15 Best Infrastructure Monitoring Tools in 2026
If you're reading this, you're probably drowning in monitoring tool options while your infrastructure grows more complex by the day. Maybe you're tired of Datadog's surprise bills, or perhaps Nagios finally feels too dated for your Kubernetes clusters. Whatever brought you here, let's talk directly about what these tools actually do, what they really cost, and which one works best for your team's specific needs.
Quick Decision Framework
Before diving into detailed reviews, here's what you need to know in 30 seconds:
| Tool | Best For | Real Monthly Cost | Setup Complexity* | Infrastructure Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Datadog | Well-funded startups/enterprises | $15-30/host + extras | Medium (2-3 weeks) | Full-stack |
| SigNoz | Teams wanting OTel-native observability or deployment freedom | Free OSS or transparent cloud pricing | Medium (2-3 weeks) | Full-stack APM, metrics, and logs |
| New Relic | Application-centric orgs | ~$0.40/GB + $49-99/user | Medium (2-3 weeks) | Full-stack |
| Prometheus + Grafana | Technical teams with k8s | Free OSS or Grafana Cloud (usage-based pricing) | High (4-6 weeks) | Flexible/custom |
| Dynatrace | Large enterprises | $29/month (infra) or $58/month (full-stack) | Low (1-2 weeks) | Full-stack with AI |
| Zabbix | Traditional IT environments | Free + time investment | Very High (6-8 weeks) | Network, server, cloud |
| Nagios | Legacy environments | Free + massive time cost | Very High (8-12 weeks) | Network, server |
Setup complexity estimates based on typical enterprise deployments, including agent installation, dashboard configuration, alert setup, and team training. These timelines are derived from user-reported experiences in production environments, vendor documentation, and implementation guides. Important: Actual implementation times vary significantly based on environment complexity, infrastructure size, team expertise, and specific requirements. Simple deployments may be faster, while complex multi-cloud environments typically take longer.
The Core Tools: Detailed Analysis
Datadog
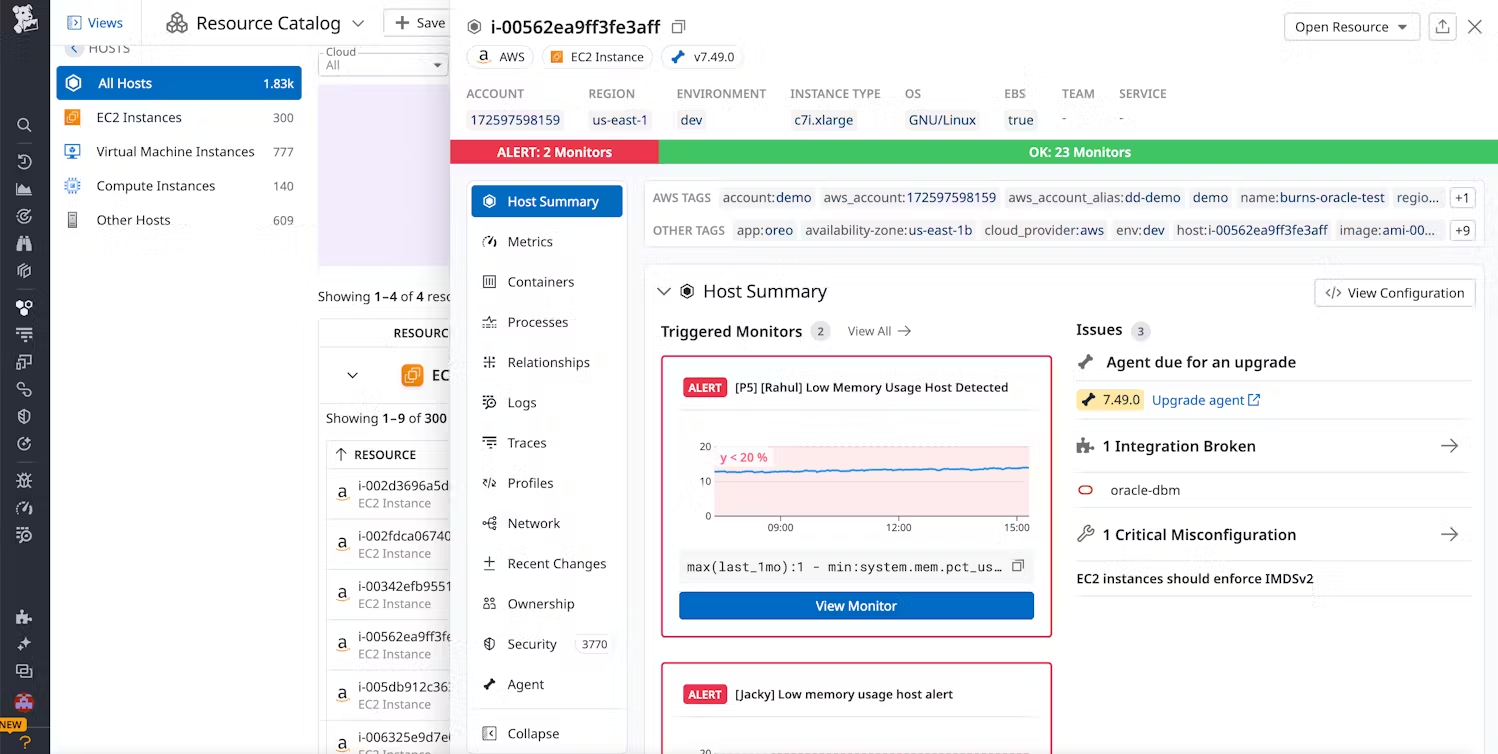
Infrastructure Coverage: Full-stack (network, server, application, containers, logs, cloud)
The Reality: Setting up Datadog typically takes 2-3 weeks to reach production readiness. While the initial agent deployment can happen quickly (especially on Kubernetes with Helm charts), achieving production-grade monitoring requires configuring integrations, creating dashboards, and tuning alerts. According to user experiences, the main complexity isn't technical setup but rather understanding the pricing model to avoid unexpected costs. Teams report that configuration errors can easily result in thousands of dollars in unexpected charges.
