Elasticsearch vs MongoDB - Battle of Search and Store
Elasticsearch is primarily a search engine optimized for fast, complex search queries, especially text searches, and is often used for log and event data analysis. MongoDB, on the other hand, is a general-purpose, document-oriented database that excels in storing and retrieving structured and semi-structured data. It is commonly used for mobile, social, and IoT applications. While Elasticsearch provides superior search capabilities, MongoDB offers more robust data processing and storage features.
- Search Functionality: Elasticsearch excels in full-text search and analytics, making it ideal for applications like search engines, log monitoring, and real-time data analysis.
- Data Storage and Structure: MongoDB is more versatile for storing diverse data formats and structures, suitable for content management, e-commerce platforms, and social media applications.
- Scalability and Performance: Elasticsearch offers superior performance in search-related operations, while MongoDB provides more efficient scalability for large and complex data sets.
- Real-time Processing: Elasticsearch is better suited for real-time processing and analysis of data, whereas MongoDB is preferred for robust data storage and retrieval in various application types.
Before we deep-dive into key differences between Elasticsearch and MongoDB, let's have a brief overview of both technologies.
An overview of Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is an open-source full-text search engine built on Apache Lucene and developed in Java. Indexing and data analysis are its major capabilities. Along with Kibana and Logstash , it functions as part of the Elastic Stack for data analysis.
Elasticsearch allows you to store, search, index, and analyze huge volumes of data easily. Also, It provides real-time search and analytics of all data types. The ability to get search responses quickly is because it searches an index instead of a text.
In simple terms, with Elasticsearch, you can take data from any source and format. Then in real-time, you can search, analyze and visualize it. It improves the search's speed and accuracy.
Data in Elasticsearch is stored in schema-less JSON and use REST APIs for storing and searching. Elasticsearch is a tool that enables you to use it simultaneously without interfering with one another.
Features of Elasticsearch
- Full-text search: Elasticsearch can conduct a fast full-text search
- It is compatible with JSON and REST APIs.
- It is easy to use.
- Elasticsearch can scale large volumes of data.
- It offers real-time data visualization.
- Elasticsearch does searches on structured and unstructured data.
An overview of MongoDB
MongoDB is an open-source NoSQL database that uses a document-oriented data model for large-volume data storage. MongoDB allows you to store, manage, and retrieve document-oriented data. Unlike traditional relational databases, which store data in tables and rows, MongoDB uses collections and documents to store data.
A database in MongoDB is a container of collections. Documents are stored in collections, which MongoDB uses to keep track of related data. The conventional database structure of MongoDB is shown in the figure below.
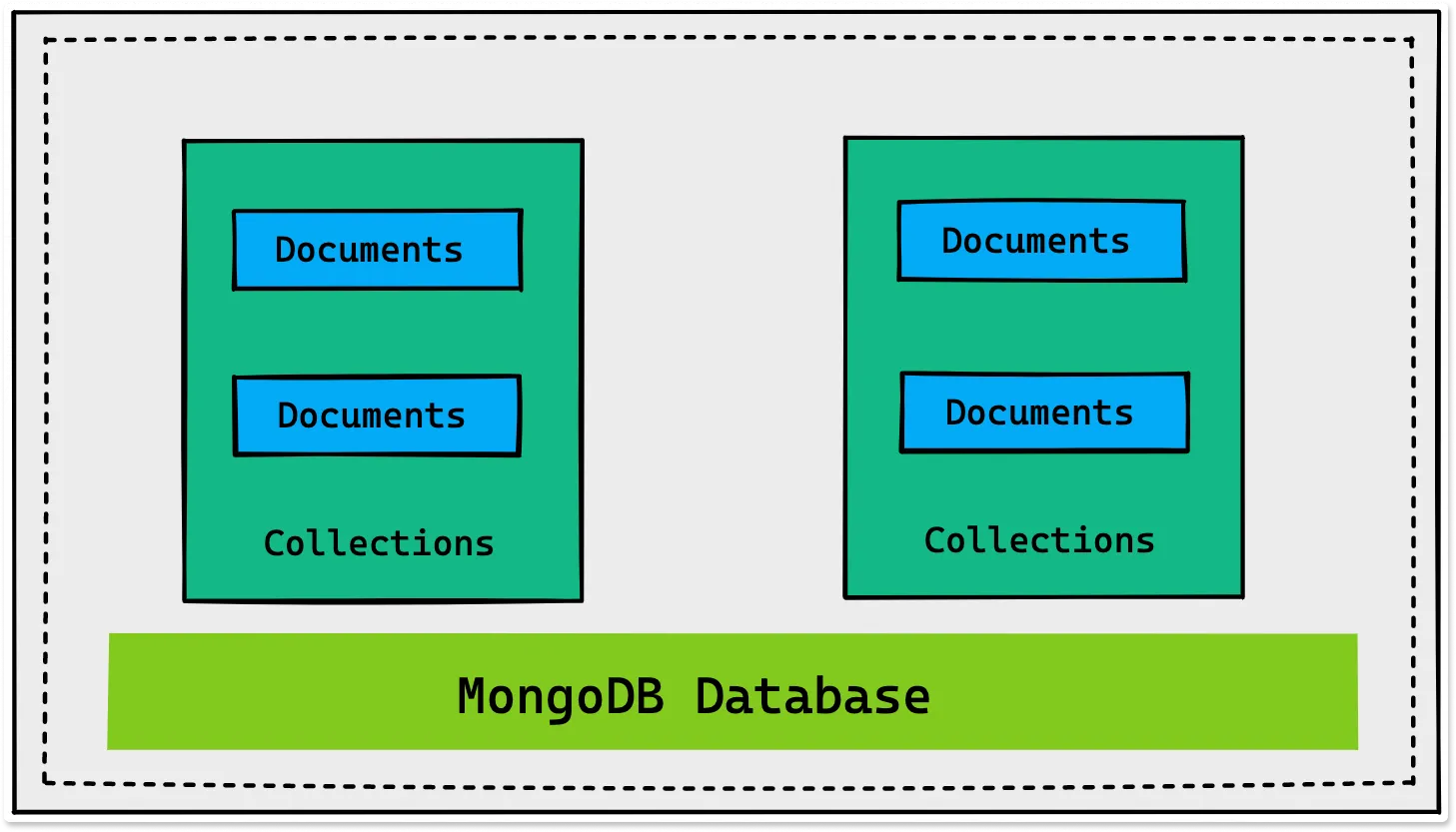
MongoDB Collections
A collection in MongoDB is a fundamental component containing the same document set.
