How to Calculate Average Memory Usage in Prometheus
Monitoring memory usage is crucial for maintaining healthy systems and optimizing application performance. Prometheus, a popular open-source monitoring system, offers powerful tools for tracking and analyzing memory metrics. This guide will show you how to calculate average memory usage in Prometheus, helping you gain valuable insights into your system's performance.
Understanding Memory Usage Metrics in Prometheus
Before diving into calculations, it's essential to understand the key memory metrics Prometheus collects.
Memory usage refers to the amount of RAM (Random Access Memory) currently utilized by your system. It's a crucial indicator of system health; high memory usage can lead to performance degradation or even system crashes if left unmonitored.
Prometheus collects various system metrics related to memory usage. Key metrics include:
node_memory_MemTotal_bytes: Total memory available on the system.node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes: Memory available for use by applications and the OS (includes free memory and cache).node_memory_MemFree_bytes: Completely unused memory.node_memory_Buffers_bytes: Memory used by kernel buffersnode_memory_Cached_bytes: Memory used by the page cache and slabs
Note: Memory usage differs from memory availability. Usage refers to the amount of memory currently in use, while availability indicates the memory that can be allocated to processes without swapping.
Common Memory Usage Queries in Prometheus
To get started with memory usage analysis, here are some basic Prometheus queries:
Basic Query for Total Memory Usage
To calculate the total memory used as a percentage of total memory:
(node_memory_MemTotal_bytes - node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes)Query for Percentage of Memory Used
To get the percentage of memory in use:
(node_memory_MemTotal_bytes - node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes) / node_memory_MemTotal_bytes * 100Query for Memory Usage Over Time
The
rate()function can be used with a memory-related metric that has a counter-like behavior. For example, if you're tracking memory usage via a process or container metric that increases over time, you can use:Example Query for Memory Usage Increase Over Time:
rate(container_memory_usage_bytes[5m])Note: The above works for containers and not Linux-based servers.
Calculating Average Memory Usage with PromQL
Prometheus Query Language (PromQL) provides powerful functions for calculating average memory usage. The two main functions you'll use are avg() and avg_over_time().
Here's a step-by-step guide to constructing an average memory usage query:
Calculate the used memory:
node_memory_MemTotal_bytes - node_memory_MemAvailable_bytesCalculate the average over time:
avg_over_time(node_memory_MemTotal_bytes[1h]) - avg_over_time(node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes[1h])Calculate the average across multiple instances:
avg(node_memory_MemTotal_bytes - node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes) by (instance)
This query calculates the average memory usage across all monitored nodes over the past hour. Adjust the time range [1h] as needed for your specific use case.
Advanced Memory Usage Calculations
For more complex scenarios, you can use advanced PromQL features:
Calculate memory usage across multiple nodes:
sum(node_memory_MemTotal_bytes - node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes) by (instance)sum()withby (instance)gives total memory usage per instance. If you want the average memory usage across instances, you could do:avg(sum(node_memory_MemTotal_bytes - node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes) by (instance))Use label selectors to filter data:
To filter memory usage by a specific label (e.g., job):
avg(node_memory_MemTotal_bytes{job="webserver"} - node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes{job="webserver"})
Memory Usage on Different Operating Systems
Based on different operating systems, different metrics are used for monitoring memory usage:
Linux-Based Systems
Prometheus provides robust support for Linux-based systems, allowing easy collection of memory metrics via exporters like node_exporter. Commonly used metrics include node_memory_MemTotal_bytes, node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes, and node_memory_MemFree_bytes, as previously discussed.
Windows-Based Systems
The wmi_exporter (now known as windows_exporter) is commonly used to monitor memory usage on Windows systems. This exporter collects a variety of Windows performance metrics, including memory usage. Key metrics available for Windows include:
windows_memory_physical_total: Total physical memory available on the system.windows_memory_physical_available: Memory currently available for use.windows_memory_physical_in_use: Memory currently in use.
Example Query for Windows Memory Usage
To calculate memory usage on a Windows system, you can use the following PromQL query:
(windows_memory_physical_total - windows_memory_physical_available) / windows_memory_physical_total
This query calculates the percentage of memory in use.
