Troubleshooting Kubernetes HPA - Fixing Metric Retrieval Issues
Kubernetes Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) automatically scales your applications based on resource utilization. However, you may encounter issues with metric retrieval, hindering HPA's ability to make scaling decisions. This article addresses the common error: “Unable to get metrics for resource memory: no metrics returned from resource metrics API” and provides a comprehensive guide to troubleshooting and resolving HPA metric retrieval problems.
Understanding Kubernetes HPA and Metric Retrieval Issues
Kubernetes HPA automatically adjusts the number of pods in a deployment or replica set based on observed CPU utilization or other select metrics. It relies on the metrics server to collect and provide resource usage data. However, sometimes HPA faces issues in retrieving metrics. These problems can occur for various reasons, such as misconfigurations or issues with the metrics server (which provides data to HPA). If HPA can't get the right metrics, it might not scale your application properly, either leaving it under-resourced or over-resourced.
The error "Unable to get metrics for resource memory" indicates that HPA is unable to fetch memory metrics from the resource metrics API. This could be caused by problems with the metrics server, communication issues, or incorrect settings in HPA.
Common Causes of HPA Metric Retrieval Failures
The Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) adjusts the number of pods in a Kubernetes application based on real-time metrics like CPU or memory usage. However, failures in retrieving these metrics can disrupt this scaling process. Below, You will see some of the common causes of HPA metric retrieval failures, along with examples that highlight the challenges.
- Misconfigured or missing metrics server: The metrics server might be improperly deployed or entirely absent from your cluster.
- Resource metrics API issues: Problems with the API itself or its communication with the metrics server can disrupt metric retrieval.
- Incorrect HPA configuration: Misconfigurations in the HPA definition can lead to failed metric queries.
- Networking problems: Network issues between HPA and the metrics sources can prevent successful metric retrieval.
- The reliability of HPA depends on accurate metric collection and processing. Some common problems with metric retrieval that can affect HPA include:
- Missing Metrics: HPA might fail to retrieve metrics due to misconfigurations or missing components.
- Incorrect Metrics: The metrics returned by the Metrics API may not reflect the actual state of the system.
- Metrics API Not Available: If the Kubernetes Metrics API server is not running or is improperly configured, HPA won't be able to retrieve the necessary data.
- Metrics Server Down: The Kubernetes Metrics Server, which provides resource usage data (CPU, memory, etc.), might be unavailable.
- Insufficient Permissions: The HPA might not have the correct Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) permissions to access the Metrics API
Diagnosing Metric Retrieval Issues in HPA
Diagnosing Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) metric retrieval issues can be complex, as it involves searching for various components of the Kubernetes system. The following detailed steps will guide you through the process of identifying and troubleshooting the root causes of these issues. Each step is crucial to ensuring that HPA can access the necessary metrics to make scaling decisions.
- Examine HPA Status and Error Messages
The first step in diagnosing metric retrieval issues is to inspect the status of the HPA itself. You can use the below command to check the status of HPA.
Run the following command to view the status of your HPA:
kubectl describe hpa <hpa-name> -n <namespace>
It provides valuable information about the current state of the HPA, including any error messages or conditions that might indicate why it is failing to retrieve metrics along with detailed information about the HPA, including the current number of replicas, target metrics, and error messages if any.
Example:
After running the command, you may see an error message such as being unable to fetch metrics from resource metrics API. This message suggests that there is a communication issue between the HPA and the metrics server or that the metrics API is unavailable. You can see the below output HPA for nginx-deployment gives you errors but in the next step we have created another hpa which does not give you an error.
