Getting Started with OpenTelemetry Visualization - A Practical Guide
OpenTelemetry is a Cloud Native Computing Foundation(CNCF) project aimed at standardizing the way we instrument applications for generating telemetry data(logs, metrics, and traces). However, OpenTelemetry does not provide storage and visualization for the collected telemetry data. For OpenTelemetry visualization, you need to use an observability backend that can ingest the collected data and provide a web UI to visualize it.
Quick Start Guide: OpenTelemetry Visualization in 5 Steps
Get started with OpenTelemetry visualization quickly using this step-by-step guide:
1. Instrument your application with OpenTelemetry SDKs
- Choose the appropriate OpenTelemetry SDK for your programming language
- Install the SDK using your language's package manager (such as
npmorpip) - Add instrumentation code to your application
- Configure global settings like service name and version
Example (Python):
from opentelemetry import trace
from opentelemetry.sdk.resources import Resource
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace import TracerProvider
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace.export import BatchSpanProcessor
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.grpc.trace_exporter import OTLPSpanExporter
trace.set_tracer_provider(TracerProvider(resource=Resource.create(
attributes={
"service.name": "application-svc",
"service.version": "1.2.0",
"deployment.environment": "staging",
}
)))
tracer = trace.get_tracer(__name__)
otlp_exporter = OTLPSpanExporter(endpoint="your-collector-endpoint:4317", insecure=True)
span_processor = BatchSpanProcessor(otlp_exporter)
trace.get_tracer_provider().add_span_processor(span_processor)
# Your application code here
with tracer.start_as_current_span("main"):
# ...
2. Set up the OpenTelemetry Collector
- Download and install the OpenTelemetry Collector
- Configure the Collector to receive data from your application
- Set up appropriate processors for data manipulation (if needed)
- Configure exporters to send data to your chosen backend
Example config.yaml:
receivers:
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:4317
processors:
batch:
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: "your-backend:4317"
tls:
insecure: true
service:
pipelines:
traces:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlp]
3. Choose a visualization tool
Select a tool based on your needs:
- Grafana: Highly customizable dashboarding platform
- Jaeger: Specialized in distributed tracing visualization
- SigNoz: Full-stack open-source APM with native OpenTelemetry support
For this guide, we'll use SigNoz as an example due to its ability to visualize traces, metrics, and logs in one pane.
4. Configure data export from the Collector to your chosen tool
Update your Collector's config.yaml to export data to SigNoz:
exporters:
otlp:
# replace <region> with your chosen data region (in, us, etc.)
endpoint: "https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443"
headers:
# add your ingestion key here
signoz-ingestion-key: "<SIGNOZ-INGESTION-KEY>"
service:
pipelines:
traces:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlp]
You can self-host SigNoz if you wish to keep data on-premise. When running SigNoz in self-hosted mode, you will need to send data to the SigNoz OTel Collector instead of the cloud endpoint:
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: "signoz-otel-collector:4317"
tls:
insecure: true
...
5. Create your first dashboard to visualize key metrics and traces
- Log in to your SigNoz dashboard