A collection doesn't need to be present to insert a document. When you add the first document or store data for a collection, MongoDB creates a collection if it doesn't exist. To put it another way, when the first document is inserted, a collection is created.
MongoDB Documents
In MongoDB, a document is a set of key-value pairs. It is the fundamental building block of data. The document is represented as the JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) document. This is because MongoDB is a schema-less database.
Data is stored in BSON, a binary representation of JSON documents. BSON is used as it accepts more data types. The data values accepted are various data types, documents, and arrays.
Features of MongoDB
- Flexibility: MongoDB can run on servers. Data is duplicated to protect the database system against hardware failure.
- Indexing: Fields in the document can be indexed. MongoDB uses indexing to process large volumes of data in a short time.
- Scalability: MongoDB distributes data across various servers using sharding. MongoDB has an automatic loading feature due to sharding.
- Replication: MongoDB enables data availability by ensuring multiple copies of data on the servers (redundancy). If one server is down, you can retrieve data from another server.
- Queries: It supports document-based queries.
- Document Oriented: Databases contain collections that contain sets of documents.
Key Differences between Elasticsearch vs. MongoDB
Elasticsearch and MongoDB technologies are similar in one way or another due to their design and features. But both technologies differ greatly. Elasticsearch is a search engine server, while MongoDB is a database that allows you to store, manage, and retrieve data. Let us look at their differences in some key aspects.
1. Search Capabilities
Elasticsearch excels in search functionality, particularly known for its full-text search capabilities. It can efficiently handle complex search queries, including fuzzy searches, autocomplete, geolocation searches, and more. Elasticsearch is designed specifically for search-related tasks, offering robust performance in this area.
MongoDB, while capable of handling search queries, especially through MongoDB Atlas Search, is generally less specialized in search compared to Elasticsearch. MongoDB's search capabilities have improved, but it's primarily a database with search features added on, not a dedicated search engine like Elasticsearch.
In summary, for pure search-focused tasks, Elasticsearch usually outperforms MongoDB, but MongoDB offers a broader set of database functionalities with added search capabilities.
2. Data Storage
Elasticsearch is developed in Java and implemented on top of Apache Lucene. It writes data to inverted indexes using Lucene segments. Elasticsearch maintains a transactional log for each index in order to avoid a low-level Lucene commit for each indexing operation. Transaction logs can also help in data recovery in the event of a crash or data corruption incident.
MongoDB data storage model is different from that of Elasticsearch. It is written in C++ and stores data in Binary JSON format (BSON) MongoDB uses a memory-mapped files to map on-disk data files to in-memory byte arrays. It manages and organizes data using a linked data structure. Documents have linked lists to each other and to any BSON-encoded data. In the event of a hard shutdown, MongoDB employs journal logs to assist with database recovery.
