How to Fix Kubectl Error - Troubleshooting API Group List Issues
Kubernetes administrators often encounter the frustrating kubectl error: memcache.go:265". This error can cause cluster mismanagement and hinder critical operations. Understanding its causes and implementing effective solutions is crucial for maintaining a smooth Kubernetes workflow. This comprehensive guide walks you through the error's encountered, common causes, and step-by-step troubleshooting methods to resolve the issue and prevent future occurrences.
Understanding the Kubectl Error: memcache.go:265 API Group List Issue
The kubectl error "[memcache.go:265] couldn't get current server API group list: Get" typically occurs when kubectl fails to retrieve the list of API groups from the Kubernetes API server. This error message consists of two main components:
- memcache.go:265 Refers to the specific line in the kubectl source code where the error originates.
- couldn't get current server API group list: Get: This indicates the failure to fetch the API group list from the server.
This error can arise in various scenarios, such as:
- Executing kubectl commands to manage resources: For example, when running
kubectl get podsorkubectl apply -f <file.yaml>, this error can prevent these commands from executing successfully, as kubectl cannot determine the available API groups. - Attempting to view or modify cluster configurations: Commands like
kubectl config vieworkubectl edit configmapmight fail if kubectl cannot access the necessary API groups. - Running scripts or automation tools that interact with the Kubernetes API: Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines or custom automation scripts that rely on kubectl commands may break due to this error, leading to failed deployments or configuration changes.
- Sometimes there is no proper Kubernetes environment configured like minikube has stopped.
The impact of this error on Kubernetes cluster management can be significant:
- When kubectl cannot retrieve the API group list, it becomes unable to perform basic operations which affect administrative tasks.
- Since kubectl relies on the API group list to interact with resources, this error can prevent administrators from accessing or modifying critical cluster resources, such as deployments, services, or configmaps.
Resolving this error is crucial for maintaining operational efficiency and ensuring smooth Kubernetes cluster management.
Common Causes of the API Group List Error
Several factors can contribute to the "couldn't get current server API group list: Get" error:
- Outdated or misconfigured kubectl client: An incompatible or improperly configured kubectl version can lead to communication issues with the API server.
- Network connectivity problems: Firewall rules, DNS issues, or network interruptions can prevent kubectl from reaching the Kubernetes API server.
- Authentication and authorization issues: Expired or invalid credentials, or insufficient permissions, can block access to the API server.
- Cluster configuration changes: Recent updates to the cluster, such as API server endpoint modifications or certificate rotations, may cause communication failures.
Identifying the Root Cause
To pinpoint the exact cause of the error, use these debugging techniques:
Use verbose logging: Run kubectl commands with the
v=10flag to enable detailed logging:kubectl get pods -v=10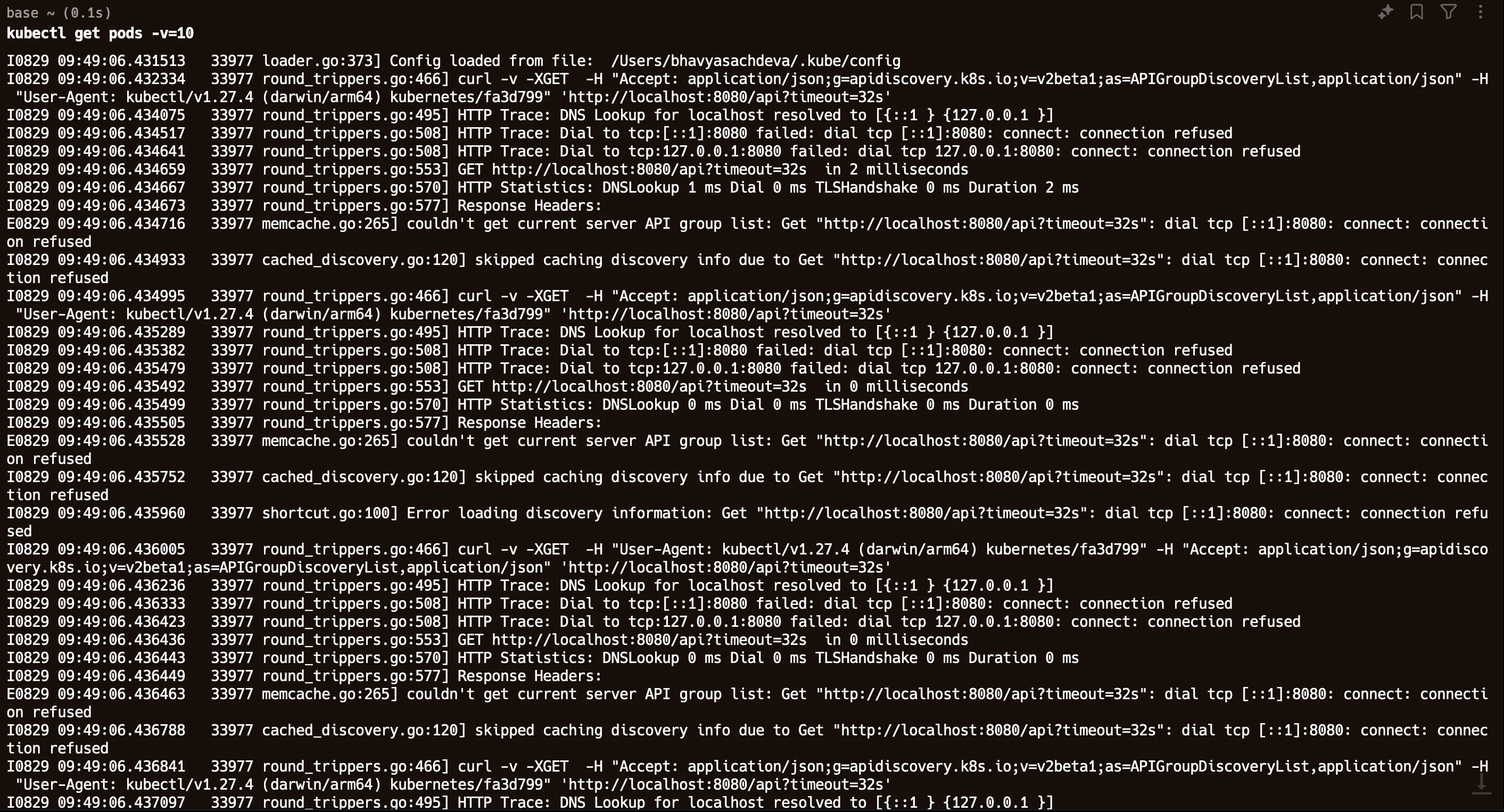
pod details This output provides insights into the API calls and potential failure points. You can see that there is an error when you run the above command. Let’s figure out why this error came, and why you are unable to get pods. Suppose you run the above command and notice that kubectl is unable to connect to the API server. If you are using Minikube, you can check its status using
minikube status.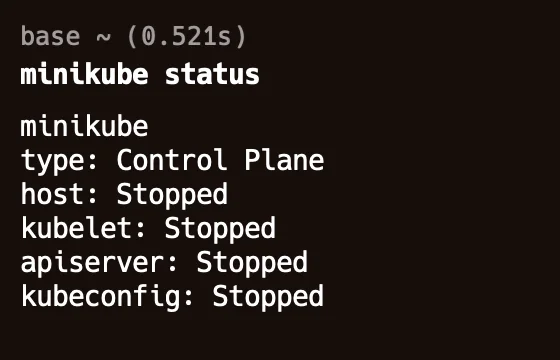
minikube status You can see from the above output that your minikube is not running. You can use
minikube startcommand to start minikube and you will be able to see pods running after starting minikube.
