How to Monitor AWS ELB Metrics with SigNoz - A Step-by-Step Guide
The first part of this series covered AWS ELB fundamentals, load balancer types, why monitoring matters, and which metrics indicate real user impact.
In this article, we move from concepts to hands-on implementation. You'll learn how to view ELB metrics in CloudWatch, understand its practical limitations at scale, and then set up real-time ALB metrics streaming to SigNoz using a one-click CloudFormation integration. Before we start handson, a quick recap of the key metrics you'll be tracking.
Key AWS ELB Metrics to Monitor
ELB metrics fall into four categories, each providing visibility into different aspects of load balancer operation.
1. Request Metrics
These metrics track the volume and nature of incoming traffic.
RequestCount- Total requests received by the load balancer.HTTPCode_ELB_4XX_Count- Client errors generated by the load balancer (e.g., 400, 403).HTTPCode_ELB_5XX_Count- Server errors generated by the load balancer (e.g., 502, 503).HTTPCode_Target_2XX_Count- Successful responses from backend targets.HTTPCode_Target_5XX_Count- Server errors from backend targets.
2. Latency Metrics
These metrics measure how quickly requests are processed.
TargetResponseTime- Time between sending a request to a target and receiving a response headers.
3. Health Metrics
These metrics indicate the state of registered targets.
HealthyHostCount- Number of targets passing health checks.UnHealthyHostCount- Number of targets failing health checks.
4. Connection Metrics
These metrics provide insight into concurrent usage.