Memory Usage in Containers
When working with containerized applications, memory usage can be monitored using cAdvisor or the Kubelet metrics. For example, if you are using Kubernetes, the following container metrics can be helpful:
container_memory_usage_bytes: Total memory currently used by a container.container_memory_working_set_bytes: Memory in use, excluding cache.
Example Query for Container Memory Usage
To calculate the average memory usage of a specific container:
avg(container_memory_usage_bytes{container="your-container-name"})
To monitor memory usage across all containers in a Kubernetes cluster:
avg(container_memory_usage_bytes) by (container)
Visualizing Average Memory Usage in Grafana
Grafana is a popular visualization tool that enables users to create dynamic and interactive dashboards for monitoring various metrics. With its support for diverse data sources, you can easily integrate Prometheus as a data source in Grafana to visualize your metrics data.
To effectively visualize average memory usage in Grafana, follow these steps:
Add a new panel to your Grafana dashboard.
Visit the
Dashboardssection and click on theNewbutton.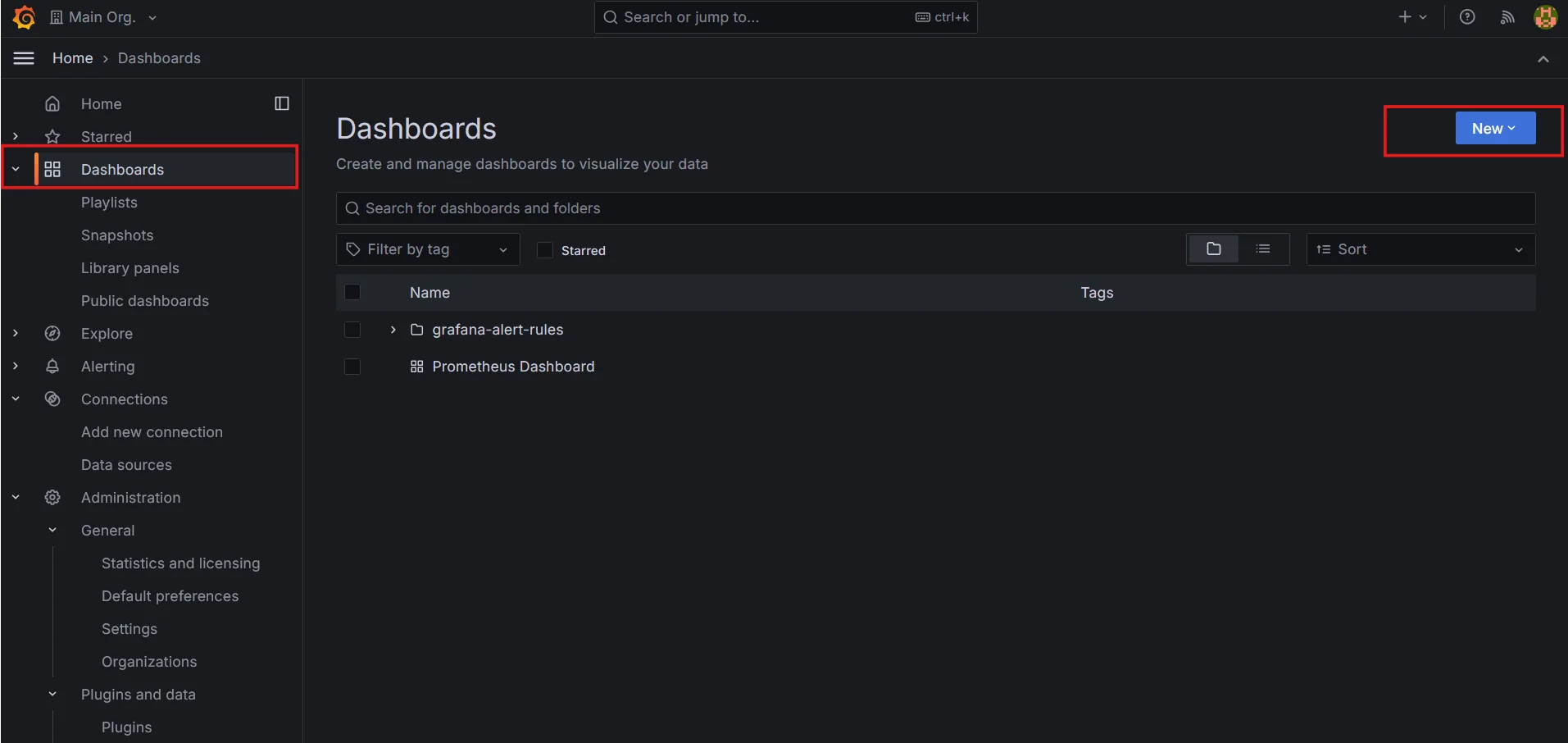
Creating new dashboards Add
New Dashboardand click theAdd visualizationbutton.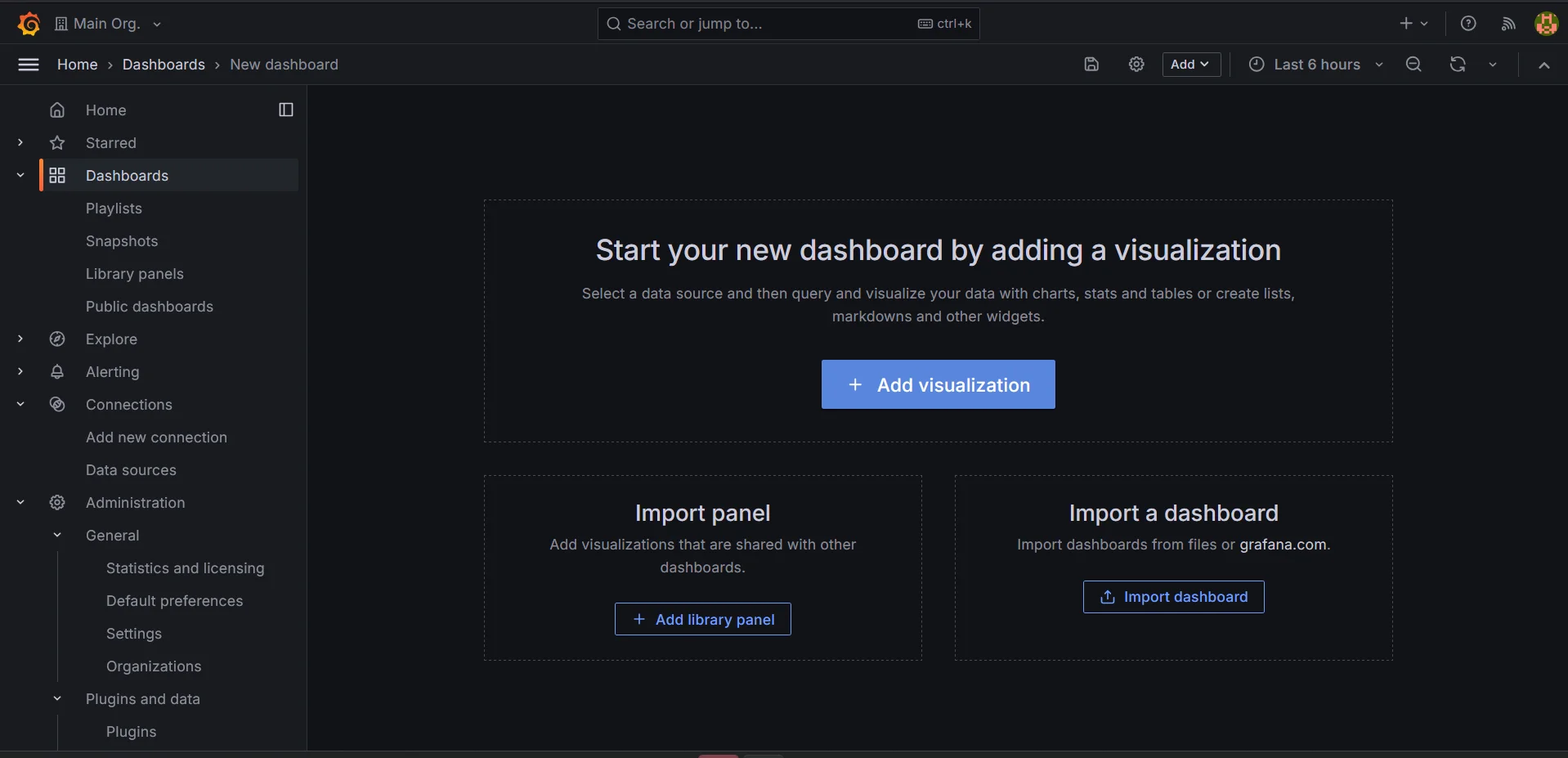
Adding visualization Select the Prometheus as your data source
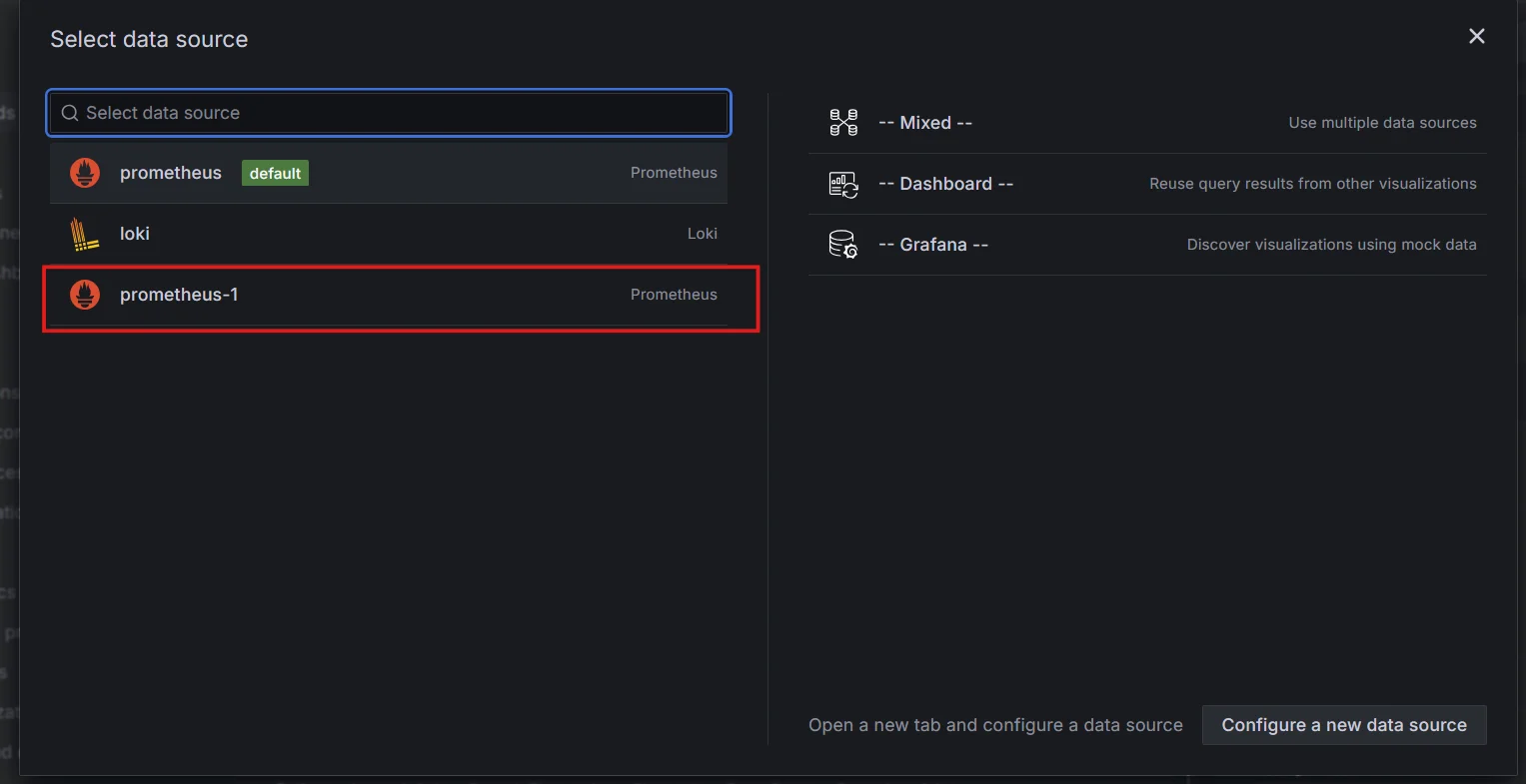
Selecting the datasource
In the query editor, enter your PromQL query for average memory usage.
