OpenTelemetry vs Grafana - Key Differences Explained
OpenTelemetry and Grafana are two essential but fundamentally different observability tools. OpenTelemetry standardizes data collection across your stack, while Grafana excels at visualization and analysis. Understanding their distinct roles and capabilities is crucial for building an effective observability strategy.
This article compares OpenTelemetry and Grafana's core features, integration capabilities, and optimal use cases to help you leverage both tools effectively.
What are OpenTelemetry and Grafana?
OpenTelemetry is a comprehensive observability framework that focuses on collecting and standardizing telemetry data. It provides a unified set of APIs, libraries, agents, and instrumentation to capture traces, metrics, and logs from your applications and infrastructure. OpenTelemetry aims to create a vendor-neutral standard for telemetry data collection, making it easier to integrate with various backends and analysis tools.
Grafana, on the other hand, is an open-source platform for data visualization and analysis. It excels at creating interactive dashboards and graphs from multiple data sources. Grafana's strength lies in its ability to query, visualize, and alert on metrics and logs, providing a centralized view of your system's performance and health.
Both tools have emerged as key players in the observability ecosystem, with OpenTelemetry focusing on data collection and Grafana on data visualization. OpenTelemetry was born from the merger of OpenCensus and OpenTracing projects in 2019, while Grafana has been around since 2014, continuously evolving its capabilities.
Can They Be Used Together?
Yes, OpenTelemetry and Grafana work very well together:
- Instrumentation with OTel: Use OpenTelemetry to instrument your applications and collect traces, metrics, and logs.
- Visualization with Grafana: Export telemetry data from OpenTelemetry to backends like Prometheus (metrics), Loki (logs), or Tempo (traces), and use Grafana to visualize and monitor the data.
Core Functionalities: OpenTelemetry vs Grafana
The primary distinction between OpenTelemetry and Grafana lies in their core functionalities:
OpenTelemetry
-
Primary Function: Data collection and standardization
OpenTelemetry's primary function is to effectively collect and standardize telemetry data, such as metrics, logs, and traces, from various sources within your application ecosystem. This standardization ensures that data is collected in a consistent and structured format, making it easier to analyze and visualize.
-
Unified Instrumentation Across Languages
OpenTelemetry provides a unified approach (API and SDKs) to instrumenting applications regardless of the programming language used. This unified approach reduces complexity and helps developers focus on building features instead of wrestling with different monitoring tools.
-
Multi-Language and Framework Support
It supports a wide range of programming languages and frameworks, including popular options like Java, Python, .NET, Go, JavaScript, and Node.js. This broad support enables you to instrument applications built with different technologies, ensuring comprehensive coverage of your telemetry data.
-
Vendor-Neutral and Agnostic Data Export
OpenTelemetry is designed to be vendor-neutral and agnostic, allowing you to export your collected telemetry data to various backend systems for analysis and visualization. This flexibility empowers you to choose the tools that best suit your needs and preferences, without being tied to a specific vendor or proprietary solution.
Grafana
-
Primary Function: Data Visualization and Dashboarding
Grafana's primary function is to visualize and analyze telemetry data. With a plethora of visualization types—from heat maps to histograms, it allows users to present data in a way that’s not only informative but also visually appealing. You can even customize these dashboards to meet specific team needs, ensuring that everyone sees the data that matters most to them.
-
Integration with Multiple Data Sources
Grafana seamlessly integrates with a wide range of data sources, including OpenTelemetry, Prometheus, Graphite, Elasticsearch, InfluxDB, CloudWatch, and many others. This flexibility means you can pull in data from multiple systems and get a holistic view of your application's performance.
-
Alerting and Proactive Monitoring
You can set up alerts based on metrics thresholds, and Grafana can notify your team through various channels, such as email, Slack, or even custom webhooks. This proactive monitoring helps teams catch issues before they escalate into major outages.