The true cost at scale starts at $15 per host per month for Pro ($23 for Enterprise), but that's just the beginning. According to Datadog's 2025 pricing, you get 100 custom metrics per host included, then pay $1 per 100 additional custom metrics. The high-watermark billing system means you're charged based on your peak usage (99th percentile), not average usage. Organizations with 100 hosts commonly pay $50,000+ monthly when factoring in custom metrics, logs, and APM charges.
Strengths:
- Unified platform eliminates tool sprawl
- Excellent Kubernetes and cloud-native support
- Strong APM with distributed tracing
- 900+ integrations out of the box
- Intuitive UI that non-technical stakeholders can use
Weaknesses:
- Complex pricing with surprise bills (high-watermark billing catches many off guard)
- Tag explosion can increase costs by 10x overnight
- Vendor lock-in concerns are real, migration is painful
- Annual contracts often required for enterprise features
- Price increases of 20-40% at renewal are common
Best For: Well-funded startups and enterprises needing unified observability quickly
Avoid If: Budget predictability is crucial or you're cost-conscious at scale
New Relic
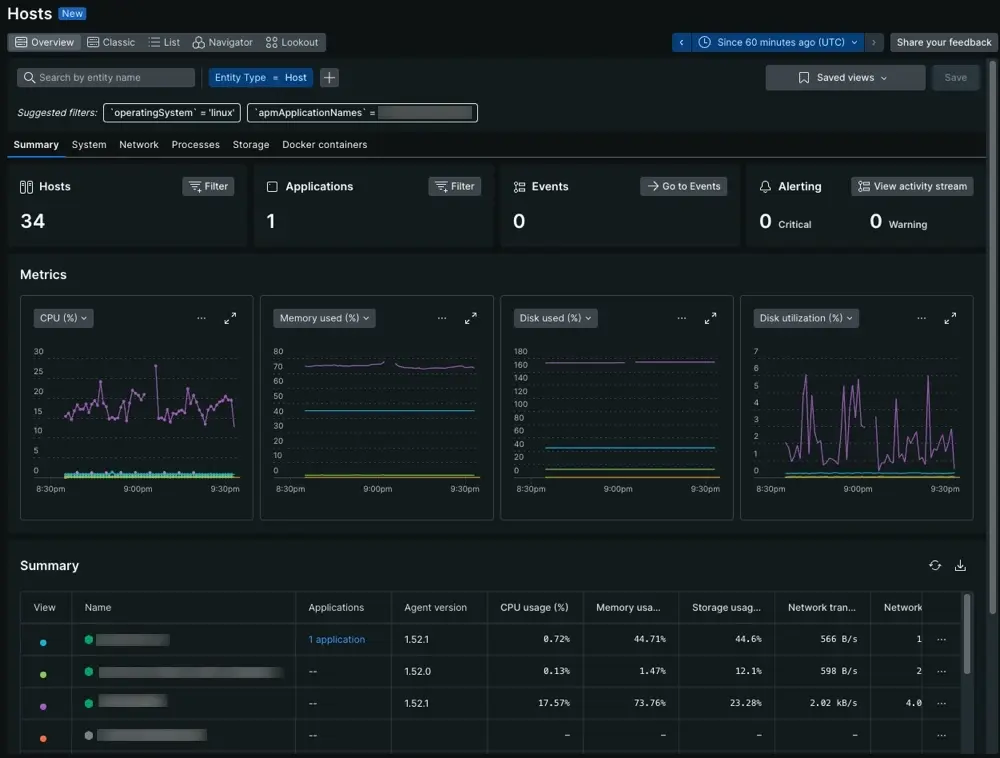
Infrastructure Coverage: Full-stack with strong APM focus, expanding infrastructure capabilities
The Reality: New Relic uses a dual pricing model: data ingestion at $0.40/GB (after 100GB free) plus seat-based pricing ($49 for Core users, Full Platform users vary by edition - Standard at $99, Pro at $349). This combination can make costs less predictable than pure consumption models. Setup complexity is similar to Datadog, taking 2-3 weeks for production deployment. The platform excels at application monitoring but infrastructure features feel secondary.