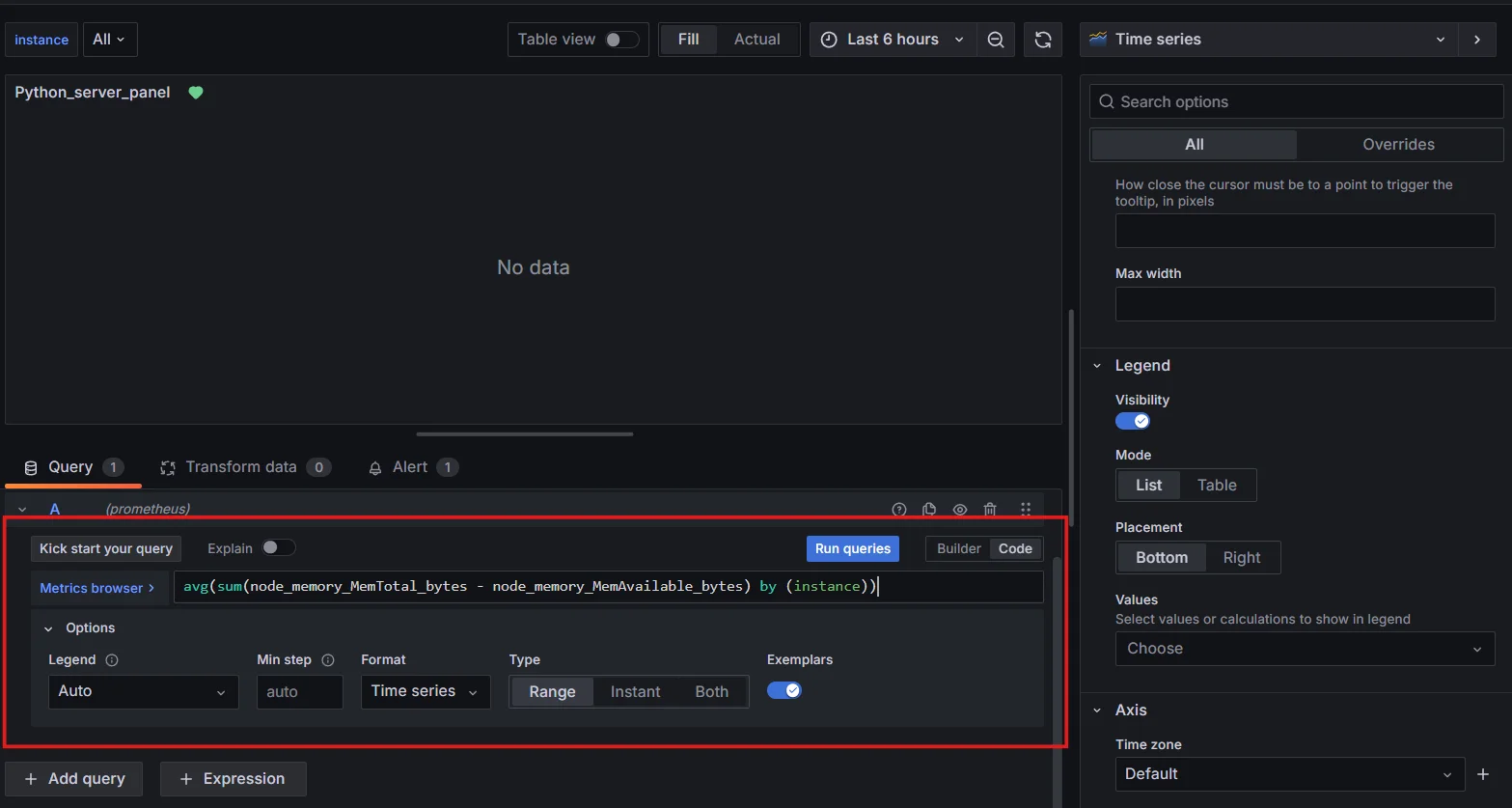
PromQL query for average memory usage Choose an appropriate visualization type (e.g., graph or gauge).