- Navigate to the "Dashboards" section
- Click "New Dashboard" and add panels for key metrics:
- Request Rate
- Error Rate
- P95 Latency
- Add a trace table panel to view recent traces
- Save your dashboard
To help save time, you can also import the APM Metrics dashboard to speed up this process for you. Once you’ve imported it, you can simply modify individual panels to suit your needs.
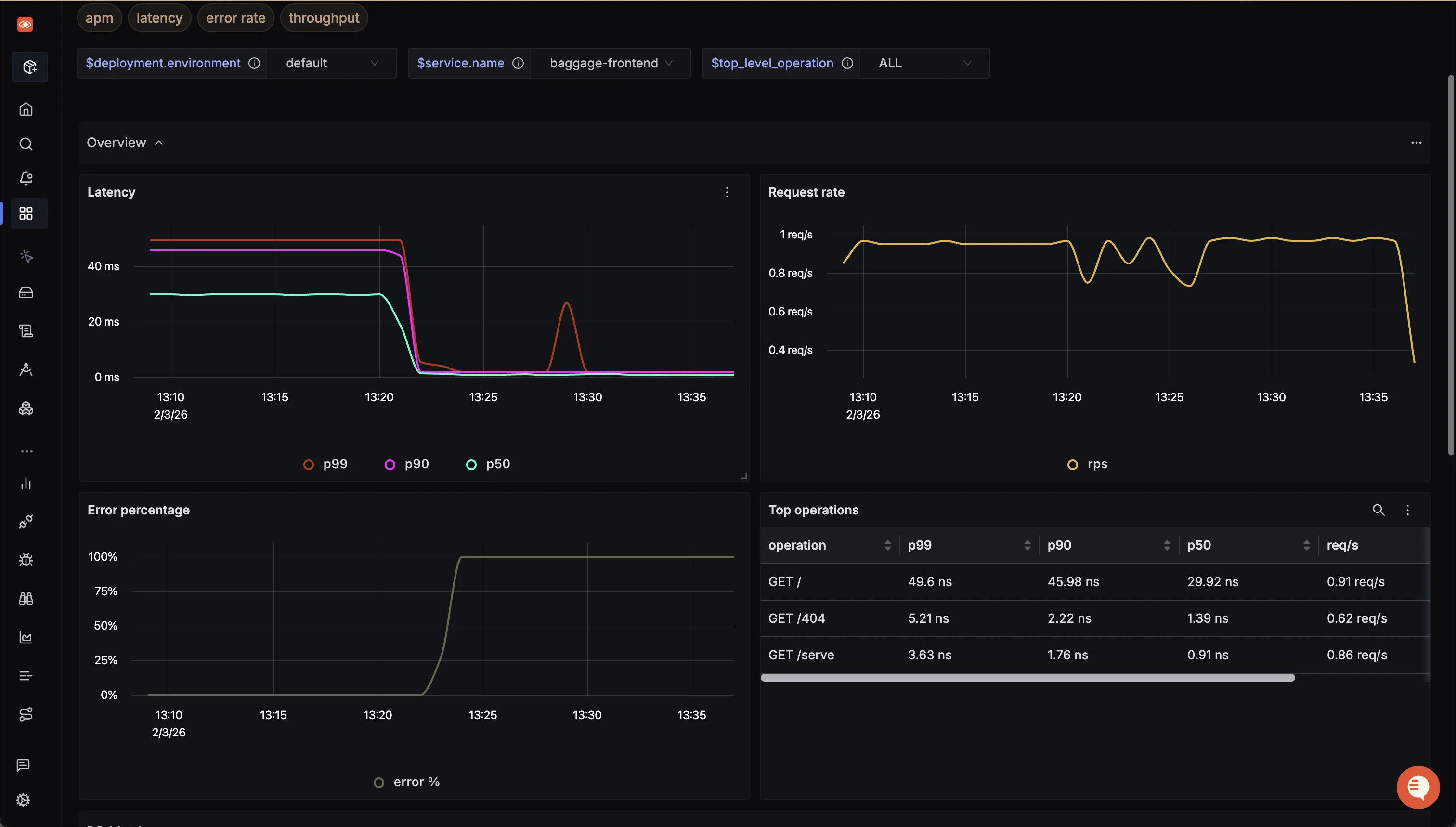
Let's now dive deeper into the concepts of OpenTelemetry visualization.
What is OpenTelemetry Visualization?
OpenTelemetry visualization is the process of transforming raw telemetry data into visual representations that are easy to understand and analyze. It combines three key elements:
OpenTelemetry: An open-source observability framework that provides a standardized way to collect and export telemetry data from your applications and infrastructure.
The OpenTelemetry specification has design and implementation guidelines for how the instrumentation libraries should be implemented. In addition, it provides client libraries (commonly known as SDKs) in all the major programming languages that follow the specification.
Telemetry Data: This includes:
- Metrics: Numerical measurements of system performance
- Traces: Detailed records of request flows through distributed systems
- Logs: Time-stamped records of events within your applications
Together these three signals form the three pillars of observability.
OpenTelemetry is the bedrock for setting up an observability framework. By instrumenting them at runtime, OpenTelemetry SDKs enable applications to generate telemetry data. Once the telemetry data is generated and collected, OpenTelemetry needs a backend analysis tool for storing and visualizing this data.
Visualization Tools: Software that takes this telemetry data and creates charts, graphs, and dashboards to help you make sense of it all.
OpenTelemetry can send data to multiple backends, and you can use different backends for each signal in OpenTelemetry. But managing different tools is not recommended as engineering teams would have to frequently switch context trying to correlate signal data across these tools. This is where SigNoz comes into the picture as it provides traces, metrics and logs correlated in one pane for effective visualization. In the later parts of this article, we will discuss more on how to get started with visualizing OpenTelemetry data with SigNoz.
Why Visualize OpenTelemetry Data?
Visualizing OpenTelemetry data offers several key benefits:
- Improved System Understanding: Complex distributed systems can be difficult to grasp. Visualization helps you see the big picture — how different components interact and where potential issues might arise.
- Faster Problem Identification: When something goes wrong, time is of the essence. Visual representations allow you to quickly spot anomalies or performance degradations, reducing mean time to resolution (MTTR).
- Enhanced Collaboration: Visualizations serve as a common language between development and operations teams. They make it easier to discuss issues, share insights, and work together towards solutions.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: With clear visualizations of system performance and user behavior, you can make informed decisions about where to focus optimization efforts or allocate resources.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerting: Visual dashboards provide at-a-glance system health checks. When combined with alerting mechanisms, they ensure you're always aware of critical issues.
