Overview
When your website, API, or internal service goes down, you want to know before your users do. This guide shows you how to set up lightweight synthetic monitoring for your HTTP endpoints in SigNoz — giving you uptime/ping monitoring, response time tracking, and error detection for any HTTP(S) URL.
What you'll achieve:
- Periodically check if your HTTP endpoints are reachable and returning expected responses
- Visualize endpoint health and response times in SigNoz dashboards
- Set up alerts that notify you when an endpoint goes down
- Optionally track SSL/TLS certificate expiry
This works by using the OpenTelemetry (OTel) Collector — a lightweight agent that runs alongside your infrastructure. The Collector's HTTP Check Receiver makes periodic HTTP requests to your endpoints on a schedule and sends the results as metrics to SigNoz.
Prerequisites
- A server or VM to run the OpenTelemetry Collector (this is where the checks run from)
- Network access from the Collector host to the endpoints you want to monitor
Setup
Step 1: Install the OpenTelemetry Collector
The OpenTelemetry (OTel) Collector is an agent that collects, processes, and exports telemetry data. In this case, it will periodically ping your HTTP endpoints and send the results to SigNoz.
Install the OTel Collector on your server by following the Collector installation guide. The guide covers setup for Docker, Kubernetes, VM, and AWS ECS environments.
Step 2: Add the HTTP Check Receiver
The HTTP Check Receiver is a component that performs synthetic checks — it makes HTTP requests to your endpoints on a schedule and records whether they respond successfully.
Add the following to the receivers section of your OTel Collector configuration file (see where to find your config file):
receivers:
httpcheck:
targets:
- endpoint: https://<your-endpoint>
method: GET
collection_interval: 60s
<your-endpoint>: The URL you want to monitor (for example,https://api.example.com/healthorhttps://yoursite.com)collection_interval: How often to check. Default is60s. Use shorter intervals (for example,30s) for critical endpointsmethod: The HTTP method to use.GETis most common for health checks
Step 3: Add the SigNoz Exporter (if not already configured)
If you followed the Collector installation guide, the SigNoz exporter is already configured — skip to Step 4.
Otherwise, add the SigNoz OTLP exporter to the exporters section of your config:
exporters:
otlp:
endpoint: "ingest.<region>.signoz.cloud:443"
tls:
insecure: false
headers:
"signoz-ingestion-key": "<your-ingestion-key>"
<region>: Your SigNoz Cloud region<your-ingestion-key>: Your SigNoz ingestion key
Step 4: Enable the HTTP Check in the Pipeline
In the service.pipelines.metrics section, add httpcheck to the list of receivers. Pipelines connect receivers, processors, and exporters — learn more in the service pipeline documentation.
service:
pipelines:
metrics:
receivers: [otlp, httpcheck]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlp]
Append httpcheck to your existing receivers list, do not replace your existing configuration. If you already have other receivers configured, keep them.
Step 5: Restart the Collector
Apply the changes by restarting the OTel Collector. The restart command depends on how you deployed the Collector — refer to the environment-specific instructions in the Collector installation guide.
Validate
After restarting, wait for at least one collection_interval (default: 60 seconds) and then verify the data is flowing:
- Go to your SigNoz Cloud dashboard
- Navigate to Dashboards → New Dashboard → New Panel
- In the Query Builder, search for
httpcheckin the metric dropdown - You should see metrics like
httpcheck.status,httpcheck.duration, andhttpcheck.error
If you see these metrics, your HTTP endpoint monitoring is working.
Enable Optional Metrics
By default, the HTTP Check Receiver reports three metrics: httpcheck.status, httpcheck.duration, and httpcheck.error. You can enable additional metrics for deeper monitoring.
SSL/TLS Certificate Expiry
Track when your HTTPS certificates are about to expire — useful for avoiding unexpected downtime from expired certificates:
receivers:
httpcheck:
metrics:
httpcheck.tls.cert_remaining:
enabled: true
targets:
- endpoint: https://yoursite.com
method: GET
collection_interval: 3600s
The httpcheck.tls.cert_remaining metric reports the number of seconds until the certificate expires. A negative value means the certificate has already expired. You can set up an alert on this metric to get notified days before expiry.