-
Extensibility with Plugins
It offers a plugin ecosystem for extensibility as Data source plugins communicate with external sources of data and return the data in a format that Grafana understands. By adding a data source plugin, you can immediately use the data in any of your existing dashboards. You can use data source plugins when you want to import data from external systems
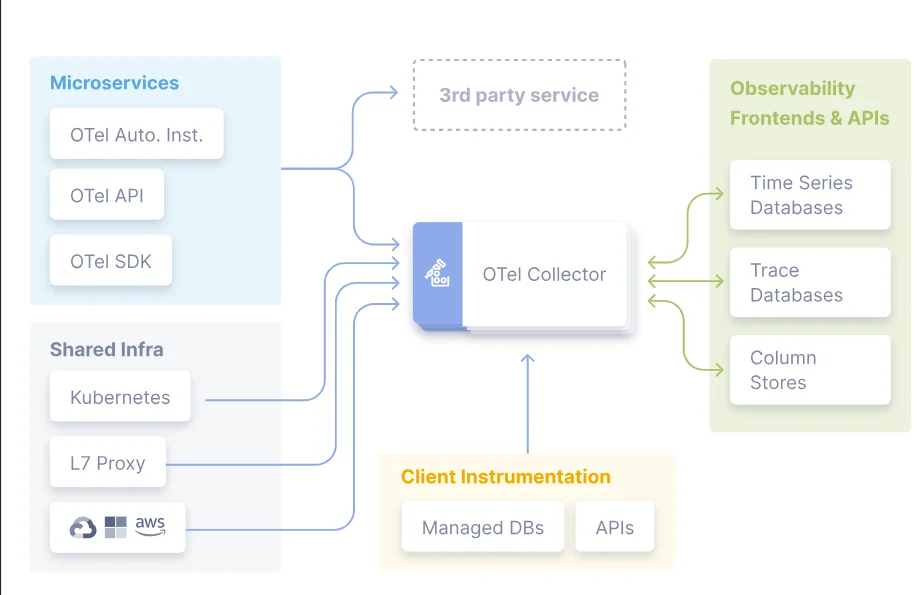
OpenTelemetry focuses on collecting telemetry data (traces, metrics, and logs) from systems and applications, while Grafana is mainly used for visualizing these telemetry data. OpenTelemetry sends the telemetry data to different backends like Prometheus, Jaeger, and Elasticsearch, Grafana connects to these same data sources for visualization.
Data Collection and Processing
OpenTelemetry's approach to data collection involves instrumenting your code with its APIs and SDKs. It automatically captures traces, metrics, and logs, providing a comprehensive view of your application's behavior. The collected data is then processed and exported to your chosen backend.
Example of OpenTelemetry instrumentation in Python:
from opentelemetry import trace
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace import TracerProvider
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace.export import ConsoleSpanExporter
trace.set_tracer_provider(TracerProvider())
tracer = trace.get_tracer(__name__)
with tracer.start_as_current_span("main"):
print("Hello, OpenTelemetry!")
Grafana, in contrast, serves as a powerful visualization tool that connects to various data sources. It uses query languages specific to each data source (e.g., PromQL for Prometheus, SQL for relational databases) to retrieve and process data for visualization. Grafana acts like a conductor, orchestrating data from multiple origins and presenting it in a cohesive, user-friendly manner.
Example of a Grafana query using PromQL:
rate(http_requests_total{job="api-server"}[5m])
The performance impact of using OpenTelemetry is designed to be minimal. It leverages asynchronous processing and batching, ensuring that your application remains responsive even while gathering telemetry data. Whereas the performance of Grafana largely depends on the complexity of your queries and the volume of data being visualized. Simple queries against indexed data sources will be quick and efficient, while complex queries or those involving large datasets may require more time and resources.
Use Cases and Best Practices
OpenTelemetry excels in cases where you need:
- A Standardized Approach to Instrumentation: If your organization is running multiple services, possibly written in different languages or frameworks, OpenTelemetry provides a consistent way to instrument them all. This uniformity simplifies troubleshooting and performance tuning, making it easier for teams to collaborate and share insights.