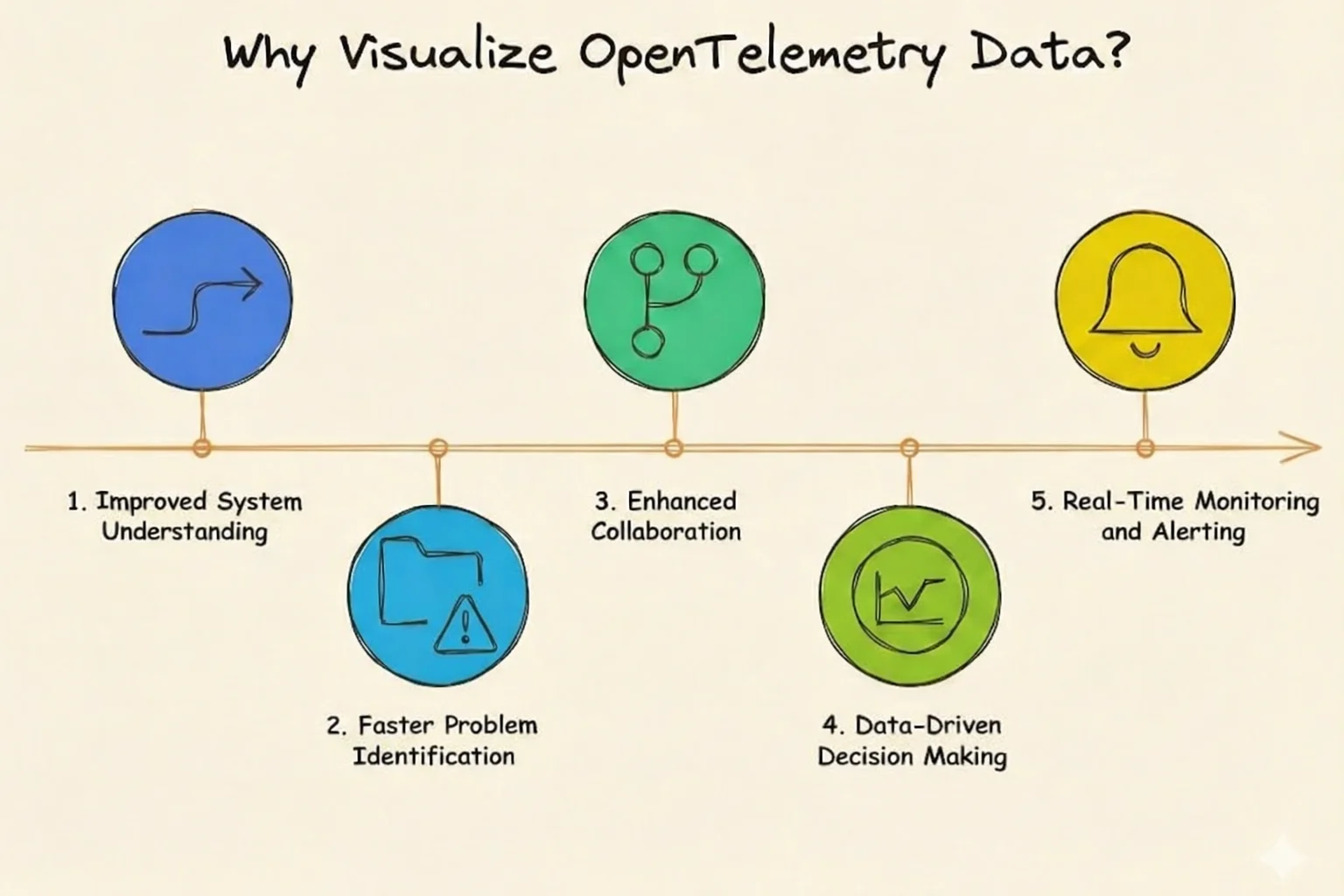
By transforming raw telemetry data into intuitive visual representations, OpenTelemetry visualization enables you to maintain healthier, more efficient systems, catch and diagnose issues as they happen, and understand data trends by correlating events across distributed systems with individual requests.
Key Components of OpenTelemetry Visualization
To effectively visualize OpenTelemetry data, you need to understand the key components involved:
- Data Collection and Instrumentation:
- OpenTelemetry SDKs: These libraries allow you to instrument your code, automatically collecting telemetry data from your applications.
- Auto-instrumentation agents: For supported languages, these can instrument applications with little or no modifications to your source code.
- OpenTelemetry Collector:
- Acts as a central hub for processing and exporting telemetry data
- Receives data from multiple sources
- Performs data transformation and filtering
- Exports data to various backends
- Backend Storage Solutions:
- Time-series databases (e.g., Prometheus, InfluxDB): Ideal for storing metrics
- Distributed tracing systems (e.g., Jaeger, Zipkin): Designed for storing and querying trace data
- Log management systems (e.g., Elasticsearch, Loki): Optimized for storing and searching log data
- Visualization Tools:
- Dashboarding platforms (e.g., SigNoz, Grafana, Kibana): Create custom visualizations and dashboards
- APM solutions (e.g., SigNoz, Datadog): Provide pre-built visualizations tailored for application performance monitoring
- Specialized tools (e.g., Jaeger UI for distributed tracing)
These components work together to create a complete OpenTelemetry visualization pipeline:
- Your instrumented applications generate telemetry data.
- The OpenTelemetry Collector receives, processes, and exports this data.
- Backend systems store the telemetry data efficiently.
- Visualization tools query the backend and create meaningful visual representations.
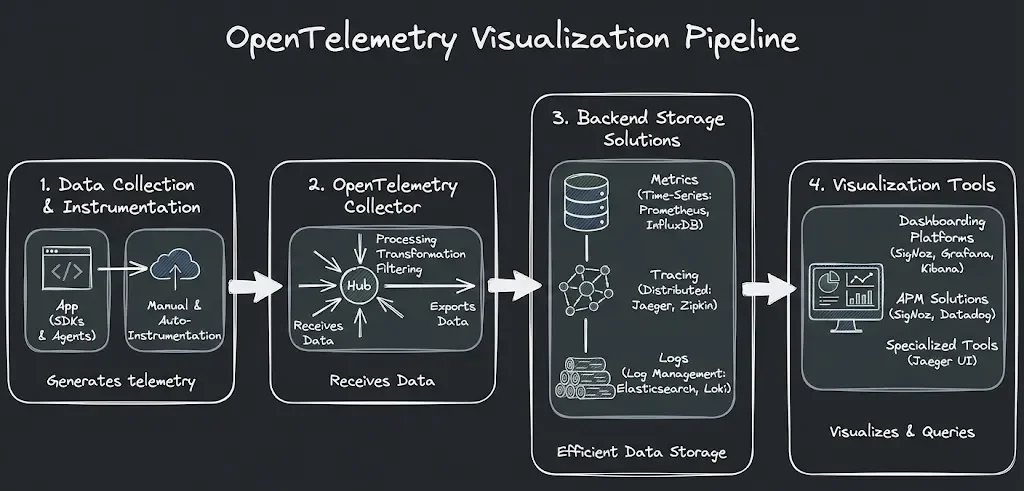
Understanding this pipeline helps you choose the right tools and configure them effectively for your specific needs.