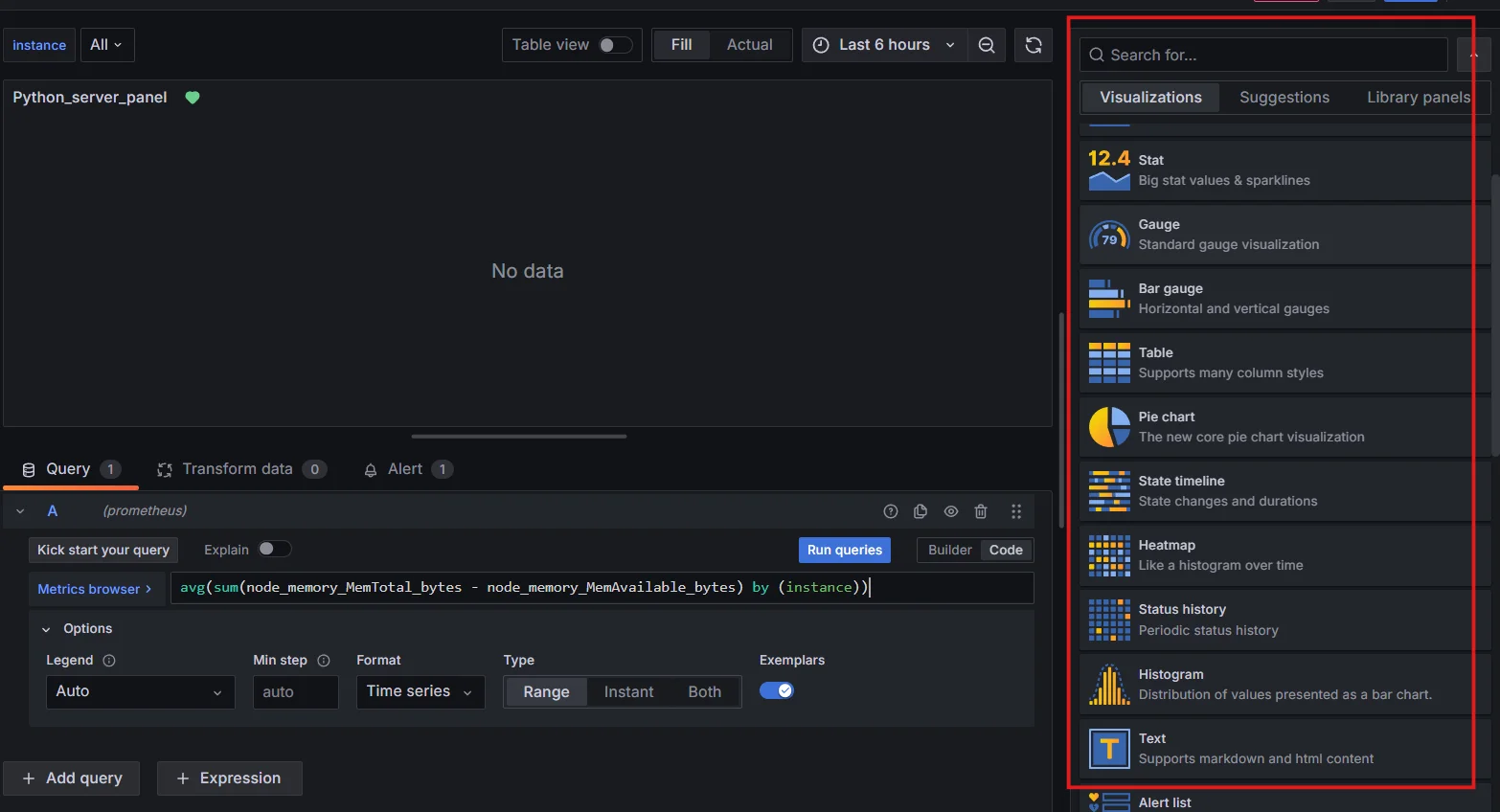
Choose an appropriate visualization type You should be able to visualize the average memory usage in your dashboard panel.
