Overview
This guide walks you through setting up monitoring and observability for Amazon Bedrock using OpenTelemetry and exporting logs, traces, and metrics to SigNoz. With this integration, you can observe model performance, capture request/response details, and track system-level metrics in SigNoz, giving you real-time visibility into latency, error rates, and usage trends for your Bedrock applications.
Many developers choose Amazon Bedrock over directly calling LLM models for its enterprise-grade features including unified API access to multiple foundation models (Claude, Llama, Titan, etc.), built-in safeguards for responsible AI, private and secure model invocations that don't leave AWS infrastructure, managed infrastructure that eliminates the need to manage model hosting, fine-tuning capabilities with your own data while maintaining privacy, and seamless integration with AWS services like S3, Lambda, and CloudWatch. These capabilities make Amazon Bedrock particularly valuable for organizations requiring production-grade reliability, compliance, and simplified model management without the complexity of direct model deployment.
Instrumenting Amazon Bedrock in your LLM applications with telemetry ensures full observability across your AI workflows, making it easier to debug issues, optimize performance, and understand user interactions. By leveraging SigNoz, you can analyze correlated traces, logs, and metrics in unified dashboards, configure alerts, and gain actionable insights to continuously improve reliability, responsiveness, and user experience.
Prerequisites
- SigNoz setup (choose one):
- SigNoz Cloud account with an active ingestion key
- Self-hosted SigNoz instance
- Internet access to send telemetry data to SigNoz Cloud
- An AWS account with Amazon Bedrock working and access granted for LLM models
- For Python:
pipinstalled for managing Python packages and (optional but recommended) a Python virtual environment to isolate dependencies
Monitoring Amazon Bedrock
No-code auto-instrumentation is recommended for quick setup with minimal code changes. It's ideal when you want to get observability up and running without modifying your application code and are leveraging standard instrumentor libraries.
Step 1: Install the necessary packages in your Python environment.
pip install \
opentelemetry-distro \
opentelemetry-exporter-otlp \
opentelemetry-instrumentation-httpx \
opentelemetry-instrumentation-system-metrics \
openinference-instrumentation-bedrock \
boto3
Step 2: Add Automatic Instrumentation
opentelemetry-bootstrap --action=install
Step 3: Configure logging level
To ensure logs are properly captured and exported, configure the root logger to emit logs at the INFO level or higher:
import logging
logging.getLogger().setLevel(logging.INFO)
This sets the minimum log level for the root logger to INFO, which ensures that logger.info() calls and higher severity logs (WARNING, ERROR, CRITICAL) are captured by the OpenTelemetry logging auto-instrumentation and sent to SigNoz.
Step 4: Run an example
import boto3
import os
import logging
logging.getLogger().setLevel(logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
bedrock = boto3.client(
service_name="bedrock-runtime",
aws_access_key_id=os.getenv("AWS_ACCESS"), aws_secret_access_key=os.getenv("AWS_SECRET"),
region_name="us-east-1" # or your region
)
model_id = "us.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0"
prompt = "What is SigNoz?"
logger.info(f"Sending prompt to model {model_id}: {prompt}") #sample log
body = {
"anthropic_version": "bedrock-2023-05-31",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": prompt}
]
}
],
"max_tokens": 512,
"temperature": 0.7
}
response = bedrock.invoke_model(
modelId=model_id,
body=json.dumps(body)
)
response_body = json.loads(response['body'].read())
output_text = response_body['content'][0]['text']
print("Model output:\n", output_text)
📌 Note: No logs are automatically emitted by the BedrockInstrumentor. If you would like logs, you need to emit them manually via
logger.info()or other logging methods.
Step 5: Run your application with auto-instrumentation
OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES="service.name=<service_name>" \
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT="https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443" \
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS="signoz-ingestion-key=<your-ingestion-key>" \
OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL=grpc \
OTEL_TRACES_EXPORTER=otlp \
OTEL_METRICS_EXPORTER=otlp \
OTEL_LOGS_EXPORTER=otlp \
OTEL_PYTHON_LOG_CORRELATION=true \
OTEL_PYTHON_LOGGING_AUTO_INSTRUMENTATION_ENABLED=true \
opentelemetry-instrument <your_run_command>
<service_name>is the name of your service<region>: Your SigNoz Cloud region<your-ingestion-key>: Your SigNoz ingestion key- Replace
<your_run_command>with the actual command you would use to run your application. For example:python main.py
Using self-hosted SigNoz? Most steps are identical. To adapt this guide, update the endpoint and remove the ingestion key header as shown in Cloud → Self-Hosted.