Strengths:
- Superior APM capabilities with code-level insights
- More predictable pricing model than competitors
- AI-powered insights (AIOps) actually useful
- Strong developer experience with great documentation
- Excellent for microservices architectures
Weaknesses:
- Infrastructure monitoring less mature than APM
- Limited on-premise deployment options
- Dual pricing model (data + seats) can complicate cost planning
- Can get expensive with high data volumes (10TB+ monthly = $3,000+ just for data)
- Fewer infrastructure-specific integrations than Datadog
Best For: Application-centric organizations, e-commerce platforms, SaaS companies
Avoid If: Primary focus is network/infrastructure rather than applications
Prometheus + Grafana Stack
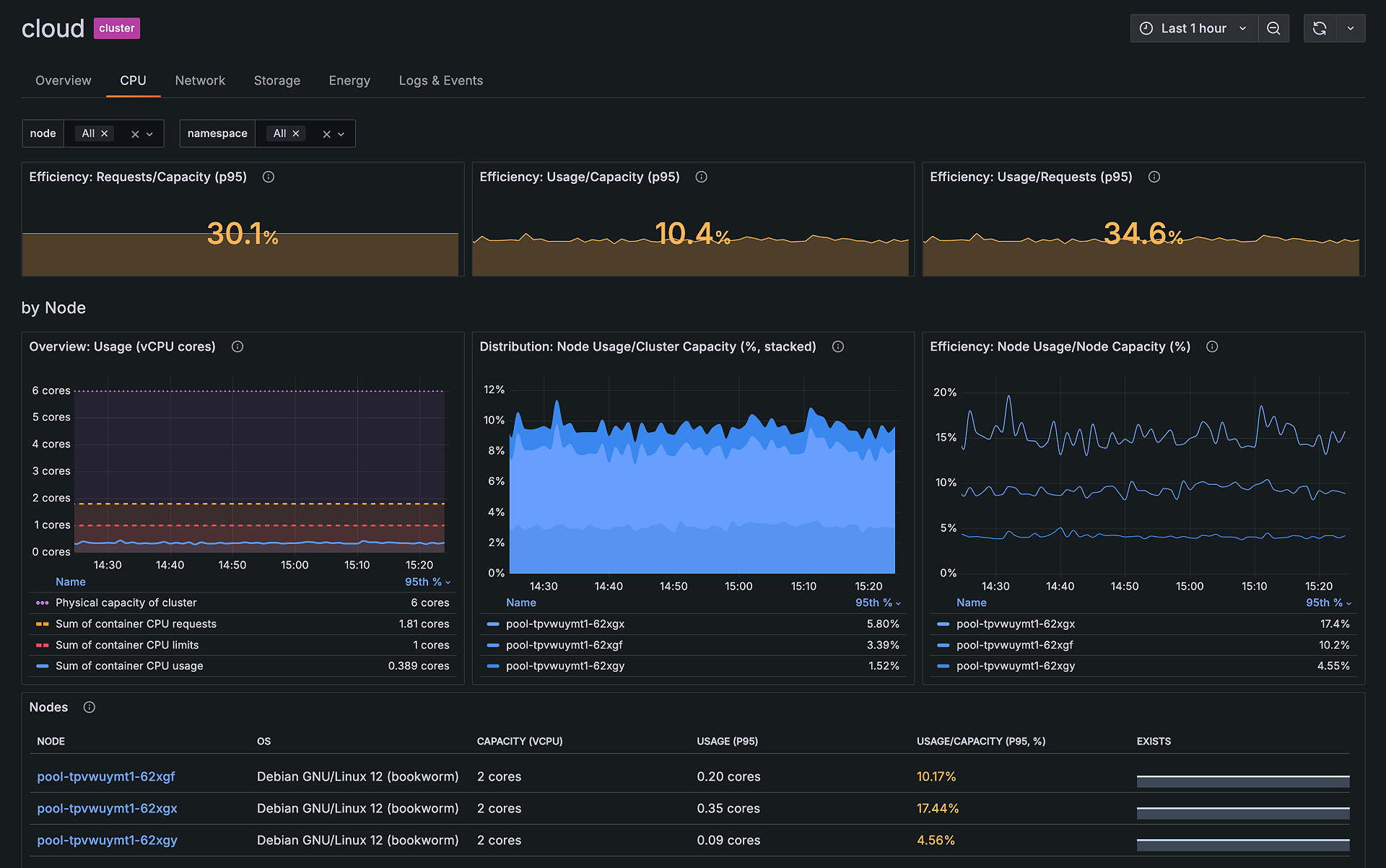
Infrastructure Coverage: Flexible (depends on exporters - typically server, containers, custom metrics)
The Reality: The "free" in free and open source is misleading. While the software costs nothing, expect 4-6 weeks for production readiness based on teams deploying the kube-prometheus-stack. You'll need expertise in PromQL, understanding of time-series databases, and knowledge of Kubernetes. For those wanting managed services, Grafana Cloud uses usage-based pricing (not per-user) and includes the full LGTM stack (Loki, Grafana, Tempo, Mimir).