- Vendor-Neutral Data Collection: OpenTelemetry's vendor-neutral format allows you to avoid vendor lock-in. If you decide to change your backend or use multiple backends, you can do so without having to rewrite your entire instrumentation setup. This flexibility is especially valuable in dynamic environments where technology choices might evolve.
- Detailed Tracing of Distributed Systems: In microservices architectures, tracing requests across multiple services can be challenging. OpenTelemetry excels in providing detailed traces that show how requests flow through your system. This capability helps identify bottlenecks and performance issues, making it easier to optimize your application’s architecture.
Grafana shines when you require:
- Customizable, interactive dashboards: If your teams need a way to visualize data in a way that makes sense for their specific needs, Grafana is the go-to tool. With its rich set of visualization options and customizable dashboards, you can create an interface that resonates with different stakeholders
- Visualization of data from multiple sources: Grafana’s ability to connect to various data sources means you can bring together metrics, logs, and traces into one cohesive view. This capability is invaluable for getting a holistic understanding of your system's performance and health.
- Alerting based on complex queries: You can set up alerts based on the results of complex queries, ensuring that your team is notified when things go awry before users even notice.
Best Practices for Implementing OpenTelemetry and Grafana
- Set clear goals: Before jumping in, it's important to define what you need to monitor. Identify the key metrics and traces that are essential for your system’s performance. Having clear goals makes sure your setup is focused and effective, so you’re not overwhelmed with unnecessary data. This focus helps you prioritize the most critical areas, making troubleshooting faster and easier when issues arise.
- Keep an eye on performance impact: Make sure the process of collecting data with OpenTelemetry and visualizing it in Grafana doesn’t slow things down. To load data without sacrificing performance you can employ techniques like sampling and filtering. This ensures that your monitoring system itself doesn't become a bottleneck, allowing your applications to run smoothly while still getting the insights you need.
- Maintain Consistent Naming Conventions: To make querying data simpler, adopt consistent naming conventions for traces, metrics, and logs. Inconsistent naming can make it harder to identify patterns and trends, slowing down your analysis.
- Avoid Over-Instrumentation: While it’s tempting to instrument everything, too much data can lead to high storage costs and make it difficult to sift through. Focus on instrumenting only the critical components and metrics that matter to your goals. This approach keeps costs in check while providing the necessary visibility.
- Set Up Alerts and Notifications: A good observability setup isn't just about viewing data—it's about getting notified when something goes wrong. You can use Grafana to create alerts based on key metrics and logs, enabling proactive monitoring. This way, your teams can address issues before they escalate into major problems.
Pros and Cons: OpenTelemetry vs Grafana
When it comes to observability, OpenTelemetry and Grafana each play distinct roles, but knowing their strengths and challenges can help you make the most out of both tools. Let’s break down what they offer and where you might run into limitations:
OpenTelemetry Pros
- Standardization: One of OpenTelemetry's standout features is its ability to provide a consistent method for instrumenting applications. With its comprehensive SDKs and libraries, you can automatically collect and trace telemetry data—be it metrics, traces, or logs—across various programming languages. This consistency simplifies the integration process, especially in heterogeneous environments.
- Vendor-Neutral: This flexibility allows you to change backends as needed without overhauling your instrumentation, making it a future-proof choice for organizations that may evolve over time.
- Full-Stack Observability: Comprehensive coverage of traces, metrics, and logs enables teams to monitor their applications from various angles, facilitating deeper insights into system health.
OpenTelemetry Cons
- Steep learning curve: Understanding how to instrument your applications effectively, manage configurations, and set up various components may require a bit of effort, especially for teams new to observability.
- Backend Dependency: OpenTelemetry acts as a collection framework, which means you need to choose and configure a backend for storing and analyzing your telemetry data. This additional step can be a barrier for teams looking for a plug-and-play solution.
- Lack of Multi-Tenancy and user management: OpenTelemetry, being a framework, does not possess native capabilities for multi-tenancy or user management; this aspect depends on the observability platform to which the telemetry data is sent.
