RabbitMQ is a system that helps different parts of an application communicate by passing messages between them. It acts like a middleman, ensuring smooth and reliable message delivery. To manage its important data, RabbitMQ uses Mnesia, a type of database built in Erlang, designed to work across multiple computers.
Mnesia helps RabbitMQ in several ways:
- It stores details about messages, queues, and connections.
- Manages user accounts and access permissions.
- Keeps track of how different parts of the system are connected.
In RabbitMQ clusters, these Mnesia tables are shared across all nodes (computers) to ensure the system remains available, even if one node fails. However, if there’s a problem with the Mnesia tables, you might see the error message: "Error while waiting for Mnesia tables."
Common scenarios where you might encounter Mnesia table errors include:
- Improper node shutdowns
- Disk space issues
- Network partitions in a cluster
- Inconsistent cluster states
Identifying "Error while waiting for Mnesia tables"
The "Error while waiting for Mnesia tables" message is more than just a nuisance — it's a critical issue that prevents RabbitMQ from starting properly. This error occurs when RabbitMQ is unable to access or initialize its Mnesia database, which is essential for its operation.
When you see this error, it typically means:
- The Mnesia database is in an inconsistent state
- RabbitMQ cannot read or write to the Mnesia tables
- There's a synchronization issue in a multi-node cluster
To identify this error, check your RabbitMQ logs. You can usually find these logs in /var/log/rabbitmq/ on Linux systems or in the RabbitMQ application data directory on Windows in C:\Users\<YourUsername>\AppData\Roaming\RabbitMQ\log\ and in MacOS it is generally located at this location: /opt/homebrew/var/log/rabbitmq
Look for lines similar to:
2023-05-30 10:15:23.123 [error] <0.123.0> Error while waiting for Mnesia tables: {timeout_waiting_for_tables,[rabbit@node1,rabbit@node2]}