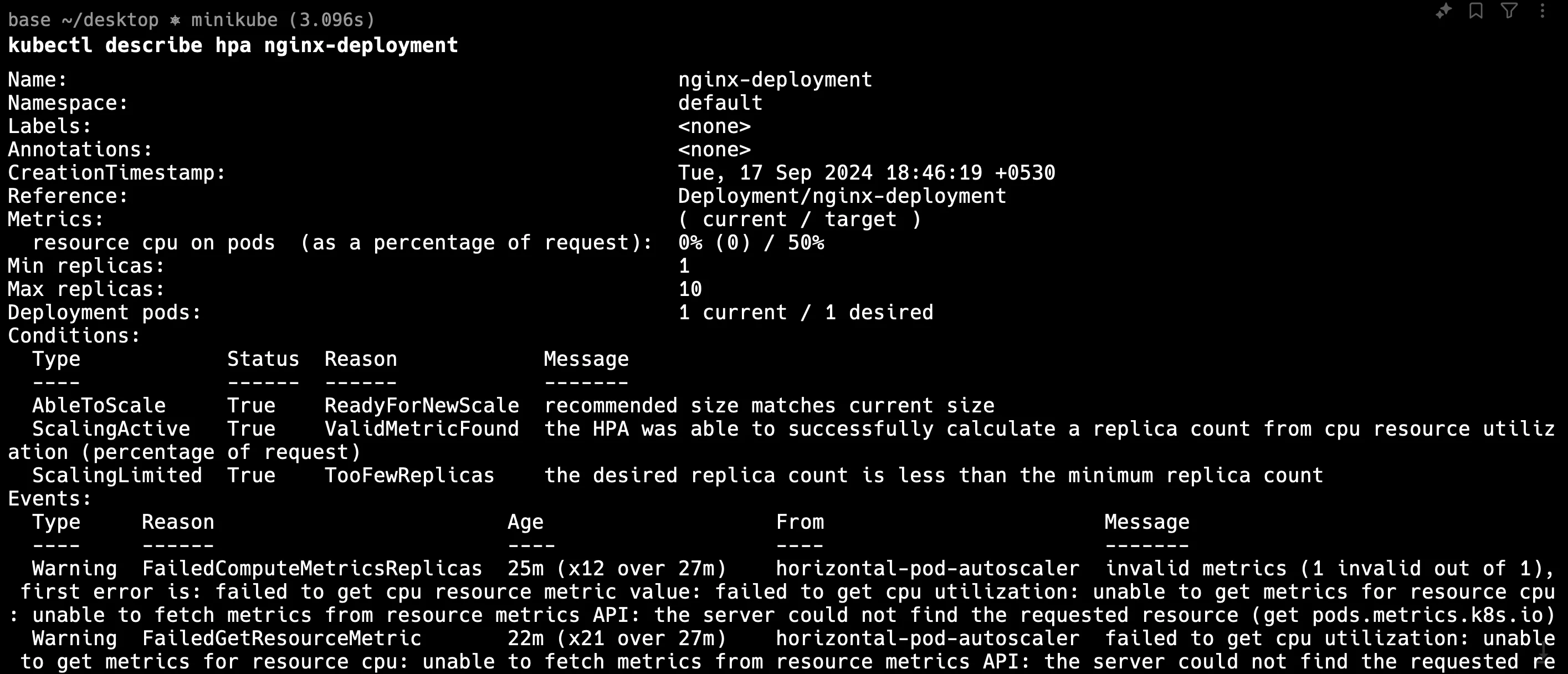
You can see here the below image and there is no error and in the next section, we will learn to troubleshoot.
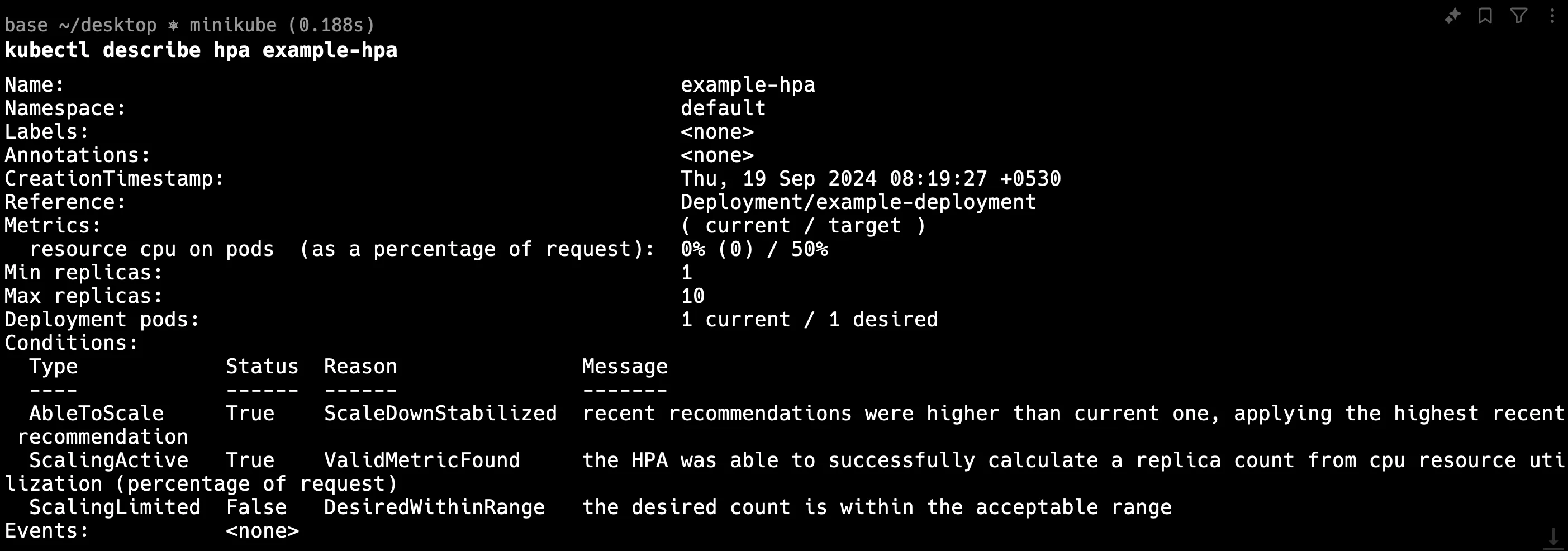
What to Look For:
Error Messages: Pay attention to any error messages or warnings in the output. These can tell you whether the issue is related to missing metrics, a misconfigured HPA, or connectivity issues with the metrics API.