ActiveConnectionCount- Total concurrent TCP connections from clients to the load balancer and from load balancers to targets.NewConnectionCount- New TCP connections established during the period.RejectedConnectionCount- Connections rejected due to limits.
Monitoring these key metrics together gives you a complete picture of your load balancer's health, performance, and capacity utilization.
How to View ELB Metrics in CloudWatch?
AWS automatically publishes ELB metrics to CloudWatch. The ApplicationELB namespace contains metrics for Application Load Balancers, while the ELB namespace covers Classic Load Balancers. This guide uses Application Load Balancer as the primary example, though the concepts apply to other ELB types with minor namespace differences.
Before you start, make sure you have an ALB running with registered targets and traffic flowing through it. Once your load balancer is active, CloudWatch gives you two ways to explore metrics: the Metrics explorer for ad-hoc analysis, and Dashboards for saved, shareable visualizations
Accessing Metrics via Metrics Explorer
Step 1: Open the AWS Management Console and navigate to CloudWatch.
Step 2: In the left sidebar, click on "Metrics" and then "All metrics".
Step 3: Under "AWS namespaces", select "ApplicationELB".
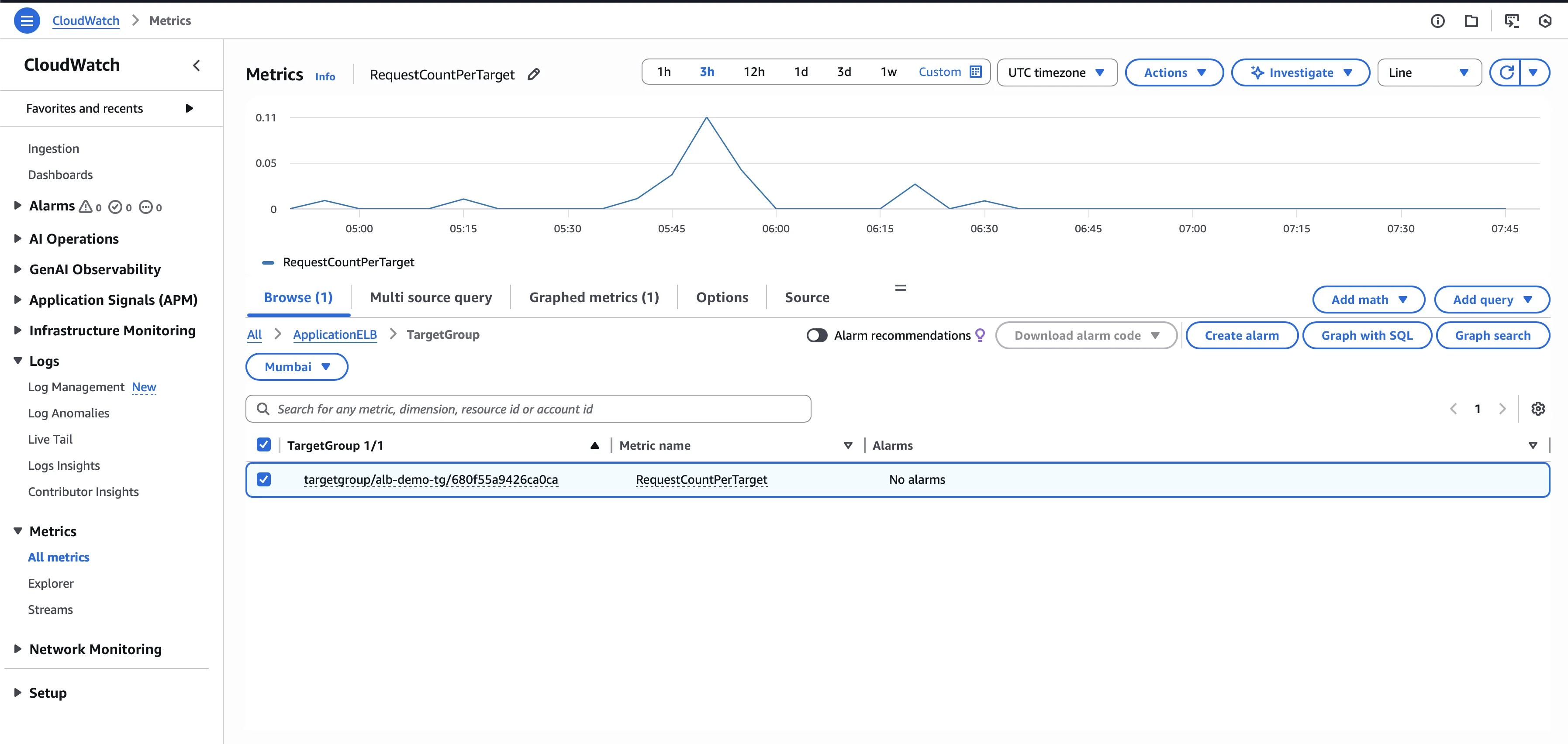
Step 4: CloudWatch organizes metrics by dimensions. Choose a dimension to filter by. For example, TargetGroup.
Step 5: Select the specific metrics you want to view. For example, RequestCountPerTarget.
Step 6: The graph appears automatically in the upper panel.
Using CloudWatch Dashboards
CloudWatch provides pre-built dashboards for common AWS services.
Step 1: Open the AWS Management Console and navigate to CloudWatch.
