Overview
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) is a managed Kubernetes service provided by Google that simplifies the deployment, management, and operation of Kubernetes clusters. This document will help you send traces from your GKE cluster to SigNoz.
Prerequisites
- A GKE cluster
- kubectl installed to access the GKE cluster
- Helm installed
Quick Start
Before we begin, let's verify their cluster status with the following commands:
kubectl get nodes
Make sure all the nodes are in Readystate.
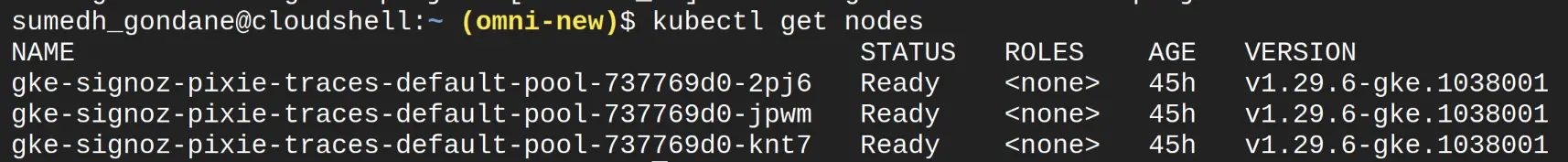
GKE Cluster Status
Step 1: Add the SigNoz helm repo using this command
helm repo add SigNoz https://charts.signoz.io
Step 2: Install OTel Agent and Deployment using signoz/k8s-infra Helm chart
helm install -n signoz kubelet-otel signoz/k8s-infra \\
--set signozApiKey=<ingestionKey> --set otelCollectorEndpoint="ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443" --set OtelInsecure=false --create-namespace
After applying the above commands, check whether the signoz namespace pods are running successfully or not:
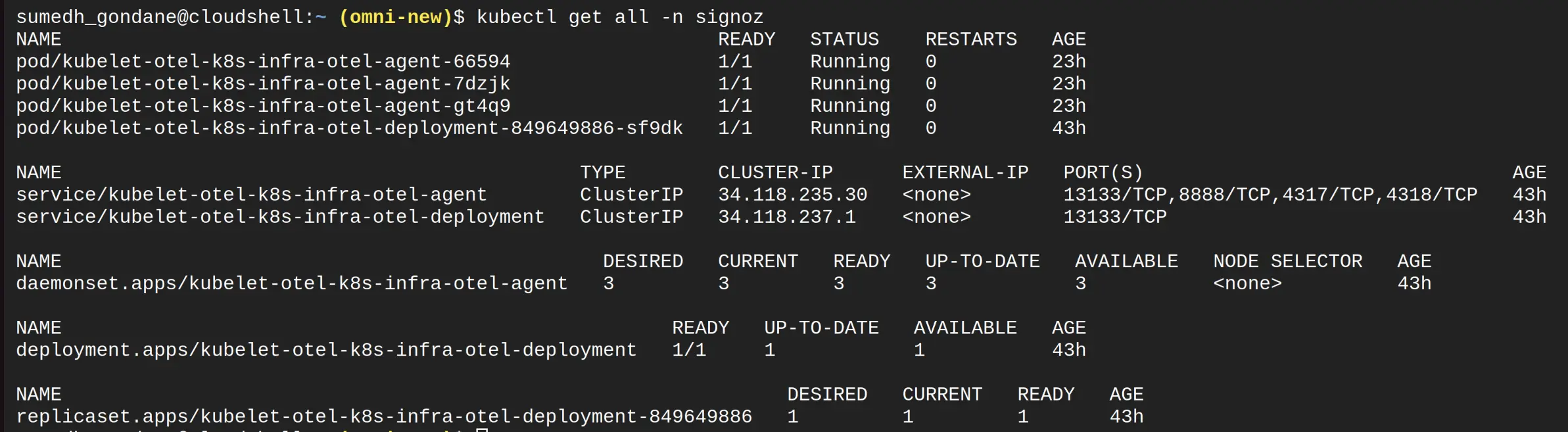
Resources Status
The OTel collector configurations can be found in Ote's config map as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
name: kubelet-otel-k8s-infra-otel-agent
data:
otel-agent-config.yaml: |2-
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: "ingest.{region}.signoz.cloud:443"
headers:
signoz-ingestion-key: "<your-ingestion-key>"
tls:
insecure: false
extensions:
health_check:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:13133
pprof:
endpoint: localhost:1777
zpages:
endpoint: localhost:55679
processors:
batch:
send_batch_size: 10000
timeout: 200ms
k8sattributes:
extract:
metadata:
- k8s.namespace.name
- k8s.pod.name
- k8s.pod.uid
- k8s.pod.start_time
- k8s.deployment.name
- k8s.node.name
filter:
node_from_env_var: K8S_NODE_NAME
passthrough: false
pod_association:
- sources:
- from: resource_attribute
name: k8s.pod.ip
- sources:
- from: resource_attribute
name: k8s.pod.uid
- sources:
- from: connection
resourcedetection:
detectors:
- system
override: true
system:
hostname_sources:
- dns
- os
timeout: 2s
resourcedetection/internal:
detectors:
- env
override: true
timeout: 2s
resource/env:
attributes:
- key: deployment.environment
value: prod # can be dev, prod, staging etc. based on your environment
action: upsert
receivers:
filelog/k8s:
exclude:
- /var/log/pods/signoz_kubelet-otel*-signoz-*/*/*.log
- /var/log/pods/signoz_kubelet-otel*-k8s-infra-*/*/*.log
- /var/log/pods/kube-system_*/*/*.log
- /var/log/pods/*_hotrod*_*/*/*.log
- /var/log/pods/*_locust*_*/*/*.log
include:
- /var/log/pods/*/*/*.log
include_file_name: false
include_file_path: true
operators:
- id: get-format
routes:
- expr: body matches "^\\{"
output: parser-docker
- expr: body matches "^[^ Z]+ "
output: parser-crio
- expr: body matches "^[^ Z]+Z"
output: parser-containerd
type: router
- id: parser-crio
output: extract_metadata_from_filepath
regex: ^(?P<time>[^ Z]+) (?P<stream>stdout|stderr) (?P<logtag>[^ ]*) ?(?P<log>.*)$
timestamp:
layout: "2006-01-02T15:04:05.000000000-07:00"
layout_type: gotime
parse_from: attributes.time
type: regex_parser
- id: parser-containerd
output: extract_metadata_from_filepath
regex: ^(?P<time>[^ ^Z]+Z) (?P<stream>stdout|stderr) (?P<logtag>[^ ]*) ?(?P<log>.*)$
timestamp:
layout: '%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%LZ'
parse_from: attributes.time
type: regex_parser
- id: parser-docker
output: extract_metadata_from_filepath
timestamp:
layout: '%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%LZ'
parse_from: attributes.time
type: json_parser
- id: extract_metadata_from_filepath
output: add_cluster_name