Response Timing Breakdown
For performance monitoring, enable detailed timing metrics to see where time is spent during the request:
receivers:
httpcheck:
metrics:
httpcheck.dns.lookup.duration:
enabled: true
httpcheck.client.connection.duration:
enabled: true
httpcheck.tls.handshake.duration:
enabled: true
httpcheck.client.request.duration:
enabled: true
httpcheck.response.duration:
enabled: true
targets:
- endpoint: https://yoursite.com
method: GET
collection_interval: 60s
These metrics help identify whether slow responses are caused by DNS resolution, connection setup, TLS handshake, or server processing.
Monitor Multiple Endpoints
You can add multiple endpoints under the targets list:
receivers:
httpcheck:
targets:
- endpoint: https://api.example.com/health
method: GET
- endpoint: https://yoursite.com
method: GET
- endpoint: https://internal-service.local:8080/ping
method: GET
collection_interval: 60s
Use Different Check Intervals
If some endpoints are more critical than others, create separate receiver instances with different intervals. Use the format httpcheck/<name> for additional instances:
receivers:
httpcheck/critical:
targets:
- endpoint: https://api.example.com/health
method: GET
collection_interval: 30s
httpcheck/standard:
targets:
- endpoint: https://blog.example.com
method: GET
- endpoint: https://docs.example.com
method: GET
collection_interval: 300s
Then include all instances in your pipeline:
service:
pipelines:
metrics:
receivers: [otlp, httpcheck/critical, httpcheck/standard]
processors: [batch]
exporters: [otlp]
The receiver name format must use a forward slash: httpcheck/critical. Writing httpcheckcritical (without the slash) causes a configuration error.