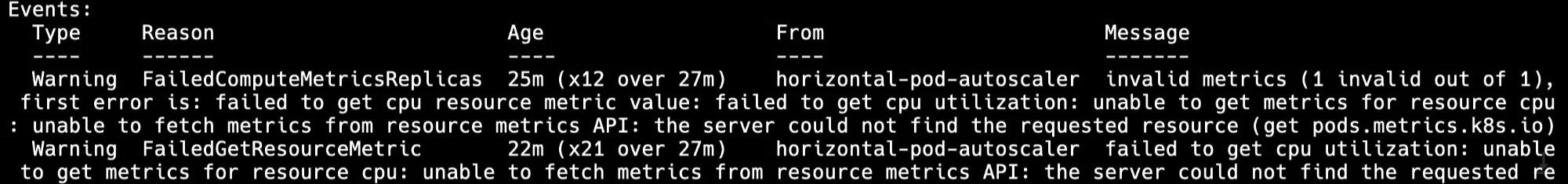
hpa-error Current Metrics Status: Check whether the HPA is receiving any metrics at all. If the current value for CPU or memory utilization is
N/A, it indicates that the HPA is not able to retrieve the metrics needed for scaling.
- Check Metrics Server Logs for Issues
The Kubernetes Metrics Server is responsible for gathering and providing metrics from nodes and pods. If there is a problem with the metrics server, the HPA will not be able to retrieve the required data. Checking the logs of the metrics server is essential to diagnose any internal issues.
Run the following command to view the logs of the metrics server:
kubectl logs -n kube-system $(kubectl get pods -n kube-system -l k8s-app=metrics-server -o name)
This command will output the logs of the metrics server pod, which can help you identify whether the server is running correctly or if it is encountering errors.
Example:
In the logs, you might see messages like failed to scrape node metrics or unable to connect to the node. This could indicate that the metrics server is having difficulty collecting metrics from certain nodes or that there are network issues preventing communication between the server and the nodes. In the below output, the metrics-server is working properly but sometimes the error is maybe related to the metrics-server.
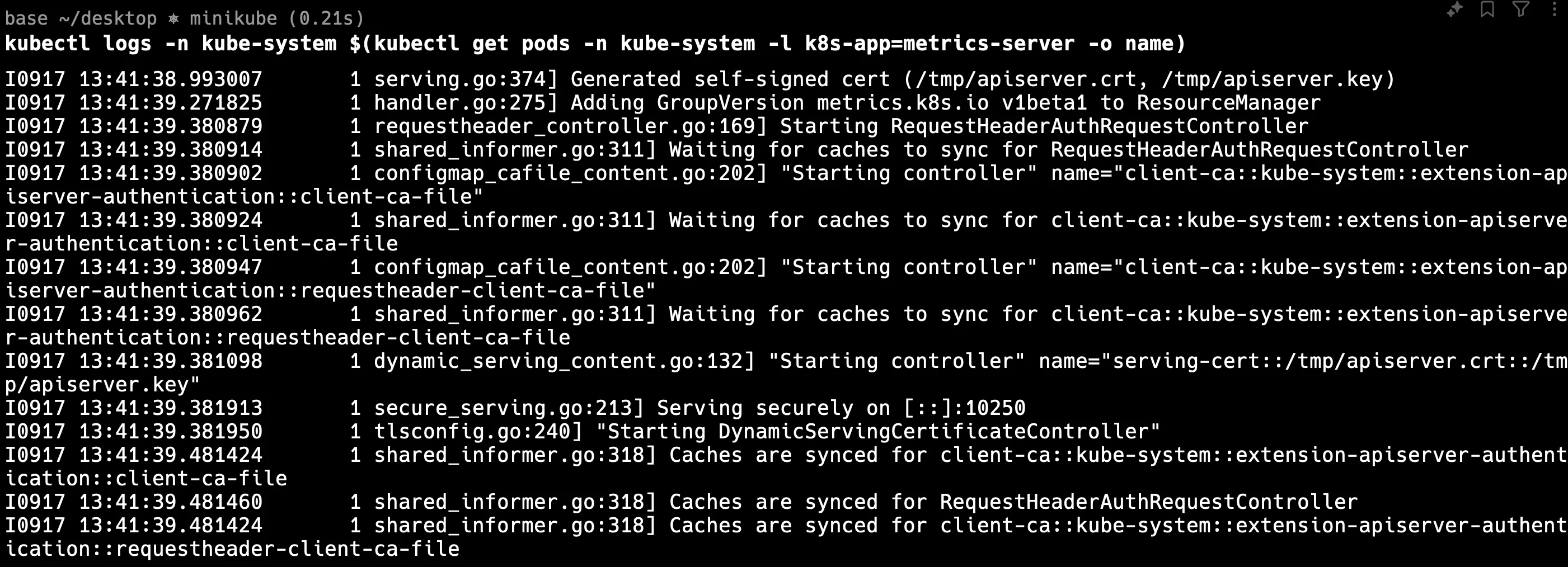
What to Look For:
- Errors in the Logs: Look for any errors or warnings in the logs that suggest why the metrics server might be failing to provide metrics. Issues such as network timeouts, memory limits, or internal crashes will often appear in the logs.