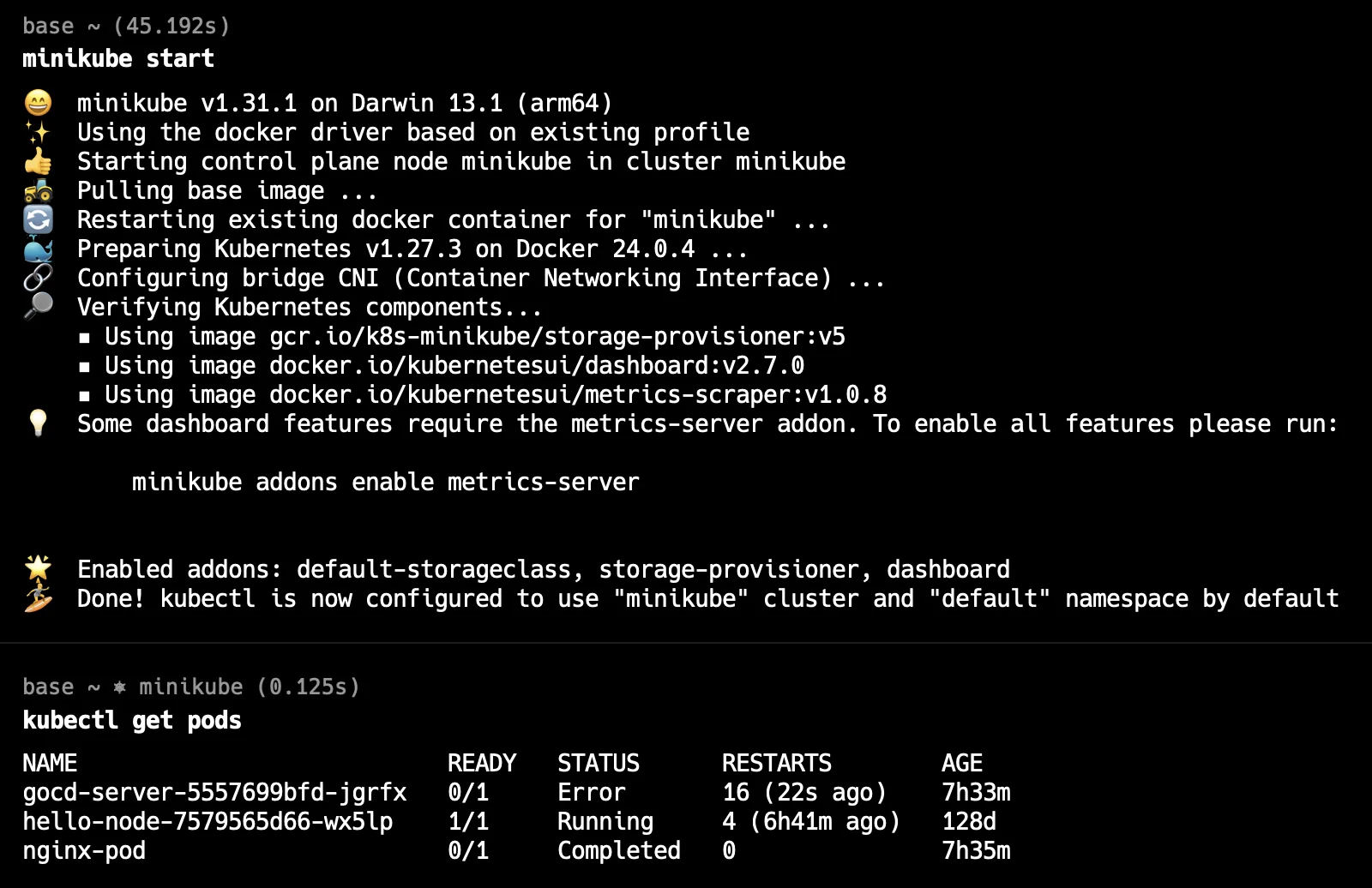
- Analyze server logs: Review the Kubernetes API server logs for any error messages or warnings related to API group list retrieval. You can find logs in
/var/log/kubernetes/kube-apiserver.logon the control plane locally or integrate SigNoz to view the pod logs. - Check network connectivity: Sometimes there is an issue with network connectivity. Verify that your local machine can reach the API server using the below command. Use this command
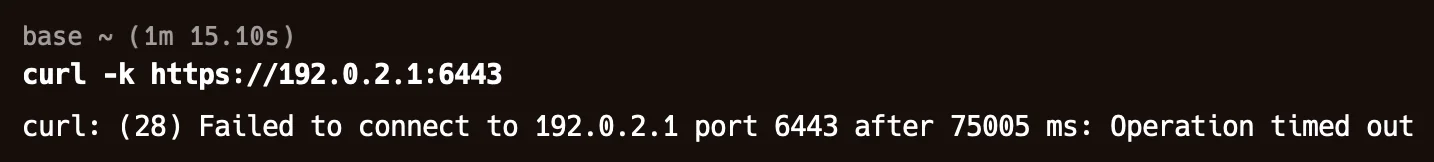
curl -k https://<api-server-endpoint>to test whether your local machine can reach the Kubernetes API server. If the connection fails, it suggests a network issue, such as a misconfigured firewall or DNS problem.curlcommand fails to connect, you might need to check your firewall settings to ensure that traffic to the API server's port (typically 6443) is allowed. Alternatively, verify that your DNS configuration correctly resolves the API server's hostname.You will see in the below section how to fix this network issue. Sometimes you need to change the endpoints if they are configured in the wrong way.