Choosing the Right OpenTelemetry Visualization Tool
Selecting the appropriate visualization tool is crucial for maximizing the value of your OpenTelemetry data. Consider these factors when making your choice:
- Scalability: Can the tool handle your current data volume? Will it grow with your needs?
- Data Retention: How long does the tool store historical data? Is this sufficient for your use cases?
- Query Language: Is the tool's query language powerful enough for your analysis needs? Is it easy for your team to learn and use?
- Support for OpenTelemetry Semantic Conventions: Does the tool understand and properly display OpenTelemetry's standardized attributes and metrics?
- Integration Capabilities: Can the tool easily connect with your existing infrastructure and other tools in your observability stack?
- User Interface and Customization: Is the interface intuitive? Can you create custom dashboards and visualizations to match your specific requirements?
- Cost: For commercial solutions, does the pricing model align with your budget and expected usage?
- Community and Support: For open-source options, is there an active community? For commercial tools, what level of support is provided?
Remember — there's no one-size-fits-all solution. The best tool depends on your specific needs, existing infrastructure, and team expertise.
Visualizing OpenTelemetry data with SigNoz
Noting the above requirements, SigNoz aims to provide a comprehensive visualization experience across all features (and not just Traces, Metrics, and Logs). While a dashboard might be the first place an engineer looks at when debugging a critical issue, that is just the starting point. Building on its OpenTelemetry-native foundations, SigNoz provides several forms of visualizations, let's understand what these are.
Application Metrics
SigNoz comes with out-of-box charts for the popular RED(requests, error, and duration) metrics. Acting as the "bird's eye view", these metrics help you quickly track application health, derive high-level insights and take actions (via telemetry correlation) as you notice anomalies.
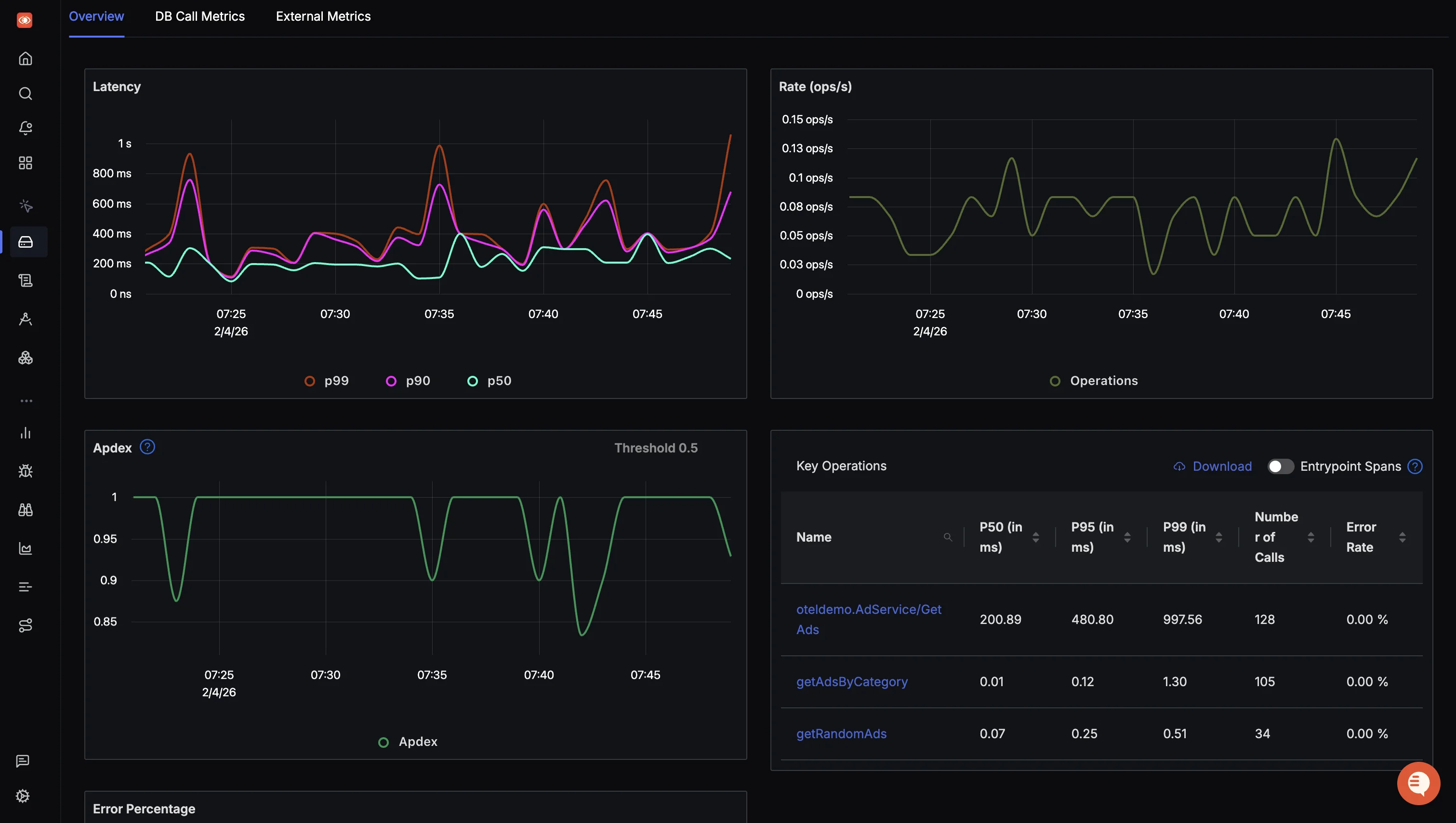
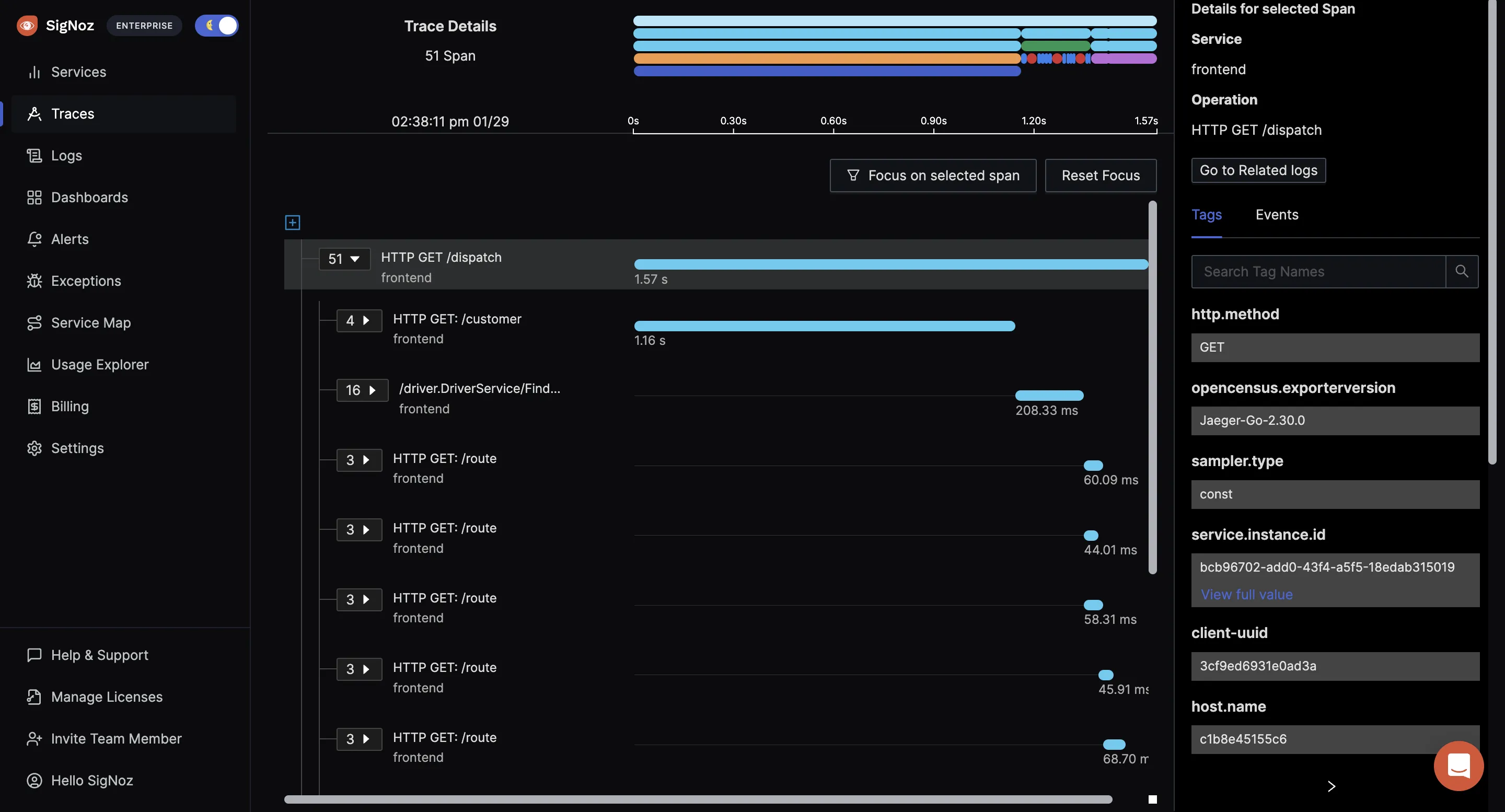
Distributed tracing with Flamegraphs and Gantt Charts
The tracing data captured with OpenTelemetry can be visualized with the help of Flamegraphs and Gantt charts. This view gives you a complete breakdown of a single user request as it travels across services and protocols.
