How to Check Pod Ports with kubectl - A Quick Guide
Kubernetes has revolutionized container orchestration, but it can be challenging to navigate its complexities. One common task that often stumps developers is checking which port a pod is listening on, especially when you are not using Dockerfile, deployment file, or defining a port manually. This guide will show you how to use kubectl to quickly and efficiently check pod ports, enhancing your ability to troubleshoot and manage Kubernetes deployments.
Understanding Kubernetes Pods and Ports
Before diving into the commands, let's clarify some key concepts. Kubernetes pods are the smallest deployable units in a Kubernetes cluster. They encapsulate one or more containers, sharing network resources. Container ports are the ports that applications inside containers listen on, while pod ports are how these are exposed to the cluster.
Knowing which port a pod is listening on is crucial for:
- Debugging network issues
- Configuring services and traffic
- Ensuring proper communication between microservices
- Optimizing security policies
Quick Guide: Checking Pod Ports with kubectl
Here's how you can quickly check pod ports using kubectl:
Use
kubectl describe podThis command provides a detailed view of a specific pod's configuration and status. When you run
kubectl describe pod <pod-name>, it gives you output about that particular port such as containers, images, ports that each container is configured to listen on, environment variables, volumes, and network settings.kubectl describe pod <pod-name>You can use this command to check for the port and for that, you need to replace
<pod-name>with your actual pod. Let’s say you have nginx-pod running in your system. You want to check for its port by looking for the Containers section in the output, you will be able to see a pod named nginx-pod and search for a port property like it is shown below: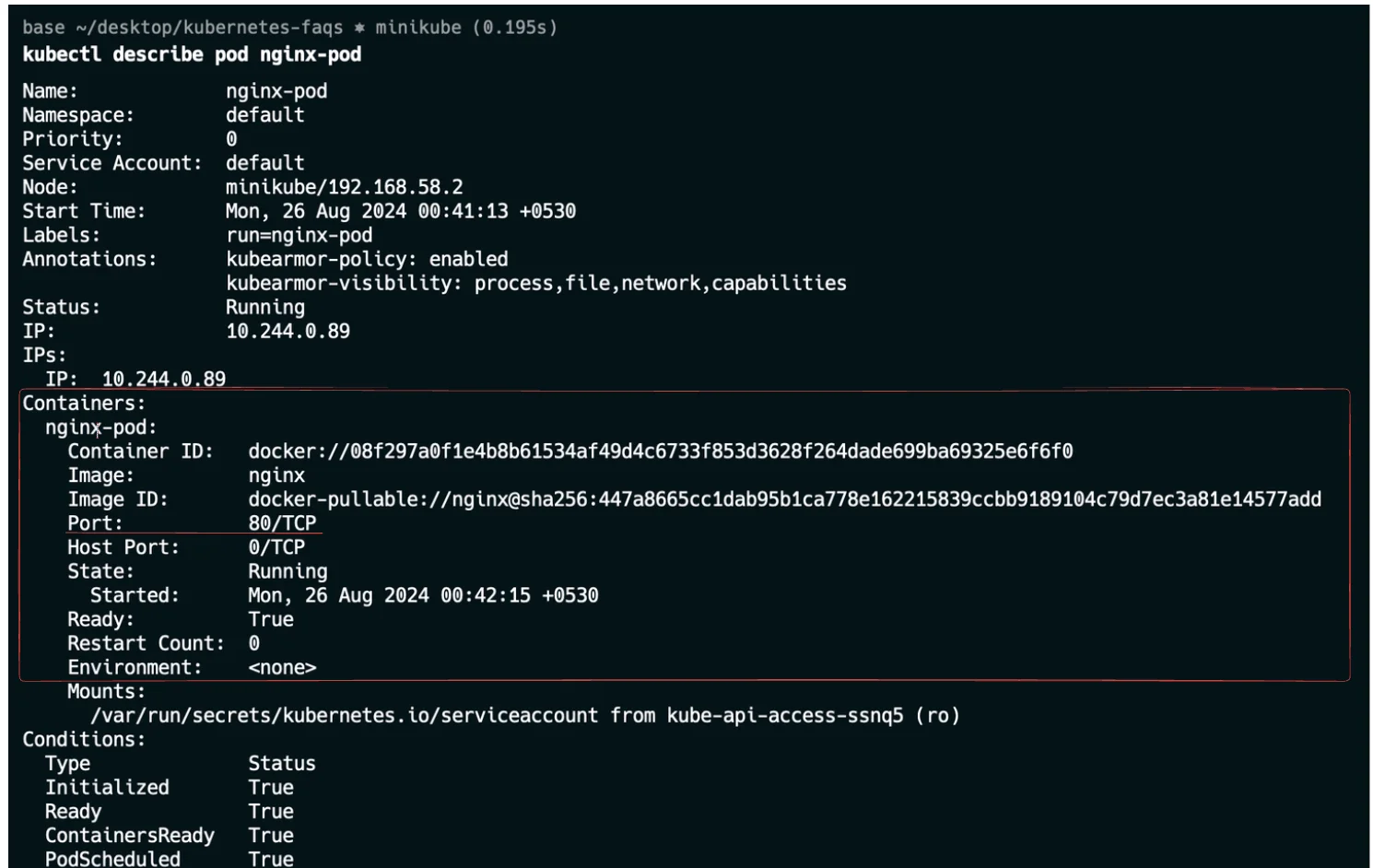
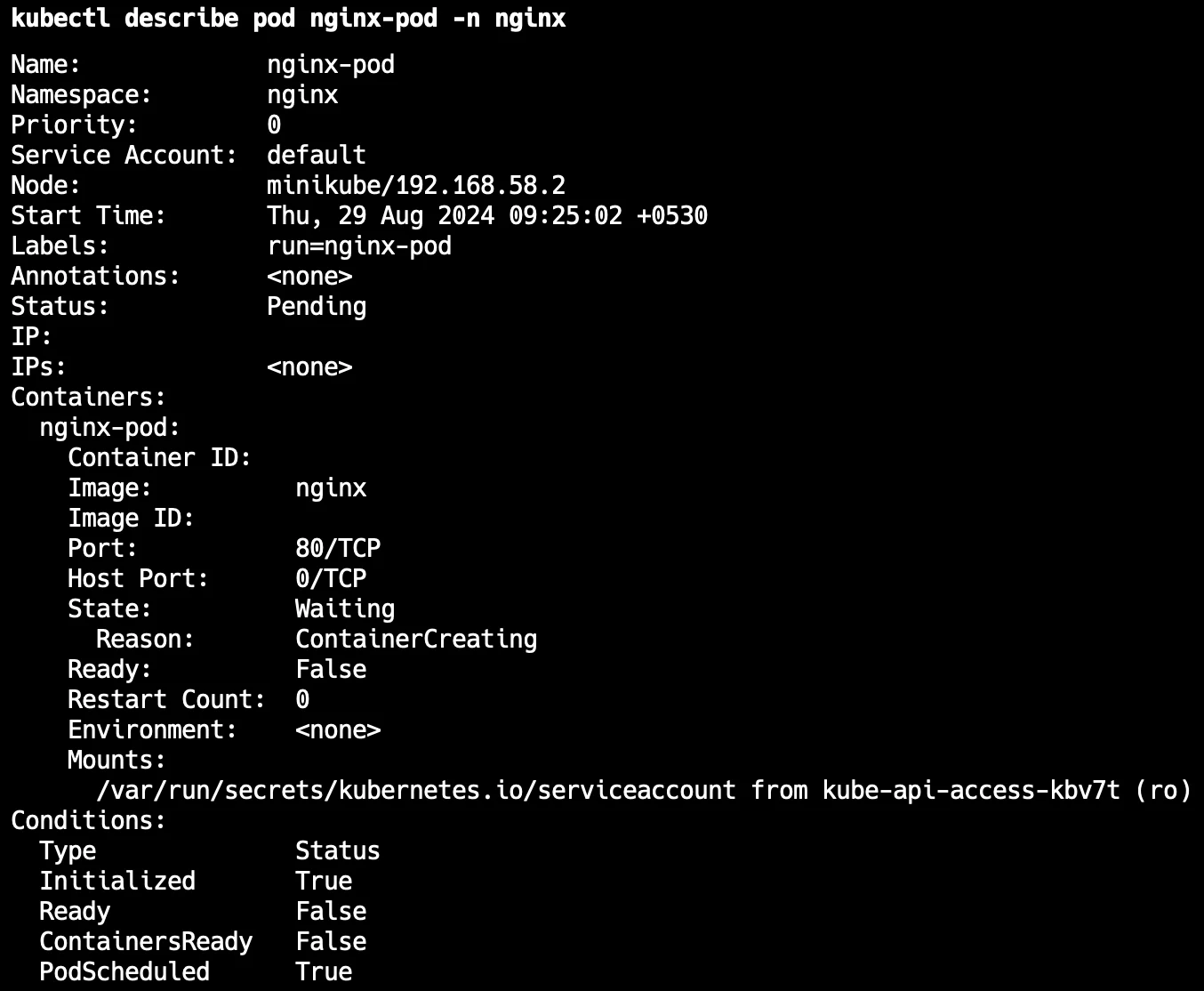
Describe pod Let’s say you need to check the port for the pod in any specific namespace, so for that you need to use the below command:
Kubectl describe pod <pod-name> -n <namespace>You can see the below output:
To see which processes are listening on ports:
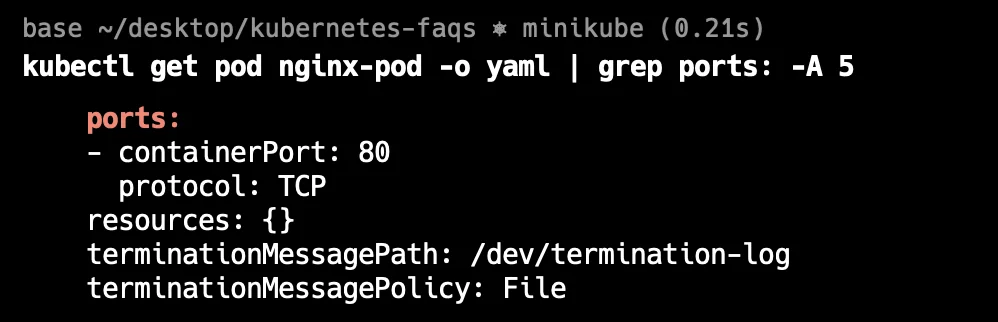
For a more concise view, you can use the command kubectl get pod <pod-name> -o yaml shows the full YAML configuration of a pod . By using grep ports: -A 5 with this command, it will give you information about port configurations and the next five lines. This makes it easier to find port settings without looking through the entire configuration.
