Logs are essential for diagnosing downtimes, identifying security breaches, and troubleshooting errors. As systems and applications are in operation, they tend to produce a vast array of log files depending on the complexity of the system, the number of applications running, and the configurations in place. In the event of an application or system error, manually gathering and reviewing these logs for troubleshooting purposes can be time-consuming.
Adopting a log analysis tool is highly recommended to streamline this process and remove the manual burden. Log analysis tools automate the process of collecting, parsing, and analyzing log data, making troubleshooting more efficient and less time-consuming. They are software applications that collect, parse, and analyze log data to help developers monitor, debug, and optimize their applications.
In this article, we will look at top log analysis tools in the market that are designed to streamline the process of managing and interpreting log files.
Top 10 Log Analysis Tools
In this section, we will discuss the top 10 log analysis tools you can consider using. They are:
Before we dive deep into each tool, let’s discuss some fundamentals.
What Are Log Analysis Tools and Why Do IT Pros Need Them?
Log analysis tools are software applications designed to collect, process, and analyze log data generated by various IT systems and applications. These tools serve as the eyes and ears of IT operations, providing critical insights into system performance, security events, and user behavior.
Key benefits of using log analysis tools include:
- Improved Security: Detect and respond to security threats in real-time.
- Faster Troubleshooting: Quickly identify the root cause of issues.
- Enhanced Performance Monitoring: Track system health and performance metrics.
- Compliance Management: Meet regulatory requirements through comprehensive log retention and analysis.
Log analysis tools can process various types of logs, including:
- Server logs (e.g., application logs, system logs)
- Network device logs (e.g., firewall logs, router logs)
- Database logs
- Application logs (e.g., web server logs, custom application logs)
By centralizing and analyzing these diverse log sources, IT professionals gain a holistic view of their infrastructure, enabling proactive management and rapid issue resolution.
Essential Features of Effective Log Analysis Tools
To maximize the benefits of log analysis, look for tools that offer the following key features:
- Real-time Log Ingestion and Processing: Ability to collect and analyze logs as they are generated, enabling immediate insights and alerts.
- Advanced Search and Filtering: Powerful search capabilities to quickly locate relevant log entries and patterns.
- Visualization and Dashboarding: Intuitive dashboards and data visualization tools for easy interpretation of complex log data.
- Alerting and Notification Systems: Customizable alerts to notify IT teams of critical events or anomalies.
- Machine Learning and AI-powered Anomaly Detection: Advanced algorithms to identify unusual patterns or behaviors that may indicate issues or security threats.
- Scalability: Ability to handle growing volumes of log data as your infrastructure expands.
- Integration Capabilities: Easy integration with existing IT tools and systems for a unified monitoring approach.
- Compliance and Security Features: Built-in compliance reporting and security controls to meet regulatory requirements.
SigNoz
SigNoz is a full-stack open-source observability tool that provides log collection and analytics. SigNoz uses a columnar database ClickHouse to store logs, which is very efficient at ingesting and storing logs data. ClickHouse is designed for faster analytics with advanced querying. It makes SigNoz 2.5x faster than Elasticsearch while consuming 50% less resources.
SigNoz provides logs, metrics, and traces under a single pane of glass. Since everything is under a single datastore, you can have rich insights by correlating signals like logs and traces. It also saves you from the overhead of managing multiple tools for monitoring and observability.
SigNoz uses OpenTelemetry for instrumenting applications. OpenTelemetry, backed by CNCF, is quietly becoming the world standard for instrumenting cloud-native applications. You can collect logs from your application using the OpenTelemetry SDK or just forward your logs to OpenTelemetry collector using your existing logging pipeline.
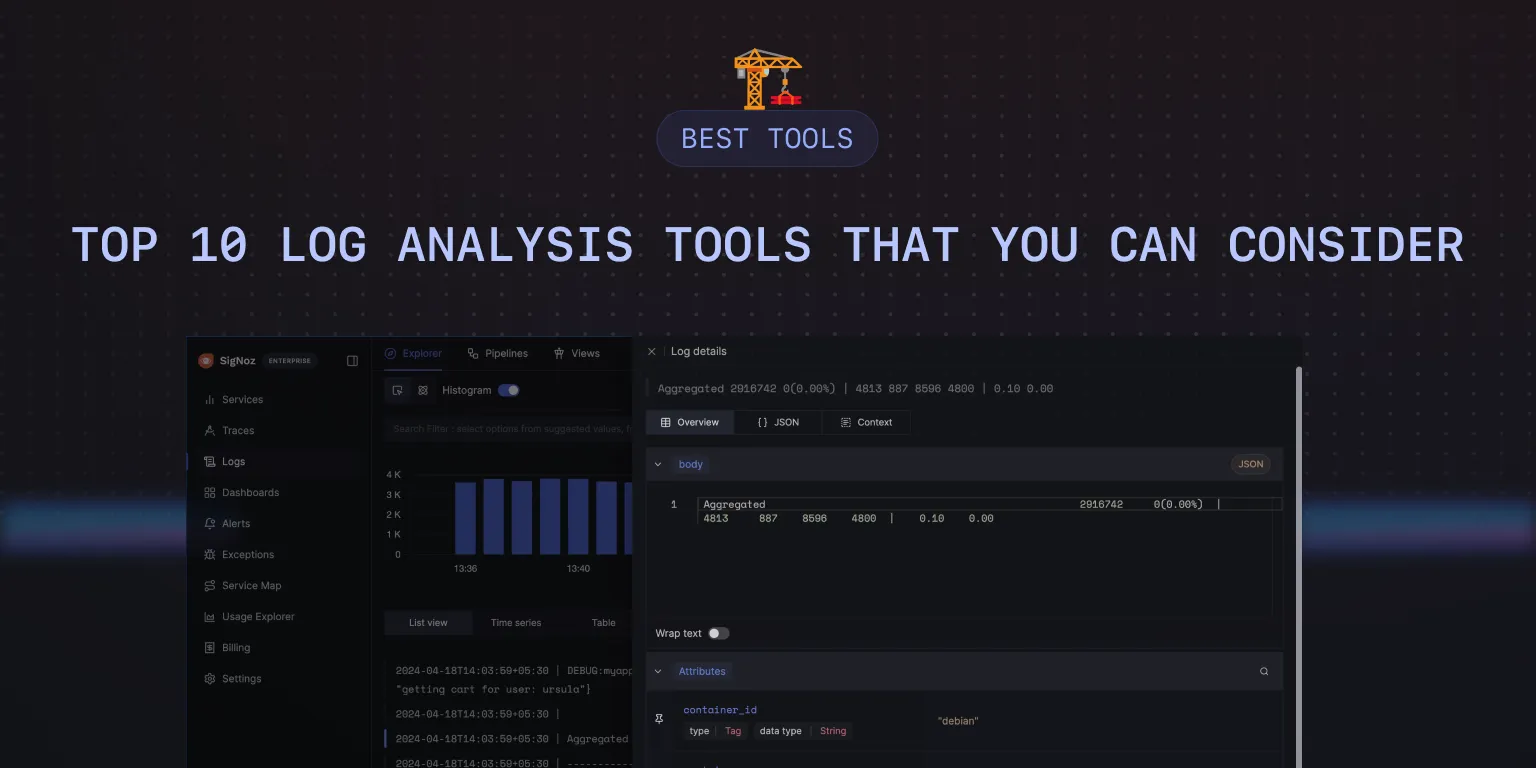
After sending logs to SigNoz, you can use an intuitive query builder to filter and search through your logs. You can build charts, save views for quick access, and set up alerts.
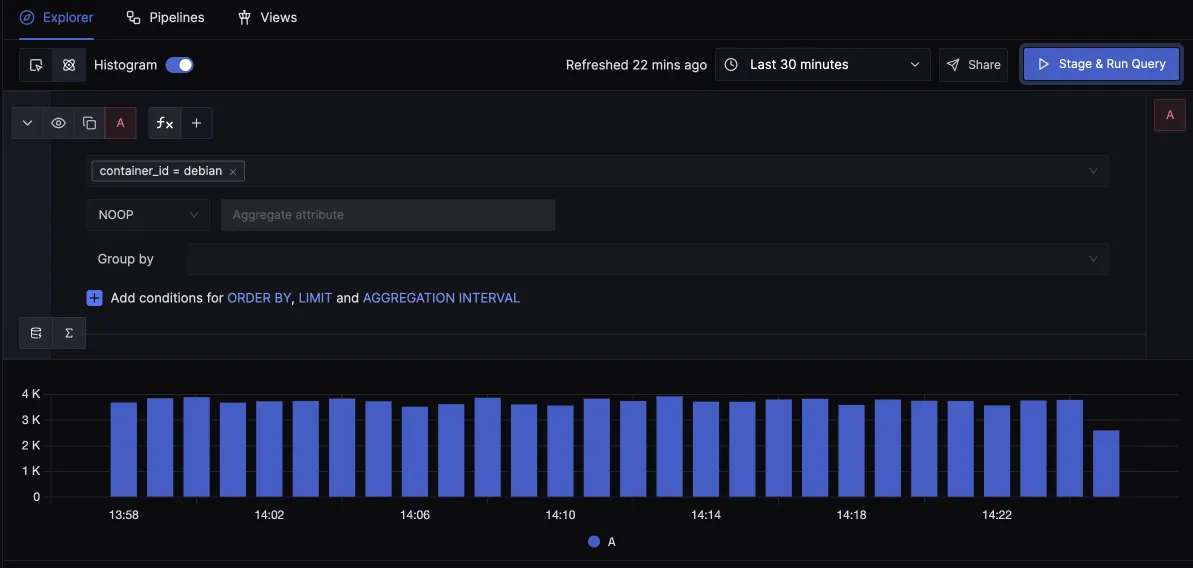
Save views for quick access later.
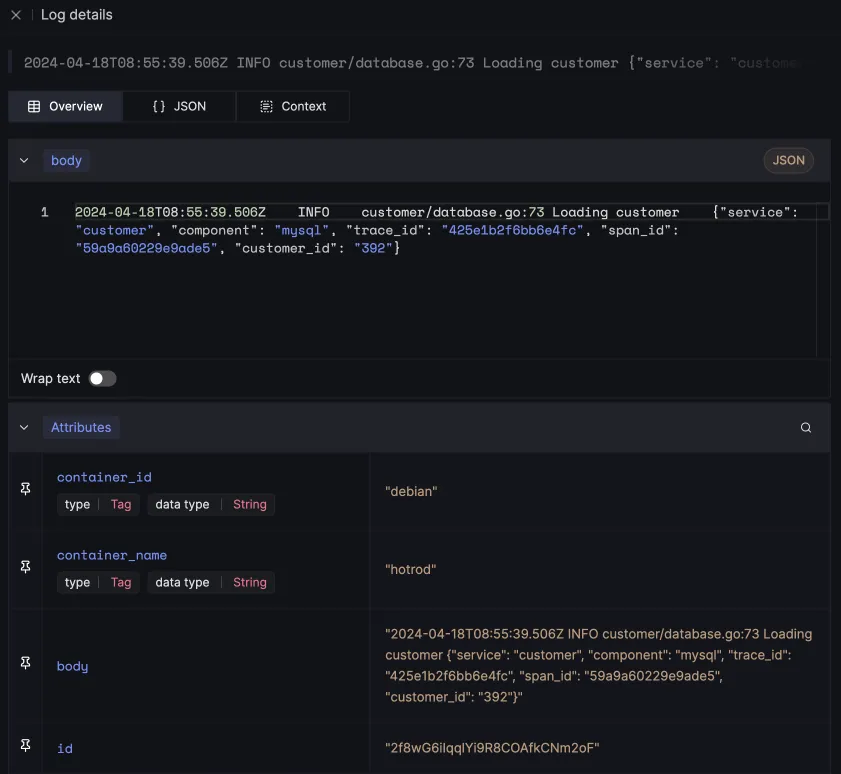
You can view your logs in detailed view with attributes, in json format and context tab that shows logs before and after the selected log from the same source.