- Verify client and server version compatibility: Ensure your kubectl version is compatible with the Kubernetes cluster version. This command shows the versions of both the kubectl client and the Kubernetes API server. If there is a significant version mismatch, it may lead to compatibility issues which results in the API group list error.
kubectl version --short
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
Follow these steps to resolve the "couldn't get current server API group list: Get" error:
Update kubectl to the latest version: Using the latest version of kubectl ensures compatibility with the most recent Kubernetes API changes and reduces the chances of bugs or deprecated features.
- Download the latest kubectl binary from the official Kubernetes release page.
- Replace your existing kubectl binary with the updated version.
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl" sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectlVerify and reconfigure kubectl context: Ensuring kubectl uses the correct context is important for proper connection with the Kubernetes API server.
Steps:
Run the below command to check your current configuration.:
kubectl config view- Identify and switch to the correct context using :
kubectl config use-context <your-context-name>- If the context is misconfigured, manually edit the kubeconfig file or regenerate it with valid details.
Example: In a multi-cluster setup, using the wrong context may cause issues. Switch to the correct context to resolve them.
You can see this in the below output:

- Check and renew Kubernetes credentials:
- Review your kubeconfig file for expired certificates.
- Regenerate client certificates if necessary.
- Ensure proper network access to the API server:
- Verify firewall rules allow traffic to the API server port (typically 6443).
- Check DNS resolution for the API server hostname.
Advanced Debugging Techniques
For persistent issues, try these advanced troubleshooting methods:
Use kubectl config view to inspect the current configuration: You can use the below command which outputs your entire kubeconfig file in raw format, including any sensitive data like certificates and tokens. It's a helpful way to examine the full configuration and ensure that all settings, such as contexts, clusters, and users, are correct.
kubectl config view --rawLeverage kubectl auth can-i for permission checks:
kubectl auth can-i --listThis command lists all actions that the currently authenticated user is authorized to perform. It helps diagnose RBAC-related issues that might be preventing access to the API group list.If you notice that certain permissions are missing or incorrect, you can update the RBAC policies by creating or editing Roles and RoleBindings to ensure the user has the necessary access.