Grafana Pros
- Powerful and Flexible Data Visualization: Grafana excels at transforming data into visual insights. With a wide array of visualization options—from graphs and heatmaps to tables and alerts—Grafana allows teams to build dashboards tailored to their specific needs. This flexibility makes it a favorite for monitoring and analysis.
- Wide Range of Supported Data Sources: One of Grafana’s key strengths is its ability to connect to numerous data sources. Whether you’re using Prometheus, Elasticsearch, or even relational databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL, Grafana can pull in data from various origins to provide a unified view.
- Active Plugin Ecosystem: Grafana has a vibrant plugin ecosystem that extends its capabilities. You can find plugins for different data sources, visualization types, and even custom features, allowing you to tailor Grafana to fit your specific use cases.
- Multi-Tenancy and User Management: Grafana includes robust features for multi-tenancy and user management, making it easy for organizations to create and manage different teams, users, and access permissions. This granularity allows you to control who sees what, ensuring that data and dashboards are only accessible to the right people.
Grafana Cons
- Data Source Dependency: While Grafana shines in visualization, it doesn’t collect data itself. Instead, it relies on external data sources and plugins, which means you need to set up and manage those data pipelines separately.
- Can Be Resource-Intensive with Complex Dashboards: When working with large datasets or complex dashboards, Grafana can become resource-intensive. This could lead to performance issues, particularly if your infrastructure isn’t equipped to handle the load.
Integration and Compatibility
OpenTelemetry is designed to integrate seamlessly with various backends like Jaeger for tracing, Prometheus for metrics, and Elasticsearch for logs, giving you flexibility in building your observability stack.
Grafana's extensive plugin ecosystem allows it to connect to a variety of data sources, such as Prometheus for metrics or Elasticsearch for logs, and visualize the data in user-friendly dashboards. It also supports time-series and relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and InfluxDB, allowing for visualization of key metrics. This makes it suitable for organizations with different setups and requirements.
When integrating OpenTelemetry with Grafana, you can configure OpenTelemetry to send metrics to Prometheus, which Grafana uses as a data source for querying and visualizing data. This integration not only provides you with detailed insights into your application’s performance but also allows you to create alerts based on the data, ensuring you stay on top of potential issues.
When building an observability stack using OpenTelemetry and Grafana, it’s crucial to carefully evaluate the supporting tools and technologies you integrate with them:
- Data Storage: OpenTelemetry can gather extensive telemetry data, but you need a compatible backend that can efficiently store and manage this data over time. Select backends compatible with OpenTelemetry's data formats and Grafana's querying capabilities.
- Scalability: OpenTelemetry handles large-scale data collection efficiently with features like batching and sampling. Grafana's scalability depends on the performance of its data sources, so ensure that the tools can handle large data sets for smooth dashboard performance and are capable of scaling as your infrastructure grows.
- Integration: OpenTelemetry supports various backends for data storage and processing, while Grafana connects to multiple data sources for visualization. Ensure that the tools you select can seamlessly integrate with your existing infrastructure and other technologies.
- Vendor Lock-In: While OpenTelemetry and Grafana are open-source, some supporting tools may be proprietary. Evaluate the trade-offs between open-source and commercial solutions. Consider factors like long-term flexibility, support options, feature sets, and total cost of ownership when making your decision.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
Both OpenTelemetry and Grafana have distinct performance and scalability characteristics that cater to different aspects of observability. Here is a closer look at how each tool addresses these critical factors and their impact on your overall monitoring strategy.
- Efficient Sampling Techniques:
OpenTelemetry uses smart sampling techniques to manage the amount of data it collects, like capturing a percentage of requests in high-traffic environments. This helps keep performance smooth without overloading the system. Whereas, Grafana doesn’t have its own sampling capabilities and so it relies on the efficiency of the data sources. This is why it’s recommended to craft well-optimized queries.