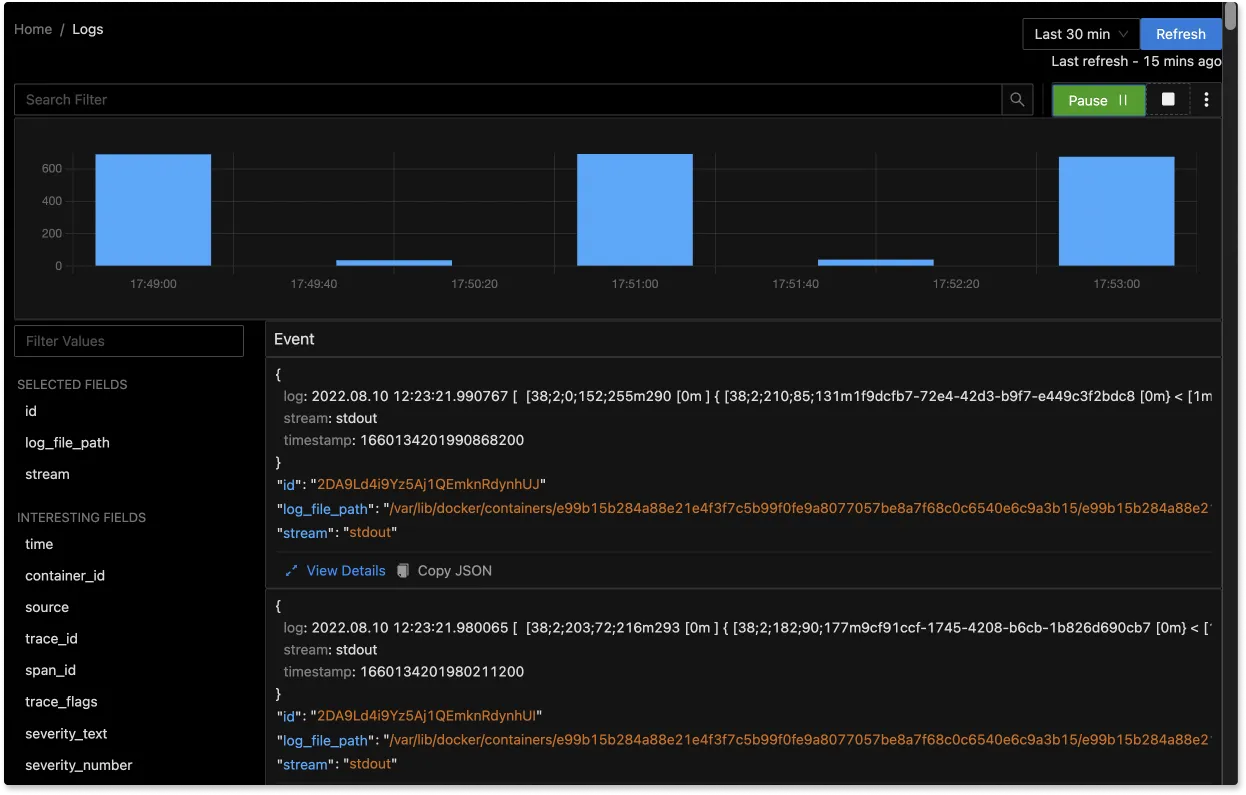
You can also view logs in real time with live tail logging.
With Logs Pipelines, you can transform logs to suit your querying and aggregation needs before they get stored in the database, thus saving a lot of cost.
SigNoz cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
Splunk
Splunk is a software platform that specializes in the collection, analysis, and visualization of machine-generated big data.
Splunk ingests data from various sources, including logs, network traffic, and other machine-generated data. This data is then indexed and stored in a searchable format. Users can query this data using Splunk's proprietary search language, SPL (Search Processing Language), to find specific events, patterns, or anomalies within the data.