You can see the below output where there is no permission for user pod-nginx in namespace nginx to list the pod :

auth list You can edit role pod-nginx and add verb to create, get and list the pods using below command:
kubectl edit role pod-nginx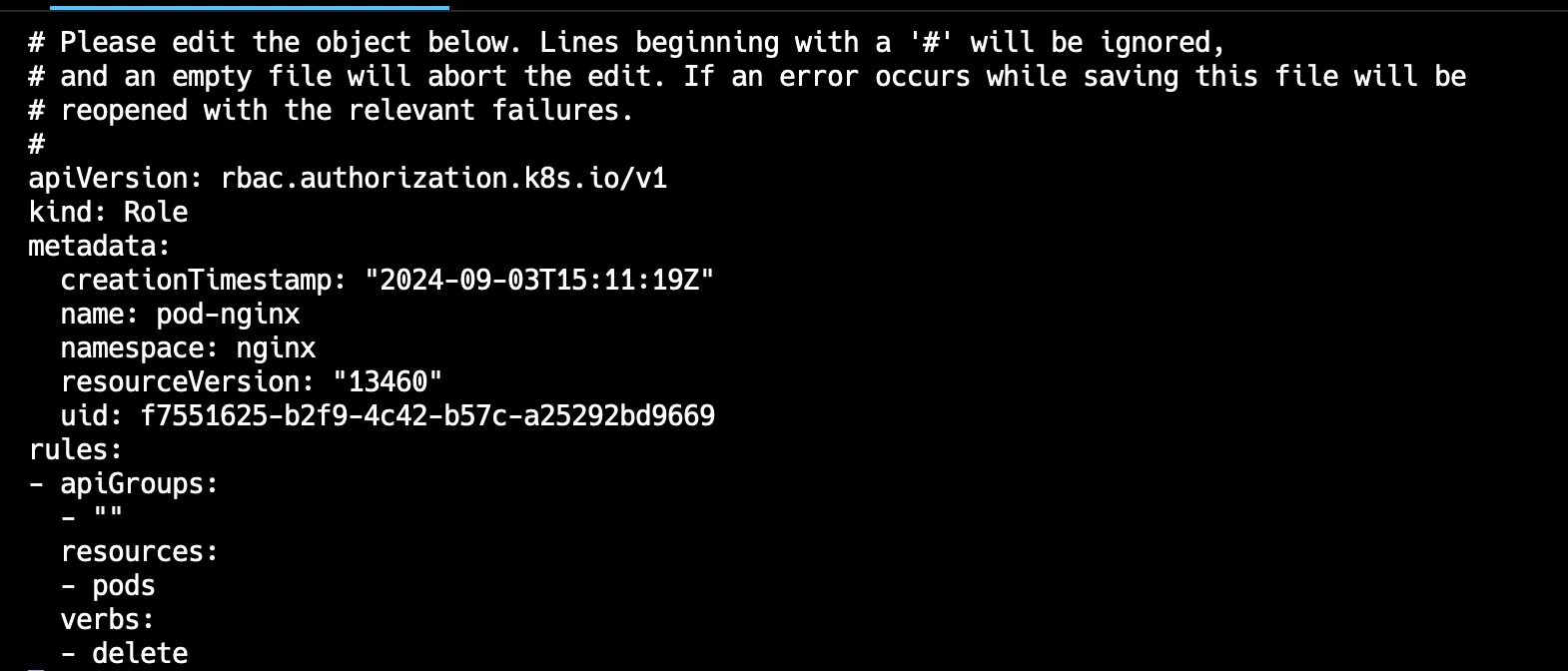
Role You can see that only you are able to delete pod so you can add these verbs as shown in below image:
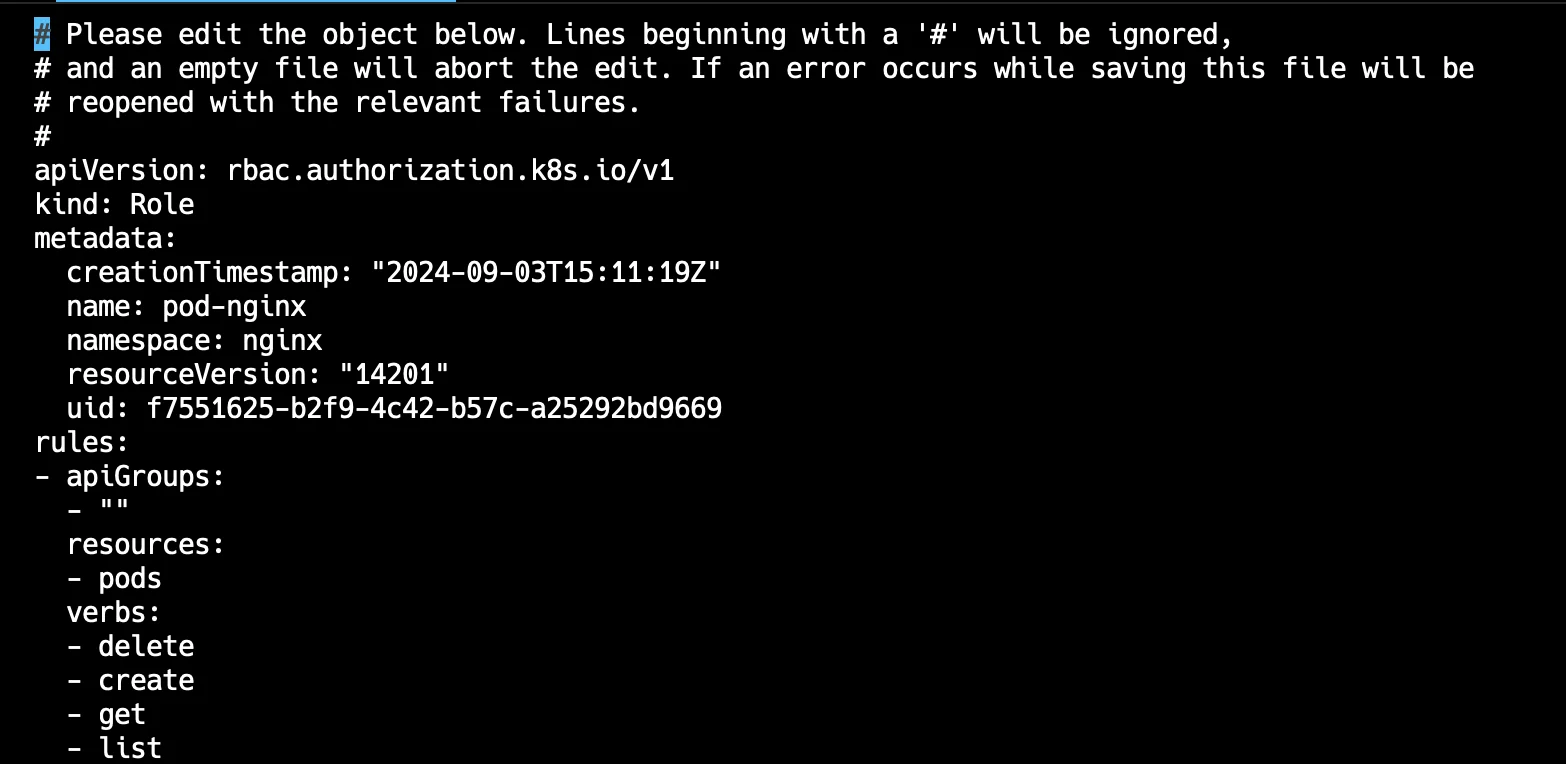
Role edited Use kubectl cluster-info dump for comprehensive diagnostics: This command gathers and displays detailed information about the cluster’s current state, including configurations, logs, and events from all components. It’s particularly useful when dealing with complex issues that require a broad overview of the cluster’s status.
kubectl cluster-info dump
Cluster-info dump This command provides complete information about your cluster's current state.
Utilize kubectl proxy to isolate client-side issues:
kubectl proxysets up a proxy server that relays requests from your local machine to the Kubernetes API server. This setup can help isolate issues by determining whether the problem lies with kubectl or with the API server itself. You can use the below command for this:kubectl proxy curl <http://localhost:8001/api/>If accessing the API server through
kubectl proxyworks but direct access does not, the issue is likely with your local network configuration or direct API server accessibility.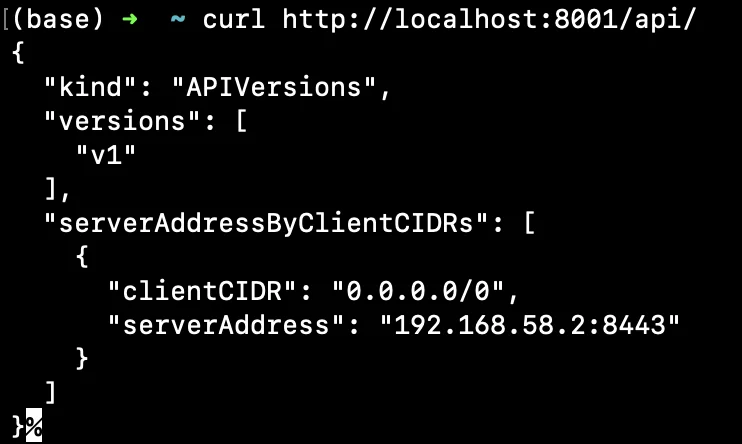
output of curl command
Resolving Common Scenarios
Here are solutions for frequently encountered situations:
Fixing "Unable to connect to the server" errors: This error typically indicates a connectivity issue between your machine and the Kubernetes API server. It may result from incorrect endpoints, blocked ports, or DNS issues. You can follow the below steps to resolve this:
- Verify the API server endpoint in your kubeconfig file: Ensure that the endpoint is correct and up-to-date.