kubectl get pod <pod-name> -o yaml | grep ports: -A 5
You should see a similar output:
Inspect running processes
To see which processes are listening on ports:
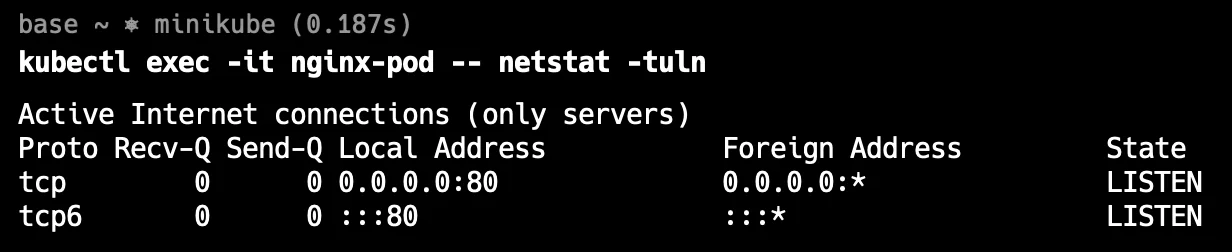
kubectl exec <pod-name> -- netstat -tulpnThis command runs
netstatinside the pod, showing active network connections and listening ports. The-tulpnoptions specify that it should show TCP and UDP connections, listening ports, process IDs, and numerical addresses.Let’s say if you are running this command in your Macbook then you do need to install net-tools because it is supported in Linux only.
Using Exec command You should see a similar output below:
Advanced Kubectl commands for Port Information
When you need precise and detailed information about the ports that Kubernetes pods are using, some advanced kubectl commands can provide deeper insights. Here's how you can leverage these commands to get more specific port information:
Use JSON output with jq
To extract just the port information, you can use the
jqtool, which is a powerful JSON processor. The command used for this is below:kubectl get pod <pod-name> -o json | jq '.spec.containers[].ports'This command filters the JSON output to show only the port configurations of the containers within the specified pod. It is incredibly useful for automation scripts or when you need to programmatically process port information across multiple containers and pods.
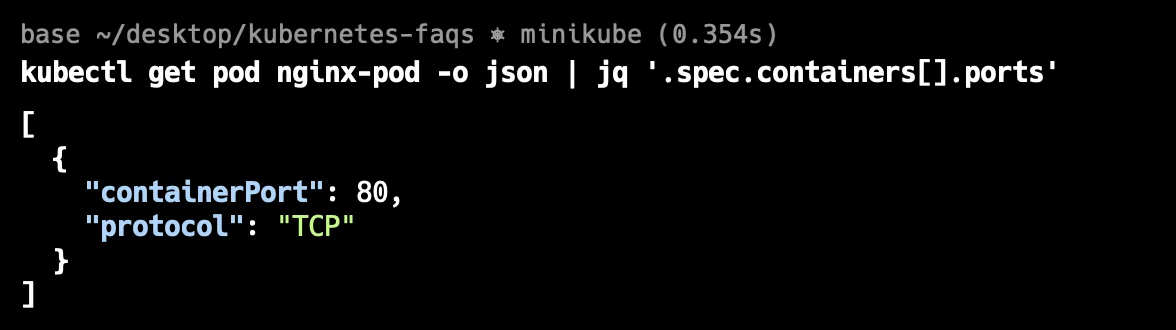
Using jq tool Checking Service Endpoints
Kubernetes services abstract pod IP addresses and ports into a single access point. To find out where a service points and which ports it exposes, use:
kubectl get endpoints <service-name>This command retrieves the endpoints associated with a service, showing IP addresses and ports that are available for communication. This is crucial for debugging service connectivity issues and ensuring that services are correctly linked to their underlying pods.