Code-based instrumentation gives you fine-grained control over your telemetry configuration. Use this approach when you need to customize resource attributes, sampling strategies, or integrate with existing observability infrastructure.
Step 1: Install the necessary packages in your Python environment.
pip install \
opentelemetry-api \
opentelemetry-sdk \
opentelemetry-exporter-otlp \
opentelemetry-instrumentation-httpx \
opentelemetry-instrumentation-system-metrics \
openinference-instrumentation-bedrock \
boto3
Step 2: Import the necessary modules in your Python application
Traces:
from openinference.instrumentation.bedrock import BedrockInstrumentor
from opentelemetry import trace
from opentelemetry.sdk.resources import Resource
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace import TracerProvider
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace.export import BatchSpanProcessor
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.http.trace_exporter import OTLPSpanExporter
Logs:
from opentelemetry.sdk._logs import LoggerProvider, LoggingHandler
from opentelemetry.sdk._logs.export import BatchLogRecordProcessor
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.http._log_exporter import OTLPLogExporter
from opentelemetry._logs import set_logger_provider
import logging
Metrics:
from opentelemetry.sdk.metrics import MeterProvider
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.http.metric_exporter import OTLPMetricExporter
from opentelemetry.sdk.metrics.export import PeriodicExportingMetricReader
from opentelemetry import metrics
from opentelemetry.instrumentation.system_metrics import SystemMetricsInstrumentor
from opentelemetry.instrumentation.httpx import HTTPXClientInstrumentor
Step 3: Set up the OpenTelemetry Tracer Provider to send traces directly to SigNoz Cloud
from opentelemetry.sdk.resources import Resource
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace import TracerProvider
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace.export import BatchSpanProcessor
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.http.trace_exporter import OTLPSpanExporter
from opentelemetry import trace
import os
resource = Resource.create({"service.name": "<service_name>"})
provider = TracerProvider(resource=resource)
span_exporter = OTLPSpanExporter(
endpoint= os.getenv("OTEL_EXPORTER_TRACES_ENDPOINT"),
headers={"signoz-ingestion-key": os.getenv("SIGNOZ_INGESTION_KEY")},
)
processor = BatchSpanProcessor(span_exporter)
provider.add_span_processor(processor)
trace.set_tracer_provider(provider)
<service_name>is the name of your serviceOTEL_EXPORTER_TRACES_ENDPOINT→ SigNoz Cloud trace endpoint with appropriate region:https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443/v1/tracesSIGNOZ_INGESTION_KEY→ Your SigNoz ingestion key
Using self-hosted SigNoz? Most steps are identical. To adapt this guide, update the endpoint and remove the ingestion key header as shown in Cloud → Self-Hosted.
Step 4: Instrument Bedrock using BedrockInstrumentor and the configured Tracer Provider
from openinference.instrumentation.bedrock import BedrockInstrumentor
BedrockInstrumentor().instrument()
📌 Important: Place this code at the start of your application logic — before any Bedrock functions are called or used — to ensure telemetry is correctly captured.
Step 5: Setup Logs
import logging
from opentelemetry.sdk.resources import Resource
from opentelemetry._logs import set_logger_provider
from opentelemetry.sdk._logs import LoggerProvider, LoggingHandler
from opentelemetry.sdk._logs.export import BatchLogRecordProcessor
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.http._log_exporter import OTLPLogExporter
import os
resource = Resource.create({"service.name": "<service_name>"})
logger_provider = LoggerProvider(resource=resource)
set_logger_provider(logger_provider)
otlp_log_exporter = OTLPLogExporter(
endpoint= os.getenv("OTEL_EXPORTER_LOGS_ENDPOINT"),
headers={"signoz-ingestion-key": os.getenv("SIGNOZ_INGESTION_KEY")},
)
logger_provider.add_log_record_processor(
BatchLogRecordProcessor(otlp_log_exporter)
)
# Attach OTel logging handler to root logger
handler = LoggingHandler(level=logging.INFO, logger_provider=logger_provider)
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, handlers=[handler])
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
<service_name>is the name of your serviceOTEL_EXPORTER_LOGS_ENDPOINT→ SigNoz Cloud endpoint with appropriate region:https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443/v1/logsSIGNOZ_INGESTION_KEY→ Your SigNoz ingestion key
📌 Note: No logs are automatically emitted by the BedrockInstrumentor. If you would like logs, you need to emit them manually via
logger.info()or other logging methods.
Using self-hosted SigNoz? Most steps are identical. To adapt this guide, update the endpoint and remove the ingestion key header as shown in Cloud → Self-Hosted.