Elasticsearch and MongoDB differ significantly in their storage capabilities. Elasticsearch, primarily designed for search, is optimized for fast data retrieval but is not as efficient for data storage compared to traditional databases. It's more suited for scenarios where search and quick data access are prioritized.
MongoDB, on the other hand, is a general-purpose database that excels in storing large volumes of data efficiently. Its document-oriented approach allows for flexible data modeling, making it a better choice for applications requiring diverse data types and structures. MongoDB's storage mechanism is more versatile and scalable for general database use compared to Elasticsearch.
3. Programming Language Support
Elasticsearch is written in Java and MongoDB in C++. Both technologies support a wide range of programming languages. Elasticsearch supports JAVA, Python, .NET, JavaScript, Go, Rust, etc.
MongoDB, on the other hand, offers multiple drivers for languages. MongoDB supports C++, C, C#, Node.js, PHP, Go, Python, Java, Ruby, etc.
4. JSON Adaptability
Elasticsearch can handle JSON documents in indices. Its excellent search library enables users to manage and analyze data easily. In Elasticsearch, there is no binary conversion like in MongoDB. With Elasticsearch, it's possible to analyze data present in a document. Indexes are created after analyzing data, and values are fetched from the document.
MongoDB, on the other hand, can manage JSON documents and convert them to the binary version (BSON). BSON is optimized for speed and flexibility. The primary aim for JSON documents is that users have the flexibility to model their data based on their applications’ requirements.
5. Data Recovery and Backup
Elasticsearch and MongoDB offer data backup and recovery functionalities. Elasticsearch handles data backups using a snapshot. The snapshots are incremental. This means that Elasticsearch will not duplicate any data that has previously been backed up in an index snapshot that it has already created. Snapshots are restored using the restore API. The snapshot API does not offer a query backup. Thus Elasticsearch has been reported to lose data and is not considered a good option for data backup and recovery.
MongoDB provides a variety of backup options. The majority of DevOps employ mongodump, which is available. Both queryable backup and full database backup are offered by Mongodump. Due to its inability to manage incremental backups and inefficiency with large databases, the program has some drawbacks.
You must utilize the MongoDB oplog to implement incremental backup on MongoDB. Additionally, you can take file system snapshots and use those to make a backup of your MongoDB deployment. The underlying data files for MongoDB are copied as a result. With MongoDB enterprise, you have access to MongoDB Atlas, MongoDB Cloud Manager, and MongoDB Ops Manager.
Mongodumps, unlike Elasticsearch snapshots, will save on local disks or any other MongoDB cloud storage.
6. Use cases
Your use case will be essential in choosing the best technology. Anytime full-text search is necessary, Elasticsearch is the preferable option. In terms of log analytics, Elasticsearch also dominates since it provides a large selection of aggregation queries and supports tools like Kibana and Logstash. The tools make log analysis easier.
Application and website search, business analytics, and data analytics are some technologies using Elasticsearch to search and index different data types.
On the other hand, MongoDB is a reliable option when the data is in NoSQL format and you need a highly scalable database for CRUD operations without full-text search capability.
Finance and e-commerce organizations frequently use MongoDB to store product information and specific details. Additionally, you can keep your brand's product catalog there. You can also use MongoDB to store and model machine-generated data. MongoDB is used by various web applications to store data. Some MongoDB use cases are content management systems (CMS), the Internet of things (IoT), and Real-time analytics.
Elasticsearch vs. MongoDB:
Elasticsearch Advantages
- Elasticsearch carries out searches for both structured and unstructured data.
- In Elasticsearch, data can be accessed using a query in any format.
- Elasticsearch is fast. It perform searches quickly as it can analyze multiple records.
- Elasticsearch copy data in multiple servers leading to high data availability.
- It finds matches for full-text searches fast, even from large data sets.
Elasticsearch Disadvantages
- Elasticsearch is not a good alternative for data storage compared to MongoDB.
- Although it is a strong and adaptable distributed database search engine, it can be challenging to understand.
MongoDB Advantages
- Flexibility to store various data types.
- High speed and performance.
- Ease of use as it offers simple query syntax that is much easier to understand.
- It uses sharding when handling large datasets
- It offers Ad-hoc query support
MongoDB Disadvantages
- Data duplication is common in MongoDB
- High memory usage.
- Limited data size.