- Resource Usage: If the metrics server is crashing or hanging, it might be due to insufficient resources (CPU or memory). Check for resource exhaustion errors, which can be a signal that you need to allocate more resources to the metrics server pod.
- Verify API Server Connectivity
The HPA relies on the Kubernetes Metrics API to retrieve metrics from the metrics server. If the API server cannot connect to the metrics server or is misconfigured, HPA will not receive any metrics. Ensuring that the API server is reachable and functioning is an important diagnostic step. You can test the connectivity between the API server and the metrics server by running the following command:
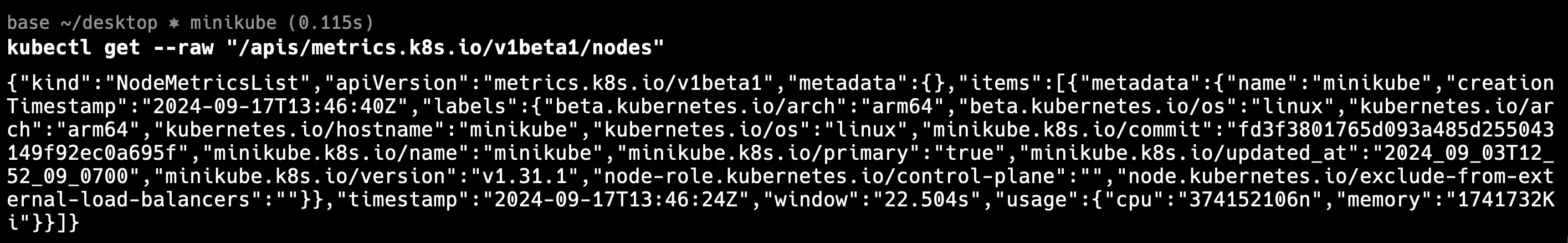
kubectl get --raw "/apis/metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/nodes"
This command queries the metrics API for node-level metrics. If the API is working properly, you should see a JSON output containing node metrics like CPU and memory usage.
Example:
If the API call fails, you might receive an error message like error: the server could not find the requested resource. This indicates that the metrics API is either not available or not properly configured.
What to Look For:
- Valid JSON Response: Ensure that the command returns a valid JSON response with the node metrics. If you receive an error or an empty response, the problem might lie with the metrics API server, which could be down or misconfigured.
- API Availability: If the API is unavailable, check the API server logs and configuration to ensure that it is set up correctly and has the necessary permissions to access the metrics server.
- Examine Pod Resource Requests and Limits
HPA scales pods based on resource usage like CPU and memory. If the resource requests and limits for a pod are not correctly defined, it could affect the HPA’s ability to scale properly. For example, if a pod does not request any CPU or memory, the metrics server won’t have any data to provide to the HPA. To examine the resource requests and limits of a specific pod, use the following command:
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> -n <namespace>
This command will provide detailed information about the pod, including its resource requests and limits.
Example:
You might find that a pod has no defined resource requests for CPU or memory, meaning that the metrics server cannot collect usage data for these resources. Without this data, HPA has nothing to scale against, leading to scaling failures.
What to Look For:
Correctly Defined Resource Requests: Ensure that the pod has appropriate resource requests and limits for CPU and memory. This will allow the metrics server to collect usage data, which the HPA can then use to make scaling decisions.