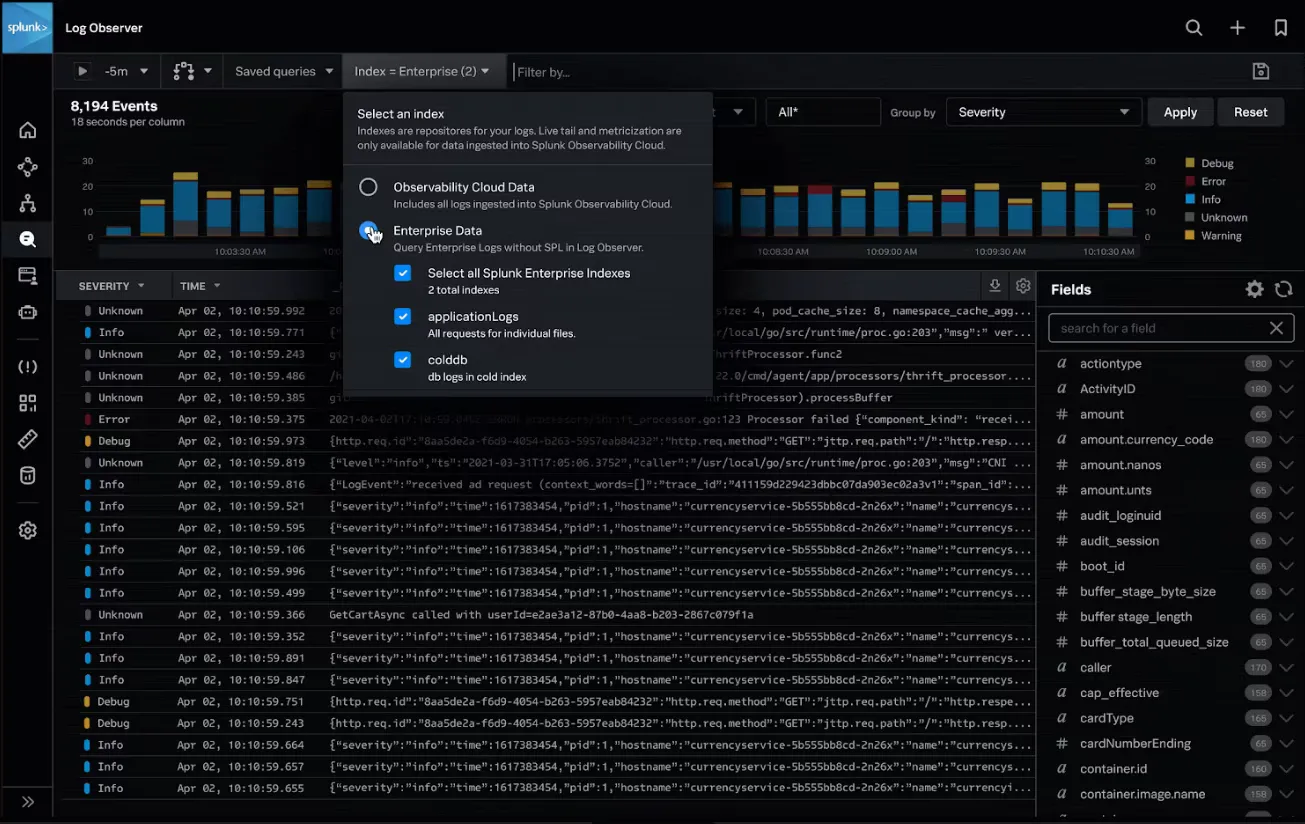
Some key features of Splunk are:
- In-depth log analytics
- Extensive search capability
- Powerful search and filtering
- ML-based analytics
Graylog
Graylog is a powerful open-source log management platform that helps in collecting, indexing, and analyzing log data from various sources. It is designed to handle large volumes of data and provides a centralized location for storing, searching, and analyzing log data.
Graylog ingests log data from various sources, including servers, applications, and network devices. Once the data is ingested, Graylog parses it into a structured format that can be easily searched, analyzed, and visualized. This structured data is stored in a database, allowing for efficient querying and analysis.
Graylog supports a wide range of data formats, including syslog, log4j, and many others, making it versatile for analyzing different types of log data.
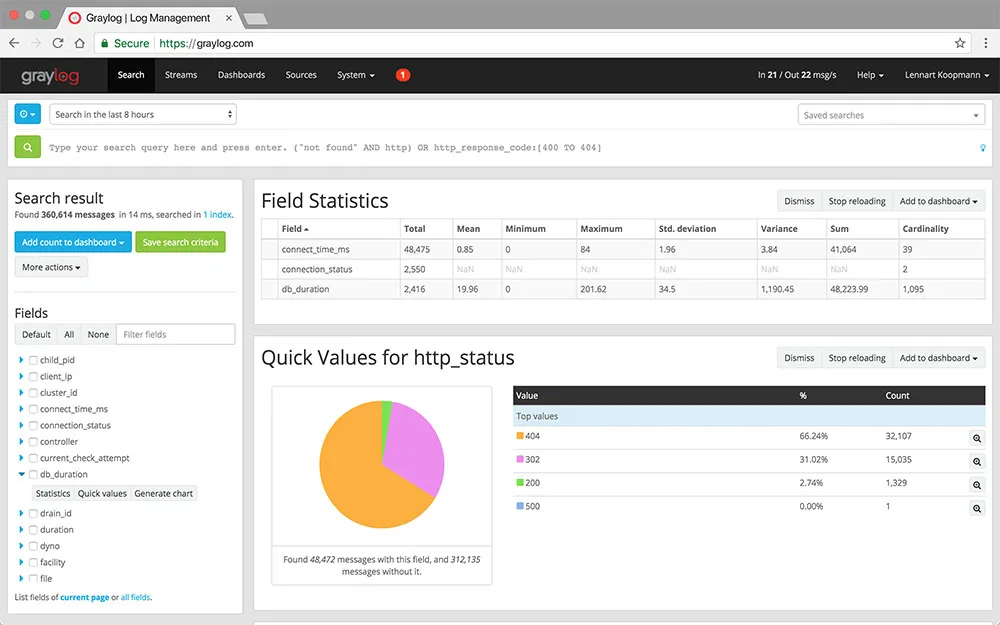
Some key features of Graylog are:
- Log data collection and analysis
- Data processing pipeline
- Search and analysis capabilities
- Alerting and notifications
- RESTful API
- Scalability
- Multi-data inputs and outputs
SumoLogic
SumoLogic is a leading cloud-native SaaS log analytics platform. It centrally collects and analyzes log data in real-time, enabling organizations to proactively troubleshoot and resolve issues before they can impact the health and performance of their applications and systems.