Step 6: Setup Metrics
from opentelemetry.sdk.resources import Resource
from opentelemetry.sdk.metrics import MeterProvider
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.http.metric_exporter import OTLPMetricExporter
from opentelemetry.sdk.metrics.export import PeriodicExportingMetricReader
from opentelemetry import metrics
from opentelemetry.instrumentation.system_metrics import SystemMetricsInstrumentor
import os
resource = Resource.create({"service.name": "<service-name>"})
metric_exporter = OTLPMetricExporter(
endpoint= os.getenv("OTEL_EXPORTER_METRICS_ENDPOINT"),
headers={"signoz-ingestion-key": os.getenv("SIGNOZ_INGESTION_KEY")},
)
reader = PeriodicExportingMetricReader(metric_exporter)
metric_provider = MeterProvider(metric_readers=[reader], resource=resource)
metrics.set_meter_provider(metric_provider)
meter = metrics.get_meter(__name__)
# turn on out-of-the-box metrics
SystemMetricsInstrumentor().instrument()
HTTPXClientInstrumentor().instrument()
<service_name>is the name of your serviceOTEL_EXPORTER_METRICS_ENDPOINT→ SigNoz Cloud endpoint with appropriate region:https://ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443/v1/metricsSIGNOZ_INGESTION_KEY→ Your SigNoz ingestion key
📌 Note: SystemMetricsInstrumentor provides system metrics (CPU, memory, etc.), and HTTPXClientInstrumentor provides outbound HTTP request metrics such as request duration. These are not Bedrock-specific metrics. Bedrock does not expose metrics as part of their SDK. If you want to add custom metrics to your Bedrock application, see Python Custom Metrics.
Using self-hosted SigNoz? Most steps are identical. To adapt this guide, update the endpoint and remove the ingestion key header as shown in Cloud → Self-Hosted.
Step 7: Run an example
import boto3
import os
bedrock = boto3.client(
service_name="bedrock-runtime",
aws_access_key_id=os.getenv("AWS_ACCESS"), aws_secret_access_key=os.getenv("AWS_SECRET"),
region_name="us-east-1" # or your region
)
model_id = "us.anthropic.claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929-v1:0"
prompt = "What is SigNoz?"