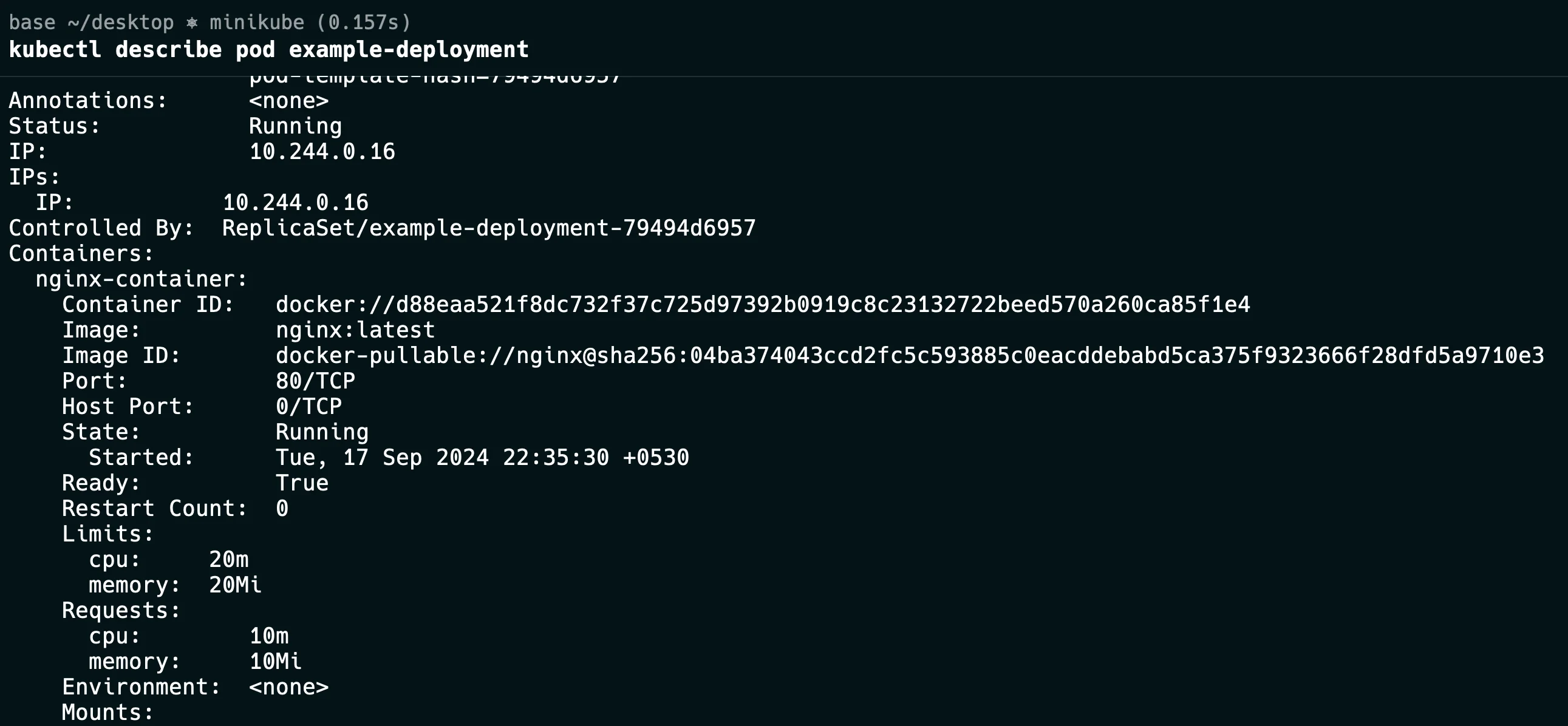
pod describe Resource Utilization: Check whether the resource utilization of the pod matches the target metrics defined in the HPA. If there is a significant discrepancy, it might indicate an issue with the way metrics are being collected or reported.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
Follow these steps to resolve HPA metric retrieval issues:
Ensure metrics server is properly deployed and running: The metrics server is essential for HPA as it aggregates resource usage data that HPA uses to make scaling decisions.
Check Metrics-Server Deployment: Use the following command to check if the Metrics-Server is deployed in the kube-system namespace:
kubectl get deployment metrics-server -n kube-systemExpected Output: You should see the deployment details of the Metrics-Server. If it's not present, you will need to install it.
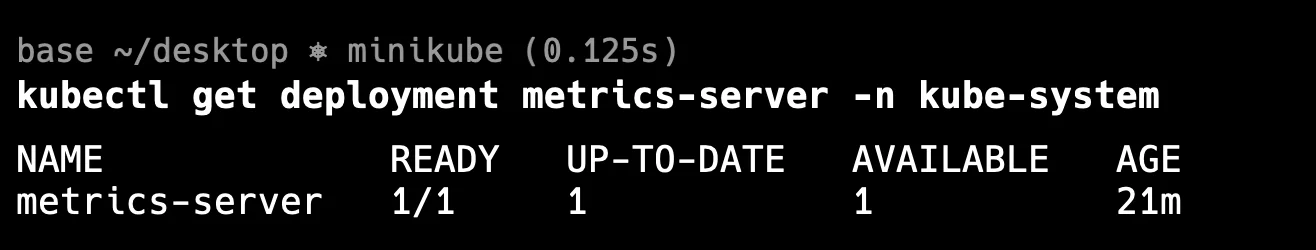
Get metrics server Installation: If the Metrics-Server is not installed, you can install it using the official Kubernetes YAML manifest. You can find the latest version of the Metrics-Server and its deployment instructions on the Kubernetes Metrics Server GitHub page.