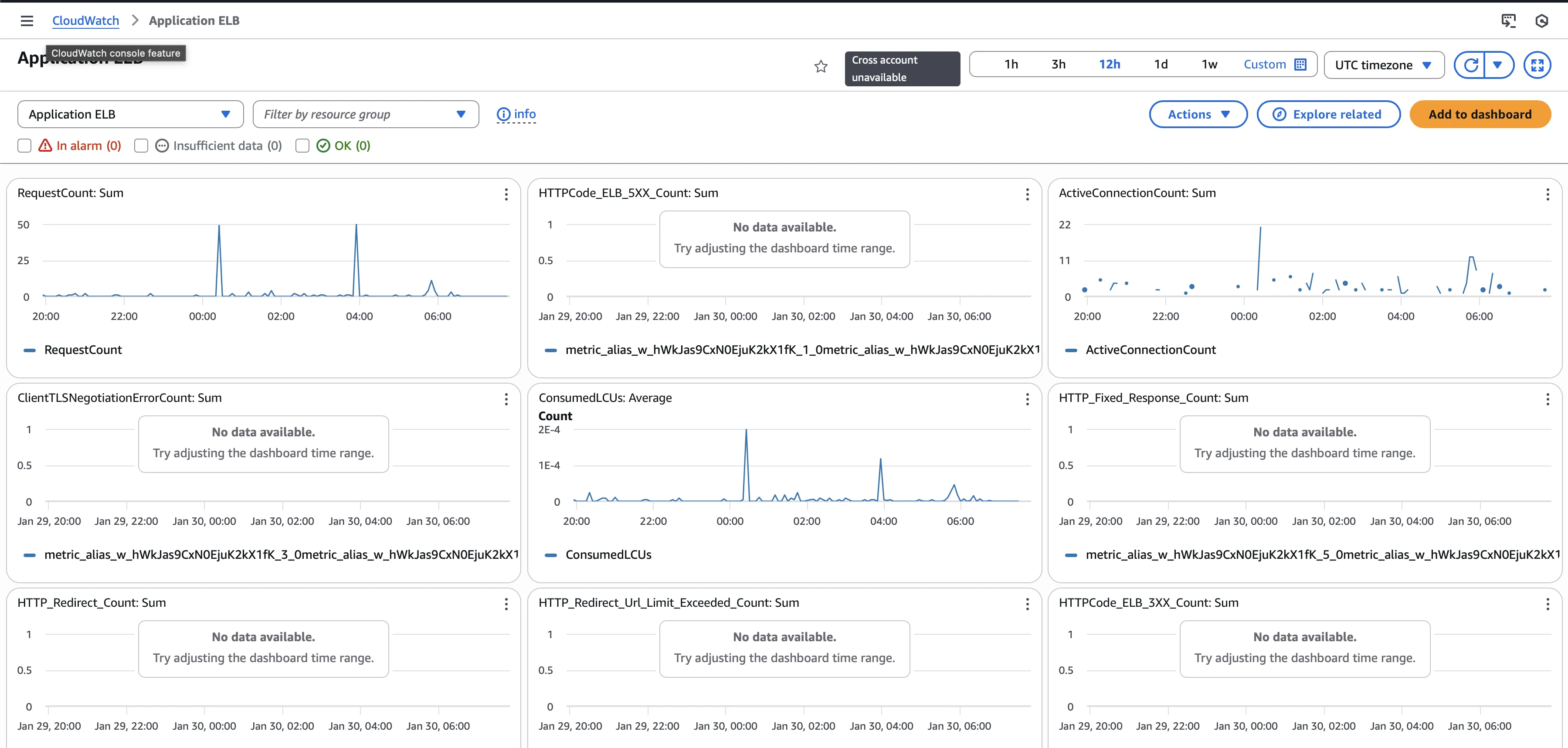
Step 2: In the left sidebar, click "Dashboards", then "Automatic Dashboards".
Step 3: Search for the "Application ELB" dashboard. This gives you immediate visibility without manual configuration.
Limitations of CloudWatch for ELB Metrics
While CloudWatch provides basic monitoring capabilities, several limitations become apparent as infrastructure scales.
Cost accumulates at scale
CloudWatch charges per metric, dashboard, and alarm. Organizations running multiple load balancers with detailed monitoring and numerous alarms find costs adding up quickly. The pricing model makes it difficult to predict monthly expenses without careful tracking.
High-resolution data has limited retention
Metrics with < 60s granularity are stored for only 3 hours before CloudWatch aggregates them. If you need to investigate an issue that occurred earlier, the detailed data may already be gone.
Logs and metrics live in silos
CloudWatch keeps metrics and logs in separate services with no built-in correlation. Linking a metric spike to specific log entries requires manual timestamp matching. AWS offers ServiceLens and Application Signals for correlation, but both require additional setup and don't natively support ALB access logs.
Visualization capabilities are basic
Dashboard customization is limited compared to dedicated observability tools. Creating complex visualizations or combining data from multiple sources requires workarounds.