- Ensure your network allows connections to the API server port: Check firewall rules and open ports as necessary.
- You can use
pingortracerouteto diagnose network paths: These tools can help you understand where the connection might be failing. - Use
minikube statusto check whether it is running with expected endpoint.
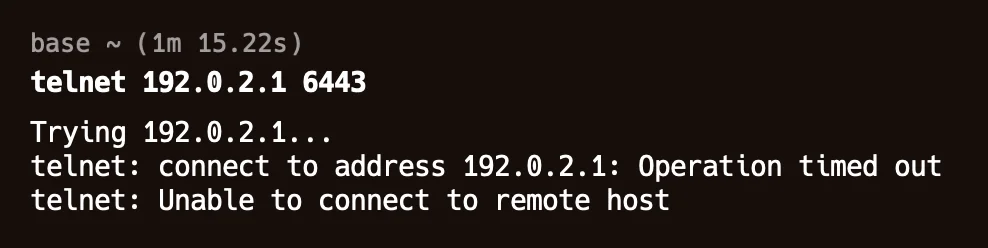
You can see the below output where expected end point is this: 127.0.0.1:62300 and you are using this: 192.0.2.1:6443
You can use the below command to set the correct end-point for server:
kubectl config set-cluster minikube --server=https://127.0.0.1:62300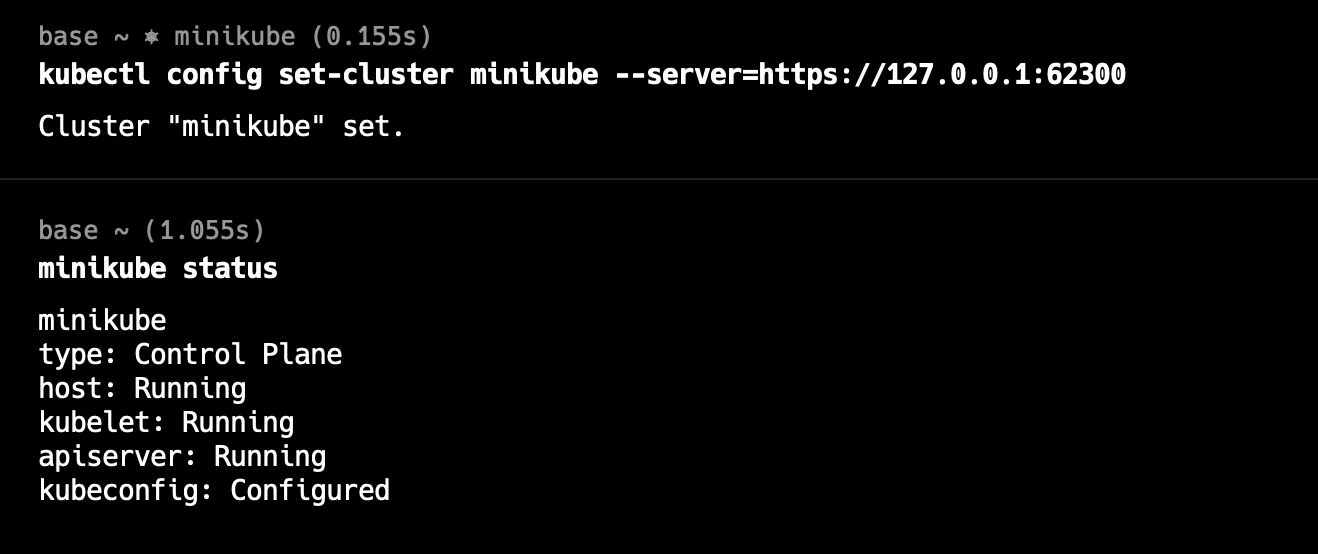
config set-cluster Addressing credential-related issues: There can be credential issues often stem from expired certificates, tokens, or misconfigured kubeconfig entries.