This error can severely impact your RabbitMQ cluster's functionality:
- Nodes may fail to start
- Message publishing and consumption may be disrupted
- Management UI might become inaccessible
Troubleshooting Mnesia Table Errors in RabbitMQ
Mnesia is a distributed database system used by RabbitMQ to store metadata such as queues, exchanges, and bindings. Errors in the Mnesia tables can lead to disruptions in RabbitMQ's functionality, making it crucial to troubleshoot and resolve them effectively. Here is a step-by-step guide to identifying and fixing Mnesia table errors:
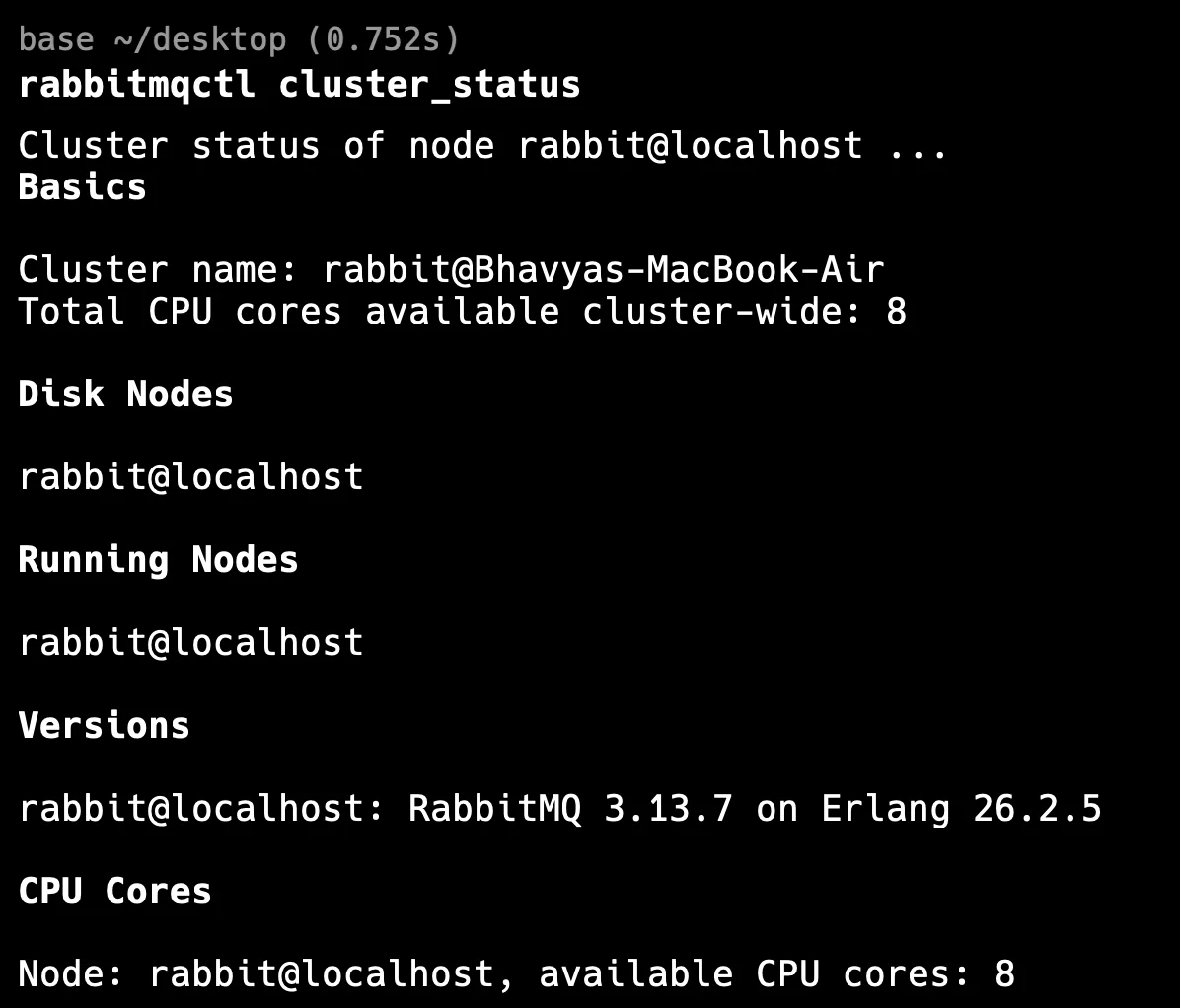
- Check Cluster Status
Start by verifying the status of your RabbitMQ cluster. This will help you determine if all nodes are healthy and part of the cluster.
rabbitmqctl cluster_status
This command provides detailed information about the nodes in the cluster, their running status, and whether any nodes are missing. Pay attention to:
- Running nodes: Check if all nodes are listed and running.
- Partitions: Network partitions can split the cluster, causing Mnesia to behave erratically.
- Node roles: Identify if nodes are acting as disc or RAM nodes, as issues could differ based on the role.
- Verify Node Connectivity
In a RabbitMQ cluster, all nodes must be able to communicate with each other. If any node is unable to connect to others, Mnesia tables will fail to synchronize properly.
rabbitmqctl ping

Run this command on each node to ensure that they can reach each other. If a node does not respond with ping, it could indicate network or configuration issues. Possible reasons for connectivity failure include:
- Firewall rules blocking communication.
- Incorrect network configuration (e.g., wrong hostname or IP).
- Node being down or unreachable.
Resolving connectivity issues is key to maintaining Mnesia's consistency across the cluster.
- Check Disk Space
Mnesia requires disk space to store its data, and insufficient disk space can cause the database to fail in writing or maintaining table records.