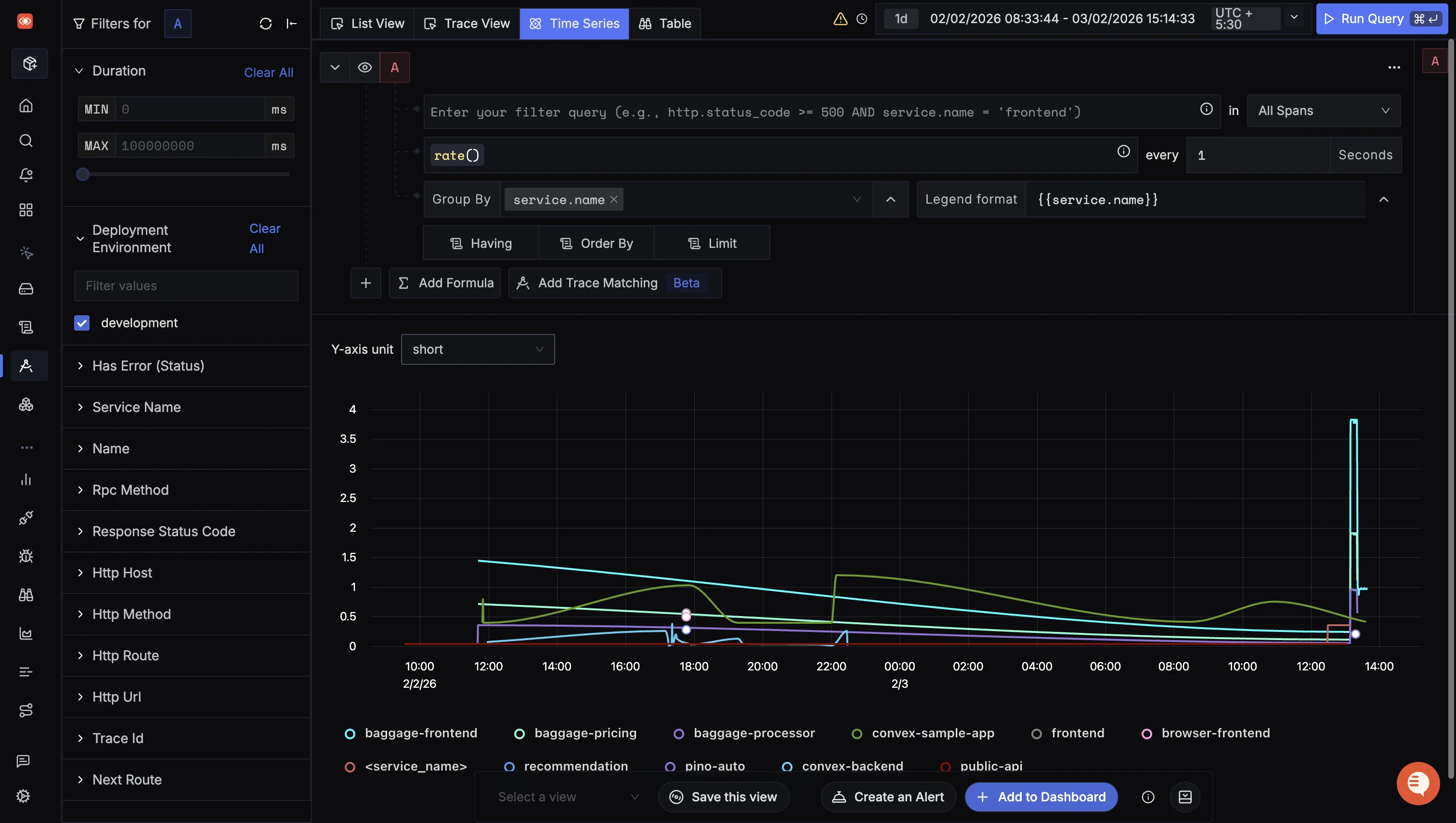
Trace Aggregates
Using SigNoz dashboards, you can visualize and dissect aggregated trace data collected with OpenTelemetry. These trace aggregates visualizations helps you create service-centric views. For example, you can see the P99 latency of all your services to pinpoint the services facing performance issues.
You can also analyze the trace data using a set of powerful filters like status, operation, HTTP codes, etc. SigNoz uses OpenTelemetry semantic conventions to visualize this data to ensure optimal compatibility with SDK implementations.
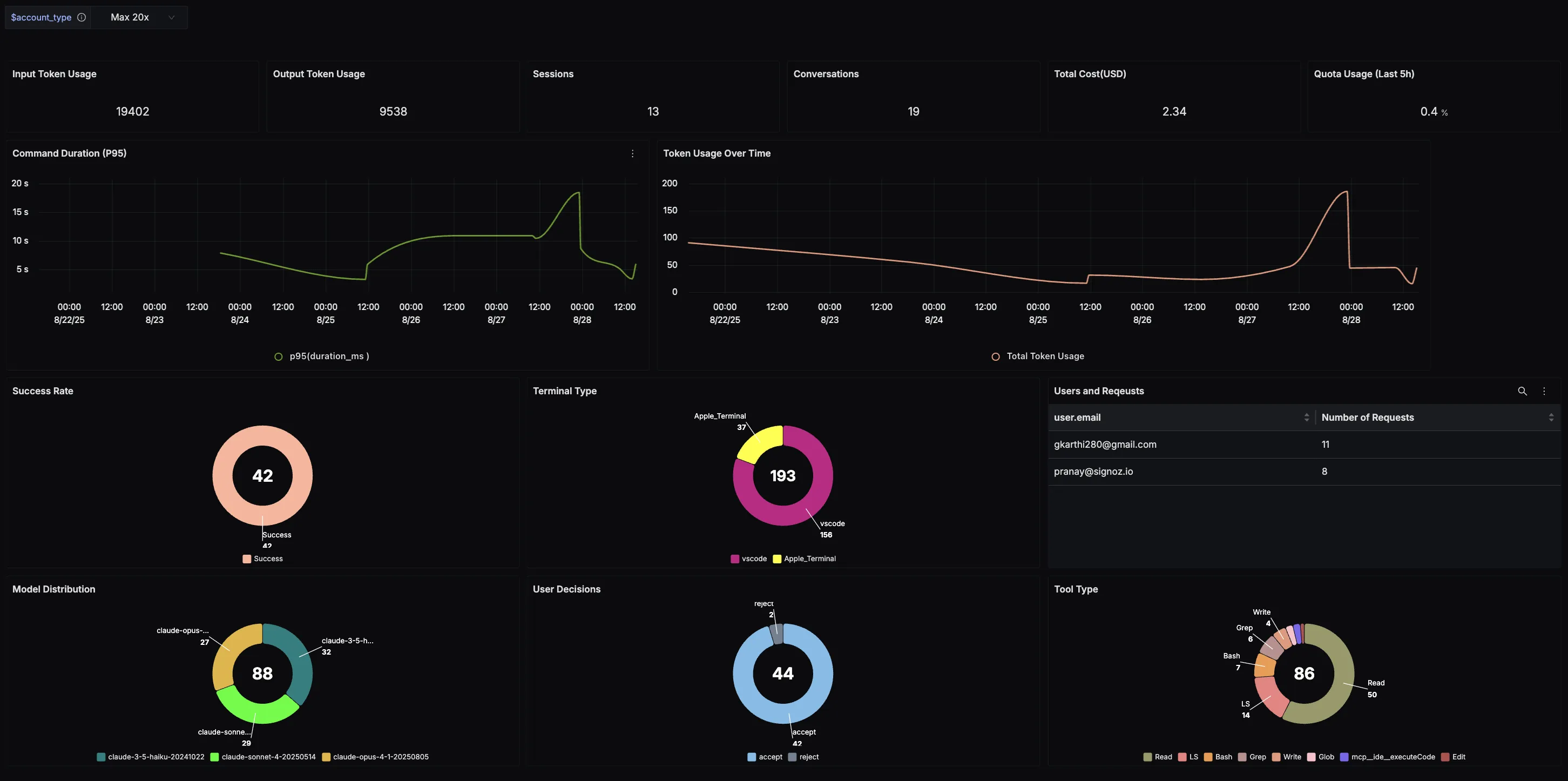
Custom Dashboards
OpenTelemetry provides receivers for receiving metrics from metrics exporters of a lot of common technologies. For example, there are receivers for Redis, AWS container insights, Docker stats, etc. Using these receivers, you can ingest data from a variety of infrastructure components to build custom dashboards with SigNoz.