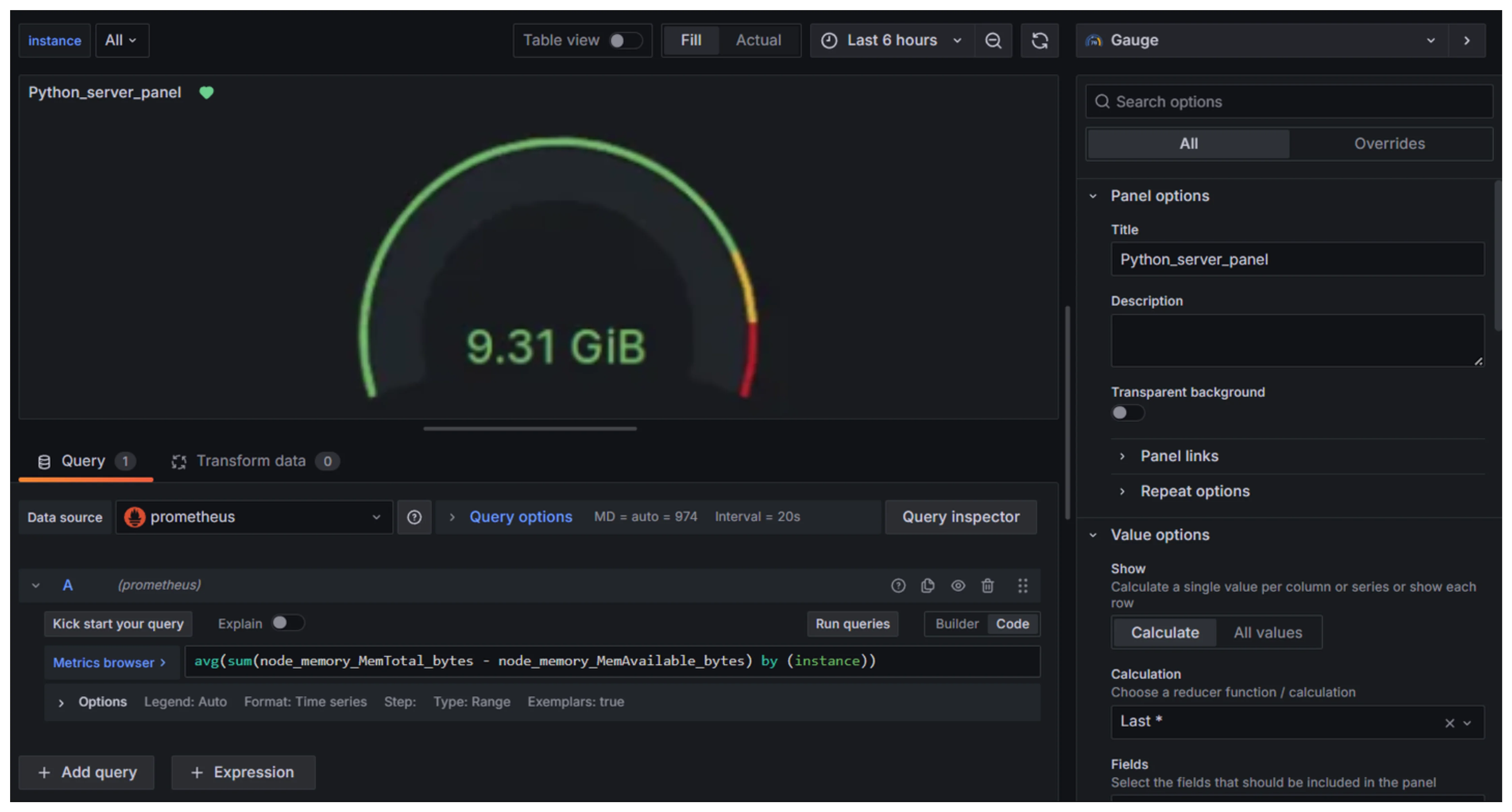
Dashboard panel for Average memory usage in Grafana
Adding Alerts for Critical Memory Usage
You can configure Grafana to trigger alerts when memory usage exceeds a certain threshold:
- Go to Alerting in your panel options.