Data stays locked in AWS
For organizations running hybrid or multi-cloud infrastructure, CloudWatch metrics remain isolated within AWS. Achieving unified visibility across cloud providers requires building custom data pipelines.
Monitoring ELB Metrics with SigNoz
SigNoz is an all-in-one, OpenTelemetry-native platform where metrics, logs, and traces can be explored in one place. While CloudWatch is the default monitoring solution for AWS services, the limitations discussed earlier become more significant as your infrastructure scales and your observability requirements mature. Organizations increasingly need unified visibility across metrics, logs, and traces without being locked into a single cloud vendor's ecosystem.
SigNoz addresses these by providing a unified observability platform where metrics, logs, and traces coexist with native correlation capabilities.
One-Click AWS ELB Metrics Integration
Instead of building custom pipelines or managing multiple tools, you can stream your ALB metrics to SigNoz using CloudWatch Metric Streams and Kinesis Data Firehose, all provisioned automatically through a single CloudFormation template.
Step 1: Navigate to SigNoz and open the Integrations section.
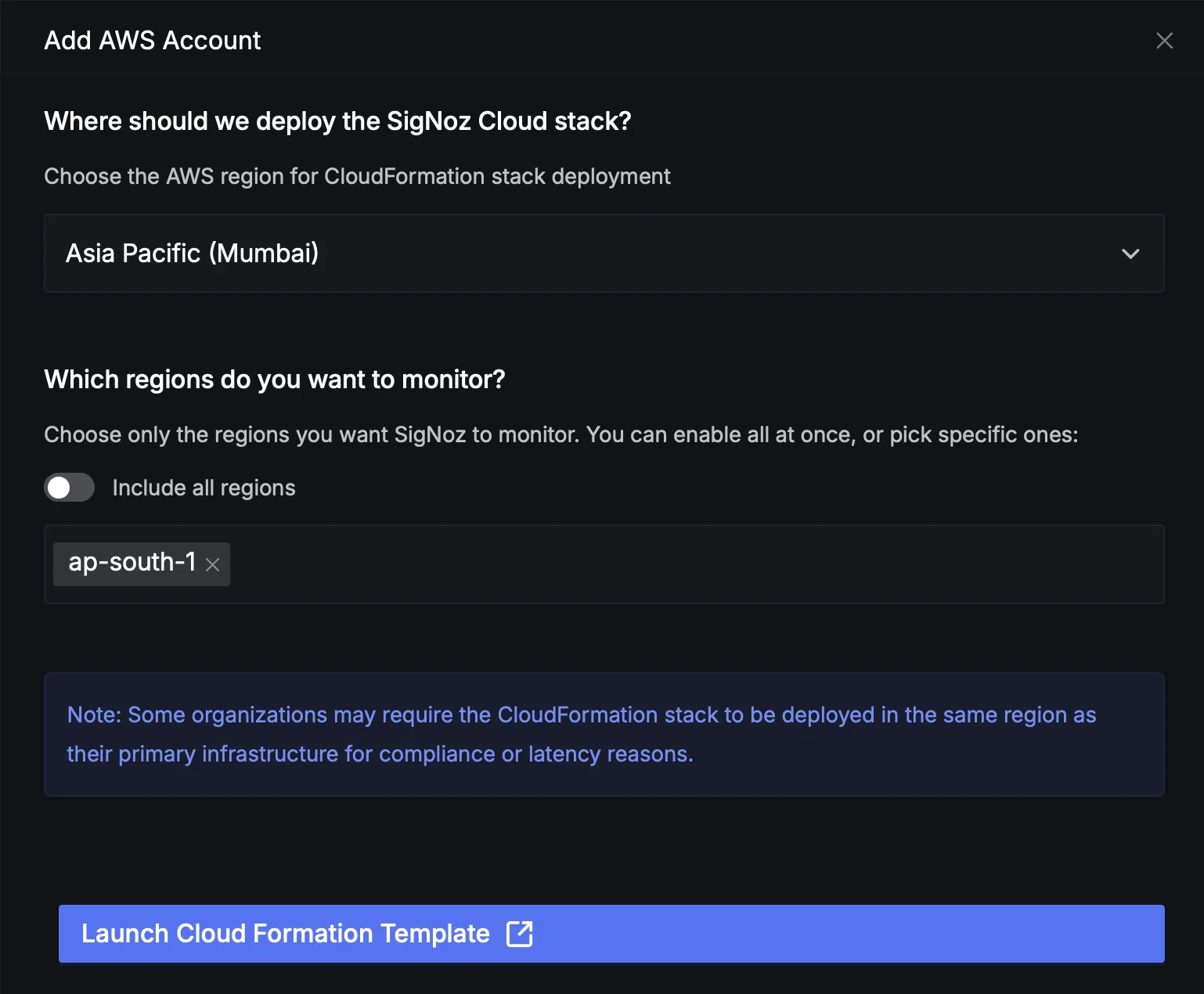
Step 2: Select AWS and click "Add New AWS Account". In the pop-up, specify the AWS regions for your services and select the region where you want the integration agent deployed. This generates a CloudFormation template URL configured with your SigNoz ingestion endpoint and credentials.