parse_from: attributes["log.file.path"]
regex: ^.*\/(?P<namespace>[^_]+)_(?P<pod_name>[^_]+)_(?P<uid>[a-f0-9\-]+)\/(?P<container_name>[^\._]+)\/(?P<restart_count>\d+)\.log$
type: regex_parser
- field: resource["k8s.cluster.name"]
id: add_cluster_name
output: move_stream
type: add
value: EXPR(env("K8S_CLUSTER_NAME"))
- from: attributes.stream
id: move_stream
output: move_container_name
to: attributes["log.iostream"]
type: move
- from: attributes.container_name
id: move_container_name
output: move_namespace
to: resource["k8s.container.name"]
type: move
- from: attributes.namespace
id: move_namespace
output: move_pod_name
to: resource["k8s.namespace.name"]
type: move
- from: attributes.pod_name
id: move_pod_name
output: move_restart_count
to: resource["k8s.pod.name"]
type: move
- from: attributes.restart_count
id: move_restart_count
output: move_uid
to: resource["k8s.container.restart_count"]
type: move
- from: attributes.uid
id: move_uid
output: move_log
to: resource["k8s.pod.uid"]
type: move
- from: attributes.log
id: move_log
to: body
type: move
start_at: beginning
hostmetrics:
collection_interval: 30s
scrapers:
cpu: {}
disk: {}
filesystem: {}
load: {}
memory: {}
network: {}
kubeletstats:
auth_type: serviceAccount
collection_interval: 30s
endpoint: ${K8S_HOST_IP}:10250
extra_metadata_labels:
- container.id
- k8s.volume.type
insecure_skip_verify: true
metric_groups:
- container
- pod
- node
- volume
otlp:
protocols:
service:
extensions:
- health_check
- zpages
- pprof
pipelines:
logs:
exporters:
- otlp
processors:
- k8sattributes
- batch
receivers:
- otlp
- filelog/k8s
metrics:
exporters:
- otlp
processors:
- k8sattributes
- batch
receivers:
- otlp
metrics/internal:
exporters:
- otlp
processors:
- resourcedetection/internal
- resourcedetection
- k8sattributes
- batch
receivers:
- hostmetrics
- kubeletstats
traces:
exporters:
- otlp
processors:
- k8sattributes
- batch
- resource/env
receivers:
- otlp
telemetry:
logs:
encoding: json
metrics:
address: 0.0.0.0:8888
This should start sending signals to SigNoz.
APM and Distributed Tracing
For application-level tracing, you can use the OpenTelemetry SDKs integrated with your application. These SDKs automatically collect and forward traces to the central collector.
Please refer to our SigNoz Documentation to find information on how to instrument your application like Spring, FastAPI, NextJS, Langchain, Node.js, Flask, Django, etc.
Sample Python Application
We will use a sample flask app. One may need to add packages for enabling instrumentation.
requirements.txt
Flask==3.0.0
pymongo==3.12.1
requests==2.26.0
opentelemetry-api==1.22.0
opentelemetry-distro==0.43b0
opentelemetry-instrumentation==0.43b0
opentelemetry-exporter-otlp==1.22.0
Install those packages in dockerfile configuration.
…
# install dependencies
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
RUN opentelemetry-bootstrap --action=install
…
Example YAML
For running this sample-flask-app as pod
sample-flask-app.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: sample-flask-app
name: sample-flask-app
spec:
containers:
- image: mongo:latest
name: mongo
ports:
- name: mongo
containerPort: 27017
- image: signoz/sample-flask-app:latest
name: sample-app
ports:
- name: flask
containerPort: 5002
env:
- name: MONGO_HOST
value: localhost
- name: OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES
value: service.name=sample-app
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT
value: http://<app-fqdn>:4317
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL
value: grpc
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
Deployment & Expose port
kubectl apply -f sample-flask-app.yaml
One can expose the application via NodePort or LoadBalancer as service.