With AI becoming a core necessity, infrastructure isn’t is the only use-case, and all modern day applications tend to interact with LLMs in some manner. An emerging use-case is the monitoring of your LLM calls to track the token burn, chat context, etc. for your models, whether it is within applications or with developer-centric tools such as Claude Code.
Infrastructure Metrics
While trace aggregates, APM metrics and the like are great for observing the business logic, they don't provide visibility into the underlying infrastructure. You are leaving a blind spot in your observability pipeline if you aren't visualizing host-level metrics such as CPU, memory, disk, etc. SigNoz provides dedicated dashboards per-host to track infrastructure health, and correlates all logs and traces emitted by the applications running on that host.
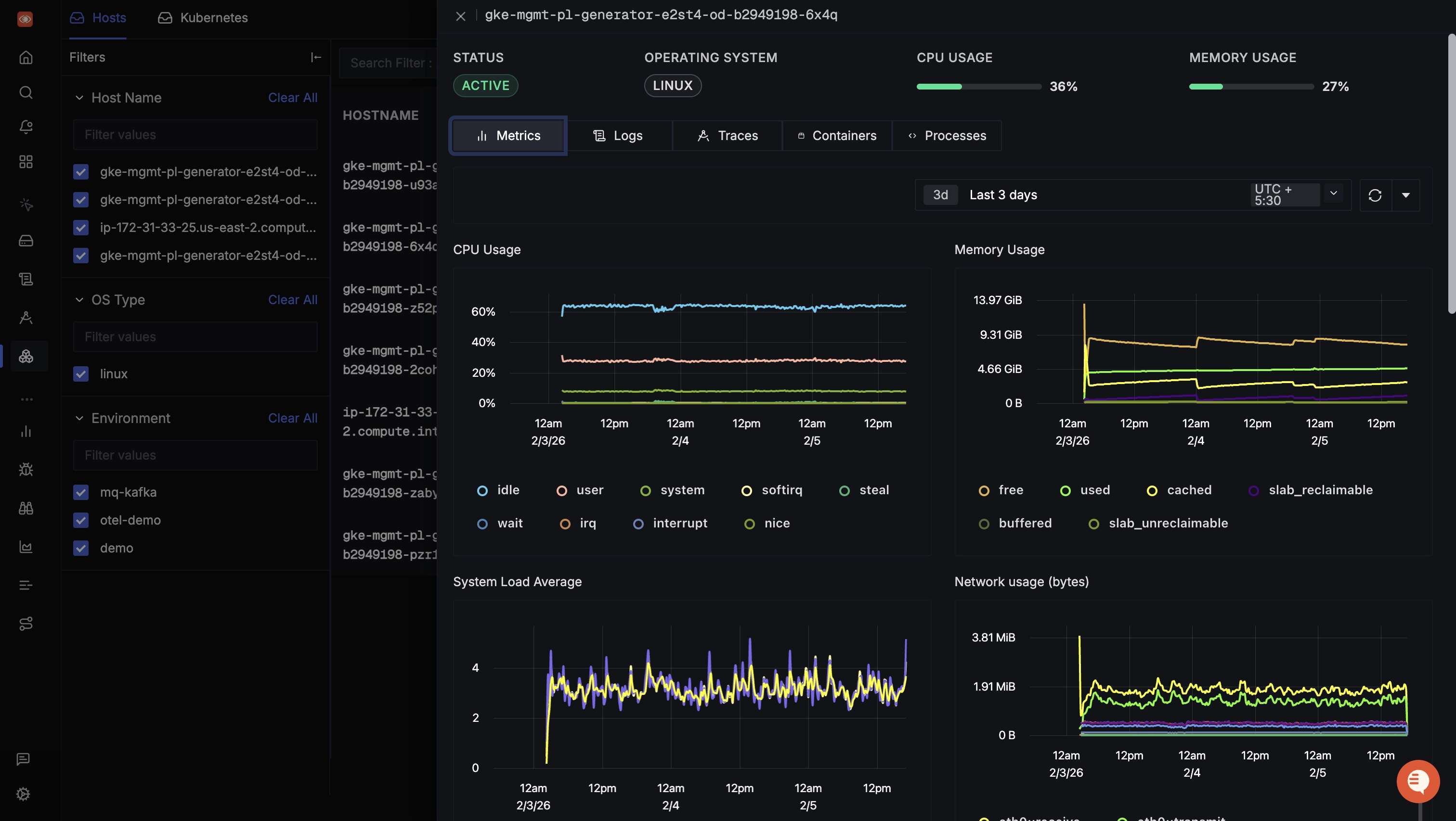
If SigNoz sounds like the right tool for visualizing the telemetry data generated by your application systems, sign up today for SigNoz Cloud or self-host the Community Edition for free.