Deployment Options:
- Self-hosted: Completely free but requires significant expertise and operational costs.
- Grafana Cloud: Managed LGTM stack with usage-based pricing
- Kube-prometheus-stack: Pre-configured Helm chart reduces setup time
Strengths:
- Industry standard for Kubernetes monitoring
- Completely free for self-hosted deployments
- Highly customizable and extensible
- No vendor lock-in, easy to migrate data
- Massive community and ecosystem
- Scales to millions of metrics
- Grafana provides best-in-class visualization for any data source
Weaknesses:
- Steep learning curve (PromQL is powerful but complex)
- Storage and cardinality challenges at scale
- No built-in long-term storage (need Thanos or Cortex)
- Requires additional tools for logs (ELK, Loki)
- Self-hosted requires ongoing maintenance
Best For: Technical teams with Kubernetes expertise, organizations with strong DevOps culture
Avoid If: Limited DevOps expertise or need turnkey solution without managed services
Dynatrace
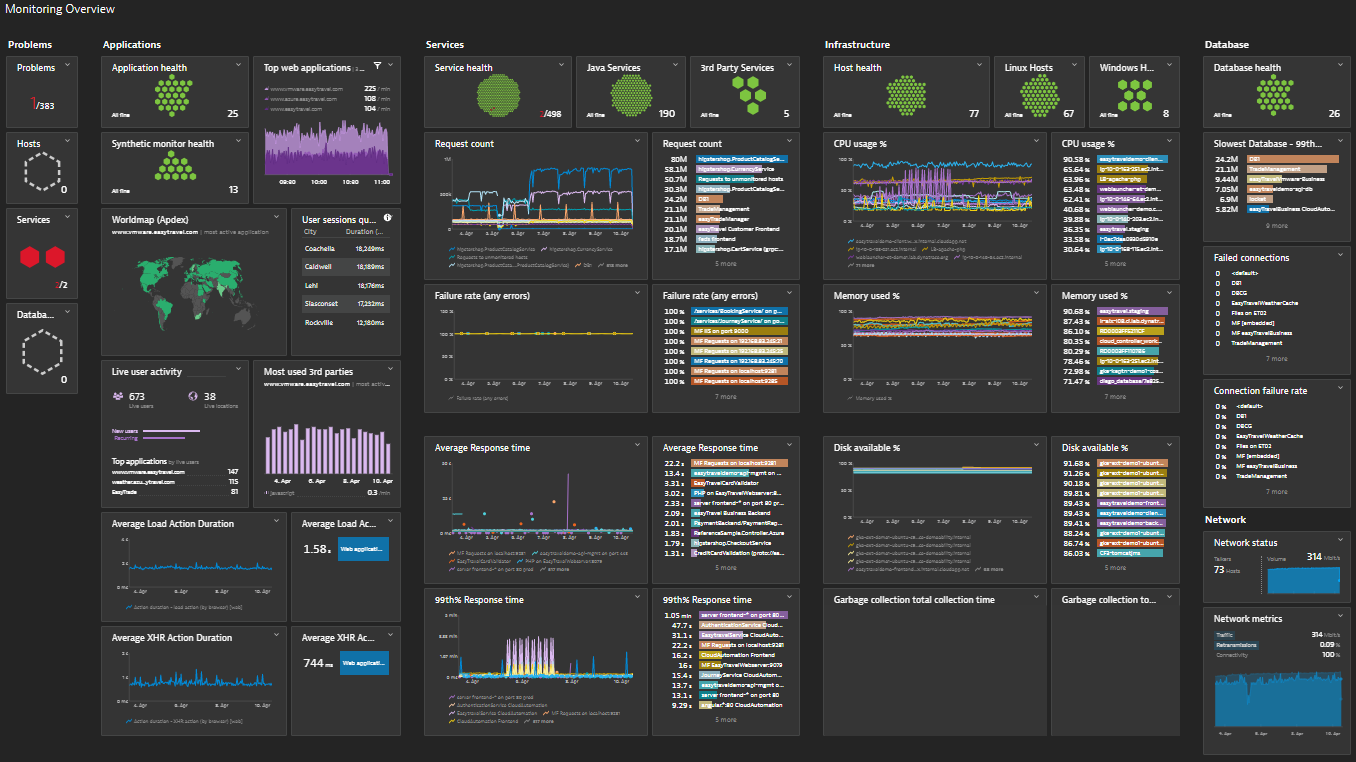
Infrastructure Coverage: Full-stack with AI-driven insights across all layers
The Reality: Dynatrace's OneAgent provides the easiest deployment experience, with automatic discovery and dependency mapping working out of the box. Most teams are operational within 1-2 weeks. Pricing in 2025 is $0.04/hour for infrastructure monitoring only (any size host, approximately $29/month), while full-stack monitoring costs $0.08/hour (approximately $58/month for an 8GB host). The AI capabilities (Davis AI) genuinely reduce alert noise and provide useful root cause analysis.