Verify metrics-server version compatibility:
Ensuring that the Metrics-Server version is compatible with your Kubernetes cluster version is critical for its proper function.
- Check Compatibility: Review the Metrics-Server release notes or documentation to confirm that its version is compatible with your cluster's Kubernetes version.
- Update Metrics-Server: If an update is necessary, apply the latest compatible Metrics-Server manifest. This can be done by downloading the updated YAML file from the Kubernetes GitHub repository and applying it with
kubectl apply.- Confirm your metrics-server version is compatible with your Kubernetes cluster version.
- Update if necessary using the appropriate manifest for your cluster version.
Check RBAC permissions: HPA and Metrics-Server require specific RBAC permissions to function properly.
Verify Cluster Roles and Bindings: Use these commands to check the necessary roles and bindings:
kubectl get clusterrole system:aggregated-metrics-reader kubectl get clusterrolebinding metrics-server:system:auth-delegatorExpected Output: These commands should return the configuration of the roles and bindings that allow Metrics-Server to access and aggregate metrics.
You can see the below output:

Clusterrole 
Clusterbinding Validate resource requests and limits: Proper configuration of resource requests and limits is crucial for accurate metrics collection by the metrics server.
Review and Adjust Resource Specifications: Check your pod specifications to ensure they have appropriate resource requests and limits. This affects how Kubernetes schedules and scales these pods. Example configuration:
resources: requests: memory: "64Mi" cpu: "250m" limits: memory: "128Mi" cpu: "500m"Adjust these values based on your application's specific needs and typical resource usage to ensure efficient scaling.
Resolving "No Metrics Returned" Errors
The "no metrics returned" error in Kubernetes typically occurs when the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) is unable to retrieve the necessary metrics from the Kubernetes Metrics Server. This issue can stem from various factors such as a misconfigured metrics server, incorrect resource requests, or outdated components. The following solutions provide detailed steps to resolve this error and ensure your HPA functions correctly.
Restart the metrics-server pod:
The Kubernetes Metrics Server is responsible for providing resource usage metrics (like CPU and memory) to the HPA. If the metrics server is experiencing issues or crashes, restarting the server pod can often resolve the problem. This action ensures that any temporary issues, such as network connectivity problems or memory leaks, are cleared.kubectl rollout restart deployment metrics-server -n kube-system
rollout deployment After restarting the metrics-server, check the pod status using:
kubectl get pods -n kube-systemIf the pod is successfully restarted, you should see the new pod in a
Runningstate. Once the metrics server is back online, check if the HPA is now able to retrieve the required metrics.Update metrics-server to the latest compatible version:
Running an outdated version of the metrics server can lead to compatibility issues with newer Kubernetes versions. It’s essential to ensure that the version of the metrics server you are running is compatible with your cluster's Kubernetes version. Newer releases often include bug fixes, security patches, and performance improvements that can resolve issues related to metrics retrieval.
To update the metrics-server:
- Visit the official metrics-server GitHub repository or Kubernetes documentation to find the latest compatible version for your Kubernetes version.
- Once you’ve identified the correct version, update your metrics server by editing the deployment or redeploying it with the correct version.
Example:
If you’re using Helm, the command to update the metrics-server might look like this:
helm upgrade --install metrics-server stable/metrics-server --version <latest_version> --namespace kube-systemAfter the update, verify that the metrics server is running the new version and check if the HPA is now receiving metrics.
Configure proper resource requests for monitored pods:
- For the HPA to function properly, the pods being monitored must have resource requests and limits defined. Without proper CPU and memory resource requests, the metrics server won’t be able to collect and report metrics, leading to the "no metrics returned" error.
- Ensure that each pod under the HPA’s control has appropriate resource requests and limits defined in its specification. This allows the metrics server to track the pod's resource utilization and provide the necessary data to the HPA.
Here’s an example of a properly defined pod specification with resource requests:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: example-pod spec: containers: - name: example-container image: nginx resources: requests: memory: "64Mi" cpu: "250m" limits: memory: "128Mi" cpu: "500m"Example:
After ensuring that the pod specifications are correctly defined, restart the pod using:
kubectl delete pod <pod-name> -n <namespace>This forces the pod to restart with the correct resource requests, allowing the metrics server to begin collecting data. Then check the HPA status to see if metrics are now being returned.
- Adjust the HPA Configuration
In some cases, the issue might be with the HPA configuration itself. The HPA may be misconfigured to query metrics that are either not available or incorrectly defined. Adjusting the HPA configuration to use the correct metrics can help resolve the error.