kubectl expose pod --port=5002 --name=sample-flask-svc –type NodePort
Update OTel config map configuration
You need to add SigNoz cloud credentials at OTel config map:
kubectl get configmap kubelet-otel-k8s-infra-otel-agent -n signoz -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
otel-agent-config.yaml: |2-
exporters:
Otlp:
endpoint: "ingest.{region}.signoz.cloud:443"
headers:
signoz-ingestion-key: "<your-ingestion-key>"
tls:
insecure: false
extensions:
health_check:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:13133
…
Visualize tracing in SigNoz cloud
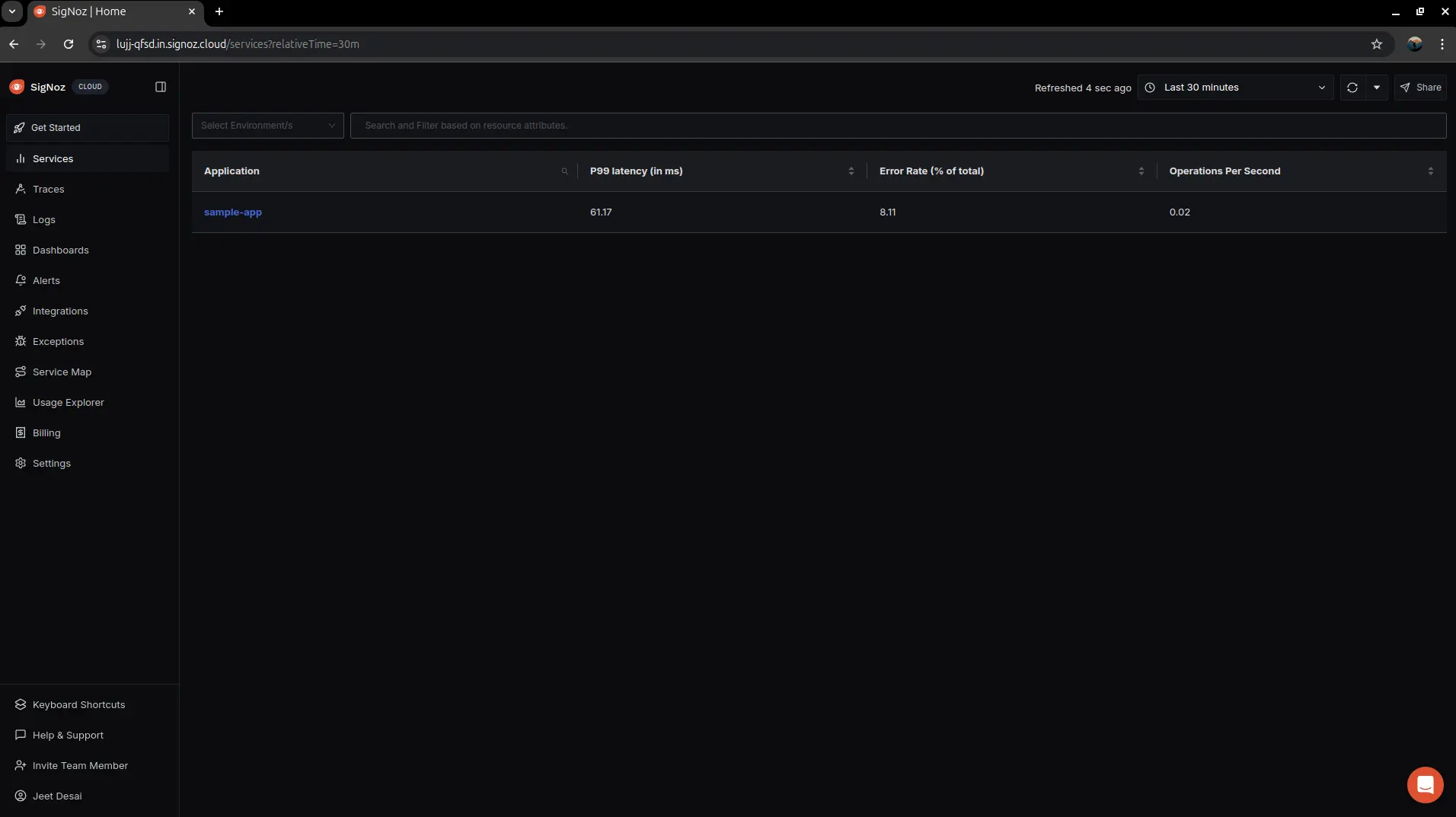
Application in SigNoz Dashboard
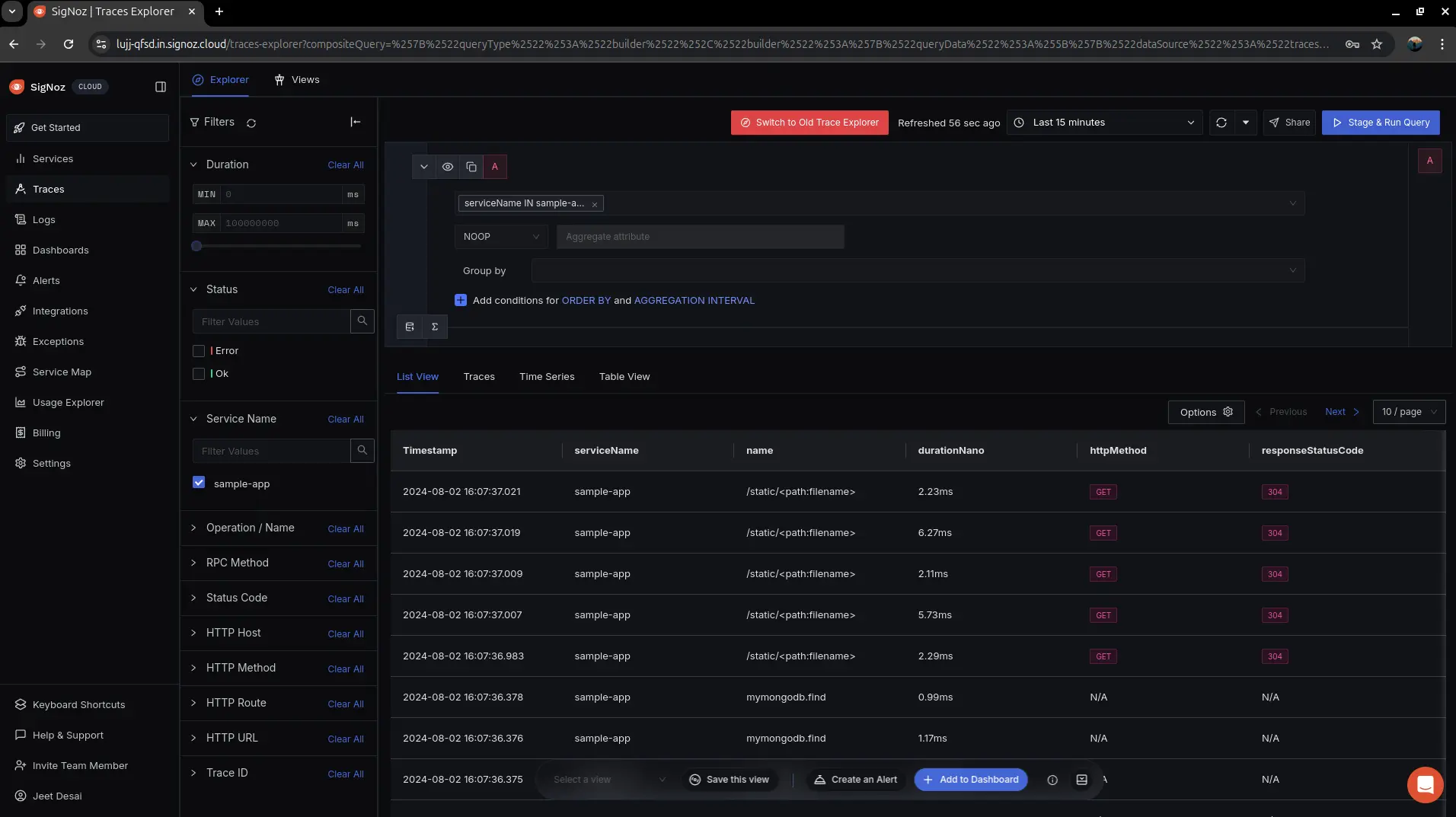
Application-level traces in SigNoz
Troubleshooting
If you encounter any issues while setting up logging and metrics for your GKE cluster, follow these troubleshooting steps:
Check the logs of the OpenTelemetry Collector:
kubectl logs -f -n signoz -l app.kubernetes.io/component=otel-agentReview the logs for any error messages or indications of misconfiguration.