Custom Output Columns for Quick Reference
When managing multiple pods, it can be helpful to have a concise view of their configurations, especially ports. The custom columns output feature of
kubectlallows you to specify exactly which data to display:kubectl get pods -o custom-columns="POD:.metadata.name,PORTS:.spec.containers[*].ports[*].containerPort"This creates a table with pod names and their corresponding ports.
4. Creating Command Aliases for Efficiency
To simplify frequent checks, create an alias in your shell. Regularly used commands can be shortened by creating aliases in your shell.
alias kports='kubectl get pods -o custom-columns="POD:.metadata.name,PORTS:.spec.containers[*].ports[*].containerPort"'Now you can simply type
kportsto get a quick overview of pod ports. This saves time and reduces the chance of errors: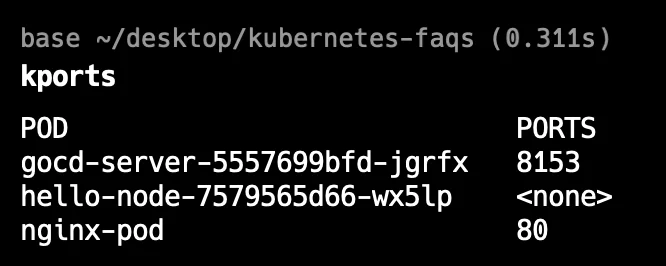
alias in kubernetes Using these aliases, anyone in your team can quickly check port configurations by typing
kportsin the terminal, making it a handy tool for ongoing monitoring and troubleshooting.
Why Not to Rely on Dockerfile for Port Information
While Dockerfiles contain EXPOSE instructions, they're not always reliable in a Kubernetes context:
EXPOSEis informational; it doesn't actually open ports- Kubernetes can override Dockerfile port settings
- Dynamic port allocation in Kubernetes can lead to discrepancies
- Containers might listen on ports not specified in the Dockerfile
Best practice: Always verify actual running configurations rather than relying solely on build-time instructions.
Troubleshooting Port-related Issues in Kubernetes
Common port-related issues and their solutions:
- Port conflicts: Use
kubectl get pods -o widewith--outputflag to check if multiple pods are trying to use the same node port. - Connection refused errors: Verify that the service is actually running and listening on the expected port using
kubectl exec. - Network policies: Ensure that network policies aren't blocking required traffic. Use
kubectl describe networkpolicyto review policies. - Container-level diagnostics: Use
kubectl execto run tools likenetstatorlsofinside containers for deeper investigation.
Monitoring Pod Network Activity with SigNoz
For ongoing monitoring of pod network activity and port usage, consider using SigNoz. SigNoz is an open-source APM tool that provides detailed insights into your Kubernetes cluster's performance. You can check out the SigNoz here:
With SigNoz, you can:
- Monitor real-time network metrics for pods
- Set up alerts for unusual port activity
- Visualize network traffic patterns
- Correlate network issues with application performance
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Best Practices for Managing Pod Ports in Kubernetes
- Implement consistent naming conventions: Use clear, descriptive names for ports in your Kubernetes manifests.
- Utilize Kubernetes Services: Services provide stable networking abstractions, making it easier to manage pod communications.
- Use ConfigMaps for port configuration: This allows for easier updates without changing deployment specs.
- Regular auditing: Periodically review pod port configurations to ensure they align with your security policies and application needs.
Key Takeaways
- kubectl offers multiple methods to check pod ports without relying on Dockerfiles
- Combining kubectl with JSON processing tools enhances port information retrieval
- Understanding the difference between container and pod ports is crucial for effective debugging
- Regular monitoring and best practices in port management improve Kubernetes cluster stability
FAQs
Can I check pod ports without kubectl access?
Yes, if you have access to the Kubernetes API server, you can use tools like curl or programming languages with Kubernetes client libraries to retrieve pod information.
How do I resolve port conflicts between pods?
Ensure each pod uses unique port numbers, or implement network policies to isolate conflicting pods. Use services to abstract away direct pod-to-pod communication.
Are exposed ports in Dockerfile always reflected in Kubernetes pods?
No, Kubernetes configurations can override Dockerfile settings. Always verify actual pod configurations rather than relying on Dockerfile instructions.
What's the difference between ContainerPort and HostPort in Kubernetes?
ContainerPort specifies which port the application inside the container is listening on. HostPort maps a container port directly to the same port on the node — use this cautiously as it can lead to conflicts.