Solution:
Review and update the HPA definition to ensure it targets the correct metrics and includes the right thresholds for scaling. For example, if the HPA is set to scale based on CPU usage, ensure the metric name is correctly specified as
cpuand that the target utilization is reasonable.Here’s an example of a properly configured HPA:
apiVersion: autoscaling/v1 kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler metadata: name: example-hpa spec: scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment name: example-deployment minReplicas: 1 maxReplicas: 10 metrics: - type: Resource resource: name: cpu targetAverageUtilization: 50Example:
In this example, the HPA is configured to scale between 1 and 10 replicas based on CPU usage. If the average CPU utilization across all pods exceeds 50%, the HPA will scale up the number of replicas.
After updating the HPA configuration, apply the changes with:
kubectl apply -f <hpa-file>.yamlYou can see the below output:
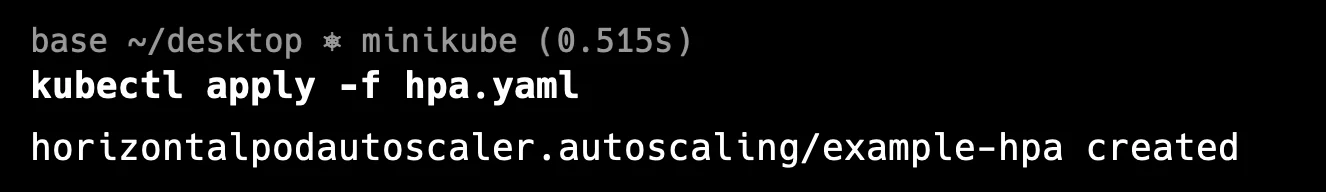
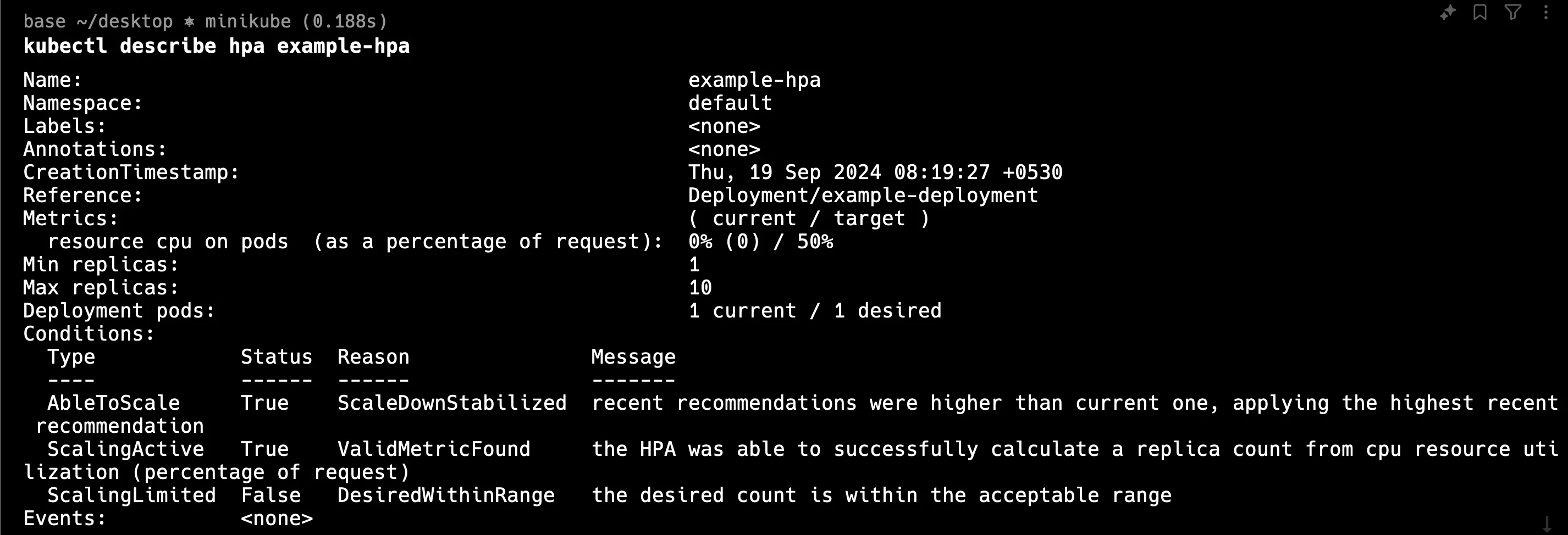
hpa apply Verify that the HPA is now functioning correctly by running:
kubectl describe hpa <hpa-name>You can see the below output:
Advanced HPA Configuration Techniques
To enhance your HPA implementation, consider these advanced techniques:
Implement custom metrics: Use custom metrics adapters to scale based on application-specific metrics. Configure HPA to Use Custom Metrics:
metrics: - type: Pods pods: metric: name: http_requests target: type: AverageValue averageValue: 1000Utilize external metrics providers: Integrate with external monitoring systems for more comprehensive scaling decisions like SigNoz.