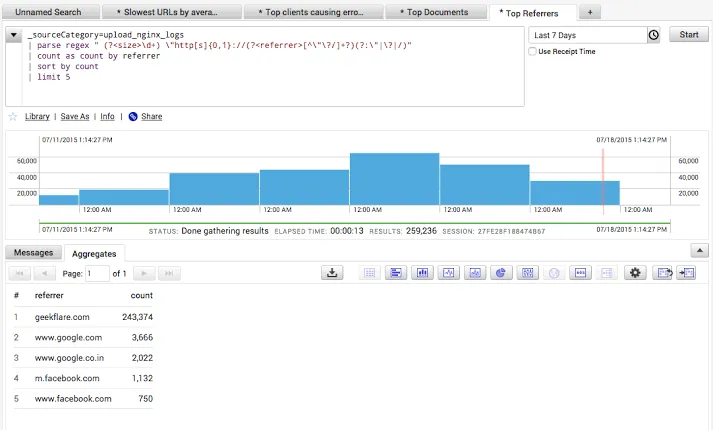
Some key features of Sumo Logic are:
- In-built pattern detection
- Predictive analysis
- Anomaly detection
- Log analytics
Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is a powerful log analysis tool that is part of the Elastic Stack (previously known as the ELK stack). It is a distributed search and analytics engine that indexes, analyzes, and searches ingested log data.
Elasticsearch works hand in hand with Logstash and Kibana for log analysis. Logstash is primarily responsible for collecting, parsing, and processing logs from a variety of sources. Once processed, these logs are then sent to Elasticsearch for analysis. Kibana, on the other hand, is utilized for visualizing the ingested log data, allowing users to filter and search through the data more effectively.
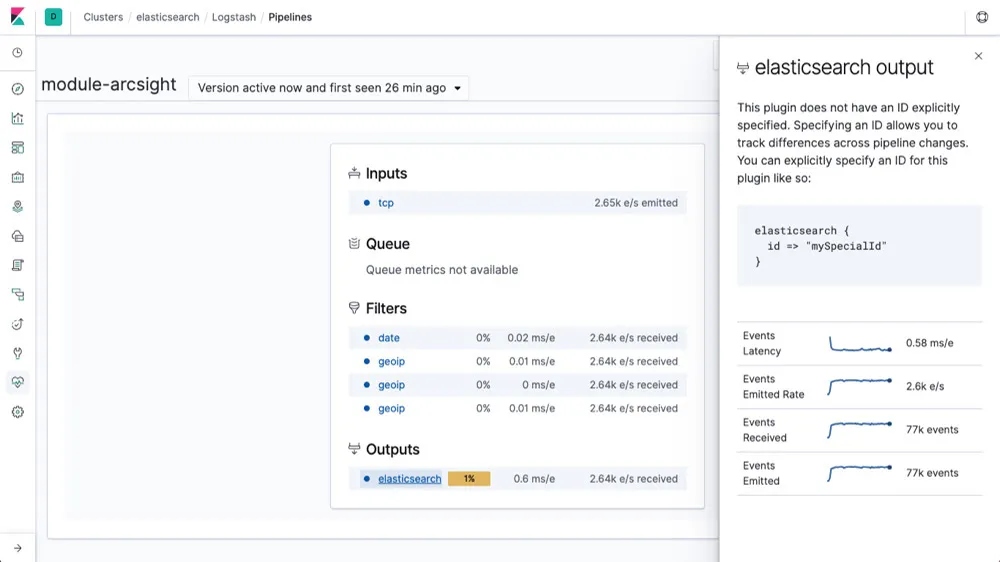
Some key features of Elasticsearch are:
- Full-Text Search
- Real time analytics
- Log and event data analysis
- Integration with other Elastic Stack components
Datadog
Datadog is a comprehensive monitoring and analytics platform that excels as a log analysis tool, offering a robust suite of features designed to simplify the process of analyzing and interpreting log data.
Datadog transforms unstructured streams of raw log data into centralized, structured datasets. It automatically applies tags to logs after ingestion and lets you analyze large volumes of log data and perform complex investigations without having to learn a complex query language.