Verify the rendered configuration:
kubectl get configmap/kubelet-otel-k8s-infra-otel-agent -n signoz -o yamlEnsure the configuration matches your expected settings, including the SigNoz API key and the OpenTelemetry Collector endpoint.
Confirm that the necessary Kubernetes resources are created:
kubectl get pods,services,configmaps -n signozCheck if the required pods, services, and config maps are running and in a healthy state.
Verify network connectivity:
- Ensure that the GKE cluster has network access to the SigNoz ingestion endpoint (
ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443). - Check if there are any network security groups or firewalls blocking the required ports.
- Ensure that the GKE cluster has network access to the SigNoz ingestion endpoint (
Double-check the SigNoz API key:
- Confirm that the provided signozApiKey is correct and has the necessary permissions to ingest data.
Check if all the Pixie deployments are in the correct order:
- Check all the configurations and deployments are in the correct order so that Pixie can forward all the scraped traces to the respective endpoint.
Prerequisites
- A GKE cluster
- kubectl installed to access the GKE cluster
- Helm installed
- Self-Hosted SigNoz in GKE Cluster ( If you are hosting SigNoz in Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), you should refer to the specific guide that outlines the minimum requirements and provides details for the override-values.yaml ) OR if you’re hosting SigNoz on VM, follow Self-Hosted SigNoz on VM .
Quick Start
Check that the nodes in your GKE clusters are in Ready state:

GKE Cluster Status
Step 1: Add the SigNoz helm repo using this command
helm repo add SigNoz https://charts.signoz.io
Step 2: Install the OTel Collector agent in GKE where SigNoz is running in GKE cluster
helm install -n signoz kubelet-otel signoz/k8s-infra \\
otelCollectorEndpoint="<self-host-signoz-otel-collector-service-fqdn>:4317 " --set otelInsecure=true --create-namespace
Step 2: Install the OTel Collector agent in GKE where SigNoz is running in a Self-hosted VM.
helm install -n signoz kubelet-otel signoz/k8s-infra \\
otelCollectorEndpoint="<self-host-signoz-vm-ip>:4317" --set otelInsecure=true --create-namespace
Depending on how you have set up your infrastructure, the otelCollectorEndpoint can be different from the VM IP.
After applying the above commands, check whether the pods are running successfully or not

Resources Status
The OTel collector configurations can be found in Otel's config map as follows:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
name: kubelet-otel-k8s-infra-otel-agent
data:
otel-agent-config.yaml: |2-