Choosing between Elasticsearch and MongoDB
Both Elasticsearch and MongoDB are popular and established data stores. As we have explained the use-cases, you can choose between Elasticsearch and MongoDB based on your use-case. Elasticsearch is a distributed, document-oriented database best suited for search and analytics use cases. On the other hand, MongoDB is a popular choice of data store for unstructured data.
If you are looking at setting up analytics on your data, Elasticsearch can be a good choice. For example, Elasticsearch combined with Logstash and Kibana is used for Log analytics. But recently, big companies like Uber and Cloudflare have shifted their log analytics from Elastic search to ClickHouse, a columnar database much more suited to store telemetry data like logs.
Use Cases: When to Choose Elasticsearch or MongoDB
Selecting the right database depends on your specific requirements. Here are some scenarios where each system shines:
Elasticsearch excels in:
- Log and event data analysis
- Full-text search engines
- Real-time analytics dashboards
- Recommendation systems
MongoDB is ideal for:
- Content management systems
- Mobile app backends
- IoT data storage and analysis
- E-commerce product catalogs
Consider these factors when making your choice:
- Data structure: Is your data primarily text-based or varied in format?
- Query patterns: Do you need complex search capabilities or general CRUD operations?
- Scalability needs: How much data growth do you anticipate?
Real-world examples:
- GitHub uses Elasticsearch for code search functionality
- Uber leverages MongoDB for storing rider and driver data
If your use case is log analytics than SigNoz, an open-source log management tool based on ClickHouse can be a better choice. It provides logs, metrics, and traces under a single pane of glass, thus serving as a one-stop observability solution.
Getting started with SigNoz
SigNoz Cloud is the easiest way to run SigNoz. Sign up for a free account and get 30 days of unlimited access to all features.
You can also install and self-host SigNoz yourself since it is open-source. With 24,000+ GitHub stars, open-source SigNoz is loved by developers. Find the instructions to self-host SigNoz.
Performance Comparison
When it comes to performance, both Elasticsearch and MongoDB have their strengths:
- Query Performance:
- Elasticsearch: Faster for complex text searches and aggregations
- MongoDB: Efficient for simple queries and document retrieval
- Indexing Speed:
- Elasticsearch: Rapid indexing with near real-time search
- MongoDB: Fast inserts and updates, with index building in the background
- Resource Utilization:
- Elasticsearch: Higher memory usage for text analysis and caching
- MongoDB: More efficient storage for varied data types
Benchmarking results vary depending on the specific use case and data size. For search-heavy applications, Elasticsearch typically outperforms MongoDB. However, MongoDB may have an edge in scenarios requiring frequent updates and flexible data structures.
Data Storage and Management
Understanding how each system handles data is crucial for making an informed decision:
- Document Size Limitations:
- Elasticsearch: Default max size of 100MB per document
- MongoDB: Maximum BSON document size of 16MB
- Data Consistency:
- Elasticsearch: Eventually consistent by default
- MongoDB: Supports various consistency levels, including strong consistency
- Backup and Recovery:
- Elasticsearch: Snapshot and restore functionality
- MongoDB: Supports point-in-time recovery and incremental backups
- Data Migration:
- Elasticsearch: Reindex API for data migration between indices
- MongoDB: Robust tools for data import/export and migration
Search Capabilities Deep Dive
Search functionality is a key differentiator between Elasticsearch and MongoDB:
Elasticsearch offers:
- Advanced full-text search with customizable analyzers and tokenizers
- Relevance scoring using TF-IDF and BM25 algorithms
- Faceted search and complex aggregations
- Geospatial and time-series data handling
MongoDB Atlas Search provides:
- Text search capabilities built on top of Apache Lucene
- Integration with MongoDB's query language
- Support for facets and relevance-based sorting
While MongoDB has improved its search capabilities, Elasticsearch remains the go-to choice for advanced search requirements.