df -h
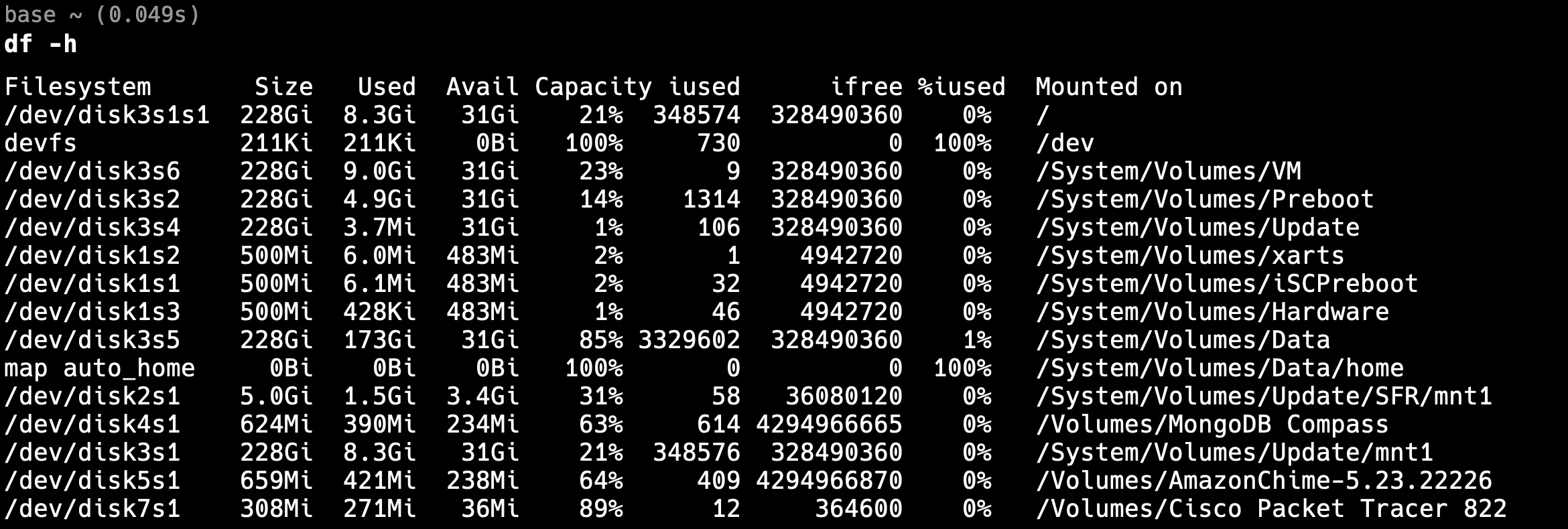
This command shows disk usage for the system. Pay attention to:
- Filesystem usage: Ensure that the partition where RabbitMQ stores its data (
/var/lib/rabbitmq/mnesia/) has sufficient space. - Threshold: It's a good practice to have at least 10-15% free disk space to avoid unexpected issues.
If disk space is low, free up space or allocate additional resources to the system. This step is often overlooked but is critical for Mnesia’s smooth operation.
- Examine File Permissions
Incorrect file permissions can prevent RabbitMQ from accessing the Mnesia tables, leading to database errors. Ensure that the RabbitMQ user has the appropriate read and write permissions for the Mnesia directory. A lack of proper permissions can result in errors when RabbitMQ tries to read from or write to its Mnesia files. You can check the permissions in linux using the below command :
ls -l /var/lib/rabbitmq/mnesia/
You need to change the path for your Mac, as shown in below image:
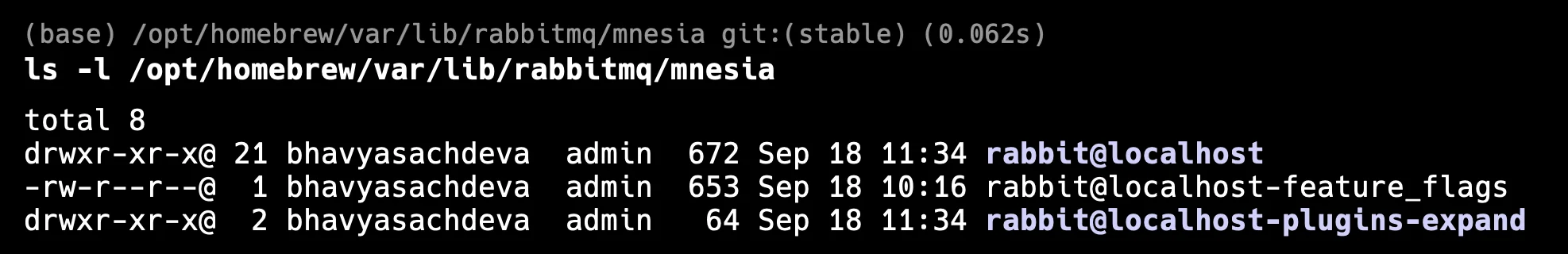
- Ownership: The directory should be owned by the RabbitMQ user.