Available Metrics Reference
For the full upstream specification, see the HTTP Check Receiver documentation.
Default Metrics (always enabled)
| Metric | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
httpcheck.status | 1 if the check resulted in a status code matching the status class, 0 otherwise | 1 |
httpcheck.duration | Measures the duration of the HTTP check | ms |
httpcheck.error | Records errors occurring during HTTP check (for example, connection refused, DNS failures, timeouts) | {error} |
Optional Metrics (must be enabled in config)
| Metric | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
httpcheck.dns.lookup.duration | Time spent performing DNS lookup | ms |
httpcheck.client.connection.duration | Time spent establishing TCP connection | ms |
httpcheck.tls.handshake.duration | Time spent performing TLS handshake | ms |
httpcheck.client.request.duration | Time spent sending the HTTP request | ms |
httpcheck.response.duration | Time spent receiving the HTTP response | ms |
httpcheck.response.size | Size of response body | By (bytes) |
httpcheck.tls.cert_remaining | Time until TLS certificate expires, as specified by NotAfter field in the x.509 certificate. Negative values mean the certificate has already expired | s (seconds) |
httpcheck.validation.failed | Number of response validations that failed | {validation} |
httpcheck.validation.passed | Number of response validations that passed | {validation} |
Key Attributes
Attributes vary by metric. The table below shows all attributes and which metrics they apply to:
| Attribute | Description | Applies To |