Deployment and Maintenance
Consider the following aspects when planning your database deployment:
- Deployment Options:
- Elasticsearch: On-premises, cloud, or Elastic Cloud (managed service)
- MongoDB: Self-hosted, cloud providers, or MongoDB Atlas (managed service)
- Operational Complexity:
- Elasticsearch: Requires expertise in cluster management and query optimization
- MongoDB: Generally easier to set up and maintain for small to medium-scale deployments
- Upgrade Processes:
- Elasticsearch: Rolling upgrades with potential downtime for major versions
- MongoDB: In-place upgrades with minimal downtime
Security and Compliance
Both Elasticsearch and MongoDB offer robust security features:
- Authentication and Authorization:
- Elasticsearch: Built-in security with role-based access control
- MongoDB: Role-based access control and field-level encryption
- Encryption:
- Elasticsearch: Node-to-node encryption and encrypted REST API
- MongoDB: TLS/SSL for data in transit and encryption at rest
- Audit Logging:
- Elasticsearch: Detailed audit logs for security events
- MongoDB: Configurable audit logs for tracking database operations
Cost Considerations
When evaluating the total cost of ownership, consider these factors:
- Licensing:
- Elasticsearch: Dual license (Apache 2.0 and Elastic License)
- MongoDB: Server Side Public License (SSPL)
- Hardware Requirements:
- Elasticsearch: Memory-intensive, benefits from SSDs
- MongoDB: More flexible in terms of hardware requirements
- Operational Costs:
- Elasticsearch: May require specialized expertise for optimization
- MongoDB: Generally lower operational overhead for smaller deployments
- Scaling Costs:
- Elasticsearch: Linear cost increase with data volume
- MongoDB: Costs can vary based on sharding strategy and data distribution
Key Takeaways
- Elasticsearch excels in search and analytics, while MongoDB is versatile for general-purpose data storage
- Choose based on your primary use case: search-heavy applications favor Elasticsearch, while flexible data models benefit from MongoDB
- Consider scalability, performance, and maintenance requirements when making a decision
- Both systems offer robust features, but differ in query languages, data models, and optimal use cases
FAQs
Can Elasticsearch be used as a primary database?
While Elasticsearch can store and retrieve data, it's not designed to be a primary database. It's best used alongside a traditional database for search and analytics functionality.
How does MongoDB's Atlas Search compare to Elasticsearch?
MongoDB Atlas Search provides full-text search capabilities, but it's not as feature-rich or performant as Elasticsearch for complex search scenarios. For basic to moderate search needs, Atlas Search may be sufficient.
Which is better for real-time analytics: Elasticsearch or MongoDB?
Elasticsearch generally performs better for real-time analytics, especially when dealing with large volumes of text data or log analysis. However, MongoDB can handle real-time analytics effectively for certain use cases, particularly when combined with its aggregation framework.
Can Elasticsearch and MongoDB be used together in a single application?
Yes, many applications use both databases in tandem. For example, you might store your primary data in MongoDB and use Elasticsearch for powering search functionality or performing complex analytics on that data.
What are the main differences between Elasticsearch and MongoDB?
Elasticsearch is primarily a search engine optimized for fast, complex search queries, especially text searches, while MongoDB is a general-purpose, document-oriented database. Elasticsearch excels in search functionality and real-time data analysis, while MongoDB is better for storing diverse data formats and structures.
When should I choose Elasticsearch over MongoDB?
Choose Elasticsearch when your primary needs involve full-text search, log and event data analysis, real-time analytics dashboards, or recommendation systems. It's ideal for applications that require complex search capabilities and quick data retrieval.
In what scenarios is MongoDB a better choice than Elasticsearch?
MongoDB is preferable for content management systems, mobile app backends, IoT data storage and analysis, and e-commerce product catalogs. It's best suited for applications that need flexible data modeling, efficient CRUD operations, and storage of diverse data types.
Can Elasticsearch and MongoDB be used together in a single application?
Yes, many applications use both databases in tandem. For example, you might store your primary data in MongoDB and use Elasticsearch for powering search functionality or performing complex analytics on that data.
How do Elasticsearch and MongoDB differ in terms of scalability?
Both Elasticsearch and MongoDB offer good scalability, but in different ways. Elasticsearch distributes data across multiple nodes for fast search and retrieval, making it highly scalable for search operations. MongoDB uses sharding to distribute data across multiple servers, allowing it to handle large volumes of data and high write loads efficiently.
What are the key performance differences between Elasticsearch and MongoDB?
Elasticsearch generally performs better for complex text searches, aggregations, and real-time analytics, especially with large volumes of text data. MongoDB is more efficient for simple queries, document retrieval, and scenarios requiring frequent updates. The performance can vary depending on the specific use case and data size.
How do the storage mechanisms differ between Elasticsearch and MongoDB?
Elasticsearch stores data in inverted indexes using Lucene segments, optimized for quick search and retrieval. MongoDB stores data in BSON format (Binary JSON) and uses memory-mapped files, which is more versatile for general database use and supports a wider range of data types and structures.
What are the main security features offered by Elasticsearch and MongoDB?
Both offer robust security features. Elasticsearch provides built-in security with role-based access control, node-to-node encryption, and encrypted REST API. MongoDB offers role-based access control, field-level encryption, TLS/SSL for data in transit, and encryption at rest. Both systems also support audit logging for tracking database operations and security events.
Related Posts
SigNoz - A Lightweight Open Source ELK alternative
OpenTelemetry Logs - A Complete Introduction & Implementation