You can update your kubeconfig with the new certificate using the below command:
kubectl create certificatesigningrequest <csr-name> --from-file=<csr-file> kubectl certificate approve <csr-name>Ensure that the new certificates are correctly configured in your kubeconfig file.
Resolving version mismatch problems: Mismatched versions between kubectl and the Kubernetes API server can lead to compatibility issues. You can upgrade or downgrade kubectl to match your cluster version:
curl -LO "<https://dl.k8s.io/release/$>(kubectl version --short | awk -Fv '/Server Version: /{print $3}')/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
- Troubleshooting network-related API access issues: Network issues are often at the root of connectivity problems with the Kubernetes API server. You can use tools like traceroute or tcpdump to diagnose network connectivity problems and also verify that your local DNS resolves the API server hostname correctly.
Best Practices for Preventing API Group List Errors
Implement these practices to minimize the occurrence of API group list errors:
- Regular updates of kubectl and cluster components:
- Set up automated update notifications for kubectl and your Kubernetes distribution.
- Test updates in a non-production environment before applying them to critical clusters.
- Implement proper credential management and rotation:
- Use tools like cert-manager for automated certificate management.
- Implement a regular schedule for rotating cluster credentials.
- Monitor cluster health and API server performance:
- Set up alerts for API server response times and error rates.
- Regularly review API server logs for potential issues.
- Maintain consistent client-server version compatibility:
- Document your cluster version and required kubectl version.
- Implement version checks in your CI/CD pipelines to ensure compatibility.
Leveraging SigNoz for Enhanced Kubernetes Monitoring
SigNoz offers a powerful solution for monitoring Kubernetes clusters and quickly identifying API-related issues. Here's how SigNoz can help prevent and resolve kubectl errors:
- Real-time API server monitoring: Track API server performance metrics and detect anomalies before they cause errors.
- Detailed error tracking: Capture and analyze kubectl errors, including stack traces and contextual information.
- Custom alerting: Set up alerts for specific error patterns or API server performance thresholds.
- Distributed tracing: Visualize the flow of API requests through your cluster, identifying bottlenecks and errors.
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Key Takeaways
- The "memcache.go:265" error often stems from configuration or connectivity issues.
- Verbose logging and systematic troubleshooting are crucial for resolving this kubectl error.
- Regular updates and proper credential management help prevent these errors.
- Monitoring tools like SigNoz significantly improve error detection and resolution in Kubernetes environments.
FAQs
What causes the "couldn't get current server API group list" error?
This error typically occurs due to network connectivity issues, outdated kubectl versions, misconfigured contexts, or authentication problems. It indicates that kubectl cannot retrieve the list of available API groups from the Kubernetes API server.
How can I quickly diagnose the root cause of this kubectl error?
Use the -v=10 flag with your kubectl command to enable verbose logging. This provides detailed information about the API calls and can help identify the specific point of failure. Additionally, checking your kubectl configuration and network connectivity to the API server can quickly reveal common issues.
Are there any specific kubectl versions prone to this error?
While this error can occur in various kubectl versions, it's more common when there's a significant version mismatch between kubectl and the Kubernetes cluster. Always ensure your kubectl version is compatible with your cluster version to minimize the risk of encountering this error.
Can this error occur even with proper authentication in place?
Yes, even with valid authentication, this error can occur due to network issues, API server problems, or misconfigurations. While proper authentication is necessary, it doesn't guarantee successful communication with the API server. Always check for other potential causes, such as network connectivity or API server health, when troubleshooting this error.