Best Practices for Effective OpenTelemetry Visualization
To get the most out of your OpenTelemetry visualizations, follow these best practices:
- Implement Consistent Naming Conventions and Tagging:
- Use clear, descriptive names for services, endpoints, and metrics
- Apply consistent tags to aid in filtering and grouping data
- Follow OpenTelemetry semantic conventions where applicable
- Design Informative and Actionable Dashboards:
- Create role-specific dashboards (e.g., for developers, operations, management)
- Use a logical layout that tells a story about your system's performance
- Include both high-level overviews and the ability to drill down into details
- Utilize Heat Maps and Service Dependency Graphs:
- Heat maps help identify patterns and anomalies in large datasets
- Service dependency graphs visualize the relationships between components in your system
- Correlate Metrics, Traces, and Logs:
- Link related data types for comprehensive analysis
- Use trace IDs to connect logs with specific request flows
- Combine metrics with traces to understand the impact of performance issues
- Implement Effective Alerting:
- Set up alerts based on key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Use dynamic thresholds to reduce noise and catch real issues
- Ensure alerts are actionable and provide context for troubleshooting
- Regularly Review and Refine Visualizations:
- Continuously improve your dashboards based on user feedback
- Remove unused or redundant visualizations to maintain clarity
- Update visualizations as your system evolves
- Standardize What Key Metrics Mean:
- Maintain the key metrics on a per-team level
- Create central dashboards capturing above metrics to avoid redundancy and prevent configuration “drift”
- Example: two devs monitoring system uptime using different queries and/or separate dashboards
By following these practices, you'll create OpenTelemetry visualizations that provide clear, actionable insights into your system's behavior.
Overcoming Common Challenges in OpenTelemetry Visualization
As you implement OpenTelemetry visualization, you may encounter several challenges. Here's how to address them:
- High-Cardinality Data:
- Problem: Too many unique values in your data can slow down queries and make visualizations cluttered.
- Solution: Use sampling techniques, implement data aggregation, and design your instrumentation to limit unnecessary high-cardinality fields.
- Data Volume and Retention:
- Problem: Storing and querying large volumes of telemetry data can be expensive and slow.
- Solution: Implement intelligent sampling, use efficient storage solutions (e.g., columnar databases), and set up appropriate data retention policies.
- Data Consistency Across Services:
- Problem: Inconsistent naming or tagging across different services can make it difficult to correlate data.
- Solution: Establish and enforce consistent naming conventions and tagging strategies across your organization.
- Security and Privacy Concerns:
- Problem: Telemetry data may contain sensitive information.
- Solution: Implement data masking, use encryption for data in transit and at rest, and ensure compliance with relevant data protection regulations.
- Tool Sprawl:
- Problem: Using multiple visualization tools can lead to fragmented insights and increased complexity.
- Solution: Aim for a consolidated observability platform that can handle metrics, traces, and logs in a unified interface.
- Alert Fatigue:
- Problem: Too many alerts can lead to important issues being overlooked.
- Solution: Use dynamic thresholds, implement alert grouping, and regularly review and refine your alerting rules.
By anticipating and addressing these challenges, you can create a more effective and sustainable OpenTelemetry visualization strategy.
Key Takeaways
- OpenTelemetry visualization transforms raw telemetry data into actionable insights, crucial for understanding and optimizing complex distributed systems.
- Effective visualization requires proper instrumentation, data processing, and choosing the right tools for your specific needs.
- Popular visualization options include open-source tools like SigNoz, Jaeger and Grafana, as well as commercial solutions like DataDog.
- Best practices include consistent naming conventions, correlating different types of telemetry data, and regularly refining your visualizations.
- Common challenges include dealing with high-cardinality data and managing large data volumes.
FAQs
What's the difference between OpenTelemetry and visualization tools?
OpenTelemetry is a framework for collecting and exporting telemetry data. Visualization tools take this data and create graphical representations that help make sense of the ingested telemetry data. While OpenTelemetry standardizes data collection, visualization tools focus on presenting that data in meaningful ways for the end users.
Can OpenTelemetry data be visualized in real-time?
OpenTelemetry data can be visualized in near real-time. OpenTelemetry exporters send data in batches over gRPC to observability backends like SigNoz, which then process and visualize the data using high performance databases like ClickHouse.
How does OpenTelemetry visualization improve application performance?
Visualization helps you quickly identify performance bottlenecks, understand system dependencies, and spot anomalies. This insight allows you to make targeted improvements to your application's performance.
Is it possible to visualize OpenTelemetry data from multiple programming languages in a single dashboard?
Absolutely. OpenTelemetry's standardized approach ensures that data from different languages can be collected and visualized consistently. Most visualization tools can combine data from multiple sources into unified dashboards.