Strengths:
- Best-in-class AI/ML capabilities for anomaly detection
- Automatic discovery eliminates manual configuration
- Code-level visibility without code changes
- Excellent root cause analysis
- Minimal ongoing maintenance required
Weaknesses:
- Expensive at scale (100 hosts = ~$35k/year for infrastructure monitoring, ~$70k for full-stack)
- Can be overwhelming with feature complexity
- Less flexibility than open-source alternatives
- Requires significant resources (CPU/memory) on monitored hosts
Best For: Large enterprises wanting minimal configuration, organizations with complex applications
Avoid If: Small teams, tight budgets, or simple infrastructure
Zabbix
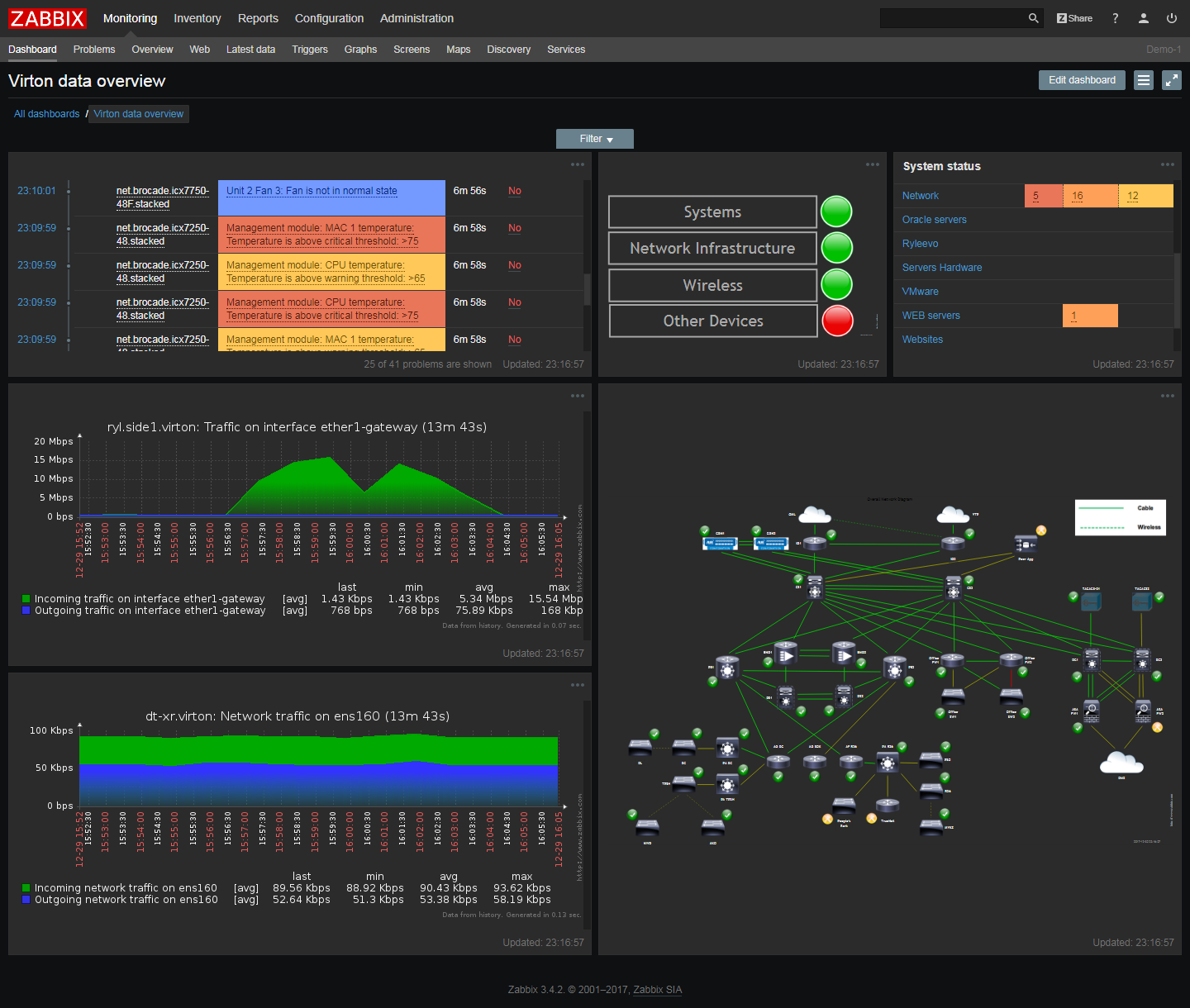
Infrastructure Coverage: Network, server, cloud, applications (with templates)
The Reality: Zabbix requires serious commitment. Plan for 6-8 weeks before your team is proficient. The configuration is extensive, requiring understanding of templates, triggers, and the Zabbix proxy architecture. While completely free, the time investment is substantial. We've seen teams spend months perfecting their Zabbix setup.