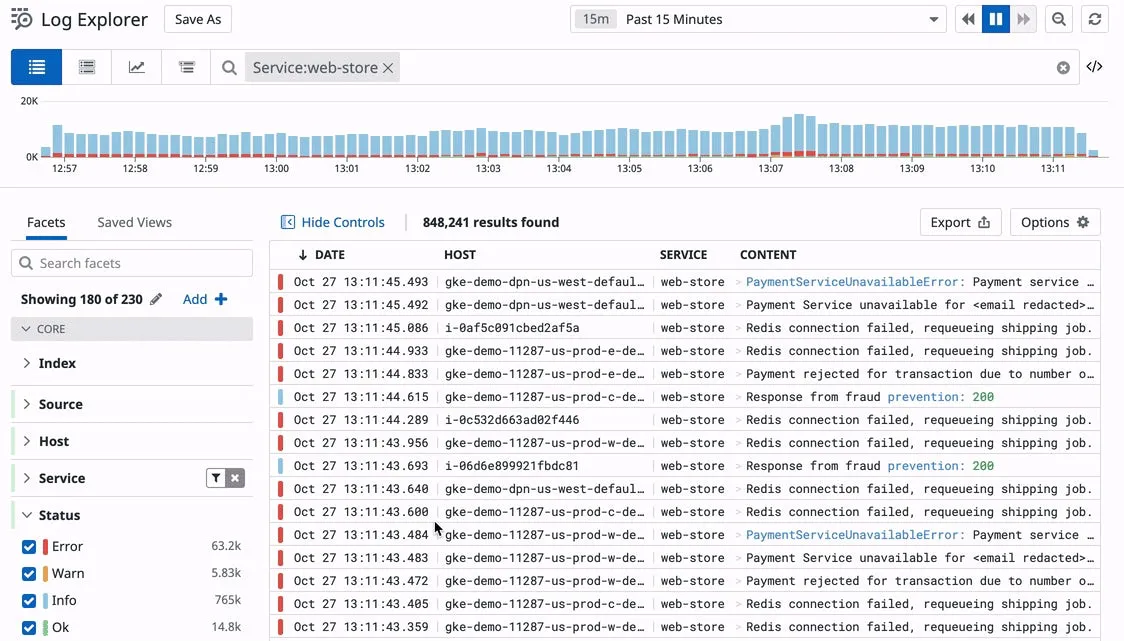
Some key features of Datadog are;
- Log anomaly detection
- Logging without limits
- Log analysis
- Log pattern and
Logwatch
Logwatch is an open-source log analysis tool designed to automatically parse and analyze log files from various services and applications running on Linux or Unix-based systems. It presents a summary of the log data, including system activity, security events, and potential issues in a detailed, easy-to-read format, making it simple to identify and troubleshoot problems.
Some key features of Logwatch:
- Log data analysis
- Customizable filter scripts
- Output filtering and control
- Summary of system activity, security events, and potential problems
- Ability to filter out specific log entries
Logic Monitor
LogicMonitor is a cloud-based infrastructure monitoring and analytics platform that serves as an impressive log analysis tool. It takes a unique and unified approach to log analysis by utilizing algorithmic root-cause analysis to identify normal patterns and deviations from these patterns within log events.
As logs are being ingested into the platform, Logic Monitor parses the information contained within log lines, making it readily available for searching and data analysis. This methodology allows for a more efficient and accurate analysis of log data.
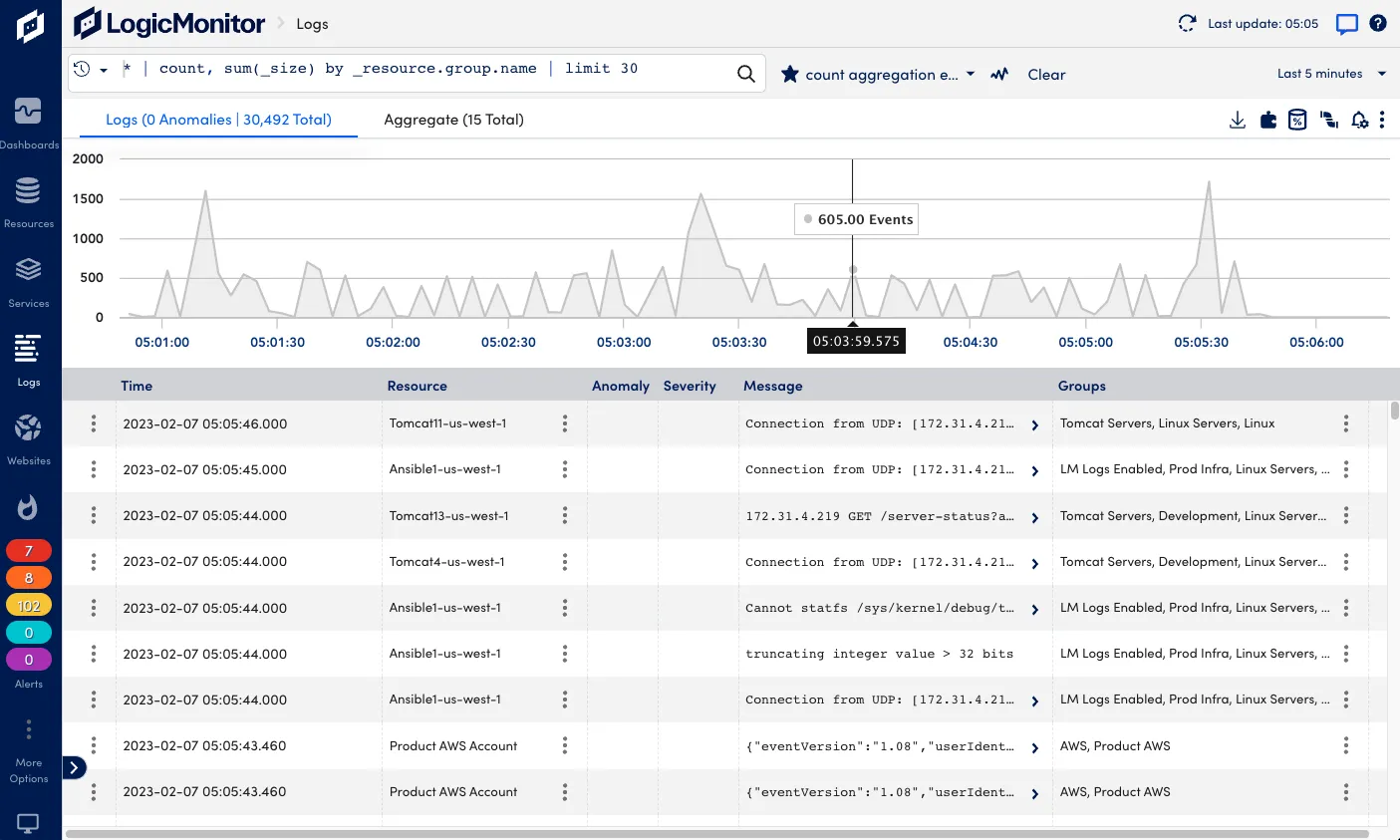
Some key features of Logic Monitor are;
- Intelligent log analytics
- Log collection
- Algorithmic Root-Cause Analysis
- Anomaly detection
Sematext
Sematext is a comprehensive log management platform that extends the capabilities of the Elastic Stack. This allows it to ingest logs from a wide variety of sources, such as log shippers, logging libraries, and more. Sematext provides robust searching, filtering, and tagging functionalities for efficient log analysis and anomaly detection.