Configure scaling policies and behaviors: Fine-tune HPA behavior with scaling policies:
behavior: scaleDown: stabilizationWindowSeconds: 300 policies: - type: Percent value: 100 periodSeconds: 15Implement multi-metric and resource-based HPAs: Combine multiple metrics for more nuanced scaling decisions:
metrics: - type: Resource resource: name: cpu target: type: Utilization averageUtilization: 50 - type: Resource resource: name: memory target: type: AverageValue averageValue: 500Mi
Solutions to Common Metric Retrieval Problems
1. Metrics Server Not Deployed
If the Metrics Server is not deployed, install it using:
kubectl apply -f <https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/latest/download/components.yaml>
After deploying, verify that the Metrics Server is running and serving requests.
2. Custom Metrics API Not Available
If using custom metrics, ensure the custom metrics adapter is properly installed. Verify the application exports the required metrics, and that the adapter can access them.
3. Incorrect Target Metrics
If your target metrics (e.g., CPU or memory) are incorrectly defined or too aggressive, HPA may fail to scale properly. Revisit the HPA configuration and adjust the target thresholds to reasonable values.
For example, if you have set CPU utilization to 90% but your pods regularly spike to 95%, this may cause under-scaling. Consider lowering the target utilization to 80-85%.
4. Restart the Metrics Server
If all else fails, restarting the Metrics Server may help resolve temporary issues. You can do this by deleting the current Metrics Server pod:
kubectl delete pod -n kube-system -l k8s-app=metrics-server

Effective monitoring is crucial for maintaining a healthy HPA setup:
- Set up logging and alerting: Configure alerts for HPA-related issues using your preferred monitoring solution.
- Use Kubernetes dashboard: Leverage the Kubernetes dashboard for visual HPA monitoring.
- Implement continuous HPA health checks: Create periodic checks to ensure HPA is functioning correctly.
- Leverage SigNoz for comprehensive monitoring: Utilize SigNoz for in-depth HPA and cluster monitoring.
Implementing SigNoz for Enhanced HPA Monitoring
SigNoz offers powerful monitoring capabilities for Kubernetes environments, including HPA performance tracking:
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
To configure SigNoz for HPA monitoring:
- Install SigNoz in your Kubernetes cluster.
- Set up a metric collection for HPA-related resources.
- Create custom dashboards to visualize HPA performance and scaling events.
- Configure alerts for abnormal HPA behavior or persistent metric retrieval issues.
Best Practices for Reliable HPA Implementation
Follow these best practices to ensure a robust HPA setup:
- Regularly update and maintain metrics-server: Keep your metrics-server up to date with the latest compatible version.
- Properly allocate resources and set limits: Ensure all pods have appropriate resource requests and limits defined.
- Implement gradual scaling policies: Use scaling policies to prevent rapid fluctuations in pod count.
- Continuously monitor and optimize HPA configurations: Regularly review and adjust your HPA settings based on application performance and resource utilization patterns.
- Monitor the Metrics Server: Regularly check the health and performance of the Metrics Server. If possible, set up alerts for downtime or failures.
- Use Proper RBAC Policies: Ensure that HPA has the necessary permissions to access the Metrics API by defining appropriate RBAC roles and bindings.
- Fine-tune HPA Configuration: Ensure that HPA targets and thresholds align with your application’s performance characteristics. Test your scaling policies in different load scenarios to ensure they behave as expected.
- Test Custom Metrics Thoroughly: If you're using custom metrics, ensure that your applications are properly exporting them and that the metrics are accurate and meaningful.
Key Takeaways
- HPA metric retrieval issues often stem from misconfigured metrics-server or resource specifications.
- Proper diagnosis involves checking HPA descriptions, metrics-server logs, and API connectivity.
- Resolving "no metrics returned" errors typically requires restarting or updating metrics server and adjusting pod configurations.
- Implementing advanced HPA configurations and robust monitoring solutions like SigNoz can enhance autoscaling reliability.
FAQs
What causes the "Unable to get metrics for resource memory" error in Kubernetes HPA?
This error typically occurs when the HPA cannot retrieve memory metrics from the resource metrics API. Common causes include a misconfigured or missing metrics-server, network issues, or incorrect pod resource specifications.
How can I verify if my metrics server is working correctly?
You can check the metrics-server status by running:
kubectl get --raw "/apis/metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/nodes"
If it returns node metrics, your metrics server is functioning properly.
Are there alternatives to using the default metrics server for HPA?
Yes, you can use custom metrics adapters or external metrics providers like Prometheus Adapter for more advanced scaling scenarios. These alternatives allow you to scale based on application-specific or external metrics.
How often should I update my metrics-server and HPA configurations?
It's recommended to keep your metrics-server updated with each Kubernetes version upgrade. Review and adjust your HPA configurations regularly, especially after significant changes to your application's resource usage patterns or performance requirements.