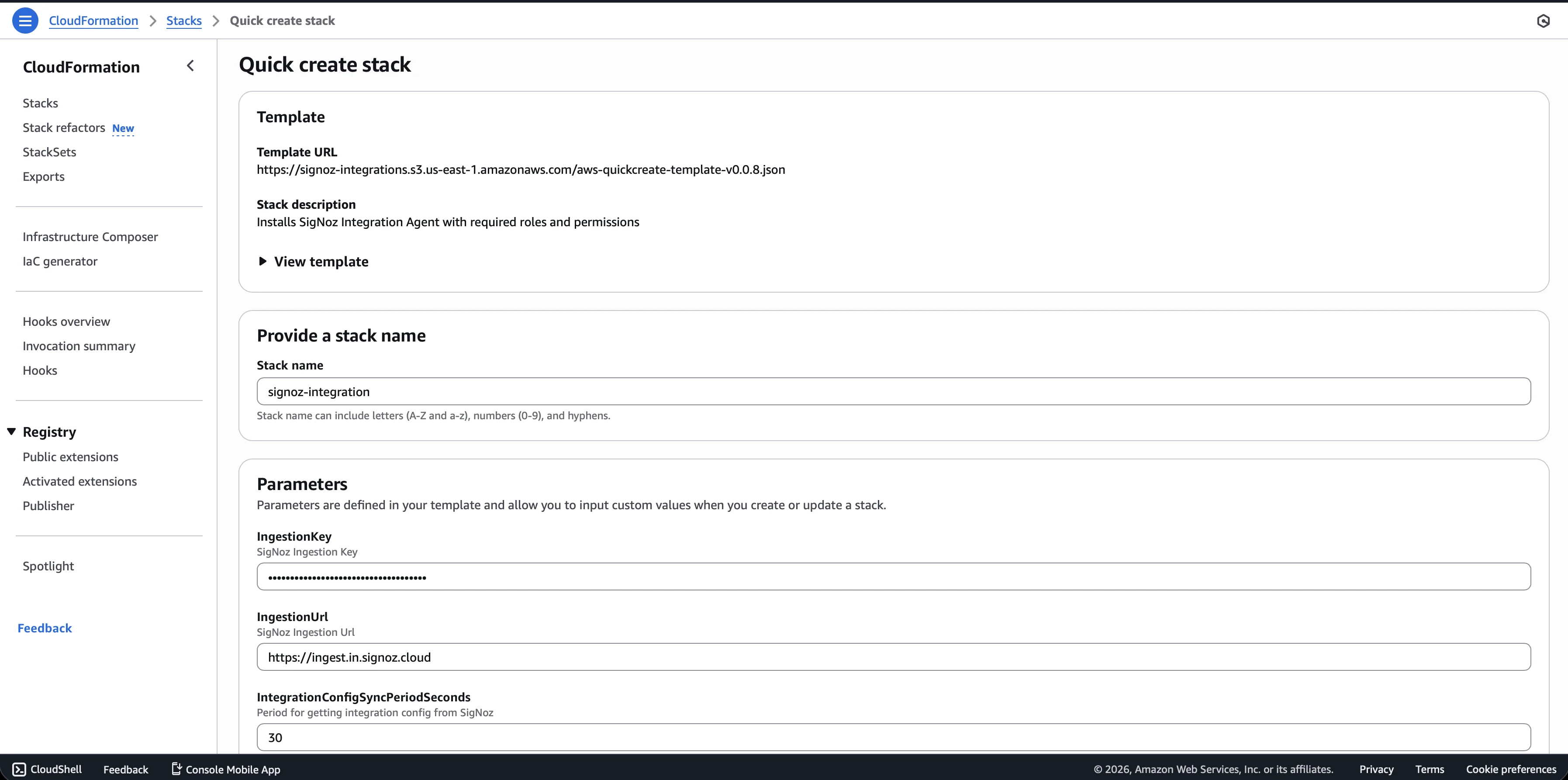
Step 3: Click "Launch CloudFormation Stack" to open the AWS Console with the template preloaded. Review the parameters, acknowledge the IAM resource creation checkbox, and click Create Stack.
Provisioning typically takes several minutes, depending on region and account conditions.
Step 4: Once the stack reaches CREATE_COMPLETE status, return to SigNoz and configure which AWS services you want to monitor. Select ALB from the available services, enable it, and metrics will start flowing within minutes.
Viewing ALB Metrics in SigNoz
Once metrics start flowing, you have two ways to explore your ALB metrics: the Metrics Explorer for ad hoc queries and the prebuilt dashboard for operational monitoring. You can also create custom dashboards for team-specific views by following our Official Dashboard Creation Documentation.
Using the Metrics Explorer to View AWS ELB Metrics