Strengths:
- Completely free and open source
- Scales to 100,000+ monitored devices
- Extremely flexible and customizable
- Strong network monitoring capabilities
- Both agent and agentless monitoring options
- Predictable resource usage
Weaknesses:
- User interface feels dated (though improving)
- Complex configuration with steep learning curve
- Limited modern cloud integrations
- Template system is powerful but complex
- Minimal built-in analytics capabilities
Best For: Large traditional IT environments with dedicated monitoring teams
Avoid If: Need modern UI, quick deployment, or lack dedicated monitoring staff
Nagios
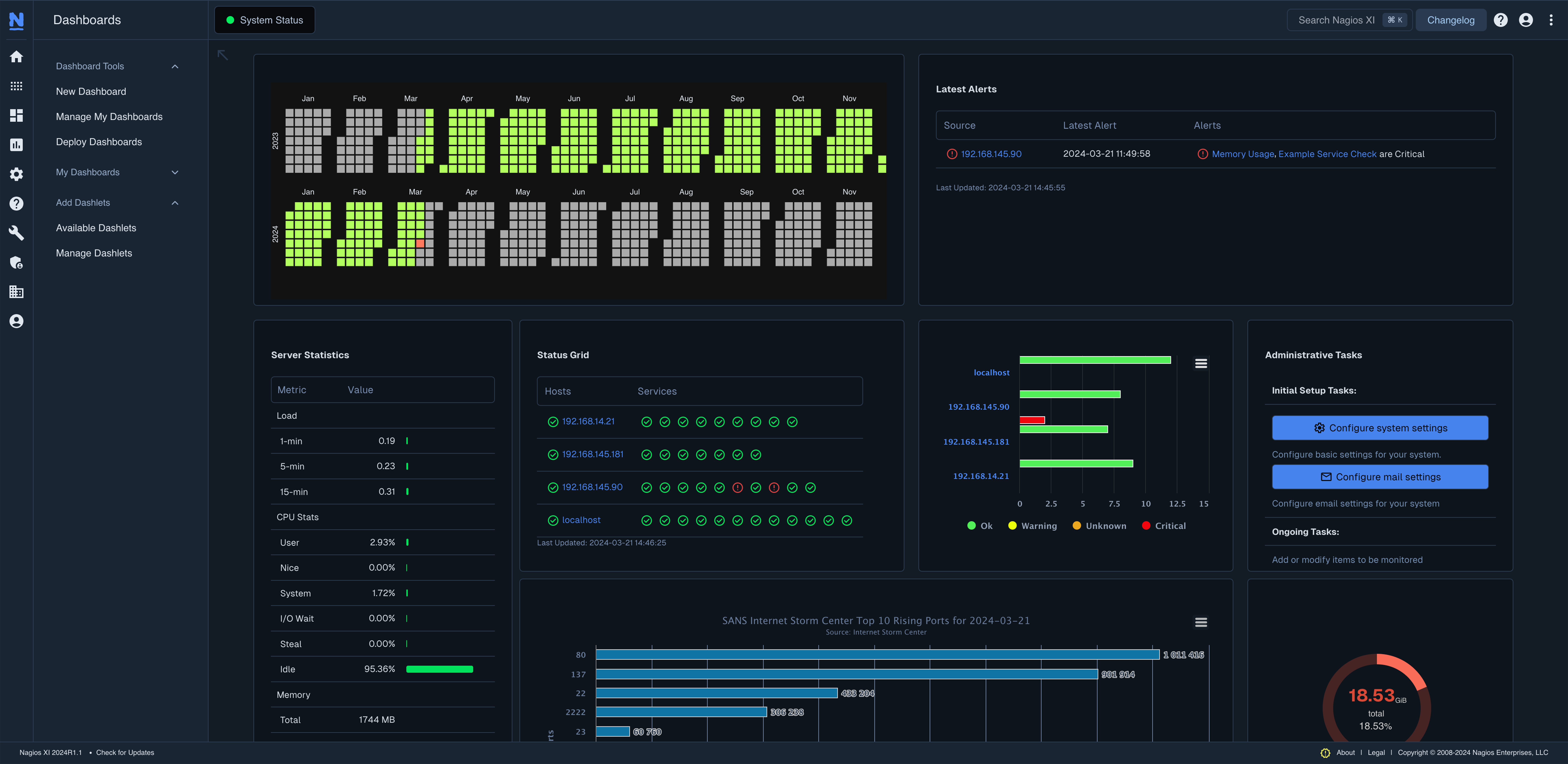
Infrastructure Coverage: Network and server monitoring (traditional infrastructure)
The Reality: Nagios is monitoring's equivalent of COBOL, still running critical infrastructure but showing its age. Expect 8-12 weeks before your team is productive. Configuration is entirely through text files, the UI hasn't meaningfully changed since 2009, and scaling for dynamic environments is painful. Yet it's rock-solid reliable.