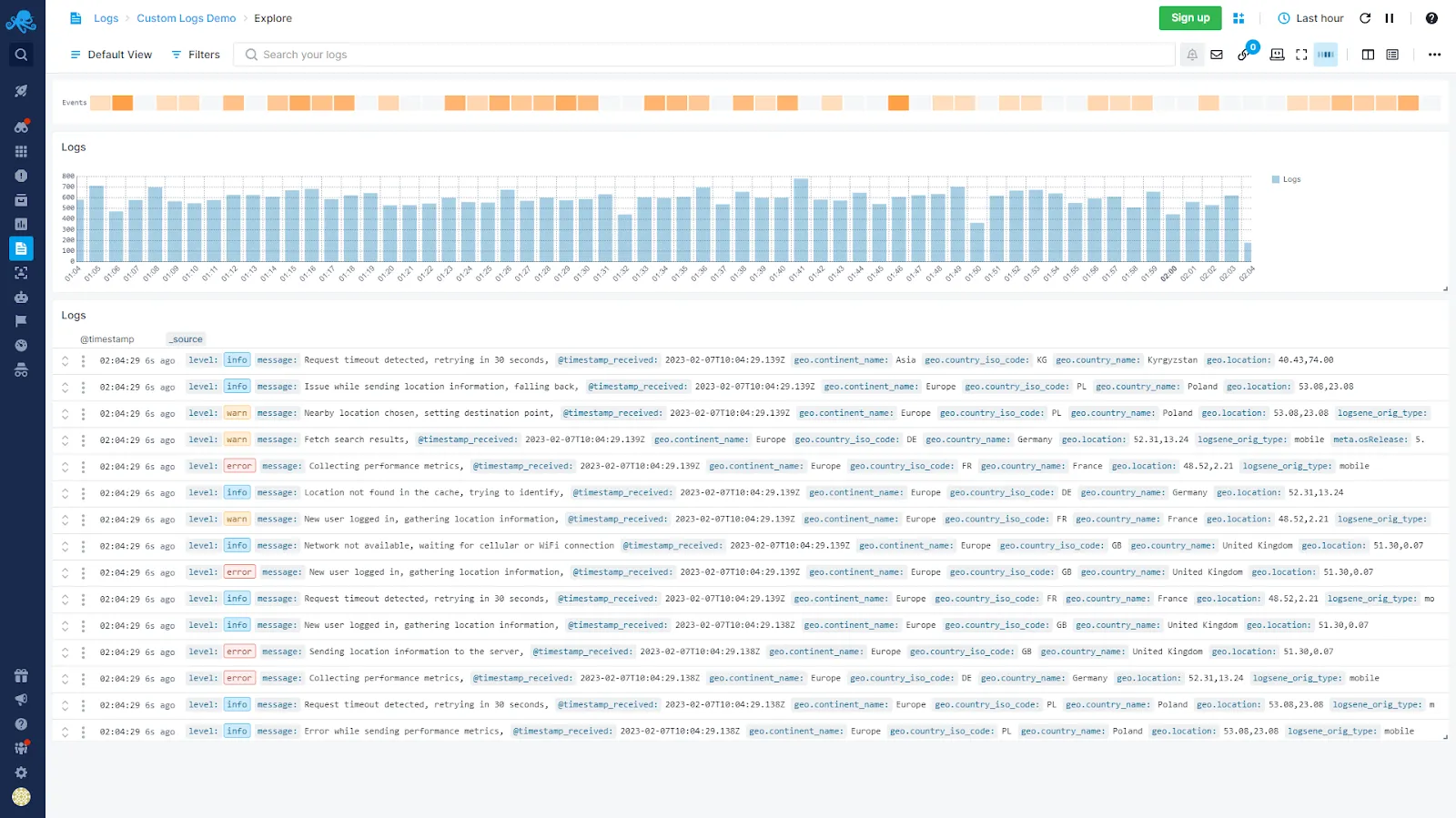
Some key features of Sematext are;
- Audit-proof logging
- Rich query syntax
- Automated Log Parsing and Structuring
- Advanced search and filtering
SolarWinds
SolarWinds provides a wide range of products designed to help organizations manage their IT infrastructure more effectively. One of its notable offerings is the SolarWinds Log Analyzer, a powerful tool that aggregates log data to provide deep insights into system performance and security.
SolarWinds Log Analyzer provides a powerful keyword search engine that allows users to search through logs without the need for any query language. Additionally, it comes with predefined filters that enable users to quickly identify logs based on criteria such as severity level and IP address, streamlining the process of troubleshooting and monitoring. As logs are ingested, it automatically assigns a severity indicator to each log entry, helping users to quickly identify and prioritize performance issues.