The Metrics Explorer lets you query and visualize any metric without building a full dashboard. This is useful for ad-hoc debugging, correlating specific metrics during an incident, or validating that your integration is working.
Step 1: Navigate to the Metrics section in SigNoz's left navigation menu and select Explorer.
Step 2: In the query builder, select the metric you want to visualize, such as
aws_ApplicationELB_ActiveConnectionCount_sum, to monitor concurrent connections to your load balancer. Add filters to narrow down to your specific resources. Once satisfied with your query, click on Run Query to plot it.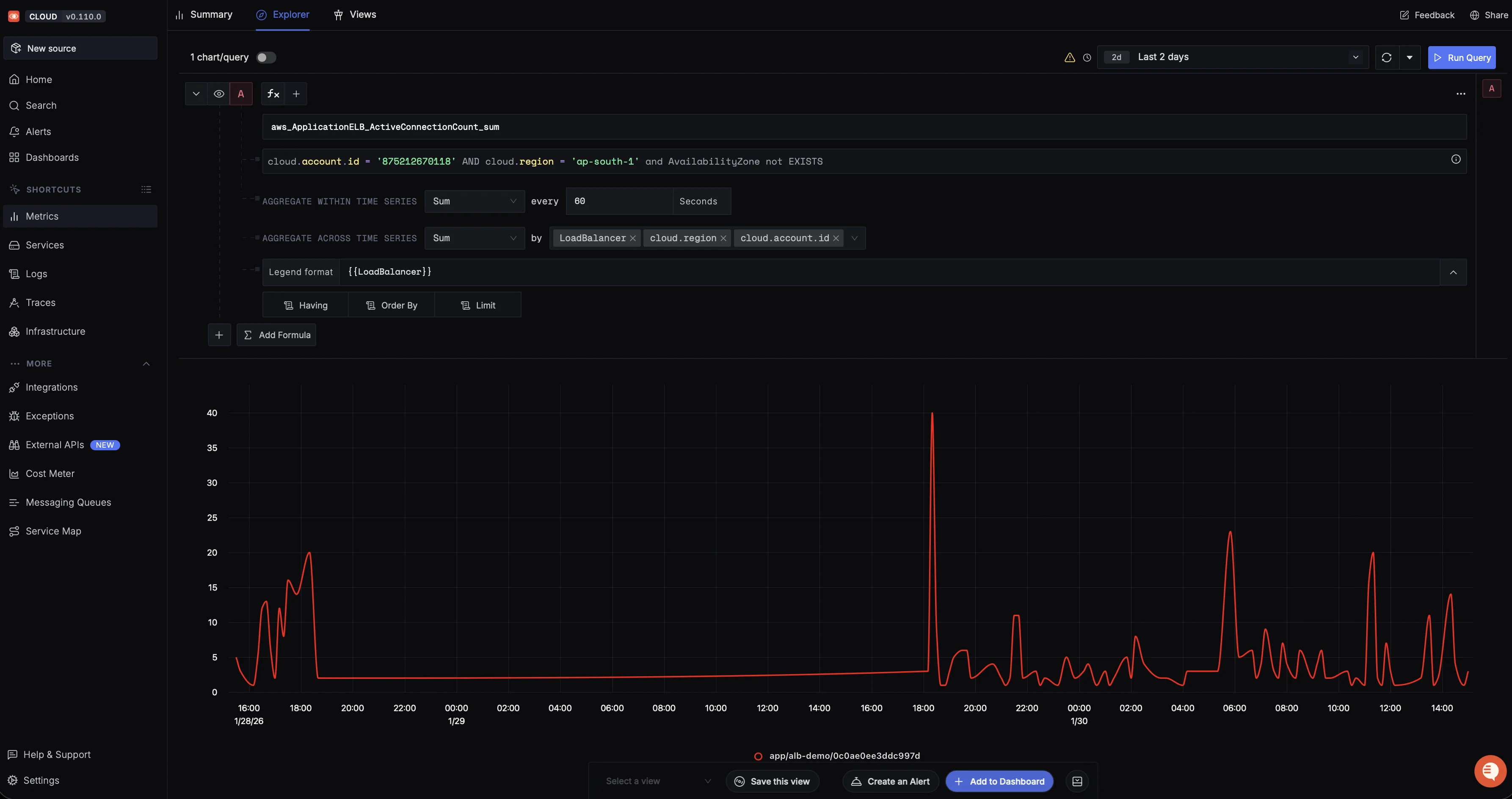
Querying ALB active connection count in SigNoz Metrics Explorer with filters applied for account, region, and load balancer grouping You can click Save this view to preserve it for future use, create an Alert to set up threshold-based notifications, or Add to Dashboard to include this visualisation in a custom dashboard.