- Batching and Compression:
As mentioned earlier, in OpenTelemetry, batching and compression can make a big difference. By grouping multiple telemetry signals into one transmission, it cuts down on network calls and speeds up the process. Grafana, however, depends on the capabilities of the connected data sources—some may not support batching or compression, which could affect how data is transmitted.
- Asynchronous Processing:
OpenTelemetry gathers data asynchronously, meaning it collects and sends telemetry in the background without slowing down your application. Grafana also displays data asynchronously, but its responsiveness hinges on how quickly the connected data sources can deliver information.
- Query Efficiency:
While OpenTelemetry focuses on efficient data collection methods, Grafana leans heavily on optimized queries to pull just the right data from sources. Poorly designed queries in Grafana can slow everything down, so getting them right is critical to avoiding performance issues.
- Caching Mechanisms:
Unlike OpenTelemetry, which focuses on data collection and doesn't offer built-in caching, Grafana allows for caching query results. This can significantly boost performance, especially in environments with many users accessing the same data, by cutting down on repeated data source requests.
- Scalable Infrastructure:
OpenTelemetry’s performance impact is generally light, but scalability depends on the backend storage solution you’re using. Grafana’s scalability, on the other hand, is more directly tied to your infrastructure—so ensuring your servers and databases are ready to handle large datasets and high traffic is essential, particularly when dealing with lots of concurrent users.
Community and Ecosystem
OpenTelemetry boasts a vibrant open-source community under the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). It benefits from contributions from major tech companies and individual developers alike.
Grafana has a strong community following and offers both open-source and commercial versions. The company behind Grafana provides extensive documentation, tutorials, and commercial support options.
Both projects have active development roadmaps, with OpenTelemetry focusing on expanding language support and refining its specifications, while Grafana continues to enhance its visualization capabilities and data source integrations.
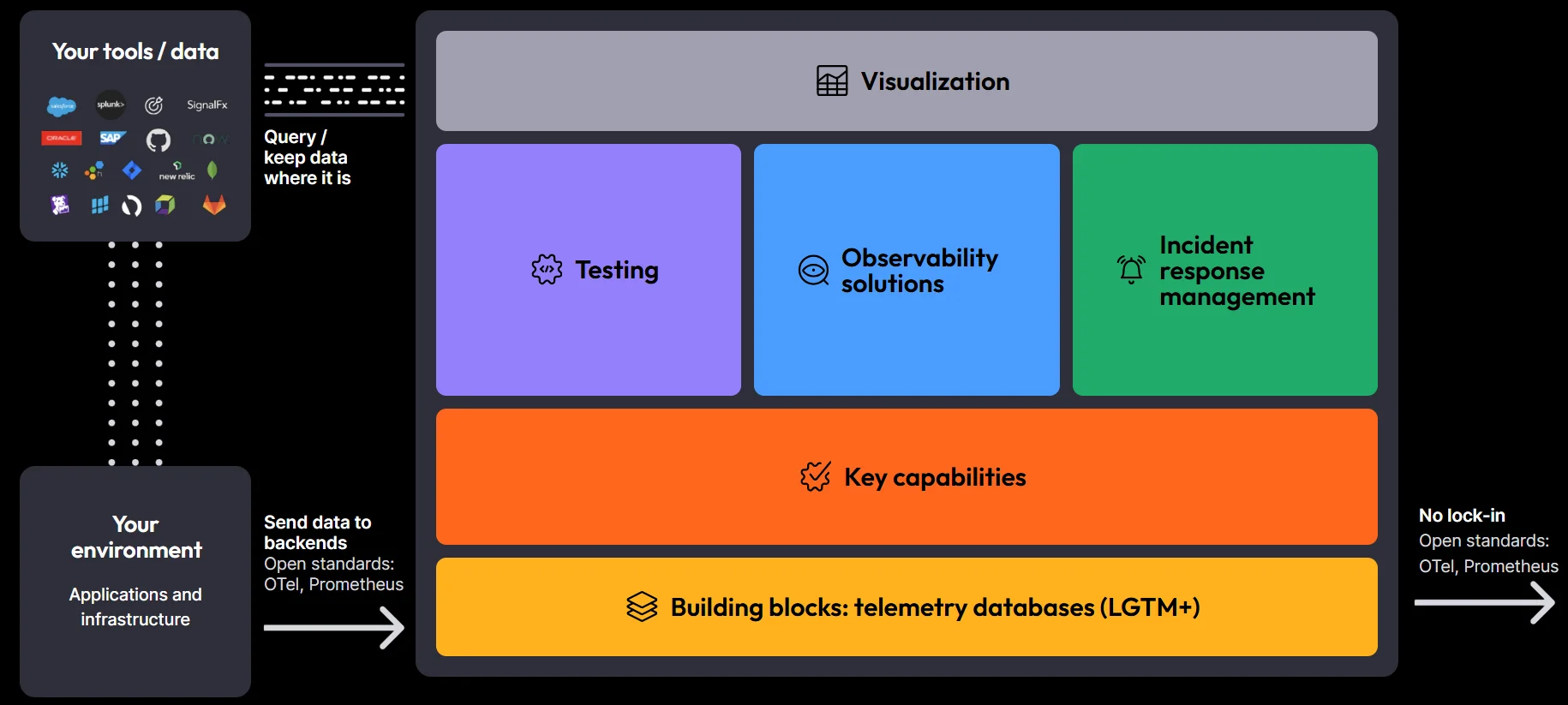
Implementing OpenTelemetry and Grafana with SigNoz
SigNoz is a comprehensive observability platform that combines the strengths of both OpenTelemetry and Grafana-like visualizations. It leverages OpenTelemetry for data collection, providing a standardized approach to instrumentation across your services. SigNoz then offers powerful visualization capabilities similar to Grafana, allowing you to create custom dashboards and alerts.