Some key features of SolarWinds are;
- Event log tagging
- Powerful search and filter
- Flat log file ingestion
- Log collection and analysis
- Log forwarding and
- Logs Observer Connect
Choosing the right log analysis tool
Selecting the appropriate log analysis tool involves evaluating several key factors to ensure it meets your organization's specific needs. Here are some considerations to keep in mind:
- Data Collection and Ingestion: Understand how the tool collects and ingests log data. This includes the types of data sources it can handle, the protocols it supports, and its ability to scale with the volume of logs.
- Cost: Consider the financial implications. This includes the upfront cost of the tool, any ongoing subscription fees, and the potential costs associated with scaling the tool as your log data grows.
- Open Source vs. Proprietary: Decide whether an open-source solution, which offers flexibility and community support, or a proprietary tool, which might provide more advanced features and dedicated support, aligns better with your organization's needs and budget.
- Scalability: Assess the tool's ability to scale with your organization. As your log data volume increases, the tool should be able to handle the load without compromising performance.
- Integration Capabilities: Evaluate how well the tool integrates with your existing IT infrastructure and other tools and systems. Seamless integration can streamline your log analysis workflow and improve overall operational efficiency.
- Ease of Use: Consider the tool's user interface and documentation. A tool that is easy to use and well-documented can reduce the learning curve and increase productivity among your team.
- Visualization Options: Look for tools that offer robust visualization capabilities. Effective visualization can help you identify trends and anomalies in your log data more easily, facilitating faster decision-making.
SigNoz is an excellent log analysis tool to consider as it ticks the above checkboxes. It provides logs, metrics, and traces under a single pane of glass with an intelligent correlation between the three types of telemetry signals.
Getting started with SigNoz
SigNoz offers a powerful, open-source solution for log analysis that combines ease of use with advanced features. Here's how to get started:
- Install SigNoz:
- Choose between self-hosted or cloud options
- Follow the documentation for your chosen deployment method
- Configure Log Sources:
- Set up log collectors for your applications and systems
- Configure log parsing and structuring rules
- Create Custom Dashboards:
- Design dashboards tailored to your specific use cases
- Utilize SigNoz's visualization tools for effective data representation
- Set Up Alerts:
- Define alerting rules based on log patterns or thresholds
- Configure notification channels (e.g., email, Slack)
- Explore Advanced Features:
- Leverage SigNoz's machine learning capabilities for anomaly detection
- Integrate with other observability data (metrics, traces) for comprehensive analysis
SigNoz cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 20,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
By following these steps, you can quickly set up a robust log analysis solution using SigNoz, enabling you to gain valuable insights from your log data.
Best Practices for Implementing Log Analysis Tools
To maximize the value of your chosen log analysis tool, follow these best practices:
- Define Clear Goals and Use Cases:
- Identify specific objectives for your log analysis implementation
- Prioritize use cases based on business impact
- Establish a Centralized Log Collection and Retention Strategy:
- Implement a consistent log collection method across all systems
- Define log retention policies based on compliance requirements and operational needs
- Implement Proper Log Security and Access Controls:
- Encrypt log data in transit and at rest
- Implement role-based access control for log data
- Train Your Team on Effective Log Analysis Techniques:
- Provide training on the chosen tool and log analysis best practices
- Encourage knowledge sharing among team members
- Regularly Review and Optimize Your Log Analysis Processes:
- Periodically assess the effectiveness of your log analysis implementation
- Continuously refine alerting rules and dashboards based on evolving needs
- Integrate Log Analysis with Other IT Processes:
- Incorporate log analysis into incident response procedures
- Use log insights to inform capacity planning and performance optimization
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your log analysis implementation delivers maximum value to your organization.
Key Takeaways
- Log analysis tools are crucial for modern IT operations, security, and compliance management.
- Essential features include real-time processing, advanced search, and AI-powered insights.
- The top 10 tools offer a range of capabilities suitable for different organizational needs.
- Choosing the right tool depends on specific requirements, scalability, and integration needs.
- Implementing best practices and staying updated on trends ensures effective log analysis.
- SigNoz provides a powerful, open-source alternative for comprehensive log analysis and observability.
FAQs
What is the difference between log management and log analysis?
Log management focuses on collecting, storing, and organizing log data, while log analysis involves interpreting and deriving insights from that data. Log analysis tools often include log management capabilities but go further by providing advanced search, visualization, and analytics features.
How do log analysis tools improve IT security?
Log analysis tools enhance security by:
- Detecting unusual patterns or behaviors that may indicate security threats
- Providing real-time alerts for potential security incidents
- Enabling forensic analysis of security events
- Helping meet compliance requirements for log retention and analysis
Can log analysis tools integrate with existing IT infrastructure?
Yes, most modern log analysis tools offer extensive integration capabilities. They can typically ingest logs from various sources and integrate with other IT management tools, such as monitoring systems, SIEM solutions, and ticketing systems.
What are the key considerations when implementing a log analysis solution?
Key considerations include:
- Defining clear objectives and use cases
- Assessing scalability and performance requirements
- Evaluating ease of use and learning curve
- Considering total cost of ownership
- Ensuring compliance with security and regulatory requirements
- Reviewing integration capabilities with existing tools and systems
By carefully considering these factors, you can select and implement a log analysis solution that best meets your organization's needs and maximizes the value of your log data.
Further Reading:
7 Open-Source Log Management Tools that you may consider in 2024