- Permissions: The RabbitMQ process should have
rwx(read, write, execute) permissions on the directory.
To fix permission issues, you can run:
sudo chown -R rabbitmq:rabbitmq /var/lib/rabbitmq/mnesia/
sudo chmod -R 755 /var/lib/rabbitmq/mnesia/
Below, I have shown in the MacOS, you can change the path according to your OS because it differs in MacOS, Windows and Linux :

After fixing the permissions, restart RabbitMQ to apply changes.
- Investigate Network Issues
Network problems such as latency, dropped packets, or partitions can interrupt the synchronization of Mnesia tables between nodes in a RabbitMQ cluster.
ping [other_node_hostname]
Use the ping command to check if nodes can reach each other over the network. If a node cannot be reached, you may be facing one of the following issues:
- Network partitioning: Nodes are isolated from each other, preventing them from syncing Mnesia tables. Use
rabbitmqctl cluster_statusto identify partitions. - High latency: Long response times might affect the performance of the RabbitMQ cluster, delaying table updates.
Resolving these network problems can often involve checking firewall settings, verifying network configurations, or even restarting nodes to re-establish connections.
By following these steps, you can systematically troubleshoot and resolve Mnesia table errors, ensuring the reliability and performance of your RabbitMQ cluster. Always keep in mind that RabbitMQ’s underlying Mnesia database relies heavily on proper node communication, disk space, and file permissions for smooth operations.
Resolving Mnesia Table Errors in Standalone Nodes
For standalone RabbitMQ nodes, you can often resolve Mnesia table errors using the rabbitmqctl force_boot command:
rabbitmqctl force_boot
This command bypasses the usual cluster consistency checks and forces the node to start. However, use it cautiously — it can lead to data inconsistencies if used improperly.
To prevent future issues:
Always use proper shutdown procedures:
rabbitmqctl stopRegularly back up your Mnesia database:
rabbitmqctl export_definitions backup.json
export defintions If necessary, recover data from Mnesia files:
cp /opt/homebrew/var/lib/rabbitmq/mnesia/backup.json /opt/homebrew/var/lib/rabbitmq/mnesia/rabbit@node_check
Backup
Fixing Mnesia Errors in RabbitMQ Clusters
Resolving Mnesia errors in a clustered environment requires more care:
Identify the last node to go down — this node likely has the most up-to-date data.
Start this node first:
rabbitmq-server -detachedOnce it's up, rejoin other nodes to the cluster:
rabbitmqctl stop_app rabbitmqctl reset rabbitmqctl join_cluster rabbit@[first_node_name] rabbitmqctl start_app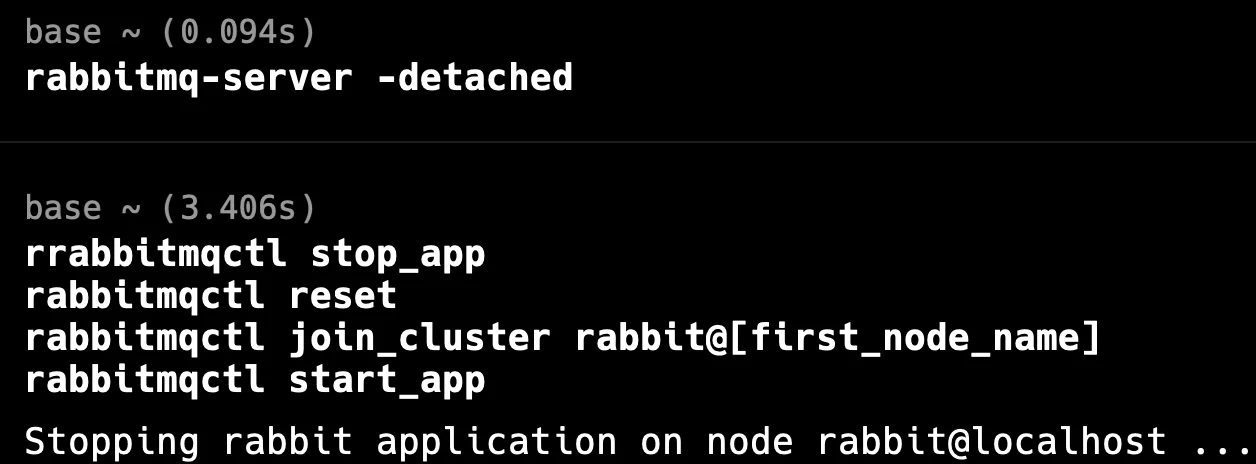
Server Detached In severe cases, you might need to use the
forget_cluster_nodecommand:rabbitmqctl forget_cluster_node --offline rabbit@[problematic_node]This removes a node from the cluster without contacting it, useful when a node is permanently lost.