|---|---|---|
http.url | Full HTTP request URL | All metrics |
http.status_code | HTTP response status code | httpcheck.status |
http.method | HTTP request method | httpcheck.status |
http.status_class | HTTP response status class (2xx, 4xx, 5xx) | httpcheck.status |
error.message | Error message recorded during check | httpcheck.error |
network.transport | OSI transport layer protocol | httpcheck.client.connection.duration |
http.tls.issuer | Certificate issuer | httpcheck.tls.cert_remaining |
http.tls.cn | Certificate common name (CN) | httpcheck.tls.cert_remaining |
http.tls.san | Certificate Subject Alternative Name | httpcheck.tls.cert_remaining |
validation.type | Type of validation (contains, json_path, size, regex) | httpcheck.validation.failed, httpcheck.validation.passed |
Create a Dashboard in SigNoz
Once metrics are flowing, create a dashboard to visualize endpoint health:
Step 1: Create a New Dashboard Panel
- In SigNoz, go to Dashboards → New Dashboard
- Click New Panel and select Time Series as the chart type
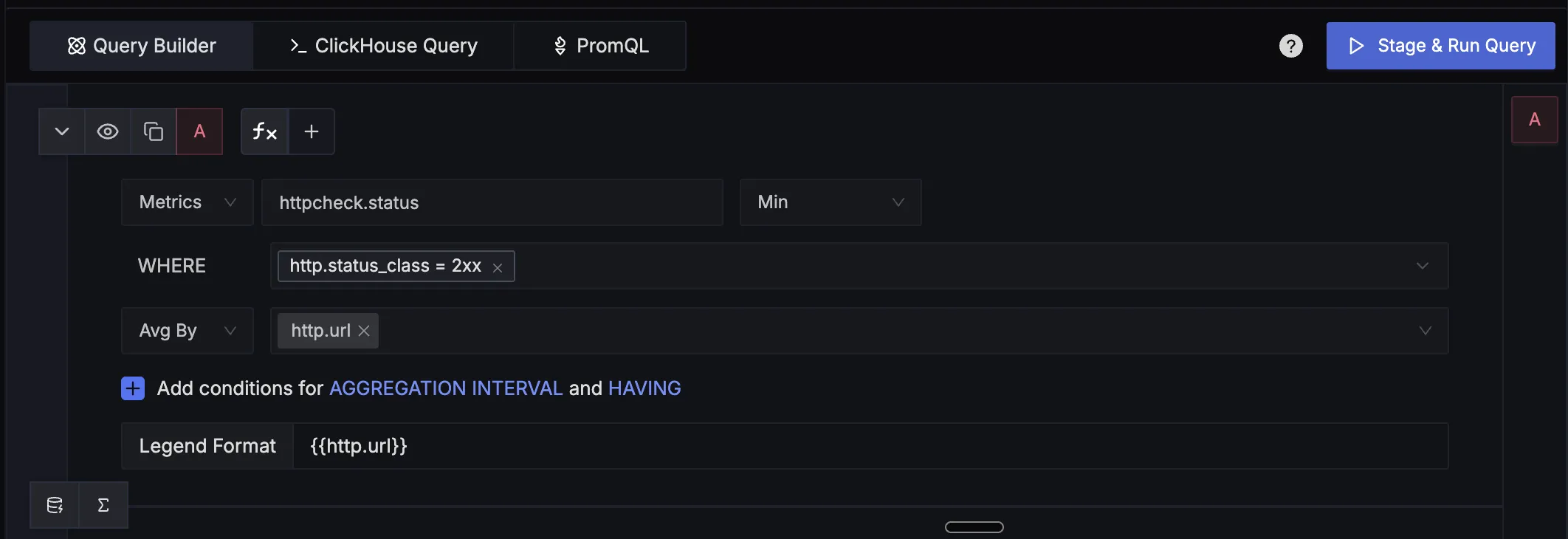
Step 2: Configure the Query
- In the Query Builder, search for
httpcheck.status - Add a WHERE clause:
http.status_class = 2xxto filter for successful responses - Set Avg By to
http.urlto see each endpoint separately
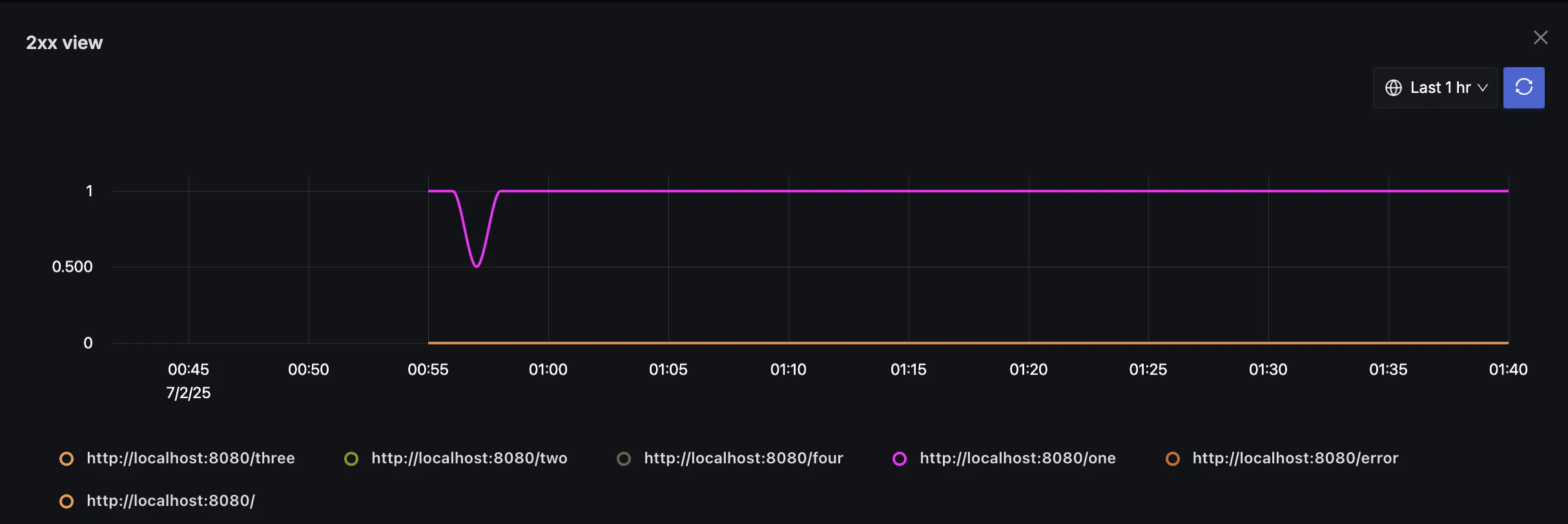
Step 3: Interpret the Chart
The chart shows:
- Value of 1: Endpoint is healthy (returning 2xx responses)
- Value of 0: Endpoint is down or returning errors
- A separate line for each endpoint when grouped by
http.url
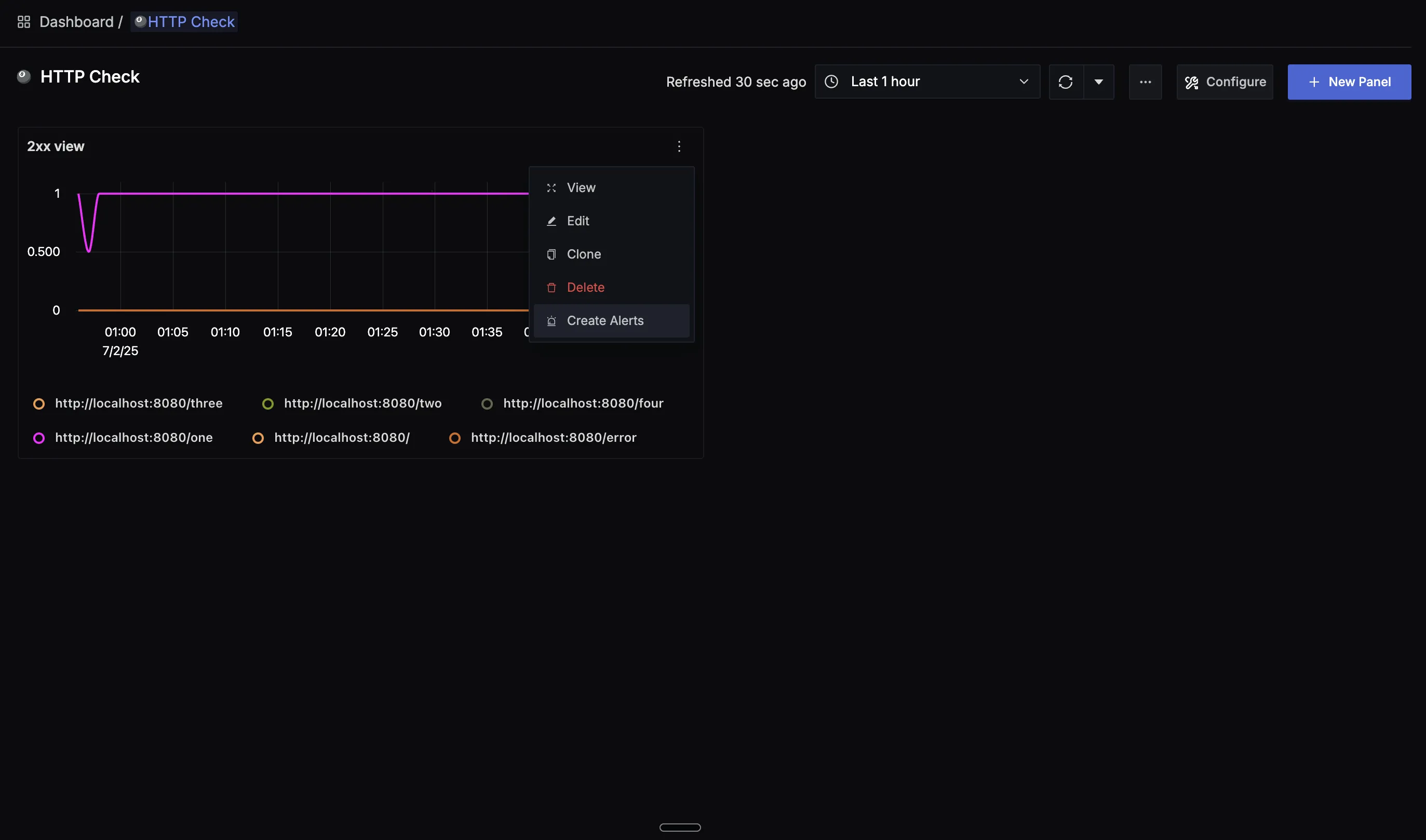
Set Up Alerts
Get notified when an endpoint goes down by creating an alert:
Step 1: Create an Alert from the Dashboard
- In your dashboard panel showing endpoint health, click the dropdown menu (⋮)
- Select Create Alerts
Step 2: Configure Alert Conditions
Set the alert to fire when an endpoint stops returning 2xx responses:
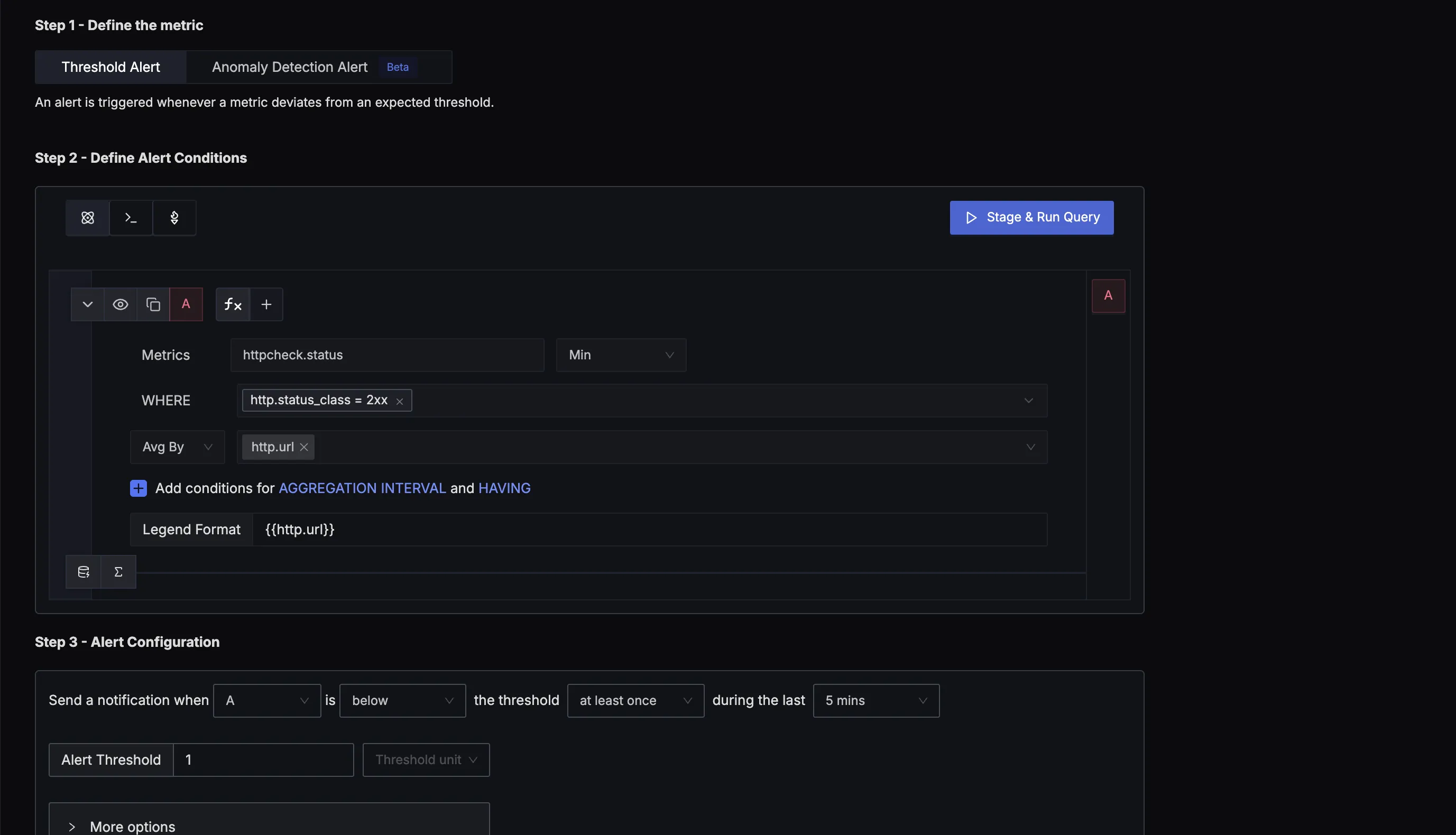
Example alert configuration:
Metric: httpcheck.status
WHERE: http.status_class = 2xx
Avg By: http.url
Condition: below the threshold at least once during the last 5 mins
Threshold: 1
This alert fires when any monitored endpoint fails to respond with a 2xx (success) status code even once during a 5-minute window. You can configure the alert to send notifications to Slack, PagerDuty, email, or other notification channels.
Troubleshooting
No httpcheck metrics appear in SigNoz
Symptoms: You configured the receiver but see no httpcheck.* metrics in the Query Builder.
Likely causes and fixes:
- Receiver not added to the pipeline — Make sure
httpcheckis listed underservice.pipelines.metrics.receiversin your config file. - Config file not loaded — Verify you are pointing to the correct config file when starting the Collector. Check the Collector startup logs for configuration errors.
- Collector not restarted — Restart the Collector after making config changes.
Connection refused or timeout errors in Collector logs
Symptoms: Collector logs show errors like connection refused or context deadline exceeded for the target endpoints.
Likely causes and fixes:
- Network access — Ensure the Collector host can reach the target endpoint. Test with
curl <endpoint>from the same machine. - Firewall rules — Check that firewalls and security groups allow outbound traffic from the Collector to the target endpoint.