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: "<App-endpoint:4317>"
tls:
insecure: true
extensions:
health_check:
endpoint: 0.0.0.0:13133
pprof:
endpoint: localhost:1777
zpages:
endpoint: localhost:55679
processors:
batch:
send_batch_size: 10000
timeout: 200ms
k8sattributes:
extract:
metadata:
- k8s.namespace.name
- k8s.pod.name
- k8s.pod.uid
- k8s.pod.start_time
- k8s.deployment.name
- k8s.node.name
filter:
node_from_env_var: K8S_NODE_NAME
passthrough: false
pod_association:
- sources:
- from: resource_attribute
name: k8s.pod.ip
- sources:
- from: resource_attribute
name: k8s.pod.uid
- sources:
- from: connection
resourcedetection:
detectors:
- system
override: true
system:
hostname_sources:
- dns
- os
timeout: 2s
resourcedetection/internal:
detectors:
- env
override: true
timeout: 2s
resource/env:
attributes:
- key: deployment.environment
value: prod # can be dev, prod, staging etc. based on your environment
action: upsert
receivers:
filelog/k8s:
exclude:
- /var/log/pods/signoz_kubelet-otel*-signoz-*/*/*.log
- /var/log/pods/signoz_kubelet-otel*-k8s-infra-*/*/*.log
- /var/log/pods/kube-system_*/*/*.log
- /var/log/pods/*_hotrod*_*/*/*.log
- /var/log/pods/*_locust*_*/*/*.log
include:
- /var/log/pods/*/*/*.log
include_file_name: false
include_file_path: true
operators:
- id: get-format
routes:
- expr: body matches "^\\{"
output: parser-docker
- expr: body matches "^[^ Z]+ "
output: parser-crio
- expr: body matches "^[^ Z]+Z"
output: parser-containerd
type: router
- id: parser-crio
output: extract_metadata_from_filepath
regex: ^(?P<time>[^ Z]+) (?P<stream>stdout|stderr) (?P<logtag>[^ ]*) ?(?P<log>.*)$
timestamp:
layout: "2006-01-02T15:04:05.000000000-07:00"
layout_type: gotime
parse_from: attributes.time
type: regex_parser
- id: parser-containerd
output: extract_metadata_from_filepath
regex: ^(?P<time>[^ ^Z]+Z) (?P<stream>stdout|stderr) (?P<logtag>[^ ]*) ?(?P<log>.*)$
timestamp:
layout: '%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%LZ'
parse_from: attributes.time
type: regex_parser
- id: parser-docker
output: extract_metadata_from_filepath
timestamp:
layout: '%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.%LZ'
parse_from: attributes.time
type: json_parser
- id: extract_metadata_from_filepath
output: add_cluster_name
parse_from: attributes["log.file.path"]
regex: ^.*\/(?P<namespace>[^_]+)_(?P<pod_name>[^_]+)_(?P<uid>[a-f0-9\-]+)\/(?P<container_name>[^\._]+)\/(?P<restart_count>\d+)\.log$
type: regex_parser
- field: resource["k8s.cluster.name"]
id: add_cluster_name
output: move_stream
type: add
value: EXPR(env("K8S_CLUSTER_NAME"))
- from: attributes.stream
id: move_stream