Preventing Future Mnesia Table Errors
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are strategies to minimize Mnesia table errors:
Implement proper shutdown procedures for all nodes.
Schedule regular backups of your Mnesia database.
Monitor disk space and system resources closely.
Configure appropriate Mnesia table properties: These settings in your
rabbitmq.conffile can help manage table loading issues.{mnesia_table_loading_retry_timeout, 30000}, {mnesia_table_loading_retry_limit, 10}
Mnesia Table Errors in Kubernetes Environments
Running RabbitMQ in Kubernetes presents unique challenges for Mnesia table management:
- Use StatefulSets to ensure stable network identities for your pods:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: rabbitmq
spec:
serviceName: "rabbitmq"
replicas: 3
...
- Configure PersistentVolumes for data persistence:
volumeClaimTemplates:
- metadata:
name: rabbitmq-data
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
- Implement proper pod restart policies:
spec:
template:
spec:
restartPolicy: Always
- Use readiness probes that account for Mnesia table initialization:
readinessProbe:
exec:
command: ["rabbitmq-diagnostics", "check_port_connectivity"]
initialDelaySeconds: 60
periodSeconds: 30
Monitoring RabbitMQ Performance with SigNoz
To prevent Mnesia table errors proactively, robust monitoring is essential. SigNoz, an open-source APM tool, offers comprehensive monitoring for distributed systems like RabbitMQ.
Here's how to set up SigNoz for RabbitMQ monitoring:
Install SigNoz using Docker:
git clone -b main <https://github.com/SigNoz/signoz.git> cd signoz/deploy/ ./install.shConfigure RabbitMQ to expose metrics:
management_agent.disable_metrics_collector = falseSet up Prometheus to scrape RabbitMQ metrics and forward them to SigNoz.
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
With SigNoz, you can:
- Monitor RabbitMQ cluster health in real-time
- Set up alerts for early detection of Mnesia-related issues
- Analyze trends in RabbitMQ performance metrics
By leveraging SigNoz's powerful analytics, you can identify potential Mnesia table issues before they escalate into critical errors.
Key Takeaways
- Mnesia table errors can severely impact RabbitMQ functionality.
- Proper diagnosis and structured troubleshooting are crucial for resolution.
- Cluster management requires special care to maintain data consistency.
- Regular maintenance and monitoring can prevent most Mnesia-related issues.
FAQs
What causes the "Error while waiting for Mnesia tables" in RabbitMQ?
This error typically occurs due to inconsistent Mnesia database states, often caused by improper node shutdowns, disk space issues, or network partitions in a cluster.
How can I prevent Mnesia table errors when running RabbitMQ in Kubernetes?
Use StatefulSets for stable network identities, configure PersistentVolumes for data persistence, implement proper restart policies, and use readiness probes that account for Mnesia table initialization.
Is it safe to use the rabbitmqctl force_boot command?
While rabbitmqctl force_boot can resolve some Mnesia table errors, use it cautiously. It bypasses cluster consistency checks and can lead to data inconsistencies if used improperly.
How often should I back up RabbitMQ's Mnesia database?
The frequency of backups depends on your specific use case and data criticality. However, a good practice is to perform daily backups and additional backups before major system changes or updates.