Strengths:
- Battle-tested with 20+ years of development
- Massive plugin ecosystem (thousands available)
- Complete control over every aspect
- Strong alerting capabilities
- Extremely stable and predictable
Weaknesses:
- Interface is painfully dated
- Configuration via text files only
- Lacks modern features (no distributed tracing, poor container support)
- Poor scalability for cloud-native environments
- Difficult to maintain at scale
Best For: Traditional IT environments with existing Nagios expertise
Avoid If: Cloud-native infrastructure, containerized environments, or modern DevOps practices
SigNoz
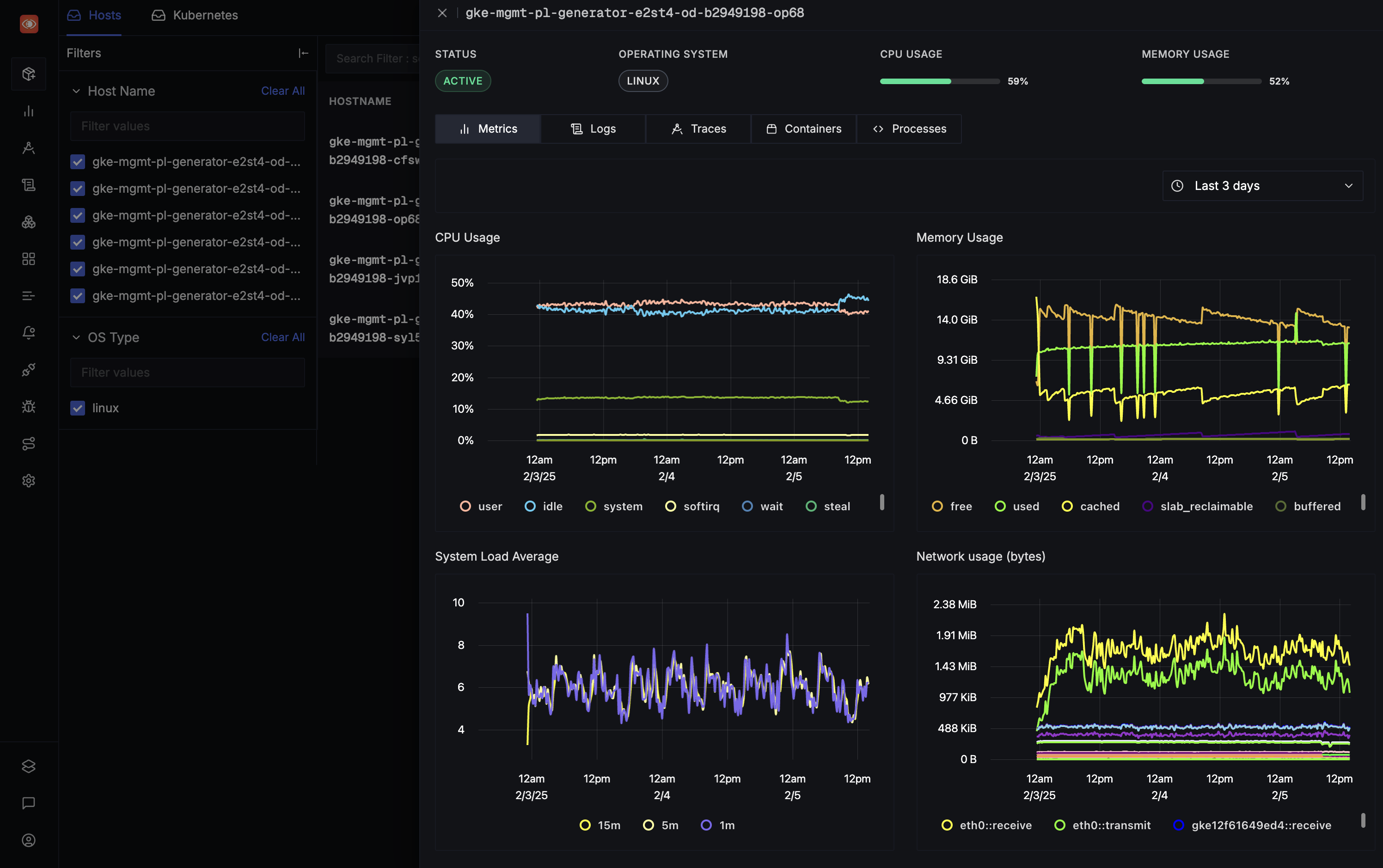
Infrastructure Coverage: Full-stack observability with APM, metrics, logs, and traces
The Reality: SigNoz offers an open-source alternative to commercial monitoring platforms, built on OpenTelemetry standards. Setup typically takes 2-3 weeks, comparable to other modern platforms. The ClickHouse backend provides efficient query performance at scale. Both cloud and self-hosted deployment options are available.