output: move_container_name
to: attributes["log.iostream"]
type: move
- from: attributes.container_name
id: move_container_name
output: move_namespace
to: resource["k8s.container.name"]
type: move
- from: attributes.namespace
id: move_namespace
output: move_pod_name
to: resource["k8s.namespace.name"]
type: move
- from: attributes.pod_name
id: move_pod_name
output: move_restart_count
to: resource["k8s.pod.name"]
type: move
- from: attributes.restart_count
id: move_restart_count
output: move_uid
to: resource["k8s.container.restart_count"]
type: move
- from: attributes.uid
id: move_uid
output: move_log
to: resource["k8s.pod.uid"]
type: move
- from: attributes.log
id: move_log
to: body
type: move
start_at: beginning
hostmetrics:
collection_interval: 30s
scrapers:
cpu: {}
disk: {}
filesystem: {}
load: {}
memory: {}
network: {}
kubeletstats:
auth_type: serviceAccount
collection_interval: 30s
endpoint: ${K8S_HOST_IP}:10250
extra_metadata_labels:
- container.id
- k8s.volume.type
insecure_skip_verify: true
metric_groups:
- container
- pod
- node
- volume
otlp:
protocols:
service:
extensions:
- health_check
- zpages
- pprof
pipelines:
logs:
exporters:
- otlp
processors:
- k8sattributes
- batch
receivers:
- otlp
- filelog/k8s
metrics:
exporters:
- otlp
processors:
- k8sattributes
- batch
receivers:
- otlp
metrics/internal:
exporters:
- otlp
processors:
- resourcedetection/internal
- resourcedetection
- k8sattributes
- batch
receivers:
- hostmetrics
- kubeletstats
traces:
exporters:
- otlp
processors:
- k8sattributes
- batch
- resource/env
receivers:
- otlp
telemetry:
logs:
encoding: json
metrics:
address: 0.0.0.0:8888
This should start sending signals to SigNoz.
eBPF Tracing
There are solution to collect metrics and traces without modifying the application code. These solutions come under the category of eBPF Tracing. These solutions are relatively new and are still in the early stages of development.
However, there are some open source projects that export metrics and traces to OpenTelemetry.
These solutions may not be suitable for all use cases, and are still may not be production-ready. It is recommended to evaluate solutions and choose the one that best fits your needs.
In this guide will deploy Pixie in the Kubernetes cluster to fetch traces from the cluster.
Step 1: Deploy Pixie in the Kubernetes cluster to fetch traces from the cluster.
For eBPF tracing we can use Pixie, which can be configured using the following instructions in this Documentation.
Step 2: Use a custom data retention script in the OpenTelemetry Pixie plugin to send the data to the SigNoz.
You can refer to this GitHub repository for the different custom scripts for the different use cases.