Using the Pre-Built Dashboard
Navigate to Dashboards in the left navigation menu. You'll find an auto-generated Application Load Balancer Overview dashboard ready to use.
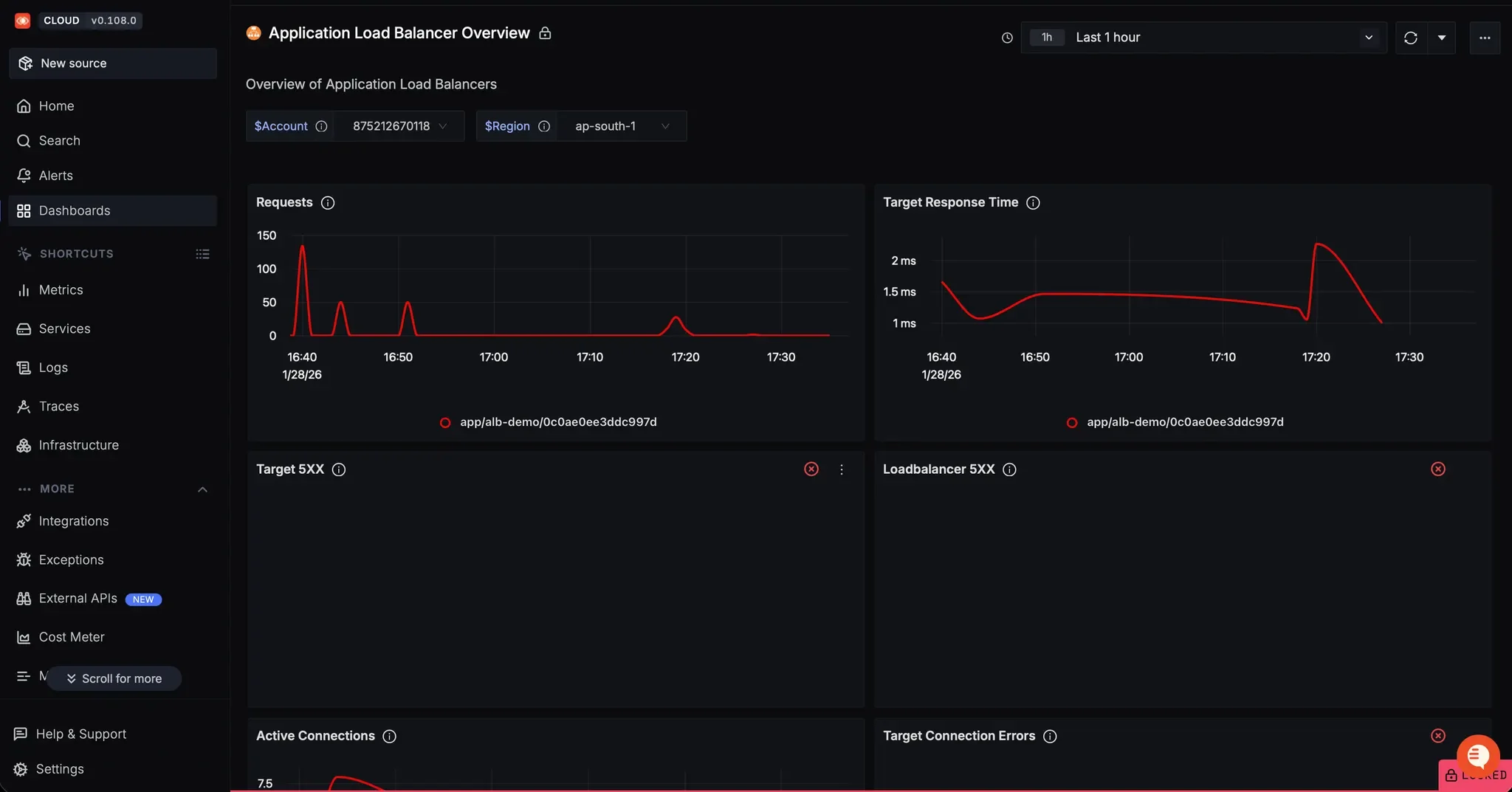
SigNoz's auto-generated ALB dashboard with key metrics including requests, latency, and error breakdowns This dashboard provides an operational view of your Application Load Balancers without any configuration required.
How SigNoz Addresses CloudWatch Limitations?
Usage-Based Pricing
The cost model differs fundamentally. SigNoz uses usage-based pricing for the data you ingest, rather than charging separately for each metric, dashboard, and alarm. For organizations running dozens of load balancers with numerous alarms, this often translates to meaningful savings.
Real-Time Visibility
Real-time visibility improves because SigNoz receives data via streaming rather than polling. The gap between an incident occurring and its visibility in your dashboards shrinks significantly.
Unified Metrics and Logs
With metrics and logs in one platform, you can reduce context switching by pivoting from a metric spike to logs filtered to the same time window.
Data Portability
Data portability matters for organisations that avoid vendor lock-in. SigNoz stores data in OpenTelemetry-native formats, meaning your instrumentation and data remain portable across observability platforms.
Next Steps
With metrics flowing, you can now detect when something goes wrong. But metrics alone can't tell you which specific requests failed or which clients were affected.
The next part of this series covers ALB access logs, how to enable them, stream them to SigNoz, and correlate log entries with your metric dashboards for complete request-level visibility.