Strengths:
- Open-source with commercial support options available
- Built on OpenTelemetry standards
- Single platform for metrics, traces, and logs
- Transparent pricing model for cloud offering
- ClickHouse backend for query performance
- Infrastructure monitoring with host metrics, Kubernetes support, and cloud integrations
Weaknesses:
- Smaller community compared to Prometheus/Grafana
- Fewer third-party integrations than Datadog (but growing)
- Documentation improving but not as extensive as mature tools
Best For: Teams wanting OpenTelemetry-native monitoring, organizations requiring flexible deployment options, teams evaluating open-source alternatives
Avoid If: Need extensive network or security monitoring capabilities.
Get Started with SigNoz
You can choose between various deployment options in SigNoz. The easiest way to get started with SigNoz is SigNoz cloud. We offer a 30-day free trial account with access to all features.
Those who have data privacy concerns and can't send their data outside their infrastructure can sign up for either enterprise self-hosted or BYOC offering.
Those who have the expertise to manage SigNoz themselves or just want to start with a free self-hosted option can use our community edition.
Secondary Tools Worth Considering
PRTG Network Monitor
Best For: Windows-centric environments and SMBs
Reality Check: Excellent user experience with sensor-based licensing (average 5-10 sensors per device). Pricing ranges from free (100 sensors) to $17,899 (10,000 sensors). Great for SMBs monitoring <500 devices. Setup is refreshingly simple compared to open-source alternatives, with most teams operational within days.
SolarWinds
Best For: Enterprise network monitoring
Reality Check: Comprehensive network monitoring capabilities but recent security breaches have damaged trust. Expensive and complex. Consider alternatives unless you specifically need their network performance monitoring strengths.
AppDynamics
Best For: Deep application performance monitoring
Reality Check: Acquired by Cisco, strong APM capabilities similar to New Relic. Complex pricing model and steep learning curve. Best suited for Java/.NET enterprise applications. Integration with Cisco ecosystem is a plus for existing Cisco customers.
Splunk
Best For: Log analysis and security operations
Reality Check: The gold standard for log analysis but eye-wateringly expensive at scale. Costs can exceed $100k/year for modest deployments. Excellent for security operations and compliance-heavy industries. Consider only if logs are your primary concern.
Site24x7
Best For: All-in-one SaaS monitoring for SMBs
Reality Check: Good value for small businesses needing basic monitoring across websites, servers, and applications. Starts at $9/month for basic monitoring, scales to $35/month for infrastructure monitoring. Limited depth compared to specialized tools but covers the basics well for smaller teams.
Checkmk
Best For: Modern alternative to Nagios
Reality Check: Builds on Nagios core but adds modern UI and easier configuration. Raw edition is free, enterprise edition provides support. Good migration path from Nagios. German engineering shows in reliability and efficiency.
Elastic Stack (ELK)
Best For: Log management and analysis
Reality Check: Powerful but complex. Requires significant expertise to run at scale. Resource-hungry, especially Elasticsearch. Free to start but operational costs add up quickly. Elastic Cloud reduces complexity but isn't cheap.
Making Your Final Decision
Start with your constraints, not features. Budget, team expertise, and existing tool investments will eliminate 80% of options immediately. A perfect tool you can't afford or operate is worse than a basic tool that works.
Consider your growth trajectory. Your 10-server setup today might be 100 servers next year. Tools like Nagios and Zabbix that work fine at small scale become maintenance nightmares as you grow. Cloud-native tools (Prometheus, SigNoz) scale more naturally with modern infrastructure.
Don't over-optimize for edge cases. Pick a tool that handles 80% of your monitoring needs well rather than chasing perfect coverage. You can always add specialized tools for specific gaps later. Most teams need solid metrics, basic APM, and log aggregation, not every feature on the vendor's checklist.
Test with real workloads. Every vendor offers trials. Use them. Deploy agents on a subset of production infrastructure, not just dev environments. You'll quickly discover deal-breakers like missing integrations, performance impacts, or UI issues that demos don't reveal.
The best monitoring tool is the one your team will actually use. Complex platforms with amazing capabilities sit unused while simple tools that solve real problems get adopted immediately. Start with your most painful monitoring gap, solve it well, then expand coverage incrementally.
Hope we answered all your questions regarding infrastructure monitoring tools. If you have more questions, feel free to use the SigNoz AI chatbot, or join our slack community.
You can also subscribe to our newsletter for insights from observability nerds at SigNoz, get open source, OpenTelemetry, and devtool building stories straight to your inbox.