Use the appropriate export URL in the script. The export url will receive all the traces captured by Pixie.
url='<endpoint-ip-of-otel-svc>':4317,
insecure=True
OR
url='<self-host-signoz-otel-collector-service-fqdn>':4317,
insecure=True
url='<endpoint-ip-of-vm>:4317',
insecure=True
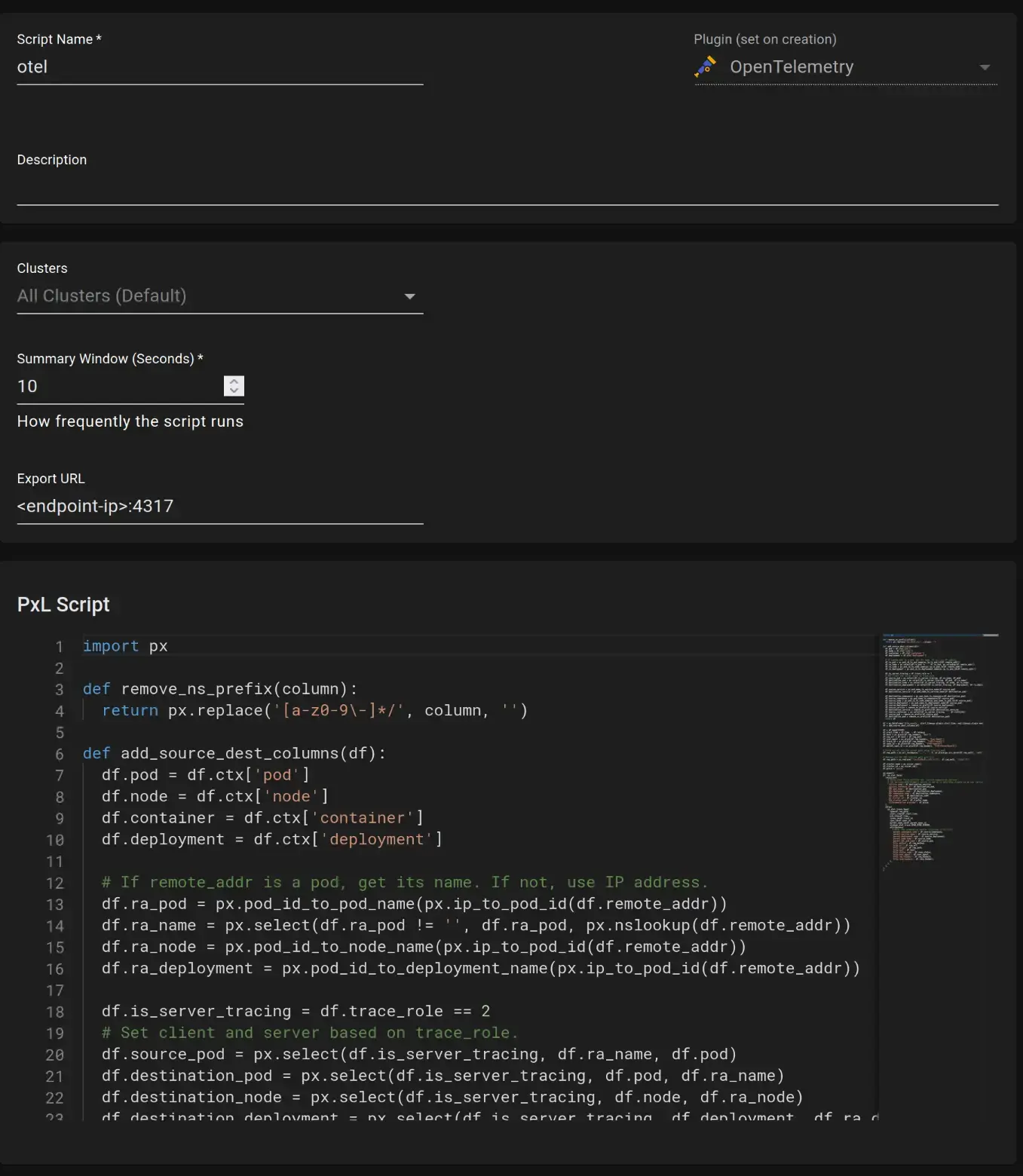
Pixie Configuration
Step 3: To test the configuration, deploy a sample application in the cluster to view its traces in the SigNoz.
kubectl run -n signoz my-hello –image=nginx –port=80
Visualize the Traces in SigNoz self-hosted
To visualize the traces, log into the SigNoz account and navigate to the traces section.
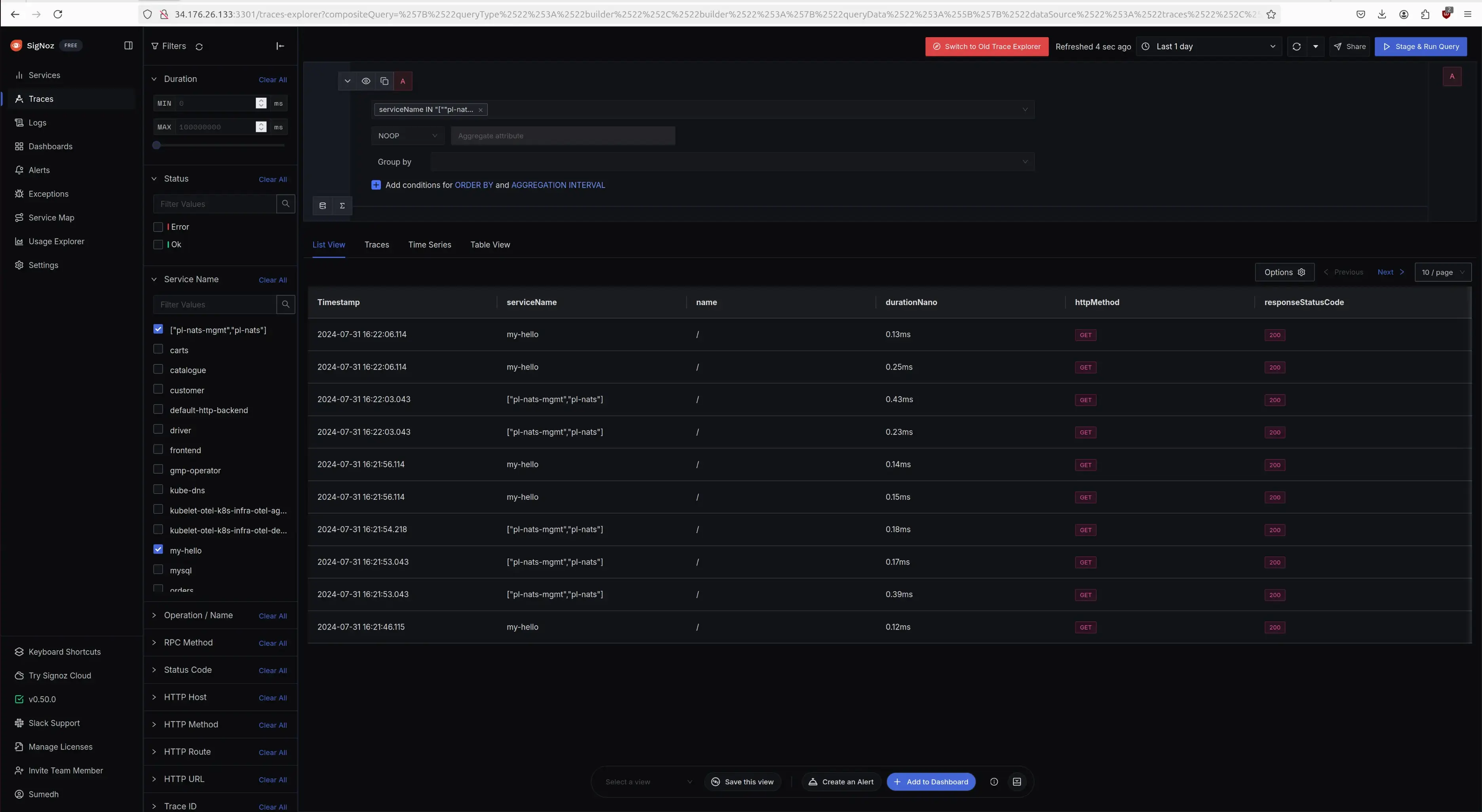
Traces in SigNoz Dashboard (self-hosted on GKE Cluster)
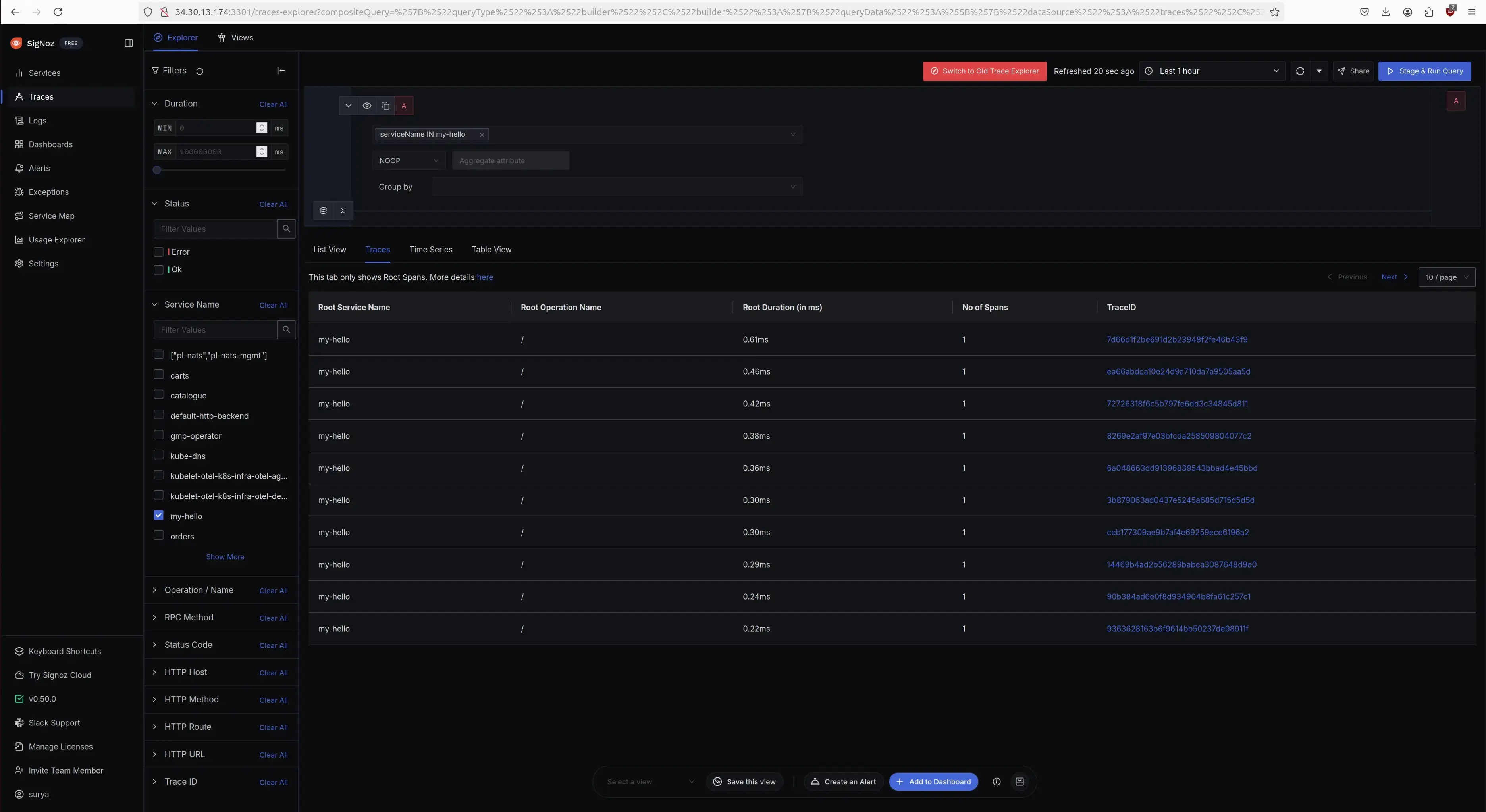
Traces in SigNoz Dashboard (self-hosted on a VM)
APM and Distributed Tracing
For application-level tracing, you can use the OpenTelemetry SDKs integrated with your application. These SDKs automatically collect and forward traces to the central collector.
Please refer to our SigNoz Tutorials or Blog to find information on how to instrument your application like Spring, FastAPI, NextJS, Langchain, Node.js, Flask, Django, etc.
Sample Python Application
We will use a sample flask app. One may need to add packages (in requirements.txt) for enabling instrumentation.
Flask==3.0.0
pymongo==3.12.1
requests==2.26.0
opentelemetry-api==1.22.0
opentelemetry-distro==0.43b0
opentelemetry-instrumentation==0.43b0
opentelemetry-exporter-otlp==1.22.0
Install those packages in dockerfile configuration.
…
# install dependencies
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
RUN opentelemetry-bootstrap --action=install
…
Example YAML
For running this sample-flask-app as pod,use the following yaml file.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: sample-flask-app
name: sample-flask-app
spec:
containers:
- image: mongo:latest
name: mongo
ports:
- name: mongo
containerPort: 27017
- image: signoz/sample-flask-app:latest
name: sample-app
ports:
- name: flask
containerPort: 5002
env:
- name: MONGO_HOST
value: localhost
- name: OTEL_RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES
value: service.name=sample-app
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT
value: http://kubelet-otel-k8s-infra-otel-agent.signoz.svc.cluster.local:4317
- name: OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_PROTOCOL
value: grpc
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
Deployment & Expose port
kubectl apply -f sample-flask-app.yaml
One can expose the application via NodePort or LoadBalancer as service.