logger.info(f"Sending prompt to model {model_id}: {prompt}") #sample log
body = {
"anthropic_version": "bedrock-2023-05-31",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": prompt}
]
}
],
"max_tokens": 512,
"temperature": 0.7
}
response = bedrock.invoke_model(
modelId=model_id,
body=json.dumps(body)
)
response_body = json.loads(response['body'].read())
output_text = response_body['content'][0]['text']
print("Model output:\n", output_text)
📌 Note: Before running this code, ensure that you have set the environment variables
AWS_ACCESSandAWS_SECRETwith your AWS credentials.
View Traces, Logs, and Metrics in SigNoz
Your Bedrock commands should now automatically emit traces, logs, and metrics.
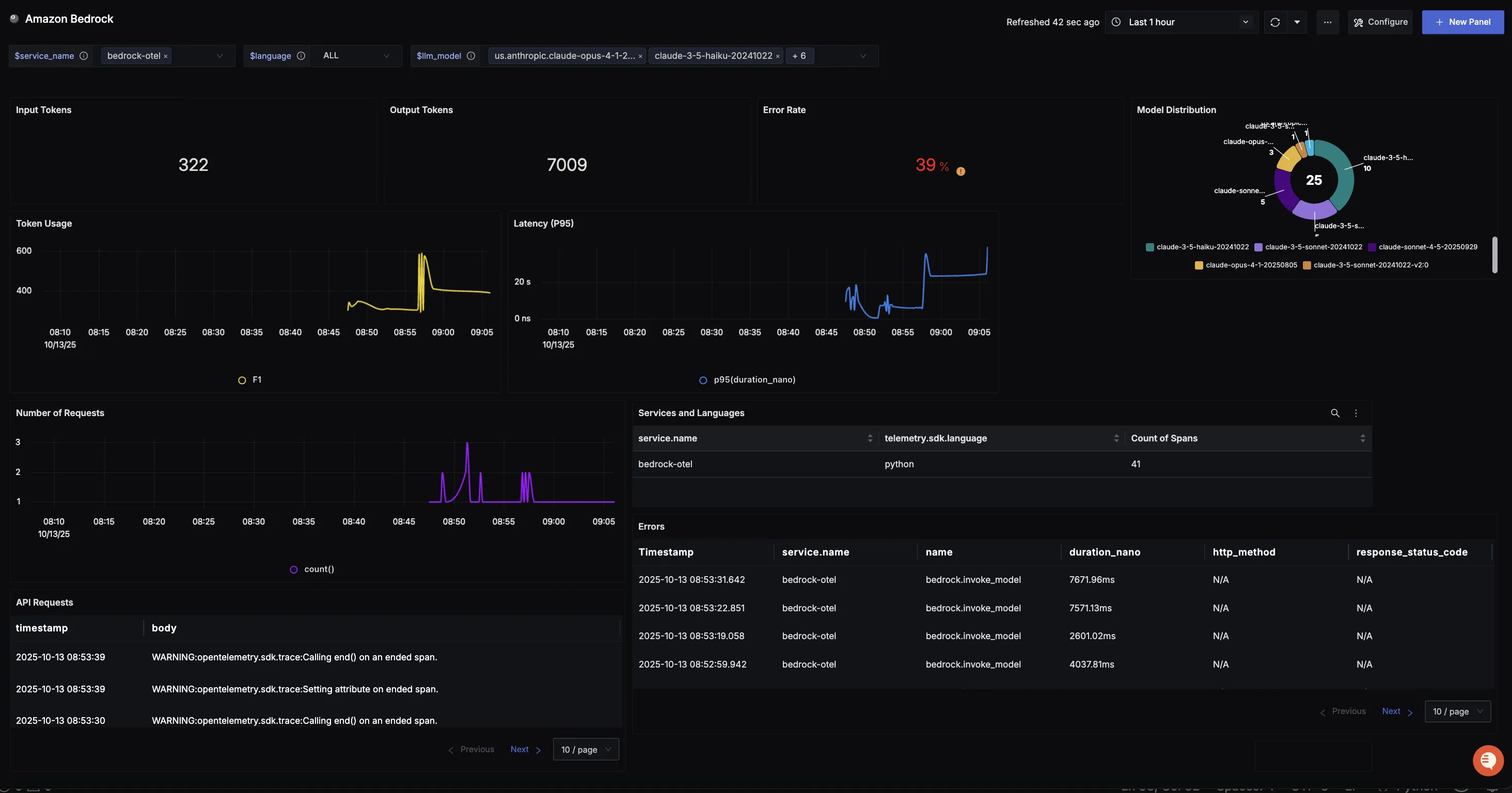
You should be able to view traces in Signoz Cloud under the traces tab:
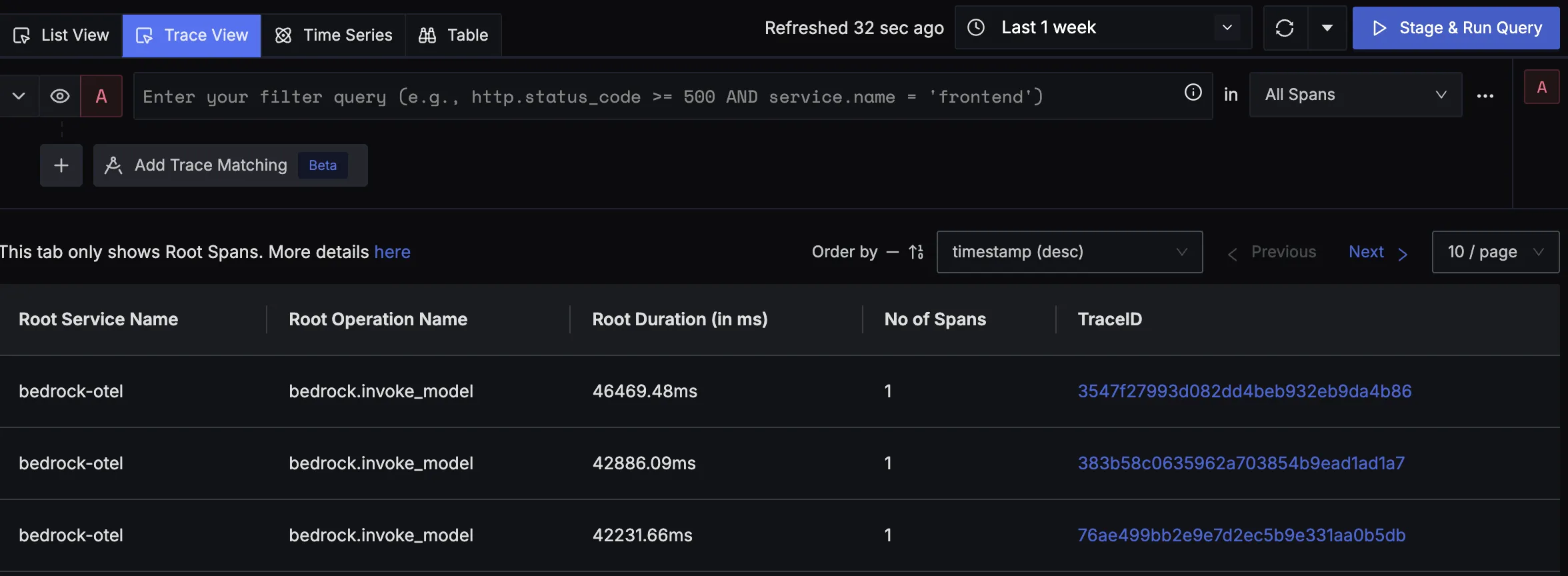
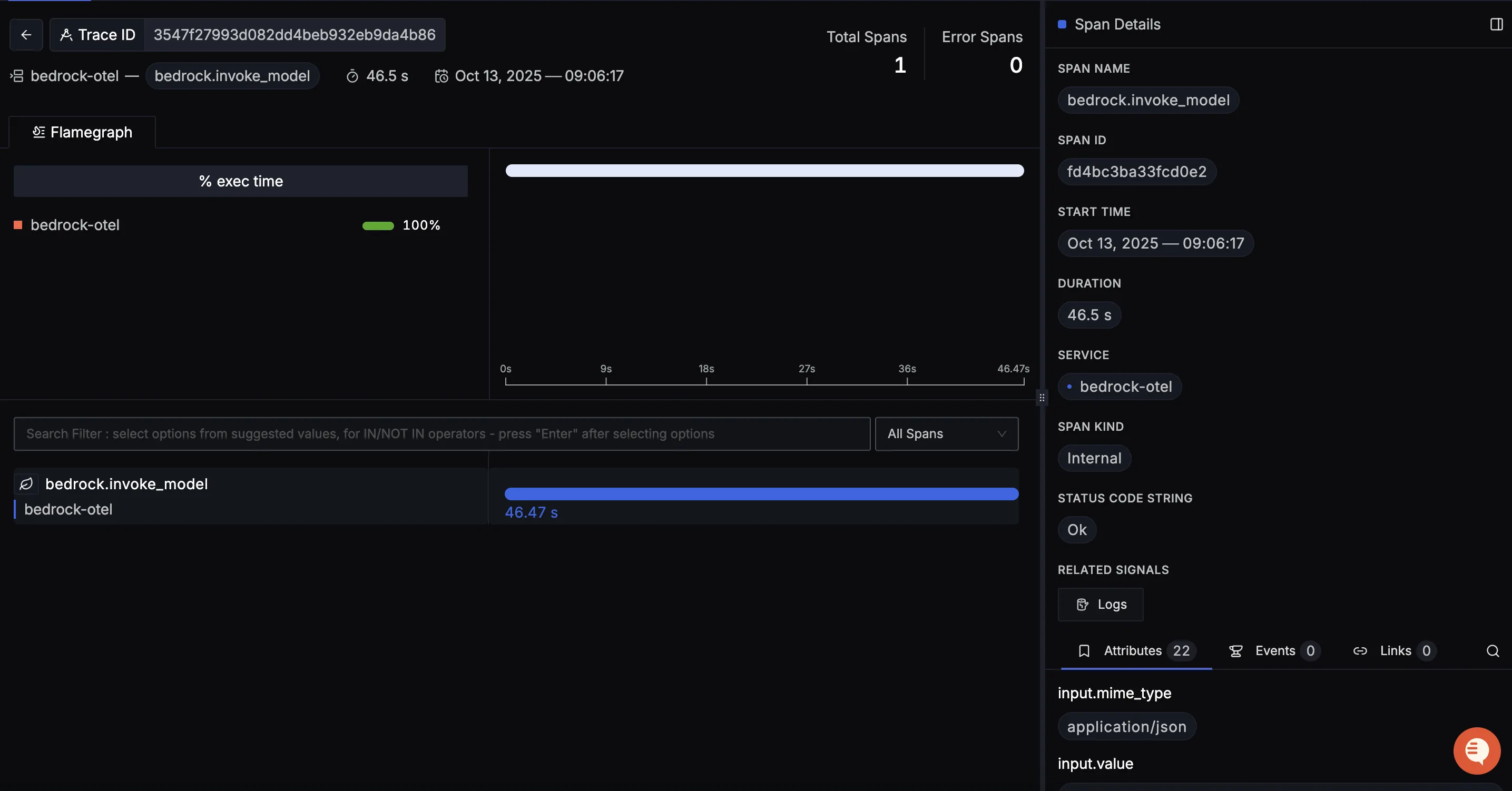
When you click on a trace in SigNoz, you'll see a detailed view of the trace, including all associated spans, along with their events and attributes.