By using SigNoz, you can:
- Consolidate your observability tools into a single platform. This simplification means less overhead in managing multiple systems and a more cohesive user experience. You won’t need to juggle different interfaces or worry about data silos, making your observability journey smoother and more efficient.
- Benefit from OpenTelemetry's standardized data collection. Whether your applications are written in Python, Java, or any other supported language, you can rely on a consistent method for collecting metrics, traces, and logs. This uniformity helps ensure that your telemetry data is accurate and easily comparable across different services.
- One of the standout features of SigNoz is its powerful visualization capabilities, reminiscent of Grafana’s dashboards. You can create custom visualizations and dashboards directly within SigNoz, eliminating the need for a separate Grafana installation. This integration allows you to build insightful dashboards quickly, tailored to your team’s needs, without the hassle of managing multiple tools.
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Key Takeaways
- OpenTelemetry provides a standardized approach to data collection across various sources, while Grafana excels in creating customizable, interactive dashboards.
- Both tools can be used complementarily for a robust observability strategy.
- Consider factors like data types, scalability, and integration needs when choosing between or combining these tools.
- SigNoz offers an integrated solution that leverages the strengths of both OpenTelemetry and Grafana-like visualizations.
FAQs
What is the main difference between OpenTelemetry and Grafana?
The main difference is their focus: OpenTelemetry concentrates on standardized data collection and instrumentation, while Grafana specializes in data visualization and dashboard creation.
Can OpenTelemetry and Grafana be used together?
Yes, OpenTelemetry and Grafana can be used together effectively. OpenTelemetry can collect and export data to a backend that Grafana supports, allowing you to visualize OpenTelemetry data in Grafana dashboards.
Which tool is better for monitoring cloud-native applications?
Both tools have their strengths in monitoring cloud-native applications. OpenTelemetry provides consistent instrumentation across services, while Grafana offers flexible visualization. The best choice depends on your specific needs — ideally, you'd use both in conjunction.
How does SigNoz compare to using OpenTelemetry and Grafana separately?
SigNoz combines the data collection capabilities of OpenTelemetry with visualization features similar to Grafana in a single platform. This integration can simplify your observability stack and provide a more streamlined experience compared to managing OpenTelemetry and Grafana separately.