kubectl expose pod --port=5002 --name=sample-flask-svc –type NodePort
Update OTel config map configuration
You need to add IP address/domain name of self hosted SigNoz at OTel config map:
Edit the config map of the OTel agent
apiVersion: v1
data:
otel-agent-config.yaml: |2-
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: "<App-endpoint:4317>"
tls:
insecure: true
Visualize tracing in SigNoz
After editing the config map, and once the application restarts, upon performing any action on the application UI/endpoint, it should send traces that should be visible over the self hosted SigNoz:
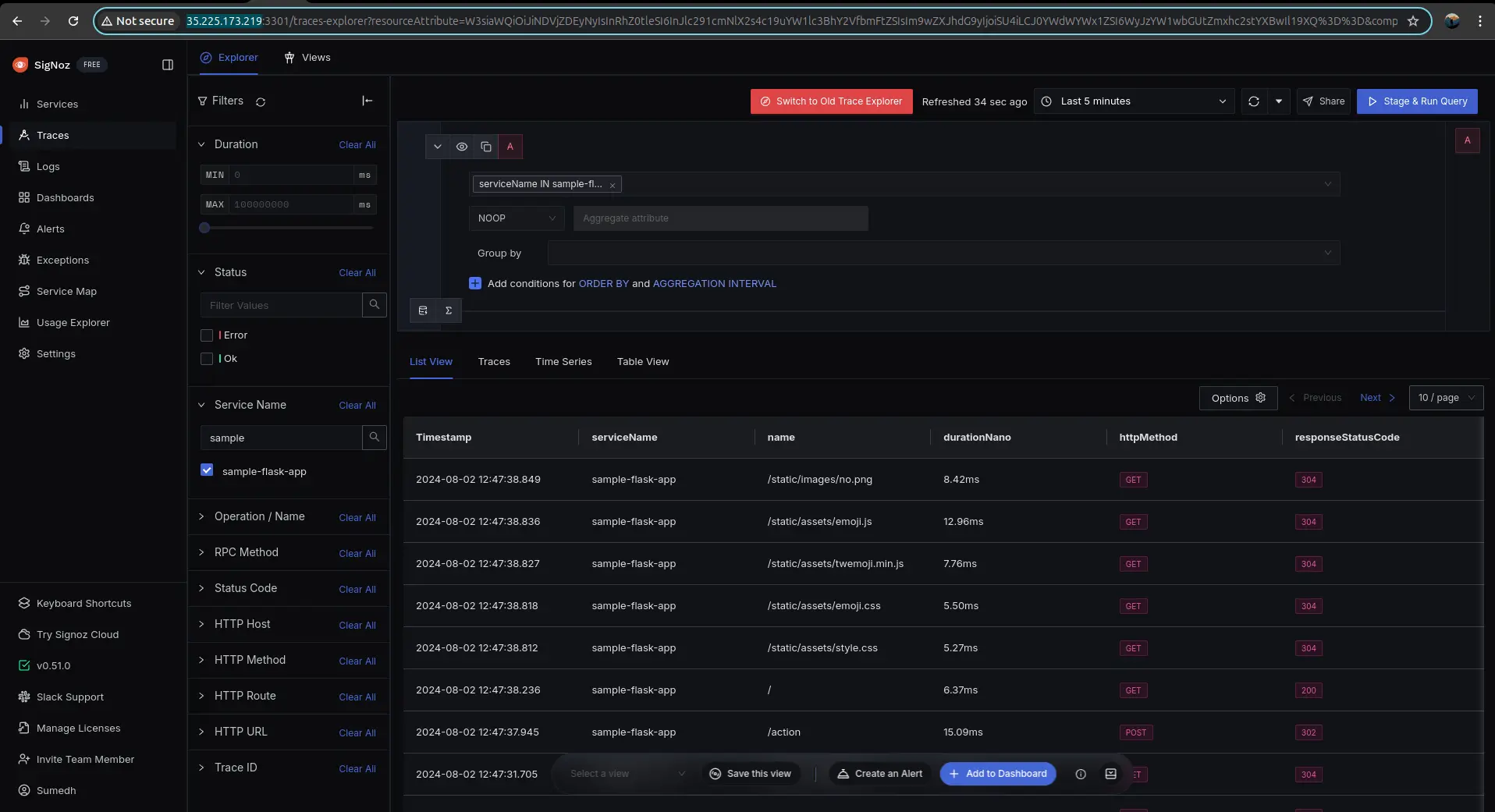
Application-level traces in SigNoz
Troubleshooting
If you encounter any issues while setting up logging and metrics for your GKE cluster, follow these troubleshooting steps:
Confirm that the necessary Kubernetes resources are created:
kubectl get pods,services,configmaps -n signozCheck if the required pods, services, and config maps are running and in a healthy state.
Check the logs of the OpenTelemetry Collector:
kubectl logs -f -n signoz -l app.kubernetes.io/component=otel-agentReview the logs for any error messages or indications of misconfiguration.
Verify the rendered configuration:
kubectl get cm/kubelet-otel-k8s-infra-otel-agent -n signoz -o yamlEnsure the configuration matches your expected settings and the OpenTelemetry Collector endpoint.
Confirm that the necessary Kubernetes resources are created:
kubectl get pods,services,configmaps -n signozCheck if the required pods, services, and config maps are running and in a healthy state.
Check if all the Pixie deployments are in the correct order (applicable for eBPF based tracing):
- Check all the configurations and deployments are in the correct order so that Pixie can forward all the scraped traces to the respective endpoint.
Check the logs of the OpenTelemetry Collector:
kubectl logs -f -n signoz -l app.kubernetes.io/component=otel-agentReview the logs for any error messages or indications of misconfiguration.
Verify the rendered configuration:
kubectl get cm/kubelet-otel-k8s-infra-otel-agent -n signoz -o yamlEnsure the configuration matches your expected settings and the OpenTelemetry Collector endpoint.
Confirm that the necessary Kubernetes resources are created:
kubectl get pods,services,configmaps -n signozCheck if the required pods, services, and config maps are running and in a healthy state.
Verify network connectivity:
- Ensure that the GKE cluster has network access to the SigNoz ingestion endpoint (Self-Hosted SigNoz VM IP:4317).
- Check if there are any network security groups or firewalls blocking the required ports.
Check the SigNoz Self-Host VM
- Confirm that all the SigNoz related services are running properly on the VM or not.
Check if all the Pixie deployments are in the correct order (applicable for eBPF based tracing):
- Check all the configurations and deployments are in the correct order so that Pixie can forward all the scraped traces to the respective endpoint.