You should be able to view logs in Signoz Cloud under the logs tab. You can also view correlated logs by clicking on the “Related Logs” button in the trace view to see correlated logs:
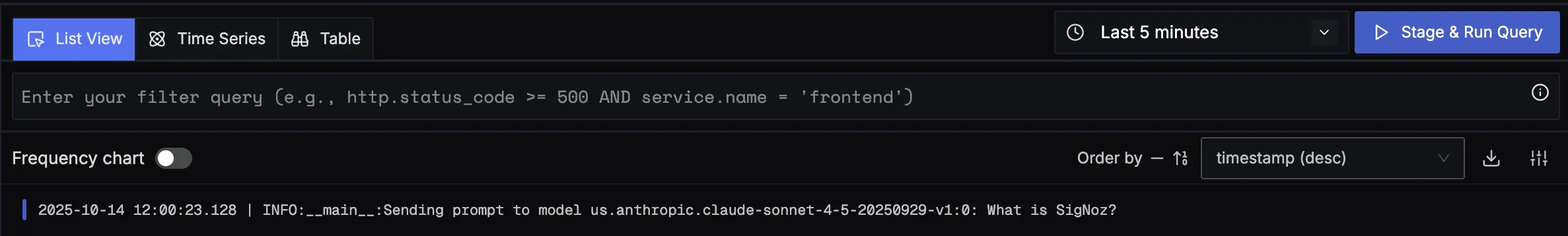
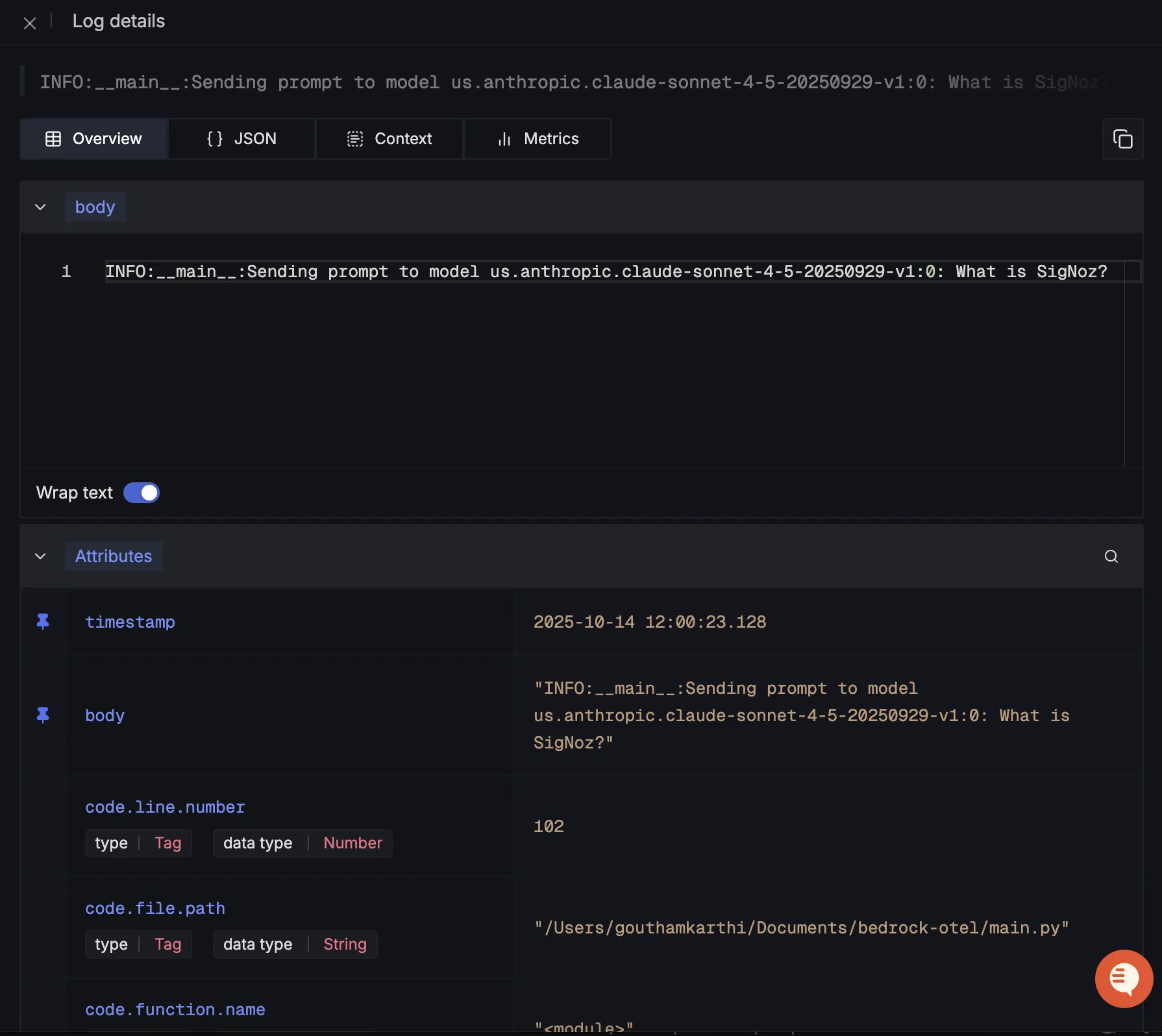
When you click on any of these logs in SigNoz, you'll