- DNS resolution — If using hostnames, verify DNS resolution works from the Collector host with
nslookup <hostname>.
SSL/TLS errors for HTTPS endpoints
Symptoms: Collector logs show TLS handshake errors or certificate-related failures.
Likely causes and fixes:
- Self-signed certificates — If the target uses a self-signed certificate, add TLS configuration to skip verification (not recommended for production):
receivers: httpcheck: targets: - endpoint: https://internal-service.local tls: insecure_skip_verify: true - Expired certificates — The target's certificate may have expired. Verify with
openssl s_client -connect <host>:443.
Metrics not reaching SigNoz Cloud
Symptoms: Collector shows successful HTTP checks in debug logs, but metrics don't appear in SigNoz.
Likely causes and fixes:
- Incorrect ingestion key — Verify the
signoz-ingestion-keyheader value in your exporter config. Get your key from SigNoz Cloud settings. - Wrong region — Ensure the
<region>in the endpoint URL matches your SigNoz Cloud region. See available regions. - Exporter name mismatch — The exporter name under
exportersmust match what is listed inservice.pipelines.metrics.exporters.
Next Steps
- Create custom dashboards to visualize endpoint health, response times, and error rates
- Set up notification channels (Slack, PagerDuty, email) for your HTTP endpoint alerts
- Learn about the OTel Collector configuration to customize processing and filtering
- Read the HTTP Check Receiver upstream documentation for advanced configuration options like request bodies, custom headers, and response validation