- Set conditions like
WHEN avg() OF query IS ABOVE 80to send alerts when memory usage exceeds 80%. Check the documentation here to set alert rules in Grafana.
Monitoring Memory Usage with SigNoz
While Prometheus and Grafana offer robust monitoring capabilities, SigNoz provides a modern, integrated solution for tracking Prometheus metrics, including memory usage. SigNoz offers:
- Pre-built dashboards for common metrics
- Easy correlation between metrics, traces, and logs
- Advanced alerting capabilities
- Long-term data retention and analysis
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Memory Usage Monitoring in SigNoz VS Prometheus
- Ease of Setup: SigNoz offers out-of-the-box dashboards, while Prometheus requires manual setup and Grafana integration.
- Metrics Storage: SigNoz uses scalable backends (e.g., ClickHouse), whereas Prometheus relies on local storage with potential scaling issues.
- Advanced Visualizations: SigNoz provides built-in memory usage visualizations, while Prometheus depends on external tools like Grafana.
- Built-in Alerts: SigNoz includes pre-configured alerts, while Prometheus requires manual alert rule creation.
Best Practices for Memory Usage Monitoring
To ensure effective memory usage monitoring:
- Scrape Intervals: Set scrape intervals to a frequency that balances granularity and performance.
- Recording Rules: Create recording rules for frequently queried metrics like memory usage to improve query performance.
- Correlate with Application Metrics: Monitoring memory alone isn’t enough. Correlate memory usage with application performance metrics (e.g., response times, error rates).
- Long-Term Storage: Use external storage for long-term data retention and trend analysis.
Troubleshooting Common Memory Usage Issues
Use Prometheus data to identify and resolve memory-related problems:
- Detect memory leaks: Look for steadily increasing memory usage over time.
- Analyze sudden spikes: Investigate rapid increases in memory consumption.
- Debug OOM events: Correlate out-of-memory incidents with memory usage patterns.
- Optimize application memory: Use Prometheus insights to guide code improvements and resource allocation.
Key Takeaways
- Average memory usage calculations are essential for understanding system performance and capacity planning.
- PromQL functions like
avg()andavg_over_time()enable powerful memory usage analysis. - Visualizing memory data in tools like Grafana or SigNoz enhances monitoring capabilities.
- Regular analysis of memory usage patterns helps in proactive system optimization and issue prevention.
FAQs
What's the difference between memory usage and memory availability in Prometheus?
Memory usage refers to the amount of memory currently in use by the system and applications. In contrast, Memory availability, represented by node_memory_MemAvailable_bytes, indicates the amount of memory that can be allocated to processes without causing the system to swap. Availability considers free memory, page cache, and reclaimable memory.
How often should I calculate average memory usage for my systems?
The frequency of average memory usage calculations depends on your specific needs. For most systems, calculating averages every 5-15 minutes provides a good balance between granularity and performance. However, you may need more frequent calculations for systems with rapid changes or less frequent for stable, long-running services.
Can Prometheus help predict future memory usage trends?
While Prometheus itself doesn't provide built-in prediction capabilities, you can use its time series data to perform trend analysis and forecasting. Tools like Grafana can visualize trends, and you can export Prometheus data to specialized forecasting tools for more advanced predictions.
How do I set up alerts for critical memory usage levels in Prometheus?
To set up alerts for critical memory usage:
- Define alert rules in Prometheus's configuration file or through Alertmanager.
- Specify the PromQL query that defines the alert condition (e.g., memory usage > 90%).
- Set the duration for which the condition must be true before alerting.
- Configure notification routes in Alertmanager to send alerts via email, Slack, or other channels.
Remember to test your alerts thoroughly to ensure they trigger appropriately and don't cause alert fatigue. You can also make use of Grafana alerts.