see a detailed view of the log, including attributes:
You should be able to see Bedrock related metrics in Signoz Cloud under the metrics tab:
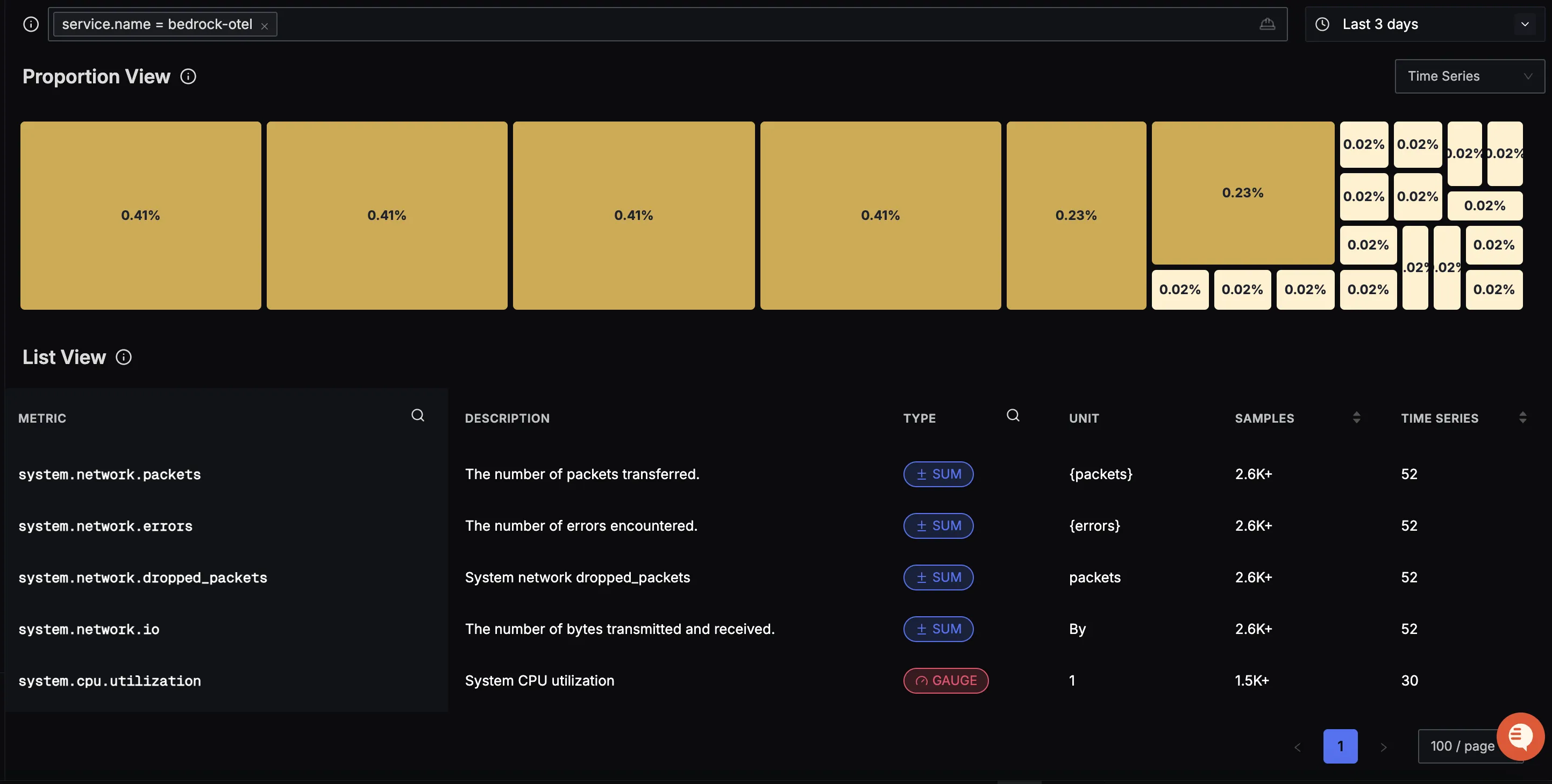
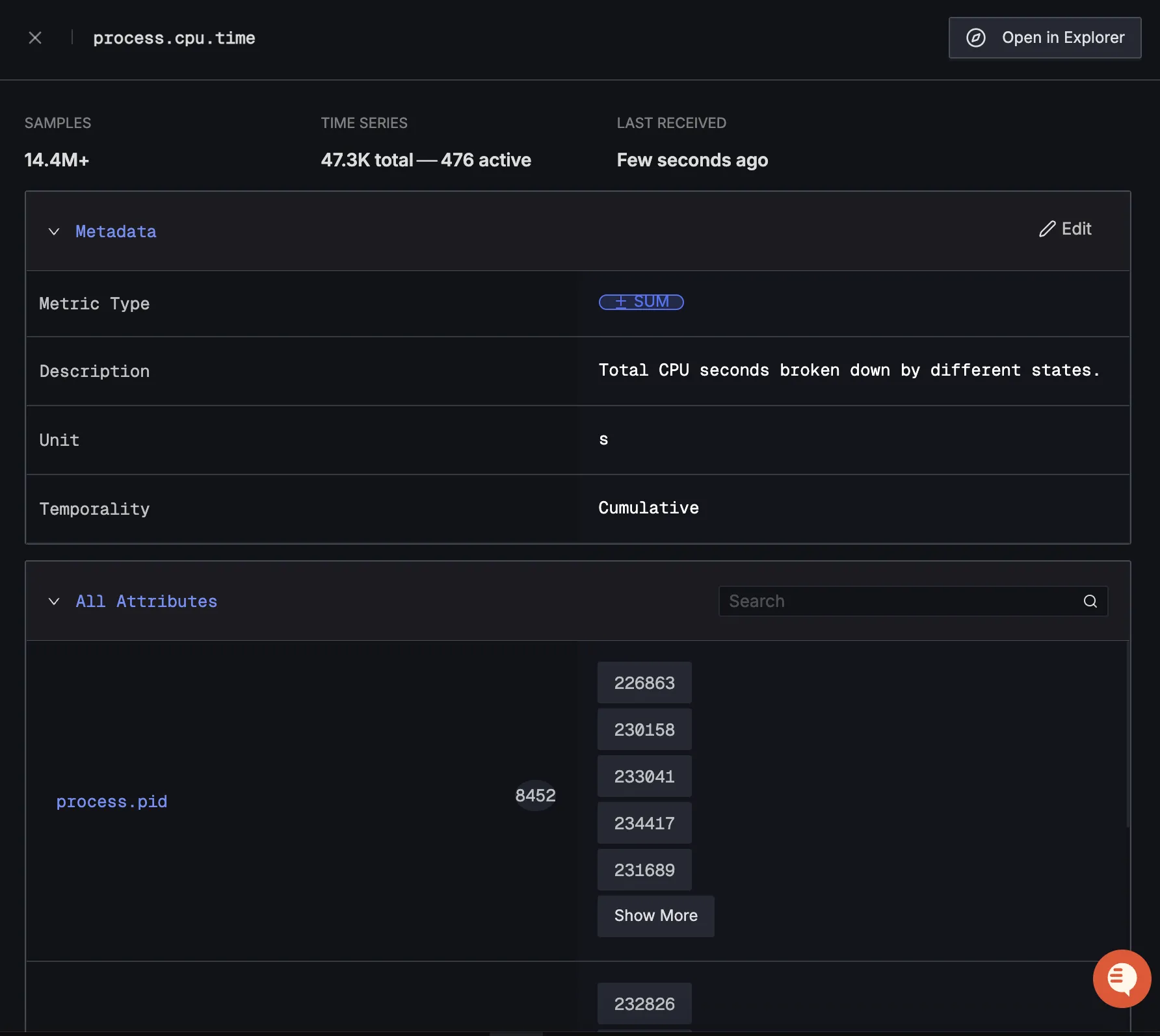
When you click on any of these metrics in SigNoz, you'll see a detailed view of the metric, including attributes:
Dashboard
You can also check out our custom Amazon Bedrock dashboard here which provides specialized visualizations for monitoring your Bedrock usage in applications. The dashboard includes pre-built charts specifically tailored for LLM usage, along with import instructions to get started quickly.